Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Waves7 - 11.5
Transféré par
AliiAmiirCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Waves7 - 11.5
Transféré par
AliiAmiirDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
11.
5 Polarization
11.5.1 Describe what is meant by polarized light.
Unpolarized light contains vibrations of the electric field that are not just in one
direction, but in any direction in a plane that is perpendicular to the direction of
travel (the transverse plane)
Polaroid lenses absorb one component of the transverse vibration, and transmit
the other
The action of removing one component of vibration is called plane polarization
Longitudinal waves cannot be polarized, but all EM waves can be
11.5.2 Describe polarization by reflection.
Polaroid filters are not the only means by which light can become polarized
light reflected from surfaces is at least partially polarized
Surfaces of glass and water generally cause partial polarization of the reflected
beam the refracted beam is also partially polarized, but to a smaller extent
11.5.3 State and apply Brewsters law.
n = sin / cos or n = tan
If light is not incident in air, n1 cannot be eliminated from the equation, and so
Brewsters law becomes
n1 / n2 = tan
11.5.4 Explain the terms polarizer and analyzer.
The polarizer is a polaroid sheet; after passing through the polarizer, the intensity
of light incident is halved by preferential absorption
After transmission, the plane polarized wave is incident on the analyzer, another
polaroid sheet intensity is reduced to zero
11.5.5 Calculate the intensity of a transmitted beam of polarized light using Malus law.
The amplitude A of the component parallel to the transmission plane is
A = Aocos
The amplitude of the light is proportional to the amplitude of the electric field, but
the intensity of the light is proportional to the square of the amplitude
I = Ao2cos2
I = Iocos2
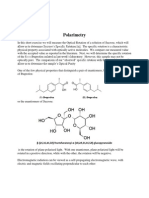
11.5.6 Describe what is meant by an optically active substance.
Many materials, especially organic compounds, affect the direction of vibration of
the traveling field of EM radiation
Effect is not detectable with unpolarized light; only in polarized light is a change
in the direction of polarization detectable
11.5.7 Describe the use of polarization in the determination of the concentration of
certain solutions.
A solution of sugar is contained in an instrument called a polarimeter a tube
that is bounded at either end with a polaroid
Polarimeter length (l), sugar concentration (C) and angle of rotation () are
combined to produce a specific angle of rotation s, known as the optical activity
s = / lC
used in the sugar industry to measure the concentration of syrups; being
developed to measure blood sugar levels in diabetics
11.5.8 Outline qualitatively how polarization may be used in stress analysis.
The optical activity of plastic and glass is dependent on stress; stress alters the
speed of the two components of polarized light
11.5.9 Outline qualitatively the action of liquid-crystal displays (LCDs).
Liquid crystals are neither solid (molecules fixed in position/orientation) nor
liquid (continually changing) molecules keep a fixed orientation while changing
position
A liquid crystal display consists of two crossed polaroids with an LC placed
between them (without the LC, light from the polarizer will be blocked by the
analyzer)
11.5.10 Solve problems involving the polarization of light.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ncert 12 Physics 2Document254 pagesNcert 12 Physics 2shivaraj p86% (7)
- PolarizationDocument38 pagesPolarizationMazaya NoveriwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 6: Light Polarization: WarningDocument15 pagesExperiment 6: Light Polarization: WarningDeepak KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Diffraction and PolarisationDocument10 pages10 Diffraction and PolarisationHelenPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4-7 Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Devices: General Comments of John SimcikDocument31 pagesModule 4-7 Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic Devices: General Comments of John SimcikOlugbenga AdeolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMDocument7 pagesPhotoelasticity Diffused Light Polariscope - 2019 - SOMKamini GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Smt. Kishoritai Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, New Kamptee.: BY Guided by Bhavik S.Kotak Dr. K.R.GuptaDocument33 pagesSmt. Kishoritai Bhoyar College of Pharmacy, New Kamptee.: BY Guided by Bhavik S.Kotak Dr. K.R.Guptadil_009100% (3)
