Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ASIC
Transféré par
Vinay GargCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ASIC
Transféré par
Vinay GargDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
[Chapterstart][Previouspage][Nextpage]
PortionsfromApplicationSpecificIntegratedCircuitsCopyright1997byAddison
WesleyLongman,Inc.
1.1TypesofASICs
ICsaremadeonathin(afewhundredmicronsthick),circularsiliconwafer,with
eachwaferholdinghundredsofdie(sometimespeopleusediesordicefortheplural
ofdie).Thetransistorsandwiringaremadefrommanylayers(usuallybetween10
and15distinctlayers)builtontopofoneanother.Eachsuccessivemasklayerhasa
patternthatisdefinedusingamasksimilartoaglassphotographicslide.Thefirst
halfdozenorsolayersdefinethetransistors.Thelasthalfdozenorsolayersdefine
themetalwiresbetweenthetransistors(theinterconnect).
AfullcustomICincludessome(possiblyall)logiccellsthatarecustomizedand
allmasklayersthatarecustomized.Amicroprocessorisanexampleofafullcustom
ICdesignersspendmanyhourssqueezingthemostoutofeverylastsquaremicron
ofmicroprocessorchipspacebyhand.CustomizingalloftheICfeaturesinthisway
allowsdesignerstoincludeanalogcircuits,optimizedmemorycells,ormechanical
structuresonanIC,forexample.FullcustomICsarethemostexpensiveto
manufactureandtodesign.Themanufacturingleadtime(thetimeittakesjustto
makeanICnotincludingdesigntime)istypicallyeightweeksforafullcustomIC.
ThesespecializedfullcustomICsareoftenintendedforaspecificapplication,sowe
mightcallsomeofthemfullcustomASICs.
WeshalldiscussfullcustomASICsbrieflynext,butthemembersoftheICfamily
thatwearemoreinterestedinaresemicustomASICs,forwhichallofthelogiccells
arepredesignedandsome(possiblyall)ofthemasklayersarecustomized.Using
predesignedcellsfromacelllibrarymakesourlivesasdesignersmuch,mucheasier.
TherearetwotypesofsemicustomASICsthatweshallcover:standardcellbased
ASICsandgatearraybasedASICs.Followingthisweshalldescribethe
programmableASICs,forwhichallofthelogiccellsarepredesignedandnoneof
themasklayersarecustomized.TherearetwotypesofprogrammableASICs:the
programmablelogicdeviceand,thenewestmemberoftheASICfamily,thefield
programmablegatearray.
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
1/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
1.1.1FullCustomASICs
InafullcustomASICanengineerdesignssomeorallofthelogiccells,circuits,or
layoutspecificallyforoneASIC.Thismeansthedesignerabandonstheapproachof
usingpretestedandprecharacterizedcellsforallorpartofthatdesign.Itmakessense
totakethisapproachonlyiftherearenosuitableexistingcelllibrariesavailablethat
canbeusedfortheentiredesign.Thismightbebecauseexistingcelllibrariesarenot
fastenough,orthelogiccellsarenotsmallenoughorconsumetoomuchpower.You
mayneedtousefullcustomdesigniftheASICtechnologyisneworsospecialized
thattherearenoexistingcelllibrariesorbecausetheASICissospecializedthatsome
circuitsmustbecustomdesigned.FewerandfewerfullcustomICsarebeingdesigned
becauseoftheproblemswiththesespecialpartsoftheASIC.Thereisonegrowing
memberofthisfamily,though,themixedanalog/digitalASIC,whichweshalldiscuss
next.
Bipolartechnologyhashistoricallybeenusedforprecisionanalogfunctions.There
aresomefundamentalreasonsforthis.Inallintegratedcircuitsthematchingof
componentcharacteristicsbetweenchipsisverypoor,whilethematchingof
characteristicsbetweencomponentsonthesamechipisexcellent.Supposewehave
transistorsT1,T2,andT3onananalog/digitalASIC.Thethreetransistorsareallthe
samesizeandareconstructedinanidenticalfashion.TransistorsT1andT2are
locatedadjacenttoeachotherandhavethesameorientation.TransistorT3isthesame
sizeasT1andT2butislocatedontheothersideofthechipfromT1andT2andhasa
differentorientation.ICsaremadeinbatchescalledwaferlots.Awaferlotisagroup
ofsiliconwafersthatareallprocessedtogether.Usuallytherearebetween5and30
wafersinalot.Eachwafercancontaintensorhundredsofchipsdependingonthe
sizeoftheICandthewafer.
