Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ex 3 7 FSC Part2
Transféré par
Fakhar AbbasTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ex 3 7 FSC Part2
Transféré par
Fakhar AbbasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Exercise 3.
7 (Solutions)
mathcity.org
Calculus and Analytic Geometry, MATHEMATICS 12
Merging man and maths
Available online @ http://www.mathcity.org, Version: 2.2.11
(2)3 (1)3
=
+ ( 2 1)
3
3
8 1
= +1
3 3
7
10
=
+1 =
sq. unit.
3
3
Example 4
Find the area bounded by the curve
f ( x) = x3 2 x 2 + 1
and the x-axis in the first quadrant.
Solution
Put f ( x) = 0
x3 2 x + 1 = 0
By synthetic division
1 1 2 0
1
1 1 1
1 1 1 0
Question # 2
y = 5 x2 ;
2
Area =
x = 1
or x =
1 1+ 4
1 5
=
2
2
1 5
Thus the curve cuts the x-axis at x = 1 ,
2
Since we are taking area in the first quad. only
1+ 5
1 5
ignoring
as it is ive.
x = 1,
2
2
1+ 5
Intervals in 1st quad. are [ 0,1] & 1,
2
Since f ( x) 0 whenever x [ 0,1]
1+ 5
and f ( x) 0 whenever x 1,
2
Area in 1 quad. =
(x
x4
x3
=
2 + x
4
3
=
=
=
x = 1 to x = 2
y 0 whenever x [1, 2]
2
Area =
(x
+ 1)dx
x dx + dx
2
x3
3
+ x
1
2
1
Question # 3
y = 3 x ;
x = 1 to x = 4
Since y 0 when x [1, 4]
4
Area =
3
1
4
= 3
x dx
1
3x 2
1 2
= + 1 0
2 3
7
=
sq. unit
12
Question # 1
y = x2 + 1 ;
)dx
(2)3
(1)3
5(2) 3 5(1) 3
8
1
10 3 5 + 3
22 14
22 14
+
=
3 3
3 3
36
= 12 sq. unit
3
2 x + 1 dx
x3
5x
3
1 (1) 2 4(1)(1)
2(1)
st
(5 x
x2 x 1 = 0
or
x = 1 to x = 2
y > 0 whenever x ( 1, 2 )
( x 1) ( x 2 x 1) = 0
x 1 = 0
Page#167
dx = 3
1
x2
dx
1
+1
x2
1
+1
2
2
= 3
3
= 3
1
3 4
x2
1
3 4
x2
3
32
= 2 (4) (1) 2
4
4
2 32
3 3
3
(4)
(1)
=
2
(2 ) 1
4
= 2 ( 8 1) = 14 sq. unit
Question # 4
to x =
2
2
Q y > 0 whenever x ,
2 2
y = cos x ;
x=
FSc-II / Ex- 3.7 - 2
Area =
sin x
Question # 7
y = x3 + 1
Putting y = 0 , we have
= sin sin
2
2
= 1 + 1 = 2 sq. unit
x3 + 1 = 0
Question # 5
y = 4 x x2
Putting y = 0 , we have
4 x x2 = 0
Now y > 0 when x ( 0, 4 )
4
2
( 4x x ) dx
0
x +1 = 0
or x 2 x + 1 = 0
x = 1
or
3 4
4x
x
2
3
2 x2
3 4
x
3
Area =
(4)
(0)3
2
= 2(4)2
2(0)
3
3
64
= 32 ( 0 0 )
3
32
=
sq. unit.
2
Question # 6
y = x2 + 2 x 3
Putting y = 0 , we have
2
x + 3x x 2 = 0
x ( x + 3 ) 1( x + 3 ) = 0
= 0
x = 3 or x = 1
Now y 0 whenever x [ 3,1]
1
Area
(x
+ 2 x 3 dx
=
=
1 (1)2 4(1)(1)
2(1)
x 2x
+
3x
3
2
x3
+ x 2 3x
3
(x
+ 1 dx
x4
+x
4
( 2)
( 1)4
=
+ 2
1
4
4
16
1
= + 2 1
4
4
3
27
= 6
=
sq. unit
4
4
4
Question # 8
y = x3 2 x + 4 ;
Putting y = 0 , we have
x2 + 2 x 3 = 0
( x + 3)( x 1)
x=
= 0
x = 0 or x = 4
( x + 1) ( x 2 x + 1)
1 1 4
2
1 3
x=
2
Which is not possible.
Now y 0 when x [ 1, 2]
x (4 x) = 0
Area =
5
32
+9 =
sq. unit
3
3
cos x dx
(1)
=
+ (1)2 3(1)
3
(3)3
+
+ (3) 2 3(3)
3
1
27
= +1 3 +
+ 9 + 9
3
3
5
= + ( 9 + 18)
3
x =1
x3 2 x + 4 = 0
By synthetic division
2 1
0 2
4
2 4 4
1 2
2
0
( x + 2 ) ( x2 2 x + 2)
= 0
x + 2 = 0 or x 2 2 x + 2 = 0
2 (2)2 4(1)(2)
2
2 4 8
=
2
2 4
=
2
This is imaginary.
