Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Common Rail Direct Injection Engine
Transféré par
nikhil sengarDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Common Rail Direct Injection Engine
Transféré par
nikhil sengarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS : INTRODUCTION
PRICIPLE OF CRDi IN GASOLINE ENGINES
DIRECT INJECTION SYSTEM
WORKING OF CRDi
COMPONENTS OF COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
ADVANTAGES OF CRDi OVER CONVENTIONAL FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMS
DISADVANTAGES OF CRDi
FUTURE TRENDS OF CRDi
CONCLUSION
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Page 1
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
INTRODUCTION:-
The growing international consciousness for environmental protection and
the consequently ever more tightened emission legislation forces the automotive industry to
reduce fuel consumption, and pollutant emission of Diesel engines. Since the injection method
has a high influence on the combustion process, huge efforts have been made to improve current
injection systems and to develop new technologies. In order to improve and to optimize the
application of these systems, it is essential to get a better understanding of the complex processes
inside the combustion engine.
Common Rail Direct Injection system is an intelligent way of controlling
a diesel engine with modern computer systems. CRDi helps to improve the power, performance
and reduce harmful emissions from a diesel engine. Conventional diesel engines (which are nonCRDi like MPFi) are sluggish, noisy and poor in performance as compared to an engine using
CRDi technique. CRDi or Common Rail Direct Injection system is also sometimes referred to by
many similar/different names. Some brands use names like CRDe/DICOR/TurboJet/DDIS/TDI
etc.
CRDi performs direct injection of the fuel into the cylinders of a diesel
engine via a single, common line, called the common rail which is connected to all the fuel
injectors. Whereas ordinary diesel direct fuel-injection systems have to build up pressure anew
for each and every injection cycle, the new common rail (line) engines maintain constant
pressure regardless of the injection sequence. This pressure then remains permanently available
throughout the fuel line. The engine's electronic timing regulates injection pressure according to
engine speed and load. The electronic control unit (ECU) modifies injection pressure precisely
and as needed, based on data obtained from sensors on the cam and crankshafts. In other words,
compression and injection occur independently of each other. This technique allows fuel to be
injected as needed, saving fuel and lowering emissions.
Page 2
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
PRINCIPLE OF CRDi IN GASOLINE ENGINES:Gasoline or petrol engines were using carburetors for supply of air-fuel mixture before the
introduction of MPFI system .but even now carburetors are in use for its simplicity and low cost.
Now a days the new technology named Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) is in use for petrol
engines. The GDI is using the principle of CRDi system. Now let us examine the various factors
that lead to introduction of GDI technology.
The fall of carburetor:- For most of the existence of the internal combustion engine, the
carburetor has been the device that supplied fuel to the engine. On many other machines, such as
lawnmowers and chainsaws, it still is. But as the automobile evolved, the carburetor got more
and more complicated trying to handle all of the operating requirements. For instance, to handle
some of these tasks, carburetors had five different circuits:
1: Main circuit Provides just enough fuel for fuel-efficient cruising
2 : Idle circuit Provides just enough fuel to keep the engine idling
3 : Accelerator pump Provides an extra burst of fuel when the accelerator pedal is first depressed,
reducing hesitation before the engine speeds up
4 : Power enrichment Provides extra fuel when the car is going up a hill or circuit towing a trailer
5 : Choke Provides extra fuel when the engine is cold so that it will start effortlessly.
In order to meet stricter emissions requirements, catalytic converters were introduced. Very
careful control of the air-to-fuel ratio was required for the catalytic converter to be effective.
Oxygen sensors monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust, and the engine control unit (ECU)
uses this information to adjust the air-to-fuel ratio in real-time. This is called closed loop
controlit was not feasible to achieve this control with carburetors. There was a brief period of
electrically controlled carburetors before fuel injection systems took over, but these electrical
carburetors were even more complicated than the purely mechanical ones.
