Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
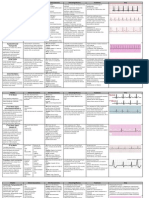
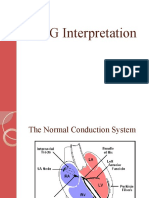
ECG Interpretation
Transféré par
Richelle Dianne Ramos-GiangCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
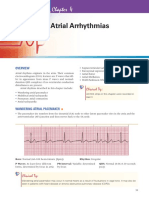
ECG Interpretation
Transféré par
Richelle Dianne Ramos-GiangDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ECG Interpretation
Study online at quizlet.com/_qymbo
1.
...
2.
2, II
12.
Atrial flutter
This is called ___.
13.
Biphasic
Both A and B are sub-types of __ degree, type __
heart block.
3.
2nd
___ degree heart block is characterized by partical
communication between atria and ventricals.
4.
3rd
With a __ degree heart block, no communication
takes place between the artia and ventricals.
5.
100
Junctional tach begins at __ beats per minute.
6.
100
Tachycardia is HR greater than __.
7.
150
Ventricular tach begins at ___ beats per minute.
8.
Asystole
These P waves are __, usually due to L atrial
enlargement.
14.
BP
__ = CO x Peripheral vascular resistance
15.
CO
___ = HR x SV
16.
Conduction
The wide QRS (above) is an example of
aberrant ventricular ____.
Name above condition.
9.
17.
Delta
Atrial
Fib
Abnormal slurring (A) of this QRS complex is
called a ___ wave.
10.
11.
Atrial
fib
Example of totally irregular (irregularly irregular)
rhythm with no consistency = ___.
18.
Ectopic
tachycardia
Atrial
Flutter
Top = AV; Bottom = Ventricular origin*
19.
Fast or slow
First question to ask when looking at an
ECG = ___.
20.
First
Prolonged PR intervals is an example of
___ degree heart block.
21.
26.
Normal
First degree
heart block
___ progression of impulse from AV to perkinje
fibers gives QRS complex above.
Delay between P and QRS (3rd arrow) is
seen with what condition?
22.
27.
Normal
28.
Notched
Two questions to ask about P waves. Do they have
a ___ appearance? Does one come before every
QRS?
I
First image is a ___ P wave.
29.
Nothing
This type of heart block is 2nd degree type
___, with increasing delays due fatiged AV
node.
23.
Idioventricular
What is wrong with this ECG?
30.
Opposite
Slow (20), ____ escape rhythm is pictured
above with a wide QRS from ___ (same)
pacemaker.
24.
Inverted
QRS complexes are ___ the direction of the T wave
= ventricular dysrhythmias.
This P' wave is ___.
25.
31.
Most __ waves are round and upright when
normal.
32.
To check whether atrial rhythm is irregular, use
calipers to measure distance between ___ waves.
33.
If atria and ventricular rhythm is associated like it
should be, every QRS will have a __ wave.
34.
P wave
Supra-ventricular tachycardia is characterized by
an absent ___.
Normal
Name above condition
35.
P wave
42.
Preexitation
Hmmm. Something's missing.
36.
PAC
37.
Pacemaker
An early atrial impulse generated outside the SA
node causes a ___.
The condition represented above is called
ventricular ___.
43.
44.
Arrow points to ___ spike seen preceding this
wide abnormal QRS.
Premature
atrial
PVC
Name above condition.
45.
Q wave.
What is missing in every cycle?
Two questions to ask about P waves. Do they
have a normal appearance? Does one come
before every ___?
Perkinje
fibers
The isoelectric line between the P wave and the
QRS is when the impulse is traveling through
the ___.
46.
QRS
39.
PR
The ___ interval encompasses the entire
impulse from SA through the Perkinje fibers.
47.
QRS
40.
PR
38.
PAC stands for ___ complex.
B. indicates a repeated and complete drop of
what complex?
A has an increasingly prolonged ___ interval
until QRS is dropped.
41.
Preexcitation
48.
49.
50.
___ (above) result from a ectopic ventricular
impulse before the SA can fire. Note QRS is wide.
To check whether verntricular rhythm is
irregular, use calipers to measure distance
between ___ waves.
Regular or
Irregular
Second question to ask when looking at an
ECT = ___.
SA node
All these P waves lack __ impulse generation.
51.
Shorter
The PR segment is ___ because the impulse
has less distance to travel. The pacemaker is
closer to the AV node.
52.
Supraventricular
58.
thyroid
Wide bizarre QRS complexes (above) are
associated with ___ impulse generation.
53.
Tachycardia
Fat or fluid in chest, and hyper____ can cause
low voltage QRS (seen above).
59.
Torsades
de pointes
This person is in ventricular ___.
54.
Tachycardia
Multiple PVC's with rotating ventricular ectopic
pacemakers (above) are called __.
60.
