Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Title: Source: Agenda Item: Document For: Category: Document Summary
Transféré par
Yamen NasrTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Title: Source: Agenda Item: Document For: Category: Document Summary
Transféré par
Yamen NasrDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
3GPP TSG-SA5 (Telecom Management) Meeting #7
Tampere, Finland, 26-29 October, 1999
Tdoc S5-99227
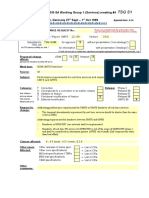
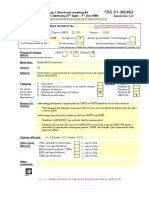
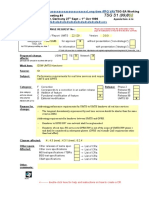
Title:
Requirements for the NMC interface of Fault Management
Source:
Sonera
kimmo.kakko@sonera.com, jarkko.konola@sonera.com
Agenda item:
9.5 (S5.FM rapporteur group)
Document for:
Decision
Category:
Contribution to 31.111 (3G Fault Management)
Document
Summary:
The attached document is a proposal to 3GPP SA5 for the draft 3G Fault
Management specification, into the chapter 8 NMC interface.
The document describes requirements for the interface, what are the
operator/service provider process needs to be supported by this interface and
finally requirements for the alarm and state management and data elements
derived from the lower interfaces (OMC-NE)
Specification(s)
involved:
3GPP SA5 32.111 3G Fault Management
Other
information:
The IRP concept and ideas proposed by Ericsson seem important and
valuable and thus Sonera can support the concept. The example interfaces,
including alarm handling, and the name Integration give an image for open
and standardised interfaces. This is a starting point to get into a more detailed
specification phase and to achieve more concrete results from SA5.
Alarm IRP will be commented by Sonera in more detail if the concept is
accepted also by other members of 3GPP SA5.
PAGE 1
Contribution to 3G TS 32.111 version 1.0.0
3G TS 32.111 V1.0.0 (1999-10)
NMC interface
This clause defines the 3G FM requirements from the NMC interface point of view. The fault management
information that is needed in this interface, depending on the implementation, can be mediated via OMC or directly
from the NEs as described in the previous sections.
8.1 Fault Management Process view
The NMC interface shall support alarm surveillance and support Network Maintenance and Restoration process as
described in the TMFs Telecom Operations Map.
8.2 Service management support
In addition to the traditional NE alarm handling capability, the NMC interface for 3G FM shall be capable to
intermediate requests and responses from Service Management processes (Service problem resolution, Service Quality
Management and Customer QoS Management) and platforms supporting them. This includes transferring
management messages, notifications and service management requests between network elements and service
management systems.
Service management sets the following requirements:
-
user complaint information that is service related shall be formed into a trouble ticket;
service problems due to a network or network element malfunctioning shall be passed via the NMC interface
for the service problem resolution.
8.3 Alarm and state management
Section 5 has defined the FM requirements mainly from the OMC point of view. This section uses, as relevant, the
functionality described earlier.
The NMC interface shall have the following information available:
-
alarm list including alarm id, element identification, time stamp and type/severity of alarm, at least;
network topology information (using possibly configuration interface(s)) that is needed to solve the fault
management problems;
state information of the network element, version number;
alarm history and threshold values for the alarms.
In the NMC interface, CORBA is proposed as a transport mechanism for alarms. Filtering mechanisms and more
developed alarm correlation and forwarding capabilities will be a part of the FM applications and thus not to be
standardised. However, all the relevant information described above shall be available to these applications.
