Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engineering Formulas - 1
Transféré par
Shanthi BhushanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electrical Engineering Formulas - 1
Transféré par
Shanthi BhushanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FORMULAS
BASIC ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT FORMULAS
CIRCUIT
ELEMENT
IMPEDANCE
VOLT-AMP EQUATIONS
absolute complex instantaneous
value
form
values
RMS values for
sinusoidal signals
ENERGY
(dissipated on R
or stored in L, C)
RESISTANCE
v=iR
Vrms=IrmsR
E=Irms2Rt
INDUCTANCE
2fL
jL
v=Ldi/dt
Vrms=Irms2fL
E=Li2/2
1/jC
i=Cdv/dt
Vrms=Irms/(2fC)
E=Cv2/2
CAPACITANCE 1/(2fC)
Notes:
R- electrical resistance in ohms, L- inductance in henrys, C- capacitance in farads, f - frequency
in hertz, t- time in seconds, 3.14159;
=2f - angular frequency;
j - imaginary unit ( j2=-1 )
BASIC ELECTRICAL THEOREMS AND CIRCUIT ANALYSIS LAWS
LAW
DEFINITION
=Z, where and - voltage and
Ohm's Law modified
current phasors, Z - complex
for AC circuits with
impedance
sinusoidal signals
(for resistive circuits: u=Ri )
RELATIONSHIP
Lorentz force law,
Faraday's law and Drude
model
Kirchhoff's Current
Law (KCL)
The sum of electric currents which
flow into any junction in an electric
circuit is equal to the sum of currents
which flow out
Conservation of electric
charge
Kirchhoff's Voltage
Law (KVL)
The sum of the electrical voltages
around a closed circuit must be zero
Conservation of energy
EQUATIONS FOR SERIES AND PARALLEL CONNECTIONS
CIRCUIT
ELEMENT
SERIES
CONNECTION
PARALLEL
CONNECTION
RESISTANCE
Rseries=
R1+R2+...
Rparallel=
1/
(1/R1+1/R2+...)
INDUCTANCE
Lseries=
L1+L2+...
Lparallel=
1/(1/L1+1/L2+...)
Cseries=
1/
(1/C1+1/C2+...)
Cparallel=
C1+C2+...
CAPACITANCE
RLC IMPEDANCE FORMULAS
CIRCUIT CONNECTION
COMPLEX FORM
Z=R+jL+1/jC
ABSOLUTE VALUE
Z R 2 ( L
Series
Z=
1/(1/R+1/jL+jC)
Parallel
1 2
)
C
1
1
1 2
)
( C
2
R
L
MAGNETIC FIELD UNITS AND EQUATIONS
QUANTITY
SYMBOL
SI UNIT
SI EQUATION
CGS
UNIT
CGS
EQUATION
CONVERSION
FACTOR
Magnetic
induction
tesla (T)
B=o(H+M)
Gauss
(G)
B = H+4M
1T=
104 G
Magnetic
field strength
ampere/
meter
(A/m)
H = 0.4NI/lc
(lc - magnetic
path, cm)
1 A/m =
4 10-3
Oe
Magnetic flux
weber
(Wb)
= BAc
(Ac - area,
m2 )
H = NI/lc
Oersted
( lc - magnetic
(Oe)
path, m)
Magnetization
ampere/
meter
(A/m)
M=m/V
(m- total
magnetic
moment,
V- volume,
m3 )
Magnetic
permeability
of vacuum
newton/
ampere2
o= 410-7
= BAc
1 Wb = 108
Maxwell
M
(M) (Ac - area, cm2 )
emu/cm3
M=m/V
(m- total
magnetic
moment,
V- volume,
cm3 )
1 A/m =
10-3
emu / cm3
410-7
henry
L=
=0.4N2Ac/lc
10-8
(N- turns,
Ac-area, cm2,
lc - magnetic
path, cm)
volt
V= -10-8
Nd/dt
(N- turns)
Inductance
Emf (voltage)
henry
L=oN Ac/lc
(N- turns,
Ac- area, m2,
lc - magnetic
path, m)
volt
V=-Nd/dt
(N- turns)
MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN FREE SPACE (IN SI UNITS)
LAW
DIFFERENTIAL FORM
INTEGRAL FORM
Gauss' law for
electricity
Gauss' law for
magnetism
Faraday's law
of induction
Ampere's law
NOTES: E - electric field, - charge density, 0 8.8510-12 - electric permittivity of free space, 3.14159,
k - Boltzmann's constant, q - charge, B - magnetic induction, - magnetic flux, J - current density, i - electric
current,
- del operator (if
c 299 792 458 m/s - the speed of light, 0 = 410-7 - magnetic permeability of free space,
.