V fib
3 PVC's in a row (above) is Ventricular
___, also with wide QRS and an ectopic
ventricular pacemaker.
55.
Tall
This person is in ___.
61.
V. Fib
__ QRS complexes (seen above) are the
result of ventricular hypertrophy or
conduction problems.
56.
Third
Name above ventricular condition.
62.
63.
This is an example of ___ degree heart
block.
57.
V. Tach
Three or more PVC's in a row is termed ___.
Weinkebach
Third degree
heart block
A. P gets further away from QRS until QRS is
dropped. This is called ___.
Name above condition.
64.
Weinke-bach
This abnormal ECG is called ___.
65.
Wide, notched
Second P wave is both ___ and ___.
66.
Wider, shorter
P' is __ than P due to its location closer to the AV node.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic EKG ECG Rhythms CheatsheetDocument1 pageBasic EKG ECG Rhythms CheatsheetAhmad83% (6)
- ECG Interpretation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageECG Interpretation Cheat Sheethirsi20051879% (24)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4Document3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4ktfosterfd2096% (97)
- EKG Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesEKG Cheat SheetAlert Twitter100% (5)
- ArrhythmiaDocument2 pagesArrhythmiaChris Pritchard93% (30)
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXD'EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- ECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsDocument23 pagesECG Mastery Improving Your ECG Interpretation SkillsHitesh Deora100% (2)
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (27)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Ophthalmology PDFDocument28 pagesOphthalmology PDFKukuh Rizwido PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!D'EverandBonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- ECG InterpretationDocument95 pagesECG InterpretationShiela Mae Lopez100% (10)
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!D'EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg StripsDocument39 pagesEcg StripsNursyNurse100% (3)
- Ecg Cheat Sheet 35Document2 pagesEcg Cheat Sheet 35jessjaylee80% (5)
- Basic EKG For DummiesDocument133 pagesBasic EKG For Dummieseduardocmoura86% (7)
- EKG ExamplesDocument9 pagesEKG ExamplesMayer Rosenberg99% (235)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsD'EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg ReadingsDocument11 pagesEcg ReadingsAnton Laurenciana100% (5)
- Basic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALDocument16 pagesBasic ECG and Arrhythmia FINALCharlotte James100% (5)
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasD'EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!D'EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG LectureDocument214 pagesECG Lecturensyuzon100% (1)
- ECG ReadingDocument11 pagesECG ReadingSuresh Shrestha100% (1)
- EKG InterpretationDocument65 pagesEKG Interpretationpaskariatne probo dewi100% (1)
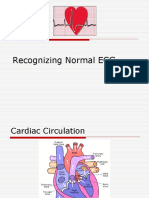
- Recognizing Normal ECGDocument50 pagesRecognizing Normal ECGJosiephine Bucalon100% (3)
- Vascular Board Questions NumberedDocument60 pagesVascular Board Questions NumberedAudrey Schlembach100% (6)
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationD'EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Guyton and Hall Chapter 40Document2 pagesGuyton and Hall Chapter 40Richelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Soap NoteDocument2 pagesSoap Notetopopirate100% (4)
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!D'EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticeDocument5 pagesName That EKG: D:/My Documents/Documents/AIME/Handouts/EKG PracticelcascolanPas encore d'évaluation
- Iggy Med Surg Test Bank Chapter 007Document10 pagesIggy Med Surg Test Bank Chapter 007Tracy Bartell100% (5)
- CCN (Feu)Document71 pagesCCN (Feu)Ashley Nicole Lim100% (1)
- Tracheostomy Care Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Care Reflective EssayAnjae Gariando100% (3)
- ToxicologyDocument197 pagesToxicologyRichelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (6)
- Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 35Document11 pagesHarper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 35Richelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (1)
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasD'EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (5)
- Trans of Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 32Document3 pagesTrans of Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 32Richelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (1)
- Recurrent Pregnancy LossDocument40 pagesRecurrent Pregnancy LossJagannath MaalePas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesEKG Pocket GuideFabian Ramirez HincapiéPas encore d'évaluation
- Valleylab Force 2 - User ManualDocument58 pagesValleylab Force 2 - User ManualelectricistPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG InterpretationDocument52 pagesECG InterpretationMarcus, RN98% (44)
- Basic ECG ReadingDocument41 pagesBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (3)