Now y 0 when x [ 2,1]
x = 2
or x =
Area =
(x
2 x + 4 dx
2
1
x3dx 2 x dx + 4 dx
FSc-II / Ex- 3.7 - 3
x4
=
4
And y 0 whenever x [ 0,1]
x2
2
2
+4 x
2
1
2
(1)4 (2)4 (1)2 (2) 2
=
4 2
2
4
+ 4 (1 (2) )
1 16 1 4
= 2 + 4 (1 + 2 )
4 4 2 2
1
1
= 4 2 2 + 4 ( 3)
4
2
15 3
= 2 + 12
4 2
15
45
= + 3 + 12 =
sq. unit
4
4
Question # 9
y = x3 4 x
Putting y = 0 , we have
x3 4 x = 0
x x 4 = 0
x ( x + 2 )( x 2 ) = 0
x = 0 or x = 2 or x = 2
Now y 0 whenever x [ 2, 0]
And y 0 whenever x [ 0, 2]
(x
y dx y dx
Area =
=
4 x dx x 4 x dx
x4
x2
4
4
2
x4
2 x2
4
2
0
x4
x2
4
4
2
x4
2 x2
4
0
2
y dx y dx
x ( x 1)( x + 1) dx
x ( x 1)( x + 1) dx
0
x3 x dx x3 x dx
0
x4 x2
=
4
2
x4 x2
4
2
(0)4 (0) 2 (1) 4 (1) 2
=
2 4
2
4
(1) 4 (1)2 (0)4 (0) 2
2 4
2
4
Question # 11
y2 = 3 x ;
Q y 0 when x [ 1, 2]
2
Area =
16
= ( 0 0 ) 8
4
16
8 + (0 0)
4
= ( 4 8 ) ( 4 8 ) = ( 4 ) ( 4 )
Putting y = 0 , we have
x ( x 1)( x + 1) = 0
x = 0 or x = 1 or x = 1
Now y 0 whenever x [ 1, 0]
3 x dx
1
2
(3 x ) 2
dx
= 4 + 4 = 8 sq. unit.
Question # 10
y = x ( x 1)( x + 1)
x = 1 to x = 2
y = 3 x
The branch of curve above the x-axis is
y = 3 x
(0)
(2)
=
2(0)2
2(2)2
4
4
4
4
(2)
(0)
2(2)2 +
2(0)2
4
4
1 1
= ( 0 0 )
4 2
1 1
+ ( 0 0 )
4 2
1 1
= 0 + 0
4 4
1 1
1
= +
=
sq. unit
4 4
2
Area =
(3 x )
1
+1
2
1 + 1 (1)
2
(3 x )
3
2
( 3 2 ) (1)
2 (3 x )
3
3
2
2 (3 2)
2 ( 3 (1) )
+
3
3
3
2 (1) 2 2 ( 4 ) 2
=
+
3
3
2 2 ( 2)
= +
3
3
3 2
2
3
2
FSc-II / Ex- 3.7 - 4
2 16
= +
3 3
When x = 0
a 0 = a sin
14
sq. unit
3
sin = 1
Question # 12
1
g ( x) = cos x ; x = to x =
2
Q g ( x) 0 when x [ , ]
When x = 2a
a 2a = a sin
x
2
sin
1
So area =
x
= 2 sin
2
= a
= a
= a
1
2
= cos
cos(0)
2
3
a2
=
2
y = 2ax x 2
Putting y = 0 , we have
x ( 2a x ) = 0
2a x = 0 x = 2a
Q y 0 when x [ 0, 2a ]
1 + cos d
(1 + cos ) d
a
+ sin
2
a2
+ sin + sin
2 2
2 2
2
Error Analyst
Waqas Muzzafar (2009-10)
2ax x 2 dx
Book: Exercise 3.7 (Page 167)
a 2 a 2 + 2ax x 2 dx
Calculus and Analytic Geometry Mathematic
12
Punjab Textbook Board, Lahore.
Edition: May 2005.
a 2 a 2 2ax + x 2
0
2a
2a
cos 2 d
0
2a
a2
( + 1 + 1)
2
a2
a 2
= ( ) =
sq. unit
2
2
2ax x = 0
On squaring
2ax x 2 = 0
a cos cos d
2a
a 2 cos 2 cos d
Question # 14
Area =
= a2
3
1 1
1 3
sq. unit.
= 1 = =
2 2
2 2
4
or
sin 2x dx
x=0
Q y 0 when x 0,
3
= a
x = 0 to x =
a 2 1 sin 2 cos d
Question # 13
cos 2 x
= 2(2) = 4 sq. unit.
Area =
a 2 a 2 sin 2 ( a cos d )
= 2 sin sin
2
2
= 2 (1 ( 1) ) = 2 (1 + 1)
y = sin 2 x ;
a = a sin
=
2
1 = sin
1
cos x dx
2
Area =
a sin = a
=
2
a2 ( a x )
Put a x = a sin
dx = a cos d
dx = a cos d
dx
dx
Made by: Atiq ur Rehman
(atiq@mathcity.org)
Available online at
http://www.mathcity.org in PDF Format.