- 0465 FB 1892452195Document7 pages0465 FB 1892452195Daudi Erasto MlangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesSeminar ReportAmal MonichanPas encore d'évaluation
- Polarization of Laser LightDocument10 pagesPolarization of Laser LightNutt ThanaboonrungrochPas encore d'évaluation
- Padashala CD and OrdDocument13 pagesPadashala CD and OrdPraveen PradeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - I: Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Oed - Question Bank - Unit - 1Document6 pagesUnit - I: Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Oed - Question Bank - Unit - 1Jai RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Course 4, Module 7 - Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic DevicesDocument21 pagesCourse 4, Module 7 - Electro-Optic and Acousto-Optic DevicesИРадојичић100% (2)
- Ec6016 OedDocument145 pagesEc6016 OedSujatha KPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report1Document9 pagesSeminar Report1Abhilash JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipin FinalDocument31 pagesBipin FinalvinayalakshmisravyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Dynamics Laboratory (ME69035) Submitted by Shaik Sydavali (19ME63R38) E04: Photo Elasticity (Four Point Bending Test)Document16 pagesDesign and Dynamics Laboratory (ME69035) Submitted by Shaik Sydavali (19ME63R38) E04: Photo Elasticity (Four Point Bending Test)sonit7kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Polarization Formula, Definition, Solved ExamplesDocument7 pagesPolarization Formula, Definition, Solved ExamplespenwithoutinkpwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ord & CDDocument30 pagesOrd & CDSaravana KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Polarized Light ExperimentDocument6 pagesPolarized Light ExperimentmirckyPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - Ion of LightDocument89 pages6 - Ion of LightBoon LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Plane PolariscopeDocument4 pagesPlane Polariscopenetname1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Rotatory DispersionDocument26 pagesOptical Rotatory DispersionPMHPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress OpticsDocument11 pagesStress Opticschantaiah100% (1)
- Polarimetry and RefratometryDocument7 pagesPolarimetry and RefratometrySosuke AizenPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Optic and Acousto OpticDocument7 pagesElectro Optic and Acousto OpticGaurav TewatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Nulling and Imaging EllipsometryDocument0 pagePrinciples of Nulling and Imaging EllipsometryGaurav AcharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Lect-5Material Science SRM 1st Year Unit 1 LECTURE NOTES-6Document54 pagesUnit 1 Lect-5Material Science SRM 1st Year Unit 1 LECTURE NOTES-6ECE A SRM VDP100% (1)
- Lab 8: Polarization of Light: Figure 1: (A) Oscillation of E Vector, (B) An Electromagnetic FieldDocument10 pagesLab 8: Polarization of Light: Figure 1: (A) Oscillation of E Vector, (B) An Electromagnetic Fieldpankajpnd1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 3052 CHAPTER 6 (Infrared Spectroscopy)Document19 pagesChem 3052 CHAPTER 6 (Infrared Spectroscopy)ashenafiPas encore d'évaluation
- CRODocument59 pagesCRONaman SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ep118 Lec07 PolarizationDocument12 pagesEp118 Lec07 PolarizationFatih TokgözPas encore d'évaluation
- PolarDocument8 pagesPolarlantea1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polarization Lab For PhysicsDocument12 pagesPolarization Lab For PhysicsSam RuelosPas encore d'évaluation
- PolarizationoteDocument14 pagesPolarizationoteOvijit KarmokarPas encore d'évaluation
- Malu's Law of PolarizationDocument10 pagesMalu's Law of PolarizationPaul LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chirality 2005Document17 pagesChirality 2005Raghunath VenkatramananPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics ProjectAkash NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensors: Organic Electroluminescent Sensor For Pressure MeasurementDocument8 pagesSensors: Organic Electroluminescent Sensor For Pressure MeasurementJennifer StevensonPas encore d'évaluation