- Educational Training Manual: Certification Board, IncDocument58 pagesEducational Training Manual: Certification Board, IncAlexander MaukinPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookD'EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular DrillsDocument12 pagesCardiovascular DrillsMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelley Eidem Recipes For CancerDocument4 pagesKelley Eidem Recipes For CancerRohinee SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization of HospitalDocument29 pagesOrganization of HospitalAnusha VerghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Easy ECG GuideDocument17 pagesEasy ECG GuideDr.Chinmay Kulkarni83% (12)
- Oral Hygiene InstructionsDocument2 pagesOral Hygiene Instructionstepokpantat100% (1)
- EcgDocument57 pagesEcgenii_ta100% (9)
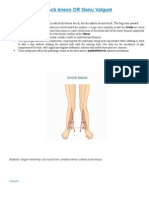
- Genu ValgumDocument2 pagesGenu ValgumPurohit_R0% (1)
- Tooth Discoloration Hypomineralization and HypoplasiaDocument5 pagesTooth Discoloration Hypomineralization and HypoplasiamirfanulhaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Pakya ECG BasicsDocument5 pagesPakya ECG BasicsFrederick CokroPas encore d'évaluation
- PC Metabolic AcidosisDocument4 pagesPC Metabolic AcidosisErine Emmanuelle Cawaling Hetrosa50% (2)
- eSP EchoDocument18 pageseSP EchoBeck100% (1)
- Nursing Responsibilities After CCDocument5 pagesNursing Responsibilities After CCSofia P. PanlilioPas encore d'évaluation
- Arritmias Supraventriculares .Document8 pagesArritmias Supraventriculares .fh2301lrPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Interpretation (WSAVA 2007, Boswood)Document5 pagesECG Interpretation (WSAVA 2007, Boswood)Kevin ChoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Arritmia SVDocument17 pagesArritmia SVCésar Lobo TarangoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX-questions ElectrolytesDocument96 pagesNCLEX-questions Electrolytesmanhua fanaticPas encore d'évaluation
- The Six Second ECG: Annotated Answer KeyDocument9 pagesThe Six Second ECG: Annotated Answer KeyRaquel GirónPas encore d'évaluation
- CardioDocument261 pagesCardioAli Aborges Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology 3Document11 pagesCardiology 3Fareed KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EcgDocument11 pagesEcgRajneesh TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ekg NetDocument15 pagesEkg NetDewi AyuPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGSarah RonquilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Commonwealth Statutory Declaration FormDocument2 pagesCommonwealth Statutory Declaration FormMiao Miao LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord1Document126 pagesSpinal Cord1Richelle Dianne Ramos-Giang0% (1)
- Nutrional AssessmentDocument12 pagesNutrional AssessmentRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumothorax Working PresentationDocument16 pagesPneumothorax Working PresentationRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Digit Subtraction AdditionDocument1 page3-Digit Subtraction AdditionRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue FeverDocument2 pagesDengue FeverRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- ToxifinalDocument34 pagesToxifinalRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Typhoid Fever - Public HealthDocument23 pagesTyphoid Fever - Public HealthRichelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (1)
- List of Philippine MunicipalitiesDocument168 pagesList of Philippine MunicipalitiesRichelle Dianne Ramos-GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- SubcutaneousDocument36 pagesSubcutaneousAlina CazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Standards: - Total Sub-Standards: - Total ESR StandardsDocument8 pagesTotal Standards: - Total Sub-Standards: - Total ESR StandardsHCX dghhqPas encore d'évaluation
- ''Traditional Arabic and Islamic Medicine''Document4 pages''Traditional Arabic and Islamic Medicine''tandraini100% (1)
- Safd HandbookDocument22 pagesSafd HandbookIrsyad Zainul AbidinPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Specs Nurs104ly 2nd Semester 4th YearDocument6 pagesCourse Specs Nurs104ly 2nd Semester 4th YearEfren Plaza MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20th Century NurseDocument5 pages20th Century NurseMisch Yeen100% (1)
- Alice Final Draft EthicsDocument8 pagesAlice Final Draft Ethicsapi-254093121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas EmilyDocument6 pagesTugas EmilyPitri YuliantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lewis COPD Case StudyDocument2 pagesLewis COPD Case Studyatarisgurl08Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11 PagesDocument15 pages11 PagesOketch MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Patient Claim Form - ConventionalDocument2 pagesIn-Patient Claim Form - ConventionalAbdul Qayyum Sipra Madduki50% (2)
- PR To Hernia Angkatan 1bDocument3 pagesPR To Hernia Angkatan 1bIntan Eklesiana NapitupuluPas encore d'évaluation
- Devitalizing Agents, Non-Vital Methods of Root Canal Therapy, Non-Vital Pulpotomy and Pulpectomy, Indications, Description of TechniquesDocument45 pagesDevitalizing Agents, Non-Vital Methods of Root Canal Therapy, Non-Vital Pulpotomy and Pulpectomy, Indications, Description of TechniquesGeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Postoperative Care: Postoperative Note and OrdersDocument4 pagesPostoperative Care: Postoperative Note and OrdersAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Terri Campbell MADocument2 pagesTerri Campbell MAapi-121348673Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Appendix? A Vestigial Organ, or One With A Purpose?Document9 pagesWhat Is The Appendix? A Vestigial Organ, or One With A Purpose?Azizah RahawarinPas encore d'évaluation