Page Setup used Legal ( 8 1 2 14 )
Last Update: 30 October 2010
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Resistance of Materials, For Beginners in Engineering (1914)Document264 pagesResistance of Materials, For Beginners in Engineering (1914)TaliaNaraPas encore d'évaluation
- String Art PDFDocument5 pagesString Art PDFioanaPas encore d'évaluation
- State 2003 MathcountsDocument11 pagesState 2003 Mathcounts3ternal67% (3)
- 3D Angles QuestionsDocument4 pages3D Angles QuestionsyddapPas encore d'évaluation
- Petkov v. (Ed.) Minkowski Spacetime.. A Hundred Years Later (FTP0165, Springer, 2010) (ISBN 9048134749) (O) (359s) - PGRDocument359 pagesPetkov v. (Ed.) Minkowski Spacetime.. A Hundred Years Later (FTP0165, Springer, 2010) (ISBN 9048134749) (O) (359s) - PGRmanojPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 1991 Paper 2Document10 pagesMathematics 1991 Paper 2hungePas encore d'évaluation
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Time and Work Problems: A. B. C. DDocument2 pagesTime and Work Problems: A. B. C. DFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- A Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsDocument5 pagesA Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasDocument13 pagesPerformance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsDocument5 pagesOn The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysDocument6 pagesMulti-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsDocument14 pagesAntenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Duality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemDocument2 pagesDuality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryDocument5 pagesGroup Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Massive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignDocument16 pagesMassive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersDocument15 pagesPerformance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
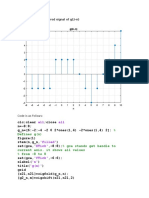
- Shifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IDocument2 pagesShifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Heaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffDocument2 pagesHeaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueDocument5 pagesUsing Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsDocument8 pagesEngineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 2 Analytical ReasonigDocument30 pagesLevel 2 Analytical ReasonigFakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Challan FormDocument1 pageChallan FormFakhar Abbas100% (1)
- SNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Document1 pageSNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Fakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Triangle Properties Graphic OrganizerDocument3 pagesTriangle Properties Graphic OrganizerJuanita GreenePas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors XIIDocument6 pagesVectors XIIDV PLAYSPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson PlanGlory Jane LuzaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus3 2017 ch3 PDFDocument190 pagesCalculus3 2017 ch3 PDFJumiana VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- DPP - Vectors - 1 1684736789618Document3 pagesDPP - Vectors - 1 1684736789618TiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- BarycentricDocument10 pagesBarycentricRohit KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Plaxis3dce v21.01 02 ReferenceDocument600 pagesPlaxis3dce v21.01 02 ReferenceBOOBOOPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 6: 2m 00 E E Ikx IkxDocument3 pagesProblem Set 6: 2m 00 E E Ikx IkxDaljot Singh KangPas encore d'évaluation
- IX - Blue Print of Question Papers CTerm - 1 (2021-22)Document8 pagesIX - Blue Print of Question Papers CTerm - 1 (2021-22)Soumya ranjan SoumyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advancing Math by Guiding Human Intuition With AIDocument10 pagesAdvancing Math by Guiding Human Intuition With AIWavePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Graduate Algebra (Math 32600)Document37 pagesNotes For Graduate Algebra (Math 32600)jscribe77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics 2 C2 Marking SchemeDocument16 pagesEdexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics 2 C2 Marking Schemegerikaalhu75% (4)
- 4.1 Motion Descriptors in Two DimensionsDocument17 pages4.1 Motion Descriptors in Two DimensionssamrenlycPas encore d'évaluation
- GEC 002 MODULE 1 Mathematics in Our WorldDocument15 pagesGEC 002 MODULE 1 Mathematics in Our WorldKarylle CatePas encore d'évaluation
- Gears: Drawing Gear Teeth Spur GearsDocument16 pagesGears: Drawing Gear Teeth Spur GearsGvgfhjPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectile ProblemsDocument2 pagesProjectile ProblemsJmPas encore d'évaluation
- Geom ConicsDocument12 pagesGeom ConicsAyan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Greek and Vedic GeometryDocument23 pagesGreek and Vedic Geometryjesse_reichelt_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1.3a Segment Addition Postulate Amp Midpoint Theorem CPDocument17 pagesUnit 1.3a Segment Addition Postulate Amp Midpoint Theorem CPgavan_dusbabek4032Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH II - II Kinematics of A Particle AllDocument79 pagesCH II - II Kinematics of A Particle AlldanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2. Taping Over An ObstacleDocument2 pagesActivity 2. Taping Over An ObstaclePaul Agustin Beseos SincoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ged102 Week 5 WGNDocument5 pagesGed102 Week 5 WGNMarielle Ansherine GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- ProblemsDocument4 pagesProblemsRoshidul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- 10th Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQDocument2 pages10th Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQBhalchandra MurariPas encore d'évaluation