At first, carburetors were replaced with throttle body fuel injection systems (also known as single
point or central fuel injection systems) that incorporated electrically controlled fuel-injector
valves into the throttle body. These were almost a bolt-in replacement for the carburetor, so the
automakers didn't have to make any drastic changes to their engine designs. Gradually, as new
engines were designed, throttle body fuel injection was replaced by multi-port fuel injection (also
known as port, multi-point or sequential fuel injection). These systems have a fuel injector for
each cylinder, usually located so that they spray right at the intake valve. These systems provide
more accurate fuel metering and quicker response.
Page 3
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
DIRECT INJECTION SYSTEMs:Direct injection means injecting the fuel directly into the cylinder instead of premixing it with air
in separate intake ports. That allows for controlling combustion and emissions more precisely,
but demands advanced engine management technologies.
Fig Evolution of injection systems
Unlike petrol engines, diesel engines dont need ignition system. Due to the inherent property of
diesel, combustion will be automatically effective under a certain pressure and temperature
combination during the compression phase of Otto cycle. Normally this requires a high
compression ratio around 22 : 1 for normally aspirated engines. A strong thus heavy block and
head is required to cope with the pressure. Therefore diesel engines are always much heavier
than petrol equivalent. The lack of ignition system simplifies repair and maintenance, the
absence of throttle also help. The output of a diesel engine is controlled simply by the amount of
fuel injected. This makes the injection system very decisive to fuel economy. Even without direct
injection, diesel inherently delivers superior fuel economy because of leaner mixture of fuel and
air. Unlike petrol, it can combust under very lean mixture. This inevitably reduces power output
but under light load or partial load where power is not much an important consideration, its
superior fuel economy shines.
Another explanation for the inferior power output is the extra high compression ratio. On one
hand the high pressure and the heavy pistons prevent it from revving as high as petrol engine
(most diesel engine deliver peak power at lower than 4500 rpm.), on the other hand the long
stroke dimension required by high compression ratio favors torque instead of power. This is why
diesel engines always low on power but strong on torque.
Page 4
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
To solve this problem, diesel makers prefer to add turbocharger. It is a device to input extra air
into the cylinder while intake to boost up the power output of the engine. Turbochargers top end
power suits the torque curve of diesel very much, unlike petrol. Therefore turbocharged diesel
engines output similar power to a petrol engine with similar capacity, while delivering superior
low end torque and fuel economy.
Page 5
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
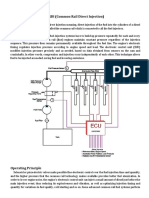
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION:
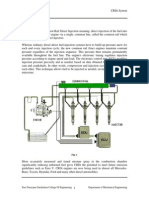
WORKING OF CRDi :-
The common rail injection system has a high pressure pump which operates continuously and
charges a high pressure rail of fuel. The fuel is led from this rail to the injector mounted on the
cylinder head through lines (thin pipes). The engine directly drives the pump of the Common
Rail system. The generated pressure is independent of the injection process unlike conventional
injection systems.
The injector is solenoid operated. The injection occurs when the solenoid is energized. The
quantity of the fuel injected is directly dependent on the duration of the pulse when the injection
pressure is constant. Sensors on the crankshaft indicates its position and speed to the ECU, and
so ECU controls the timing of injection and its frequency.
Fuel from the tank is lifted by the low pressure pump and passed through the filter. The pump is
generally run by an electric motor independent of the Engine Speed (rpm).
In the rail pressure regulator, the spring force and the electro-magnetic force generated by the
coil regulates the pressure. The pressure is controlled by ECU. The common rail also has a
pressure sensor and a pressure limiter attached to the rail.
Page 6
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
COMPONENTS OF COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE:1)Injector :A fuel injector is nothing but an electronically controlled valve. It is supplied with pressurized
fuel by the fuel pump, and it is capable of opening and closing many times per second. When the
injector is energized, an electromagnet moves a plunger that opens the valve, allowing the
pressurized fuel to squirt out through a tiny nozzle. The appearance and structure of the injector,
a key component of the direct fuel injection engine, In a direct fuel injection engine, the fuel
must be injected in a short period of time and at pressures at least 40 times higher than in port
fuel injection.
