Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
EXP 2A Bubble Cap Distillation Jan 2015
Transféré par
Anonymous T7vjZG4otTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EXP 2A Bubble Cap Distillation Jan 2015
Transféré par
Anonymous T7vjZG4otDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Separation Technology CKD 20103/EXP2A/Jan2015
Experiment 2A : Bubble Cap Distillation Process
1. Objective(s)
The students should be able to:
Operate vapour liquid separation experiment using a Bubble Cap Distillation Process Unit.
Prepare a calibration curve for Refractive Index (RI) vs Concentration of Ethanol-Water mixtures.
Analyze the sample of top and bottom product by using Refractometer to obtain the Refractive Index
(RI) in order to determine their respective composition.
Obtain the time when the distillation process is nearly finish.
2. Introduction
Distillation is one of the important unit operations in many chemical industries and has been used from
the inception of chemical and process industry. Distillation is used for the separation of components in a
liquid mixture of volatile constituents. The distillation column is usually a vertical column where the liquid
and vapour phases of the mixture are made to mix and approach equilibrium. The bubble cap distillation
column provides distinct stages at which such equilibrium can be approached.
Distillation is a process of separating the components of a solution by the application of heat
when the vapour produced by boiling the solution has a different composition to that of the solution. If the
vapour formed is condensed and subsequently reboiled it will produce, yet again, a vapour of different
composition. Repeated boiling of condensed vapours will ultimately produce a product of desired quality
rich in concentration of one of the components of the original solution.
Distillation takes place in a distillation column which, in essence, comprises a reboiler, a column
and a vapour condensed. The reboiler provides the heat for vapour generation; within the column rising
vapours continually mix with liquid flowing down the column, condense and are reboiled until vapour of
required composition leaves the column and condenses in the vapour condenser to be removed as liquid
product. A certain proportion of this condensate is returned to the column, called reflux, the proportion
being a major influence on the quality of the product achieved.
Since this experiment use batch distillation plant, therefore, it can be said that this is a process
whereby a specific quantity of a liquid mixture is separated into its components. The technique is used
extensively in laboratories and small scale production plants where the equipment is often used for
separating several different mixtures of where if only one mixture is separated, the mixture is not
produced continuously. The relatively high capital cost of continuous distillation plants with their
sophisticated control systems, often results in smaller companies operating batch distillation plants.
Batch Distillation is particularly useful for separating liquid mixtures contaminated with solids which would
otherwise foul a continuous plant.
Separation Technology CKD 20103/EXP2A/Jan2015
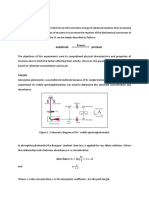
The unit consists of distillation column filled with bubble cap trays with a vacuum jacket and
thermo-siphon reboiler, vapour condenser, infinitely variable reflux control, distillate cooler and receiver,
all manufactured in borosilicate glass. Vapour generated in the reboiler rises through the column and is
condensed in a vertical water-cooled condenser. The condensed product leaves the column and passes
into an infinitely variable reflux ratio controller incorporating the variable area flow meters. Each column
component has five bubble cap plates with a temperature measurement nozzle on each plate. Vapour
and liquid compositions throughout are determined by respective temperatures. The unit is equipped with
the facility for liquid and gas sampling at the top and bottom of the column. A condenser consists of a coil
type heat exchanger. A reflux separator is provided at the top of the column. Reflux is returned to the
column and the product passes through a cooler and a graduated pipe section and can be passed either
to a receiving vessel, which allows product removal operating under vacuum or back to the boiler. A
sketch of a tray with bubble caps is as shown in the diagram below:
Figure 1: The cross-sectional diagram of bubble cap column
3. Chemicals and Ancillary Equipments
a) Chemicals required:
Industrial grade Ethanol
Water
b) Ancillary equipments/apparatus required:
TWO (2) 2000 mL beakers
TWO (2) 250ml beakers
Refractometer (for measuring sample concentrations)
Separation Technology CKD 20103/EXP2A/Jan2015
4. Operating Instructions
4.1 Safety Considerations
You must familiarize yourself with each item such as the Reboiler, Condenser, Distillation Unit and
the flow paths and apparatus before conducting of the experiment. This distillation operation usually
deals with very hot and highly flammable materials. Extreme care must be taken when handling the
apparatus, in taking readings and collecting samples.