IfweweretomakemeasurementsofthecharacteristicsoftransistorsT1,T2,and
T3wewouldfindthefollowing:
TransistorsT1willhavevirtuallyidenticalcharacteristicstoT2onthesameIC.
Wesaythatthetransistorsmatchwellorthetrackingbetweendevicesis
excellent.
TransistorT3willmatchtransistorsT1andT2onthesameICverywell,butnot
ascloselyasT1matchesT2onthesameIC.
TransistorT1,T2,andT3willmatchfairlywellwithtransistorsT1,T2,andT3
onadifferentIConthesamewafer.Thematchingwilldependonhowfarapart
thetwoICsareonthewafer.
TransistorsonICsfromdifferentwafersinthesamewaferlotwillnotmatchvery
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
2/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
well.
TransistorsonICsfromdifferentwaferlotswillmatchverypoorly.
Formanyanalogdesignstheclosematchingoftransistorsiscrucialtocircuit
operation.Forthesecircuitdesignspairsoftransistorsareused,locatedadjacentto
eachother.Devicephysicsdictatesthatapairofbipolartransistorswillalwaysmatch
morepreciselythanCMOStransistorsofacomparablesize.Bipolartechnologyhas
historicallybeenmorewidelyusedforfullcustomanalogdesignbecauseofits
improvedprecision.Despiteitspooreranalogproperties,theuseofCMOStechnology
foranalogfunctionsisincreasing.Therearetworeasonsforthis.Thefirstreasonis
thatCMOSisnowbyfarthemostwidelyavailableICtechnology.ManymoreCMOS
ASICsandCMOSstandardproductsarenowbeingmanufacturedthanbipolarICs.
Thesecondreasonisthatincreasedlevelsofintegrationrequiremixinganalogand
digitalfunctionsonthesameIC:thishasforceddesignerstofindwaystouseCMOS
technologytoimplementanalogfunctions.Circuitdesigners,usingclevernew
techniques,havebeenverysuccessfulinfindingnewwaystodesignanalogCMOS
circuitsthatcanapproachtheaccuracyofbipolaranalogdesigns.
1.1.2StandardCellBasedASICs
AcellbasedASIC(cellbasedIC,orCBICacommonterminJapan,pronounced
seabick)usespredesignedlogiccells(ANDgates,ORgates,multiplexers,andflip
flops,forexample)knownasstandardcells.WecouldapplythetermCBICtoany
ICthatusescells,butitisgenerallyacceptedthatacellbasedASICorCBICmeansa
standardcellbasedASIC.
Thestandardcellareas(alsocalledflexibleblocks)inaCBICarebuiltofrowsof
standardcellslikeawallbuiltofbricks.Thestandardcellareasmaybeusedin
combinationwithlargerpredesignedcells,perhapsmicrocontrollersoreven
microprocessors,knownasmegacells.Megacellsarealsocalledmegafunctions,full
customblocks,systemlevelmacros(SLMs),fixedblocks,cores,orFunctional
StandardBlocks(FSBs).
TheASICdesignerdefinesonlytheplacementofthestandardcellsandthe
interconnectinaCBIC.However,thestandardcellscanbeplacedanywhereonthe
siliconthismeansthatallthemasklayersofaCBICarecustomizedandareuniqueto
aparticularcustomer.TheadvantageofCBICsisthatdesignerssavetime,money,
andreduceriskbyusingapredesigned,pretested,andprecharacterizedstandardcell
library.Inadditioneachstandardcellcanbeoptimizedindividually.Duringthe
designofthecelllibraryeachandeverytransistorineverystandardcellcanbechosen
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
3/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
tomaximizespeedorminimizearea,forexample.Thedisadvantagesarethetimeor
expenseofdesigningorbuyingthestandardcelllibraryandthetimeneededto
fabricatealllayersoftheASICforeachnewdesign.
Figure1.2showsaCBIC(lookingdownonthedieshowninFigure1.1b,for
example).TheimportantfeaturesofthistypeofASICareasfollows:
Allmasklayersarecustomizedtransistorsandinterconnect.
Customblockscanbeembedded.
Manufacturingleadtimeisabouteightweeks.