Page 7
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
2)High-pressure Fuel Pump and Fuel Line System :A high-pressure fuel pump produces high fuel pressures (5 to 12 MPa). The high-pressure fuel
pump employs a single-cylinder plunger pump. The pump is driven by the engine cam shaft. The
fuel is drawn into the pump and expelled by the reciprocating motion of the plunger.
3)Electronically Controlled Unit Injectors :An electronic control unit (ECU) receives electrical signals in the form of current or voltage
from various sensors installed in various components of fuel injection system. It then uses the
stored data to operate the injectors, ignition system and other engine related devices. As a result,
less un-burnt fuel leaves the engine as emissions, and the vehicle gives better mileage. Typical
sensors for an electronic fuel injection system includes the following:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Exhaust gas or oxygen sensor
Engine temperature sensor
Air flow sensor
Air inlet temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor
Manifold pressure sensor
Cam shaft position sensor
Knock sensor
Page 8
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
ADVANTAGES OF CRDi OVER CONVENTIONAL FUEL INJECTION
SYSTEMS :1. In CRDi the fuel is injected into each cylinder at a particular time interval based on the
position of moving piston inside the cylinder .In a conventional non-CRDi system ,this
interval and the fuel quantity was determined by the mechanical components ,but in a
CRDi system this time interval and timing etc are all controlled by a central computer or
microprocessor based control system.
2. The other major difference between a CRDi engine and a non CRDi engine is the way
the fuel injectors are controlled. In conventional engines, the fuel injectors are controlled
by the mechanical systems because of which there is additional noise and also losses due
to friction. While in CRDi engines the injectors are controlled by solenoid valves which
operate on electric current and do not require complex mechanical arrangements.
Consequently, the sluggish noises are reduced and also friction is overcame.
3. Since the emissions are lesser and noises are reduced, thereby it complies with the Euro
Norms and Bharat Stages.
THEREFORE , CRDi works on intelligently controlling the diesel engine by using electronic
sensors and microprocessors. It replaces complex mechanical arrangements with advanced and
more efficient electronic systems hence increasing the performance and efficiency of the engine.
DISADVANTAGES OF CRDi :1. Since it makes use of delicate electronic systems, therefore it cant be used in old vehicles
having conventionally designed engines.
2. High costs are involved. Consequently increases the overall expenses.
Page 9
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
FUTURE TRENDS OF CRDi :Ultra-High Pressure Common Rail Injection:
Newer CRDi engines feature maximum pressures of 1800 bar. This pressure is up to 33% higher
than that of first-generation systems, many of which are in the 1600-bar range. This technology
generates an ideal swirl in the combustion chamber which, coupled with the common-rail
injectors superior fuel-spray pattern and optimized piston head design, allows the air/fuel
mixture to form a perfect vertical vortex resulting in uniform combustion and greatly reduced
NOx (nitrogen oxide) emissions. The system realizes high output and torque, superb fuel
economy, emissions low enough to achieve Euro Stage IV designation and noise levels the same
as a gasoline engines. In particular, exhaust emissions and NOx are reduced by some 50% over
the current generation of diesel engines.
CRDi And Particle Filter:
Particle emission is always the biggest problem of diesel engines. While diesel engines emit
considerably less pollutant CO and Nox as well as green house gas CO2, the only shortcoming is
excessive level of particles. These particles are mainly composed of carbon and hydrocarbons.
They lead to dark smoke and smog which is very crucial to air quality of urban area, if not to the
ecology system of our planet. Basically, particle filter is a porous silicon carbide unit; comprising
passageways which has a property of easily trapping and retaining particles from the exhaust gas
flow. Before the filter surface is fully occupied, these carbon / hydrocarbon particles should be
burnt up, becoming CO2 and water and leave the filter accompany with exhaust gas flow. The
process is called regeneration.
Page
10
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
CONCLUSION:CRDi technology revolutionized diesel engines and also petrol engines. By introduction of CRDi
a lot of advantages are obtained ,some of them are ,
More power is developed. Increase power by 25%.
Increased fuel efficiency. Cuts fuel consumption by 20%.
Reduced noise.
More stability.