ETSI
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 3G Wireless Network Management System High Level RequirementsDocument23 pages3G Wireless Network Management System High Level RequirementsMinh NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 22.002Document12 pages3GPP TS 22.002santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TR 29.998-05-1: Technical ReportDocument25 pages3GPP TR 29.998-05-1: Technical Reportdzo007Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TSG CN Plenary Meeting #21 NP-030392 17 - 19 September 2003 Frankfurt, GERMANYDocument51 pages3GPP TSG CN Plenary Meeting #21 NP-030392 17 - 19 September 2003 Frankfurt, GERMANYfouad boutatPas encore d'évaluation
- TMF814InterfaceVersion3 0Document17 pagesTMF814InterfaceVersion3 0Ahmad SardoukPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Requirement No.: TEC/GR/IT/NMS-003/01/NOV 2015Document45 pagesGeneric Requirement No.: TEC/GR/IT/NMS-003/01/NOV 2015chandrashekar_ganesanPas encore d'évaluation
- 21905-b01 VocabularyFor3GGPSpecsDocument63 pages21905-b01 VocabularyFor3GGPSpecsDavid Antonio Garcia CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Bearer Services (BS) Supported by A Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) (3G TS 22.002 Version 3.1.0)Document13 pages3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects Bearer Services (BS) Supported by A Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) (3G TS 22.002 Version 3.1.0)santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ixxat Sae j1939Document3 pagesIxxat Sae j1939Dinesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Core Network Name Identification Supplementary Services - Stage 3 (3G TS 24.096 Version 3.0.0)Document9 pages3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Core Network Name Identification Supplementary Services - Stage 3 (3G TS 24.096 Version 3.0.0)santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE EPC Technology EssentialsDocument26 pagesLTE EPC Technology EssentialsAmit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Corba For MTNMDocument32 pagesUsing Corba For MTNMKaz_BloodmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1320 CTDocument4 pages1320 CTManuel Aguirre CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Specification: RD TMDocument12 pagesTechnical Specification: RD TMsantanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- International Telecommunication Union European Telecommunications Standards Institute Third Generation Partnership ProjectDocument28 pagesInternational Telecommunication Union European Telecommunications Standards Institute Third Generation Partnership ProjectprashantdpatkePas encore d'évaluation
- Section ThreeDocument54 pagesSection ThreeRock DolphinPas encore d'évaluation
- 32435-900 XML 3GPP PDFDocument16 pages32435-900 XML 3GPP PDFRusdiantoMahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- UMTS Core Network Planning GuideDocument8 pagesUMTS Core Network Planning GuideEbere ObiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GUTRAN Frame ProtocolDocument36 pages3GUTRAN Frame Protocoljoks1mPas encore d'évaluation
- CAMEL and Optimal RoutingDocument21 pagesCAMEL and Optimal RoutingAnonymous 23CEh9jU100% (1)
- TCSM3i Functionalities: BSC3119 Nokia BSC/TCSM, Rel. S12, Product Documentation, v.5Document35 pagesTCSM3i Functionalities: BSC3119 Nokia BSC/TCSM, Rel. S12, Product Documentation, v.5Kostas RantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1320 CraftDocument4 pages1320 CraftRinoCastellanosPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Core Network Call Deflection (CD) Supplementary Service - Stage 3 (3G TS 24.072 Version 3.0.0)Document9 pages3rd Generation Partnership Project Technical Specification Group Core Network Call Deflection (CD) Supplementary Service - Stage 3 (3G TS 24.072 Version 3.0.0)santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 25.432Document8 pages3GPP TS 25.432holapaquitoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 24.067Document14 pages3GPP TS 24.067santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 22.002Document12 pages3GPP TS 22.002santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- T Rec M.20 198811 S!!PDF eDocument22 pagesT Rec M.20 198811 S!!PDF eAbdellah SamadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TR 22.944Document21 pages3GPP TR 22.944santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- 169001Document25 pages169001vanconghuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Article: Networking Heavy-Duty Vehicles Based On SAE J1939Document12 pagesTechnical Article: Networking Heavy-Duty Vehicles Based On SAE J1939jfranco78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Switching and Signalling - The New ArchitectureDocument5 pagesSwitching and Signalling - The New Architecturefuy5iojoiPas encore d'évaluation
- TSG S1 (99) 8: Long Tiem Ffpo VavDocument6 pagesTSG S1 (99) 8: Long Tiem Ffpo VavNguyen TaiPas encore d'évaluation
- TSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacsclong Tiem Ffpo VavDocument5 pagesTSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacsclong Tiem Ffpo VavNguyen TaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategies For The Efficient Dimensioning of 3G Mobile Access NetworksDocument9 pagesStrategies For The Efficient Dimensioning of 3G Mobile Access NetworksDerrick Kojo SenyoPas encore d'évaluation
- RN Design and OptimisationDocument14 pagesRN Design and OptimisationKapil SaravgiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3g CdmsDocument6 pages3g CdmshtrungPas encore d'évaluation