FIGURE1.2AcellbasedASIC(CBIC)diewith
asinglestandardcellarea(aflexibleblock)
togetherwithfourfixedblocks.Theflexible
blockcontainsrowsofstandardcells.Thisis
whatyoumightseethroughalowpowered
microscopelookingdownonthedieof
Figure1.1(b).Thesmallsquaresaroundthe
edgeofthediearebondingpadsthatare
connectedtothepinsoftheASICpackage.
Eachstandardcellinthelibraryisconstructedusingfullcustomdesignmethods,
butyoucanusethesepredesignedandprecharacterizedcircuitswithouthavingtodo
anyfullcustomdesignyourself.Thisdesignstylegivesyouthesameperformance
andflexibilityadvantagesofafullcustomASICbutreducesdesigntimeandreduces
risk.
Standardcellsaredesignedtofittogetherlikebricksinawall.Figure1.3showsan
exampleofasimplestandardcell(itissimpleinthesenseitisnotmaximizedfor
densitybutidealforshowingyouitsinternalconstruction).Powerandgroundbuses
(VDDandGNDorVSS)runhorizontallyonmetallinesinsidethecells.
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
4/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
FIGURE1.3Lookingdownonthelayoutofastandardcell.This
cellwouldbeapproximately25micronswideonanASICwith
(lambda)=0.25microns(amicronis106m).Standardcellsare
stackedlikebricksinawalltheabutmentbox(AB)definesthe
edgesofthebrick.Thedifferencebetweentheboundingbox
(BB)andtheABistheareaofoverlapbetweenthebricks.Power
supplies(labeledVDDandGND)runhorizontallyinsidea
standardcellonametallayerthatliesabovethetransistorlayers.
Eachdifferentshadedandlabeledpatternrepresentsadifferent
layer.Thisstandardcellhascenterconnectors(thethree
squares,labeledA1,B1,andZ)thatallowthecelltoconnectto
others.ThelayoutwasdrawnusingROSE,asymboliclayout
editordevelopedbyRockwellandCompass,andthenimported
intoTannerResearchsLEdit.
StandardcelldesignallowstheautomationoftheprocessofassemblinganASIC.
Groupsofstandardcellsfithorizontallytogethertoformrows.Therowsstack
verticallytoformflexiblerectangularblocks(whichyoucanreshapeduringdesign).
Youmaythenconnectaflexibleblockbuiltfromseveralrowsofstandardcellsto
otherstandardcellblocksorotherfullcustomlogicblocks.Forexample,youmight
wanttoincludeacustominterfacetoastandard,predesignedmicrocontrollertogether
withsomememory.Themicrocontrollerblockmaybeafixedsizemegacell,you
mightgeneratethememoryusingamemorycompiler,andthecustomlogicand
memorycontrollerwillbebuiltfromflexiblestandardcellblocks,shapedtofitinthe
emptyspacesonthechip.
BothcellbasedandgatearrayASICsusepredefinedcells,butthereisadifference
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
5/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
wecanchangethetransistorsizesinastandardcelltooptimizespeedand
performance,butthedevicesizesinagatearrayarefixed.Thisresultsinatradeoffin
performanceandareainagatearrayatthesiliconlevel.Thetradeoffbetweenarea
andperformanceismadeatthelibrarylevelforastandardcellASIC.
ModernCMOSASICsusetwo,three,ormorelevels(orlayers)ofmetalfor
interconnect.Thisallowswirestocrossoverdifferentlayersinthesamewaythatwe
usecoppertracesondifferentlayersonaprintedcircuitboard.Inatwolevelmetal
CMOStechnology,connectionstothestandardcellinputsandoutputsareusually
madeusingthesecondlevelofmetal(metal2,theupperlevelofmetal)atthetops
andbottomsofthecells.Inathreelevelmetaltechnology,connectionsmaybe
internaltothelogiccell(astheyareinFigure1.3).Thisallowsformoresophisticated
routingprogramstotakeadvantageoftheextrametallayertorouteinterconnectover
thetopofthelogiccells.WeshallcoverthedetailsofroutingASICsinChapter17.
Aconnectionthatneedstocrossoverarowofstandardcellsusesafeedthrough.
Thetermfeedthroughcanrefereithertothepieceofmetalthatisusedtopassa
signalthroughacellortoaspaceinacellwaitingtobeusedasafeedthroughvery
confusing.Figure1.4showstwofeedthroughs:oneincellA.14andoneincellA.23.