In emission, greenhouse gases is reduced by more than 20%.At a constant level of NOx,
carbon monoxide(CO) emissions, unburned hydrocarbons and particle emissions are reduced.
Particulates of exhaust are reduced.
Exhaust gas recirculation is enhanced.
Precise injection timing is obtained.
Pilot and post injection increase the combustion quality.
More pulverization of fuel is obtained.
A very high injection pressure can be achieved.
The powerful microcomputer make the whole system more perfect.
It doubles the torque at lower engine speeds.
The main disadvantage is that this technology increase the cost of the engine.Also this
technology cant be employed to ordinary engines.
For environmentalists and those who are out to make tighter emission rules, CRDi is a brilliant
technology that promises to reduce and give cleaner emissions to leave a healthier environment
behind for our next generation. For engineers, its a milestone achieved in the process of making
way for the emission free automobile and power plants.
Page
11
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
BIBLIOGRAPHY:1. Automotive Mechanics by S Srinivasan.
2. I C Engines By M.L.Malthur & Sharma.
3. I C Engines By V . Ganesan.
4. Automotive Engines by S Srinivasan.
5. www.toyota.ee/eng/technology.
6. www.sae.org/automag/techbriefs_11-99/06.htm
7. www.auto.howstuffworks.com/fuel-injection.htm
Presented by:~Nikhil Singh Sengar
~Rupansh Deshkar
~Vivek Kumar Singh
College-MAULANA AZAD NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF
TECHNOLOGY,BHOPAL
Page
12
COMMON RAIL DIRECT INJECTION ENGINE
Page
13
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Diesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedD'EverandDiesel Common Rail Injection Electronic Components ExplainedÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (7)
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesD'EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- CRDI Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesCRDI Seminar ReportPrateek Gandhi100% (8)
- Common Rail Direct Injection ReportDocument20 pagesCommon Rail Direct Injection ReportAshish Malik100% (3)
- 29 Junet Babu CRDi 3Document20 pages29 Junet Babu CRDi 3Jaiveer YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Fuel Injection in Diesel Engines Mechanical and Electronic InjectionDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Fuel Injection in Diesel Engines Mechanical and Electronic InjectionSanket ThoratPas encore d'évaluation
- CRDI Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesCRDI Seminar ReportBharadwaj PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CRDi Full PDFDocument20 pagesCRDi Full PDFnikhil sengar75% (4)
- CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)Document2 pagesCRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)eafz111Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Report On Common Rail Fuel Injector SystemDocument21 pagesA Report On Common Rail Fuel Injector SystemJoel MonteiroPas encore d'évaluation
- CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)Document2 pagesCRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)eafz111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Journal: Common Rail Direct InjectionDocument4 pagesJournal: Common Rail Direct InjectionSantoshPas encore d'évaluation
- History: CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)Document5 pagesHistory: CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection)SspssCaccbPas encore d'évaluation
- Dicor EngineDocument8 pagesDicor Enginepkhurana22Pas encore d'évaluation
- CRDiDocument18 pagesCRDiSuhel InamdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail High Pressure Fuel Injection 9-2010Document33 pagesCommon Rail High Pressure Fuel Injection 9-2010gmmarinov100% (5)
- Final Tdi Diesel 01Document28 pagesFinal Tdi Diesel 01rschhajedPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Diesel InjectionDocument13 pagesCommon Rail Diesel InjectionDejan Matic100% (1)
- " Gasoline Direct Injection": Seminar Report OnDocument26 pages" Gasoline Direct Injection": Seminar Report OnSahal Babu50% (2)