V is a vector function, then
V - divergence of V,
V - the curl of V).
REFERENCES:
1. EE Information Online
2. Electrical References 2014
2009 Lazar Rozenblat
SMPS Power Supply Guide ( http://www.smps.us/ ) - tutorials, electronics reference,
formulas, schematics.
Lazar Rozenblat on Google+
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Formulasssk_2k7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument0 pageElectrical Engineering FormulasPULKITJOSHI100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering FormulasVinod MuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering FormulasMehdi Aydın DuramazPas encore d'évaluation
- Bütün Fizik FormülleriDocument13 pagesBütün Fizik Formüllerimhasan13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Formulasarthur guil-anPas encore d'évaluation
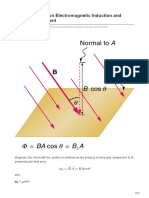
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current by AlienDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current by AlienSanatan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Form of Coulomb'S Law Basic: The Resultant Force Is and The Direction Is Given by and The Direction Is Given byDocument8 pagesVector Form of Coulomb'S Law Basic: The Resultant Force Is and The Direction Is Given by and The Direction Is Given byVijay TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3.3 Electricity and magnetism Name Symbol SI unit Notes Q ρ ρ = Q/V σ Σ = Q/A C V, φ V = dW/dQ U, U = V E E = Ψ Ψ = ∫D⋅ dA C C = Q/U ε ε ε ε εDocument2 pages1.3.3 Electricity and magnetism Name Symbol SI unit Notes Q ρ ρ = Q/V σ Σ = Q/A C V, φ V = dW/dQ U, U = V E E = Ψ Ψ = ∫D⋅ dA C C = Q/U ε ε ε ε εcvz240159Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alternating Current NotesDocument5 pagesAlternating Current Noteskamali.v777Pas encore d'évaluation
- EMI and ACDocument14 pagesEMI and ACbharathPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplitude Modulation-Voltage DistributionDocument10 pagesAmplitude Modulation-Voltage DistributionThejaswar Teja0% (1)
- Electrical and Eletronic PrinciplesDocument206 pagesElectrical and Eletronic PrinciplesvelisbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasDocument1 pageMidterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasManny LemosPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Equation ListDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equation ListChris_Barber09100% (1)
- 2 Alternating CurrentsDocument23 pages2 Alternating CurrentsKunalWadhawanPas encore d'évaluation
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFHector Ledesma IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics: U NKTDocument6 pagesThermal Physics: U NKTzzyingPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetMax MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Physics by AlienDocument10 pagesAtomic Physics by AlienSanatan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 'Physics Laws 2nd Term 2017' PDFDocument7 pages'Physics Laws 2nd Term 2017' PDFBasant HanyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Document36 pagesThe Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Lasya notesPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesDocument2 pagesPhys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesNadya B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Book Formulas Communication TeliDocument3 pagesHand Book Formulas Communication TeliJet'sPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissDocument18 pagesHigh-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissjasmonPas encore d'évaluation
- Resistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsDocument7 pagesResistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsKeith E SproatPas encore d'évaluation
- Current ElectricityDocument6 pagesCurrent ElectricityKannanSubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Document9 pagesFormulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Iñaki0% (1)
- Basic Principles Magnetic Circuits-2p PDFDocument28 pagesBasic Principles Magnetic Circuits-2p PDFgecicihesappPas encore d'évaluation
- Equations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsDocument3 pagesEquations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsLeseat NocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiber Optics 2Document36 pagesFiber Optics 2ekramul98131Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eder - Ferreira - Task 3Document8 pagesEder - Ferreira - Task 3daniel FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéPas encore d'évaluation
- BookkkkDocument207 pagesBookkkkNadin NirvanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oliver ElectronicsDocument35 pagesOliver Electronicsprem_singh_nepal100% (1)
- Formulae Using Symbols Notation: - 1 - 1 B P V eDocument5 pagesFormulae Using Symbols Notation: - 1 - 1 B P V eJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Electricity by AlienDocument20 pagesCurrent Electricity by AlienSanatan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide13 PDFDocument40 pagesGuide13 PDFAgus MursidiPas encore d'évaluation