Inbothtwolevelandthreelevelmetaltechnology,thepowerbuses(VDDand
GND)insidethestandardcellsnormallyusethelowest(closesttothetransistors)
layerofmetal(metal1).Thewidthofeachrowofstandardcellsisadjustedsothat
theymaybealignedusingspacercells.Thepowerbuses,orrails,arethenconnected
toadditionalverticalpowerrailsusingrowendcellsatthealignedendsofeach
standardcellblock.Iftherowsofstandardcellsarelong,thenverticalpowerrailscan
alsoberuninmetal2throughthecellrowsusingspecialpowercellsthatjustconnect
toVDDandGND.Usuallythedesignermanuallycontrolsthenumberandwidthof
theverticalpowerrailsconnectedtothestandardcellblocksduringphysicaldesign.
AdiagramofthepowerdistributionschemeforaCBICisshowninFigure1.4.
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
6/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
FIGURE1.4RoutingtheCBIC(cellbasedIC)shownin
Figure1.2.Theuseofregularlyshapedstandardcells,suchas
theoneinFigure1.3,fromalibraryallowsASICslikethistobe
designedautomatically.ThisASICusestwoseparatelayersof
metalinterconnect(metal1andmetal2)runningatrightanglesto
eachother(liketracesonaprintedcircuitboard).
Interconnectionsbetweenlogiccellsusesspaces(called
channels)betweentherowsofcells.ASICsmayhavethree(or
more)layersofmetalallowingthecellrowstotouchwiththe
interconnectrunningoverthetopofthecells.
AllthemasklayersofaCBICarecustomized.Thisallowsmegacells(SRAM,a
SCSIcontroller,oranMPEGdecoder,forexample)tobeplacedonthesameICwith
standardcells.MegacellsareusuallysuppliedbyanASICorlibrarycompany
completewithbehavioralmodelsandsomewaytotestthem(ateststrategy).ASIC
librarycompaniesalsosupplycompilerstogenerateflexibleDRAM,SRAM,and
ROMblocks.Sinceallmasklayersonastandardcelldesignarecustomized,memory
designismoreefficientanddenserthanforgatearrays.
Forlogicthatoperatesonmultiplesignalsacrossadatabusadatapath(DP)
theuseofstandardcellsmaynotbethemostefficientASICdesignstyle.SomeASIC
librarycompaniesprovideadatapathcompilerthatautomaticallygenerates
datapathlogic.Adatapathlibrarytypicallycontainscellssuchasadders,
subtracters,multipliers,andsimplearithmeticandlogicalunits(ALUs).The
connectorsofdatapathlibrarycellsarepitchmatchedtoeachothersothattheyfit
together.Connectingdatapathcellstoformadatapathusually,butnotalways,results
infasteranddenserlayoutthanusingstandardcellsoragatearray.
Standardcellandgatearraylibrariesmaycontainhundredsofdifferentlogiccells,
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
7/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
includingcombinationalfunctions(NAND,NOR,AND,ORgates)withmultiple
inputs,aswellaslatchesandflipflopswithdifferentcombinationsofreset,presetand
clockingoptions.TheASIClibrarycompanyprovidesdesignerswithadatabookin
paperorelectronicformwithallofthefunctionaldescriptionsandtiminginformation
foreachlibraryelement.
1.1.3GateArrayBasedASICs
Inagatearray(sometimesabbreviatedtoGA)orgatearraybasedASICthe
transistorsarepredefinedonthesiliconwafer.Thepredefinedpatternoftransistorson
agatearrayisthebasearray,andthesmallestelementthatisreplicatedtomakethe
basearray(likeanM.C.Escherdrawing,ortilesonafloor)isthebasecell
(sometimescalledaprimitivecell).Onlythetopfewlayersofmetal,whichdefine
theinterconnectbetweentransistors,aredefinedbythedesignerusingcustommasks.
Todistinguishthistypeofgatearrayfromothertypesofgatearray,itisoftencalleda
maskedgatearray(MGA).Thedesignerchoosesfromagatearraylibraryof
predesignedandprecharacterizedlogiccells.Thelogiccellsinagatearraylibraryare
oftencalledmacros.Thereasonforthisisthatthebasecelllayoutisthesamefor
eachlogiccell,andonlytheinterconnect(insidecellsandbetweencells)is
customized,sothatthereisasimilaritybetweengatearraymacrosandasoftware
macro.InsideIBM,gatearraymacrosareknownasbooks(sothatbooksarepartofa
library),butunfortunatelythisdescriptivetermisnotverywidelyusedoutsideIBM.