- Electronic Fuel Injection SystemDocument6 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection SystemJeremy MacalaladPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Diesel Injection (Done)Document14 pagesCommon Rail Diesel Injection (Done)Dejan MaticPas encore d'évaluation
- CRDiDocument22 pagesCRDiArun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Rajesh M S (4mc04au013)Document18 pagesPresented By: Rajesh M S (4mc04au013)Vinod SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Diesel InjectionDocument13 pagesCommon Rail Diesel InjectionDejan Matic67% (3)
- Common Rail Direct InjectionDocument9 pagesCommon Rail Direct InjectionJoe SparksPas encore d'évaluation
- Crdi System PDFDocument20 pagesCrdi System PDFsanath santhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Technology - CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection) PDFDocument3 pagesAutomobile Technology - CRDI (Common Rail Direct Injection) PDFSambhranta MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel Configuration For Air Flow Rationalization and Turbo Lag Reduction in CRDI EngineDocument4 pagesNovel Configuration For Air Flow Rationalization and Turbo Lag Reduction in CRDI Engineyash1239Pas encore d'évaluation
- Whitepaper Fuel SystemsDocument8 pagesWhitepaper Fuel SystemsQaiser Iqbal100% (4)
- Electronic Fuel InjectionDocument13 pagesElectronic Fuel InjectionTerrence JimPas encore d'évaluation
- Crdi EngineDocument17 pagesCrdi EngineSantosh BaraiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asitosh 23 Final SeminarDocument18 pagesAsitosh 23 Final Seminarmech mech1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel InjectionDocument17 pagesFuel InjectionKler Manpreet0% (1)
- Turbocharging of Ic EnginesDocument5 pagesTurbocharging of Ic EnginesKrishna MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel InjectionDocument18 pagesFuel InjectionsavitagupPas encore d'évaluation
- CI Engine PDFDocument39 pagesCI Engine PDFDileep VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- High Pressure Common Rail Fuel InjectionDocument6 pagesHigh Pressure Common Rail Fuel InjectionSaeed BarzegarPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Pressure Common-Rail Fuel InjectionDocument6 pagesHigh-Pressure Common-Rail Fuel InjectionAndi Anzar0% (1)
- Auto Electrical and Electronics Anoop SDocument25 pagesAuto Electrical and Electronics Anoop SkandukissPas encore d'évaluation
- RET045 SampleDocument9 pagesRET045 SampleJacob MelladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Abdur Rehman Registration Number:16 Pwmec4236 ASSIGNMENT TITLE: Developments in IC Engines Power Plant Mechanical DepartmentDocument9 pagesName: Abdur Rehman Registration Number:16 Pwmec4236 ASSIGNMENT TITLE: Developments in IC Engines Power Plant Mechanical DepartmentAnonymous HumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Qip Ice 12 Fuel Injection SystemsDocument40 pagesQip Ice 12 Fuel Injection SystemsAnonymous eyxVFR100% (1)
- Chapter 10Document78 pagesChapter 10Si Thu AungPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Resume Jurnal InternasionalDocument1 pageTugas Resume Jurnal InternasionalGalih Achmad PrawiradiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Diesel InjectionDocument2 pagesCommon Rail Diesel InjectionMOHITPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Direct Injection System: Prepared BY: Mr.N.M.Patel Automobile Dept. AditDocument18 pagesCommon Rail Direct Injection System: Prepared BY: Mr.N.M.Patel Automobile Dept. AditNikunj YagnikPas encore d'évaluation
- Latest Trends in Auto Tech IDocument45 pagesLatest Trends in Auto Tech IsutyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel InjectorDocument15 pagesDiesel InjectorAlvin AuPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemDocument17 pagesDiesel Engine Fuel Injection SystemKen ColeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4.1 New Modern Diesel Engines: Latest Developments in Marine EnginesDocument12 pagesTopic 4.1 New Modern Diesel Engines: Latest Developments in Marine EnginesAlbert DivinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No: 3: NFC-IEFR-FaisalabadDocument4 pagesAssignment No: 3: NFC-IEFR-FaisalabadaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of A Diesel Fuel Injection SystemDocument8 pagesMechanics of A Diesel Fuel Injection Systemekitriandi0% (1)