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Shibuya, Y. Fujita, S. Tamaki, E. - Analysis of Very Fast Transients in TransforDocument7 pagesShibuya, Y. Fujita, S. Tamaki, E. - Analysis of Very Fast Transients in TransforJiraya15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Formulas Conversion Formulas Area of Circle = πr: Electrical Formulas Based on 60 Hz Capacitive Reactance (XDocument4 pagesElectrical Formulas Conversion Formulas Area of Circle = πr: Electrical Formulas Based on 60 Hz Capacitive Reactance (XAkram ElhdeePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergyDocument19 pagesPhysics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergySucharita KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic PhysicsDocument8 pagesAtomic Physicsvignesh nadarPas encore d'évaluation
- EMSP 28jun2023Document9 pagesEMSP 28jun2023Mazz77Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Network Elements: 1) ResistanceDocument7 pagesThe Network Elements: 1) Resistancearpit sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 662 Microwave Devices: Transit-Time Diodes February 17, 2005Document29 pagesECE 662 Microwave Devices: Transit-Time Diodes February 17, 2005Ghulam ShabbirPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of The Variation of Power Loss With Frequency Along A RectangularDocument6 pagesStudy of The Variation of Power Loss With Frequency Along A RectangularIAEME PublicationPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplitude Modulation Part 1Document26 pagesAmplitude Modulation Part 1rwezioo100% (4)
- Task 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDocument16 pagesTask 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkHaiberPas encore d'évaluation
- FormulaeDocument34 pagesFormulaedineshvhavalPas encore d'évaluation
- 72 ReviewerDocument17 pages72 ReviewerGeronimo Allan Jerome AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsD'EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesD'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksD'EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2D'EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- BitSlicedProcessor PDFDocument1 pageBitSlicedProcessor PDFsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ge Bentlynevada 3500 Series DatasheetDocument12 pagesGe Bentlynevada 3500 Series Datasheetsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry in Everyday Life PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life PDFsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions PhysicsDocument12 pagesImportant Questions PhysicsNaziaParveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist - Purchase of Re-Sale Flat in A Registered Co - Op. Society Proposed Co - Op.societyDocument1 pageChecklist - Purchase of Re-Sale Flat in A Registered Co - Op. Society Proposed Co - Op.societysanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Interaction - 1Document23 pagesDrug Interaction - 1sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Do You Convert BTU To CFM?Document6 pagesHow Do You Convert BTU To CFM?sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- ER DiagramDocument15 pagesER Diagramsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reasoning Tricks PDFDocument53 pagesReasoning Tricks PDFrupaliPas encore d'évaluation
- CYCLECITIES CP04 D421 BSS Survey MethodologyDocument40 pagesCYCLECITIES CP04 D421 BSS Survey Methodologysanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Does An Air Conditioner WorkDocument4 pagesHow Does An Air Conditioner Worksanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Havells Power Cable Price ListDocument2 pagesHavells Power Cable Price ListRohith MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- RCD PDFDocument6 pagesRCD PDFsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bike Share ReportDocument16 pagesBike Share Reportsanjay975100% (1)
- Database Management System Set 4 - Questions & Answers 31-40Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 4 - Questions & Answers 31-40sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System Set 10 - Questions & Answers 91-100Document4 pagesDatabase Management System Set 10 - Questions & Answers 91-100sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Three Element Control BoilerDocument1 pageThree Element Control Boilersanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System Set 6 - Questions & Answers 51-60Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 6 - Questions & Answers 51-60sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System Set 7 - Questions & Answers 61-70Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 7 - Questions & Answers 61-70sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System Set 8 - Questions & Answers 71-80Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 8 - Questions & Answers 71-80sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management System Set 3 - Questions & Answers 21-30Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 3 - Questions & Answers 21-30sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Data Storage and IndexingDocument60 pages5 Data Storage and Indexingtejashraj93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice E-CommerceDocument13 pagesMultiple Choice E-CommerceChaii Chai67% (3)