Wecancompletethediffusionstepsthatformthetransistorsandthenstockpile
wafers(sometimeswecallagatearrayaprediffusedarrayforthisreason).Since
onlythemetalinterconnectionsareuniquetoanMGA,wecanusethestockpiled
wafersfordifferentcustomersasneeded.Usingwafersprefabricateduptothe
metallizationstepsreducesthetimeneededtomakeanMGA,theturnaroundtime,
toafewdaysoratmostacoupleofweeks.Thecostsforalltheinitialfabrication
stepsforanMGAaresharedforeachcustomerandthisreducesthecostofanMGA
comparedtoafullcustomorstandardcellASICdesign.
TherearethefollowingdifferenttypesofMGAorgatearraybasedASICs:
Channeledgatearrays.
Channellessgatearrays.
Structuredgatearrays.
Thehyphenationofthesetermswhentheyareusedasadjectivesexplainstheir
construction.Forexample,inthetermchanneledgatearrayarchitecture,thegate
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
8/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
arrayischanneled,aswillbeexplained.Therearetwocommonwaysofarranging
(orarraying)thetransistorsonaMGA:inachanneledgatearrayweleavespace
betweentherowsoftransistorsforwiringtheroutingonachannellessgatearrayuses
rowsofunusedtransistors.Thechanneledgatearraywasthefirsttobedeveloped,but
thechannellessgatearrayarchitectureisnowmorewidelyused.Astructured(or
embedded)gatearraycanbeeitherchanneledorchannellessbutitincludes(or
embeds)acustomblock.
1.1.4ChanneledGateArray
Figure1.5showsachanneledgatearray.Theimportantfeaturesofthistypeof
MGAare:
Onlytheinterconnectiscustomized.
Theinterconnectusespredefinedspacesbetweenrowsofbasecells.
Manufacturingleadtimeisbetweentwodaysandtwoweeks.
FIGURE1.5Achanneledgatearraydie.Thespaces
betweenrowsofthebasecellsaresetasidefor
interconnect.
AchanneledgatearrayissimilartoaCBICbothuserowsofcellsseparatedby
channelsusedforinterconnect.Onedifferenceisthatthespaceforinterconnect
betweenrowsofcellsarefixedinheightinachanneledgatearray,whereasthespace
betweenrowsofcellsmaybeadjustedinaCBIC.
1.1.5ChannellessGateArray
Figure1.6showsachannellessgatearray(alsoknownasachannelfreegatearray
,seaofgatesarray,orSOGarray).TheimportantfeaturesofthistypeofMGAare
asfollows:
Onlysome(thetopfew)masklayersarecustomizedtheinterconnect.
Manufacturingleadtimeisbetweentwodaysandtwoweeks.
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
9/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
FIGURE1.6Achannellessgatearrayorseaofgates
(SOG)arraydie.Thecoreareaofthedieis
completelyfilledwithanarrayofbasecells(thebase
array).
Thekeydifferencebetweenachannellessgatearrayandchanneledgatearrayis
thattherearenopredefinedareassetasideforroutingbetweencellsonachannelless
gatearray.Insteadwerouteoverthetopofthegatearraydevices.Wecandothis
becausewecustomizethecontactlayerthatdefinestheconnectionsbetweenmetal1,
thefirstlayerofmetal,andthetransistors.Whenweuseanareaoftransistorsfor
routinginachannellessarray,wedonotmakeanycontactstothedeviceslying
underneathwesimplyleavethetransistorsunused.
Thelogicdensitytheamountoflogicthatcanbeimplementedinagivensilicon
areaishigherforchannellessgatearraysthanforchanneledgatearrays.Thisis
usuallyattributedtothedifferenceinstructurebetweenthetwotypesofarray.Infact,
thedifferenceoccursbecausethecontactmaskiscustomizedinachannellessgate
array,butisnotusuallycustomizedinachanneledgatearray.Thisleadstodenser
cellsinthechannellessarchitectures.Customizingthecontactlayerinachannelless
gatearrayallowsustoincreasethedensityofgatearraycellsbecausewecanroute
overthetopofunusedcontactsites.