- 5G System Design: Architectural and Functional Considerations and Long Term ResearchD'Everand5G System Design: Architectural and Functional Considerations and Long Term ResearchPas encore d'évaluation
- Digit AnalysisDocument50 pagesDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- 01 - Introduction To UMTSDocument42 pages01 - Introduction To UMTSBsskkd KkdPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G-3.5 GDocument4 pages3G-3.5 GNyankoye Apollinaire LouaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance requirements for real-time services and UMTS-GPRS handoverDocument5 pagesPerformance requirements for real-time services and UMTS-GPRS handoverNguyenDucTaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 21.101Document16 pages3GPP TS 21.101santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- TSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacscscacscsaccsacascscxsaxsxlong Tiem Ffpo VavDocument5 pagesTSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacscscacscsaccsacascscxsaxsxlong Tiem Ffpo VavNguyen TaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 22.076Document10 pages3GPP TS 22.076santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- TSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacscscacscsaccsacascscxsaxsxfdvscaslong Tiem Ffpo VavDocument5 pagesTSG S1 (99) 8: Dsdsds Cscasacscscacscsaccsacascscxsaxsxfdvscaslong Tiem Ffpo VavNguyen TaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TS 22.076Document10 pages3GPP TS 22.076santanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- PCRF Policy and Charging Rules FunctionDocument40 pagesPCRF Policy and Charging Rules FunctionArindam BhattacharayaPas encore d'évaluation
- UMTS Network Monitoring April2011 HIDocument4 pagesUMTS Network Monitoring April2011 HIsizzlacalunjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens AutomationDocument13 pagesSiemens AutomationHamadou TetePas encore d'évaluation
- 3g Mobile CommunicationsDocument12 pages3g Mobile CommunicationsVamsikrishna PanugantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, inDocument6 pagesWcdma (Umts) Tdcdma Cdma2000 Wcdma (Docomo) Td-Scdma Mobiles Bluetooth Homerf/Swap Wap GPRS, HSCSD Edge Camel, invipin171986Pas encore d'évaluation
- JP-3GA-27.003 (R99) Terminal Adaptation Functions (TAF) For Services Using Synchronous Bearer CapabilitiesDocument27 pagesJP-3GA-27.003 (R99) Terminal Adaptation Functions (TAF) For Services Using Synchronous Bearer Capabilitiesatul_potdarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3GPP TR 23.039: Technical SpecificationDocument7 pages3GPP TR 23.039: Technical SpecificationsantanameroPas encore d'évaluation
- TSG S1 (99)868 - Performance requirements for real time services and requirements for handover between UMTS and GPRSDocument5 pagesTSG S1 (99)868 - Performance requirements for real time services and requirements for handover between UMTS and GPRSNguyenDucTaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Radio Interface Layer 3 MessagesDocument38 pagesMobile Radio Interface Layer 3 MessagesSaman Rizwan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsD'EverandWireless Communications Security: Solutions for the Internet of ThingsPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyD'EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenPas encore d'évaluation
- Telecom Lightning ProtectionDocument8 pagesTelecom Lightning ProtectionMN Titas TitasPas encore d'évaluation
- National GeographicDocument4 pagesNational GeographicYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Stankonia Order and RequestDocument6 pagesStankonia Order and RequestYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Permission Concept RequestDocument16 pagesPermission Concept RequestYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Mozilla ThunderbirdDocument5 pagesMozilla ThunderbirdYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei GSM-R Bts3900 Hardware Structure-20141204-Issue4 0Document47 pagesHuawei GSM-R Bts3900 Hardware Structure-20141204-Issue4 0muhammadmusakhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations and Maintenance GuideDocument321 pagesOperations and Maintenance GuideNatrajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluke 1621 Multi Tester User ManualDocument26 pagesFluke 1621 Multi Tester User ManualcenkturkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Skip To Main NavigationDocument13 pagesMain Skip To Main NavigationYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- VSWRDocument5 pagesVSWRAltafPas encore d'évaluation
- Sitrep 3 2019 NcovDocument7 pagesSitrep 3 2019 NcovYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Hamlet PDFDocument2 pagesHamlet PDFYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- 550 - Spec - Sheet - For AllDocument5 pages550 - Spec - Sheet - For AllYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei GSM-R Bts3900 Hardware Structure-20141204-Issue4 0Document47 pagesHuawei GSM-R Bts3900 Hardware Structure-20141204-Issue4 0muhammadmusakhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Smith PDFDocument4 pagesJack Smith PDFYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- LebanonDocument4 pagesLebanonYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- 3g AlarmsDocument4 pages3g AlarmsYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Telecommunications NetworkDocument3 pagesTelecommunications NetworkYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- BabilDocument48 pagesBabilYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Toward 3gDocument9 pagesGSM Toward 3gYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Ranitidine: Medical UseDocument4 pagesRanitidine: Medical UseYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Albert EinsteinDocument9 pagesAlbert EinsteinYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Saved Access ReportDocument14 pagesSaved Access ReportYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- NO Site Name Date Form Field Engineer NameDocument4 pagesNO Site Name Date Form Field Engineer NameYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Toward 3gDocument9 pagesGSM Toward 3gYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- ER1317 - ER1329 Dec - 2 - 2010Document7 pagesER1317 - ER1329 Dec - 2 - 2010Yamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Windows Phone RecDocument27 pagesWindows Phone RecYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Create A PDF File: Exercise 1 and Exercise 2 Produce The Same Result. Choose The One That Works Best For YouDocument6 pagesCreate A PDF File: Exercise 1 and Exercise 2 Produce The Same Result. Choose The One That Works Best For YouYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Windows Phone RecDocument27 pagesWindows Phone RecYamen NasrPas encore d'évaluation
- Siebel Configuration For Navigation To A Map SiteDocument6 pagesSiebel Configuration For Navigation To A Map Sitesanjeev kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Informatica Interview Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesInformatica Interview Questions and AnswersatoztargetPas encore d'évaluation
- Madhusudanan Balakrishnan: Main Road, Ganga Nagar, Maduravoyal, Chennai - 600 095, IndiaDocument2 pagesMadhusudanan Balakrishnan: Main Road, Ganga Nagar, Maduravoyal, Chennai - 600 095, Indiamadhusudanan.asbPas encore d'évaluation
- VX Search Rule-Based File SearchDocument78 pagesVX Search Rule-Based File SearchFlexensePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Introduction ToDocument18 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction ToMichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Shop Management SystemDocument121 pagesMobile Shop Management Systemrajour29% (7)
- Avaya Asterisk LoggerDocument15 pagesAvaya Asterisk LoggerArcangelo Di BattistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditing OS, network, and EDI security risksDocument1 pageAuditing OS, network, and EDI security risksjung_seohyunPas encore d'évaluation
- OmadaDocument4 pagesOmadaburexzPas encore d'évaluation
- Scs 421 Software Development II Lecture NotesDocument136 pagesScs 421 Software Development II Lecture Notesbd87glPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerMaxOS 5978.669.669 Release NotesDocument16 pagesPowerMaxOS 5978.669.669 Release NotesPavan NavPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document13 pagesChapter 8Shelly EfedhomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Egain11 4 Results First AnalyticsDocument35 pagesEgain11 4 Results First AnalyticsErnestPas encore d'évaluation
- E3 Vs E5 LicenseDocument4 pagesE3 Vs E5 LicenseWissam KhadraPas encore d'évaluation
- LinearReg CheckpointDocument26 pagesLinearReg Checkpointshrutisuman03Pas encore d'évaluation
- App InstallDocument832 pagesApp InstallHani Al-NassPas encore d'évaluation
- Malware Analysis - Dynamic and Process MonitoringDocument33 pagesMalware Analysis - Dynamic and Process MonitoringMuhammad Saeed JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Scrum Reference CardDocument6 pagesScrum Reference CardvinodkundyannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Array in C++ - Declare, Initialize, Access ElementsDocument20 pagesLearn Array in C++ - Declare, Initialize, Access ElementsAdisu BiyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating - Deleting A Reports Server in OAS 10.1.2, Integrated With EM - AS-console - JobacleDocument5 pagesCreating - Deleting A Reports Server in OAS 10.1.2, Integrated With EM - AS-console - JobacleMohammed GaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro to Computer and Network SecurityDocument66 pagesIntro to Computer and Network SecurityharizPas encore d'évaluation
- Arab 1Document2 pagesArab 1U KNOW DE WAYPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 GTAG - Change and Patch Management Controls Critical For Organizational SuccessDocument53 pages2 GTAG - Change and Patch Management Controls Critical For Organizational SuccessMönycka DelcPas encore d'évaluation
- Building An E-Commerce Presence: A Systematic Approach: Ideas For Today and TomorrowDocument35 pagesBuilding An E-Commerce Presence: A Systematic Approach: Ideas For Today and TomorrowGERBGARCIA100% (1)
- Veritas Netbackup™ For Mariadb Administrator'S Guide: Windows and LinuxDocument52 pagesVeritas Netbackup™ For Mariadb Administrator'S Guide: Windows and Linuxbilllee leePas encore d'évaluation
- No Controls Tested-90-DAY Active Directory: Audit / Assurance ObjectiveDocument73 pagesNo Controls Tested-90-DAY Active Directory: Audit / Assurance ObjectiveAneal LiverpoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortigate Cookbook 504 PDFDocument201 pagesFortigate Cookbook 504 PDFYahiaKhoujaPas encore d'évaluation
- DB CH 3Document19 pagesDB CH 3Efeson HameloPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Engineering Term Paper On Function Oriented DesignDocument16 pagesSoftware Engineering Term Paper On Function Oriented Designaassllaann100% (2)
- Tag Cyber Security Annual Cyber Security Handbook and Reference Guide Vol 3Document810 pagesTag Cyber Security Annual Cyber Security Handbook and Reference Guide Vol 3rick schwartz100% (2)