- Coreno, M 2005 - Branching Ratios in The Radiative Decay of Helium Doubly Excited StatesDocument8 pagesCoreno, M 2005 - Branching Ratios in The Radiative Decay of Helium Doubly Excited StatesAnuvab MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- Asticha Opod - 19101105038-1Document12 pagesAsticha Opod - 19101105038-1Ciptanti Putri25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Physics Important Questions-II MidDocument7 pagesApplied Physics Important Questions-II Midlaxminarayana yadavaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Optical Transmitters (10!12!12) 1Document55 pagesChapter 3 Optical Transmitters (10!12!12) 1Hồ Hải NamPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-I - Topic-PolarizationDocument12 pagesUnit-I - Topic-PolarizationMUSICAL MASTI RINGTONEPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Sugar Concentration and Type On The Angle of Rotation of Polarized LightDocument6 pagesEffect of Sugar Concentration and Type On The Angle of Rotation of Polarized Lighthaden tetwPas encore d'évaluation
- Obt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 3Document20 pagesObt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 3Jayashree SathiyanarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- ORD CD AMU NotesDocument32 pagesORD CD AMU NotesTil Sen100% (1)
- PolarimetryDocument8 pagesPolarimetryMeisin RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Refractive Index of Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate From Aqueous SolutionDocument8 pagesRefractive Index of Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate From Aqueous SolutionAnonymous wwPdGqj5GPas encore d'évaluation
- Faraday PDFDocument24 pagesFaraday PDFrajdeep paulPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPERIMENT 8. Monolayer Characterization: Contact Angles, Reflection Infrared Spectroscopy, and EllipsometryDocument9 pagesEXPERIMENT 8. Monolayer Characterization: Contact Angles, Reflection Infrared Spectroscopy, and EllipsometryavniPas encore d'évaluation
- Plugin PolarizeDocument13 pagesPlugin PolarizeDipu DesperadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physica Project 27.03.2024Document33 pagesPhysica Project 27.03.2024janaki computersPas encore d'évaluation
- Nieminen - Optical Measurement of Microscopic Torques - 2001 Journal of Modern OpticsDocument10 pagesNieminen - Optical Measurement of Microscopic Torques - 2001 Journal of Modern OpticsDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab13 PolarizationDocument8 pagesLab13 Polarizations125960Pas encore d'évaluation
- PolarimetryDocument15 pagesPolarimetryNazmul Islam AbirPas encore d'évaluation
- Abramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuDocument49 pagesAbramczy@mitr.p.lodz - PL WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/raman WWW - Mitr.p.lodz - Pl/evuChaitanya ShakyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 - Graphical TechniquesDocument1 pageLesson 3 - Graphical TechniquesAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Macbeth CastingDocument5 pagesMacbeth CastingAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1: "What Order of Magnitude?" Game - Getting A Feel For MagnitudesDocument4 pagesPart 1: "What Order of Magnitude?" Game - Getting A Feel For MagnitudesAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphing: How Do I Make A Graph?Document8 pagesGraphing: How Do I Make A Graph?AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDocument4 pages11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.5.1 Describe The Reflection and Transmission of Waves at A Boundary Between Two MediaDocument3 pages4.5.1 Describe The Reflection and Transmission of Waves at A Boundary Between Two MediaAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and WavesDocument1 pageTopic 4 - Oscillations and WavesAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - Uniform AccelerationDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Uniform AccelerationAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves8 - 11.2Document2 pagesWaves8 - 11.2AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesDocument3 pages11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Document2 pagesTopic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves5 - 4.5 Part 2Document3 pagesWaves5 - 4.5 Part 2AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - KinematicsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - KinematicsAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 - Newton2&3Document2 pagesLesson 6 - Newton2&3AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 10 MomentumDocument3 pagesLesson 10 MomentumAliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics - 4Document1 pageThermal Physics - 4AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics - 2Document1 pageThermal Physics - 2AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Physics - 7Document2 pagesThermal Physics - 7AliiAmiirPas encore d'évaluation