1.1.6StructuredGateArray
Anembeddedgatearrayorstructuredgatearray(alsoknownasmastersliceor
masterimage)combinessomeofthefeaturesofCBICsandMGAs.Oneofthe
disadvantagesoftheMGAisthefixedgatearraybasecell.Thismakesthe
implementationofmemory,forexample,difficultandinefficient.Inanembedded
gatearraywesetasidesomeoftheICareaanddedicateittoaspecificfunction.This
embeddedareaeithercancontainadifferentbasecellthatismoresuitablefor
buildingmemorycells,oritcancontainacompletecircuitblock,suchasa
microcontroller.
Figure1.7showsanembeddedgatearray.Theimportantfeaturesofthistypeof
MGAarethefollowing:
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
10/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
Onlytheinterconnectiscustomized.
Customblocks(thesameforeachdesign)canbeembedded.
Manufacturingleadtimeisbetweentwodaysandtwoweeks.
FIGURE1.7Astructuredorembeddedgate
arraydieshowinganembeddedblockinthe
upperleftcorner(astaticrandomaccess
memory,forexample).Therestofthedieis
filledwithanarrayofbasecells.
Anembeddedgatearraygivestheimprovedareaefficiencyandincreased
performanceofaCBICbutwiththelowercostandfasterturnaroundofanMGA.One
disadvantageofanembeddedgatearrayisthattheembeddedfunctionisfixed.For
example,ifanembeddedgatearraycontainsanareasetasidefora32kbitmemory,
butweonlyneeda16kbitmemory,thenwemayhavetowastehalfoftheembedded
memoryfunction.However,thismaystillbemoreefficientandcheaperthan
implementinga32kbitmemoryusingmacrosonaSOGarray.
ASICvendorsmayofferseveralembeddedgatearraystructurescontaining
differentmemorytypesandsizesaswellasavarietyofembeddedfunctions.ASIC
companieswishingtoofferawiderangeofembeddedfunctionsmustensurethat
enoughcustomersuseeachdifferentembeddedgatearraytogivethecostadvantages
overacustomgatearrayorCBIC(theSunMicrosystemsSPARCstation1described
inSection1.3madeuseofLSILogicembeddedgatearraysandthe10Kand100K
seriesofembeddedgatearraysweretwoofLSILogicsmostsuccessfulproducts).
1.1.7ProgrammableLogicDevices
Programmablelogicdevices(PLDs)arestandardICsthatareavailableinstandard
configurationsfromacatalogofpartsandaresoldinveryhighvolumetomany
differentcustomers.However,PLDsmaybeconfiguredorprogrammedtocreatea
partcustomizedtoaspecificapplication,andsotheyalsobelongtothefamilyof
ASICs.PLDsusedifferenttechnologiestoallowprogrammingofthedevice.
Figure1.8showsaPLDandthefollowingimportantfeaturesthatallPLDshavein
common:
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
11/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
Nocustomizedmasklayersorlogiccells
Fastdesignturnaround
Asinglelargeblockofprogrammableinterconnect
Amatrixoflogicmacrocellsthatusuallyconsistofprogrammablearraylogic
followedbyaflipfloporlatch
FIGURE1.8Aprogrammablelogicdevice
(PLD)die.Themacrocellstypicallyconsistof
programmablearraylogicfollowedbyaflipflop
orlatch.Themacrocellsareconnectedusinga
largeprogrammableinterconnectblock.
ThesimplesttypeofprogrammableICisareadonlymemory(ROM).Themost
commontypesofROMuseametalfusethatcanbeblownpermanently(a
programmableROMorPROM).AnelectricallyprogrammableROM,or
EPROM,usesprogrammableMOStransistorswhosecharacteristicsarealteredby
applyingahighvoltage.YoucaneraseanEPROMeitherbyusinganotherhigh
voltage(anelectricallyerasablePROM,orEEPROM)orbyexposingthedevice
toultravioletlight(UVerasablePROM,orUVPROM).
ThereisanothertypeofROMthatcanbeplacedonanyASICamask
programmableROM(maskprogrammedROMormaskedROM).AmaskedROM
isaregulararrayoftransistorspermanentlyprogrammedusingcustommaskpatterns.
AnembeddedmaskedROMisthusalarge,specialized,logiccell.