- Diesel Power PlantDocument28 pagesDiesel Power PlantIrvs SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyD'EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsD'EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual ZS250 5Document58 pagesManual ZS250 5irwin irwin100% (1)
- Proact™ I and Ii: Digital Electric Powered Governor SystemsDocument4 pagesProact™ I and Ii: Digital Electric Powered Governor Systemsashraf abdelrahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Cycle RepairingDocument22 pagesMotor Cycle RepairingVinay Tarsem Lal71% (7)
- Black Bull User'S Manual: Engine Configurations Available: Electric Starter Hand Starter HybridDocument20 pagesBlack Bull User'S Manual: Engine Configurations Available: Electric Starter Hand Starter HybridVikram DograPas encore d'évaluation
- (Doi 10.1002 - 14356007.a16 - 719.pub2) Dabelstein, Werner - Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - Automotive Fuels PDFDocument34 pages(Doi 10.1002 - 14356007.a16 - 719.pub2) Dabelstein, Werner - Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry - Automotive Fuels PDFYogga Adhitya100% (1)
- Quick Reference GuideDocument230 pagesQuick Reference GuideEmiliano Arocha CorsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Motor Honda 390 PDFDocument58 pagesManual Motor Honda 390 PDFTeofilo Paredes CosmePas encore d'évaluation
- Ex-Cell XR2750 Pressure Washer Operation ManualDocument16 pagesEx-Cell XR2750 Pressure Washer Operation Manualj_wilson85Pas encore d'évaluation
- 09b Propane Presentation (KCL)Document22 pages09b Propane Presentation (KCL)donsallusPas encore d'évaluation
- Zenith Carburetor Model 29 Service ManualDocument11 pagesZenith Carburetor Model 29 Service ManualMatt FerdockPas encore d'évaluation
- Cryogenic Pumps, Systems and Technologies: Vanzetti EngineeringDocument48 pagesCryogenic Pumps, Systems and Technologies: Vanzetti EngineeringNgoVietCuongPas encore d'évaluation
- B&S 161400-161499Document22 pagesB&S 161400-161499Bruno MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solo 433 ManualDocument19 pagesSolo 433 ManualSantiago UrgilesPas encore d'évaluation
- ECU DiagnosticsDocument12 pagesECU Diagnosticsesquisof100% (1)
- LodisagibavakefalexosugezDocument3 pagesLodisagibavakefalexosugezZuber SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- PRIMO Auto & Home Care Product CatalogDocument47 pagesPRIMO Auto & Home Care Product CatalogPrimo Talk100% (1)
- RMD ReportDocument29 pagesRMD ReportSergio PugazhPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel System: Section 3A - Fuel PumpDocument19 pagesFuel System: Section 3A - Fuel PumppedroPas encore d'évaluation
- StockDocument38 pagesStockdalemanukPas encore d'évaluation
- IMPCO Master Parts Catalog Jan 2013 HiResDocument620 pagesIMPCO Master Parts Catalog Jan 2013 HiResingemexPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop Manual-2018-2019 Xtrainer Low Res PDFDocument114 pagesWorkshop Manual-2018-2019 Xtrainer Low Res PDFZisis MavrodimosPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Taller ARN 125 CC (Idioma Ingles)Document85 pagesManual Taller ARN 125 CC (Idioma Ingles)Cordobessa50% (2)
- Johnson - Evinrude 1990-2001 Service Manual PDFDocument552 pagesJohnson - Evinrude 1990-2001 Service Manual PDFDavid Valls73% (73)
- TEST 1pathfinderDocument20 pagesTEST 1pathfinderLuis Alfonso Ortiz ESpinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Resource Management Gaining Competitive Advantage 9th Edition Noe Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Management Gaining Competitive Advantage 9th Edition Noe Solutions ManualKimberlyBennettcipym100% (33)
- User and Maintenance Manual User and Maintenance Manual: TM 4 Stroke 2009Document80 pagesUser and Maintenance Manual User and Maintenance Manual: TM 4 Stroke 2009Nelson RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- DZ 200 CdiDocument2 pagesDZ 200 CdipowerveePas encore d'évaluation
- Cessna 182 Skylane ChecklistDocument2 pagesCessna 182 Skylane ChecklistPedro Rodrigues AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- 476th VFG P-51 Flight Crew ChecklistDocument26 pages476th VFG P-51 Flight Crew Checklistalbix58100% (1)
- OPELDocument3 pagesOPELjrhcadPas encore d'évaluation