- Database Management System Set 9 - Questions & Answers 81-90Document3 pagesDatabase Management System Set 9 - Questions & Answers 81-90sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management Systems Set 5 - Questions & Answers 41-50Document3 pagesDatabase Management Systems Set 5 - Questions & Answers 41-50sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- WIFI AP EPMP User Guide v1Document250 pagesWIFI AP EPMP User Guide v1sanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- LastVegas SubtitleDocument338 pagesLastVegas Subtitlesanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Relay Assembly Test Room ExperimentsDocument9 pagesRelay Assembly Test Room Experimentssanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transmitter For FlowDocument27 pagesTransmitter For Flowsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- DP Transmitter For FlowDocument1 pageDP Transmitter For Flowsanjay975Pas encore d'évaluation
- Segmentation of Blood Vessels Using Rule-Based and Machine-Learning-Based Methods: A ReviewDocument10 pagesSegmentation of Blood Vessels Using Rule-Based and Machine-Learning-Based Methods: A ReviewRainata PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- 500 TransDocument5 pages500 TransRodney WellsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bravo MRI II Operation ManualDocument45 pagesBravo MRI II Operation ManualLuis100% (1)
- Filipino Construction TermsDocument6 pagesFilipino Construction TermsAdrian Perez75% (4)
- Pharmalytica Exhibitor List 2023Document3 pagesPharmalytica Exhibitor List 2023Suchita PoojaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFDocument3 pagesKami Export - Subject Complements-1 PDFkcv kfdsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Document115 pagesTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- Coding Decoding Sheet - 01 1678021709186Document9 pagesCoding Decoding Sheet - 01 1678021709186Sumit VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Para Lec CombinedDocument83 pagesPara Lec CombinedClent Earl Jason O. BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelDocument11 pagesFlow Zone Indicator Guided Workflows For PetrelAiwarikiaar100% (1)
- Technical Data Sheet: LPI HVSC PlusDocument2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: LPI HVSC PlusNguyễn TấnPas encore d'évaluation
- Petersen Coils Basic 20principle and ApplicationDocument3 pagesPetersen Coils Basic 20principle and ApplicationasotozuazuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Javanese PeopleDocument22 pagesJavanese PeopleDenisaPas encore d'évaluation
- End of Summer Course Test August 2021Document16 pagesEnd of Summer Course Test August 2021Thanh Nguyen vanPas encore d'évaluation
- AppearancesDocument4 pagesAppearancesReme TrujilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?Document32 pagesBulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?krds chidPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing and Building A Computer TableDocument9 pagesDesigning and Building A Computer Tablemaster_codersPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium SeriesDocument4 pagesManual of Sensorless Brushless Motor Speed Controller: Pentium Seriesfosavo5839Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test7 PointersDocument16 pagesTest7 PointersPratibha DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Biomechanics: Leigh W. Marshall, Stuart M. McgillDocument4 pagesClinical Biomechanics: Leigh W. Marshall, Stuart M. McgillMichael JunPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTDocument48 pagesECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabatePas encore d'évaluation
- Crma Unit 1 Crma RolesDocument34 pagesCrma Unit 1 Crma Rolesumop3plsdn0% (1)
- The Spirit Controlled Life Ebook PDF 1Document184 pagesThe Spirit Controlled Life Ebook PDF 1Okesola AbayomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeo Treatment of Eye Diseases and AllergiesDocument17 pagesHomeo Treatment of Eye Diseases and AllergiesZia AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and HemoglobinDocument27 pagesChapter 7: Protein Function Part I: Myoglobin and HemoglobineliPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles Involved in Baking 1Document97 pagesPrinciples Involved in Baking 1Milky BoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayDocument30 pagesAp, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayMindaugasStacevičiusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruhangawebare Kalemera Godfrey Thesis PDFDocument116 pagesRuhangawebare Kalemera Godfrey Thesis PDFYoobsan Tamiru TTolaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsDocument528 pagesEssential Calculus Skills Practice Workbook With Full SolutionsGerardo Navarro Sánchez94% (65)
- Wcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Document29 pagesWcdma Idle Mode (Ericsson)Hosein ShahbaziPas encore d'évaluation