ThesameprogrammabletechnologiesusedtomakeROMscanbeappliedtomore
flexiblelogicstructures.ByusingtheprogrammabledevicesinalargearrayofAND
gatesandanarrayofORgates,wecreateafamilyofflexibleandprogrammablelogic
devicescalledlogicarrays.ThecompanyMonolithicMemories(boughtbyAMD)
wasthefirsttoproduceProgrammableArrayLogic(PAL,aregisteredtrademark
ofAMD)devicesthatyoucanuse,forexample,astransitiondecodersforstate
machines.APALcanalsoincluderegisters(flipflops)tostorethecurrentstate
informationsothatyoucanuseaPALtomakeacompletestatemachine.
JustaswehaveamaskprogrammableROM,wecouldplacealogicarrayasacell
onacustomASIC.Thistypeoflogicarrayiscalledaprogrammablelogicarray
(PLA).ThereisadifferencebetweenaPALandaPLA:aPLAhasaprogrammable
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
12/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
ANDlogicarray,orANDplane,followedbyaprogrammableORlogicarray,orOR
planeaPALhasaprogrammableANDplaneand,incontrasttoaPLA,afixedOR
plane.
DependingonhowthePLDisprogrammed,wecanhaveanerasablePLD
(EPLD),ormaskprogrammedPLD(sometimescalledamaskedPLDbutusually
justPLD).ThefirstPALs,PLAs,andPLDswerebasedonbipolartechnologyand
usedprogrammablefusesorlinks.CMOSPLDsusuallyemployfloatinggate
transistors(seeSection4.3,EPROMandEEPROMTechnology).
1.1.8FieldProgrammableGateArrays
AstepabovethePLDincomplexityisthefieldprogrammablegatearray(FPGA
).ThereisverylittledifferencebetweenanFPGAandaPLDanFPGAisusually
justlargerandmorecomplexthanaPLD.Infact,somecompaniesthatmanufacture
programmableASICscalltheirproductsFPGAsandsomecallthemcomplexPLDs.
FPGAsarethenewestmemberoftheASICfamilyandarerapidlygrowingin
importance,replacingTTLinmicroelectronicsystems.EventhoughanFPGAisa
typeofgatearray,wedonotconsiderthetermgatearraybasedASICstoinclude
FPGAs.ThismaychangeasFPGAsandMGAsstarttolookmorealike.
Figure1.9illustratestheessentialcharacteristicsofanFPGA:
Noneofthemasklayersarecustomized.
Amethodforprogrammingthebasiclogiccellsandtheinterconnect.
Thecoreisaregulararrayofprogrammablebasiclogiccellsthatcanimplement
combinationalaswellassequentiallogic(flipflops).
Amatrixofprogrammableinterconnectsurroundsthebasiclogiccells.
ProgrammableI/Ocellssurroundthecore.
Designturnaroundisafewhours.
WeshallexaminethesefeaturesindetailinChapters48.
FIGURE1.9Afieldprogrammablegatearray
(FPGA)die.AllFPGAscontainaregular
structureofprogrammablebasiclogiccells
surroundedbyprogrammableinterconnect.The
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
13/14
08/01/2015
1.1TypesofASICs
exacttype,size,andnumberofthe
programmablebasiclogiccellsvaries
tremendously.
[Chapterstart][Previouspage][Nextpage]
http://iroi.seu.edu.cn/books/asics/Book2/CH01/CH01.1.htm#pgfId=1331
14/14
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CortexM3 Uni Intro PDFDocument41 pagesCortexM3 Uni Intro PDFVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- HVDC ControlDocument18 pagesHVDC ControlVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Close Every Sale by Joe GirardDocument32 pagesHow To Close Every Sale by Joe GirardVinay Garg67% (3)
- Simulation and Fault Analysis of HVDC On MatlabDocument9 pagesSimulation and Fault Analysis of HVDC On MatlabVinay Garg100% (1)
- ConstraintsDocument31 pagesConstraintsVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Oled Technology: Saurabh Jain Ece-B 13620802810 Class No. - 94Document30 pagesOled Technology: Saurabh Jain Ece-B 13620802810 Class No. - 94Vinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Features & Benefits: Coreel Technologies (I) Pvt. LTDDocument2 pagesKey Features & Benefits: Coreel Technologies (I) Pvt. LTDVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2 Design Flow: Previous PageDocument2 pages1.2 Design Flow: Previous PageVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: Introduction To VLSI Design Lecture 1: Motivation of The CourseDocument2 pagesModule 1: Introduction To VLSI Design Lecture 1: Motivation of The CourseVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 Economics of Asics: 1.4.1 Comparison Between Asic TechnologiesDocument8 pages1.4 Economics of Asics: 1.4.1 Comparison Between Asic TechnologiesVinay GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Clarity Line AmpDocument27 pagesClarity Line AmpPayphone.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Semikron SKD - 53 - 07232810Document3 pagesSemikron SKD - 53 - 07232810shamkhairnarPas encore d'évaluation
- SXL vs. GXL vs. TXL WireDocument14 pagesSXL vs. GXL vs. TXL WirejackPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computing ReviewerDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computing ReviewerJan Leo EgamenPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Specification STS-6000K-H1 13.8kV 60Hz For 200 - 215KTL - V6.0Document18 pagesTechnical Specification STS-6000K-H1 13.8kV 60Hz For 200 - 215KTL - V6.0Antonio CanalesPas encore d'évaluation
- PipeWeldingHandbook PDFDocument32 pagesPipeWeldingHandbook PDFSid BouhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medium Voltage Switchgear Room DesignDocument3 pagesMedium Voltage Switchgear Room DesignSunil ParikhPas encore d'évaluation
- TJ1 24122022Document2 006 pagesTJ1 24122022Eduardo Moreno PalaciosPas encore d'évaluation
- Minutes Bucket Elevator Teleconference October 5 2012Document6 pagesMinutes Bucket Elevator Teleconference October 5 2012Vinod Kumar VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serai Catalogue ENG 2017-18Document44 pagesSerai Catalogue ENG 2017-18DjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sony SLV Se100 Se200 Se250 Se300 SexxxDocument81 pagesSony SLV Se100 Se200 Se250 Se300 Sexxxvideoson100% (2)
- DH61CR ProductGuide03 EnglishDocument78 pagesDH61CR ProductGuide03 EnglishCarlos Miguel RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sinamics v60 Getting Started 201205 enDocument36 pagesSinamics v60 Getting Started 201205 envozoscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- ITB InstallationDocument11 pagesITB Installationapi-3739726100% (1)
- Avm 30 3306Document6 pagesAvm 30 3306PanochonPas encore d'évaluation
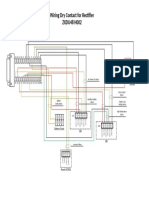
- Wiring Dry Contact ZXDU48 H002Document1 pageWiring Dry Contact ZXDU48 H002Donny Sulistyo NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Stop e MasterDocument0 pageStop e MasterAngels Córdova AlegríaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Document1 pageScada Control Room: EFS-A1 EFS-B1Prem KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- History of ComputerDocument5 pagesHistory of ComputerGlad RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluesun Hybride InvertorDocument2 pagesBluesun Hybride InvertorVadim PopovichPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual For Dynalift Vector Ii: KonecranesDocument24 pagesService Manual For Dynalift Vector Ii: KonecranesDante Williams50% (4)
- AJSL Hardware Primelift Fabricated Passenger ELEVATOR TEMPLATE 4 Floors New Grace Ogena 010324Document4 pagesAJSL Hardware Primelift Fabricated Passenger ELEVATOR TEMPLATE 4 Floors New Grace Ogena 010324ar.ikpanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- Allison - WTEC IIDocument6 pagesAllison - WTEC IICésaire Aimé NdjemPas encore d'évaluation
- Documents, Manuals, Service Bulletins and ScreensaversDocument49 pagesDocuments, Manuals, Service Bulletins and ScreensaversAntoinePas encore d'évaluation
- Pool Fittings LeafletDocument20 pagesPool Fittings LeafletmohammudaphPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Partial Discharge LTD - Online Partial Discharge Sensors 15KV Coupling CapacitorDocument2 pagesHigh Voltage Partial Discharge LTD - Online Partial Discharge Sensors 15KV Coupling CapacitorjuanmalegrePas encore d'évaluation
- XBee Arduino Compatible Coding PlatformDocument1 pageXBee Arduino Compatible Coding Platformgece25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cycle Test I Ec 1301 MPMCDocument1 pageCycle Test I Ec 1301 MPMCtmuthu123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cruisair 2014 PricebookDocument100 pagesCruisair 2014 PricebooklatrancaPas encore d'évaluation