The Flow Meters should be operated smoothly in order to avoid pressure surges within the
equipment.
Inspect the equipment visually for any damaged components or glass breakage. If any such defects
are noticed, please report them to your instructor / technician.
Goggles must be worn at all times in the laboratory.
Appropriate rubber gloves must be worn when Organic Solvents are handled.
Avoid wearing clothes which can easily catch fire.
The flow rates of liquids should not exceed the maximum of the rates shown in the flow meter.
The water supply pressure to the Condenser and the Coolers should not exceed 2 bar gauge.
Inspect the equipment visually for glass breakage and leakage.
Do not allow the water pressure to exceed 2.0 bar maximum as indicated by PI.2.
Always maintain V8 in the open position during atmospheric operation (avoid system pressurizing).
Dont isolate cooling water until the heating has been shut down (at least 10 minutes).
Dont switch on the immersion heater with the level in the reboiler below the heater elements or
when the reboiler is empty.
Dont return the product distillate collected to the reboiler vessel when the equipment is in operation.
Do not allow the liquid level to raise much above the top graduation on the tube before the stop
valves V2 and V3 are opened.
Dont drain the liquid in reboiler vessel until is cold.
Do not touch the hot components of the unit.
4.2 Calibration Curve Curve for Refractive Index vs concentration of Ethanol-Water mixtures
1.
2.
3.
4.
Prepare a 5% ethanol-water solution in a test tube.
Using a refractometer, obtain the refractive index reading for the solution.
Repeat step 1 to 2. Using increments of 5%, obtain refractive index readings for ethanol-water
mixtures up to 100 %.
Record the RI reading for each of 5% concentration in Table 1.
4.3 General Start-up Procedures
Materials needed:
a. Ethanol industrial grade
b. Water
Prepare 30 litres of 10 % v/v (volume/volume) mixture of Ethanol in Water by mixing appropriate
quantities of the Industrial Grade of Ethanol in Distilled Water.
Using the Refractive Index (RI) method, check the RI of pure ethanol and pure water and
record at Time 0 in the Table 2.
Refer to the diagram of the equipment in the lab for better / accurate view.
Ensure valves V1, RCV1, V3, V4, V5, V6, V7, V9 and FCV2 are closed.
Ensure valves V2, V8 and V10 are open.
Start fill in the Ethanol / Water mixture up to the desired level (ask lecturer / technician).
Slowly open the cooling water to the condenser (max 2.0 bars).
Make sure water is indeed flowing through it.
Separation Technology CKD 20103/EXP2A/Jan2015
Check water flows to the drain from the Cooling Water outlets.
Do not start the experiment until the Cooling Water flow is visible in the outlets to the drain.
Ensure that the Bottom Product sampling valve V5 and Top Product sampling valve V4 is closed.
Ensure that the Reboiler Vessel is already charged with the Ethanol Water mixture through the
Charge Port (Refer to the diagram).
Check that the liquid level is satisfactory (Refer to instructor / technician).
Otherwise top up with the Ethanol Water mixture through the Charge Port (Refer to instructor /
technician).
Ensure that the concentration of feed in the reboiler vessel is correct and that the liquid level is at
the vessel equator. (Refer to Lecturer / Technician)
The Reboiler Vessel should never be filled with liquid above the maximum level indicated.
The level should never recede below the minimum level while on operation.
Close the Reflux Adjustment Valve RCV1 and valve below Product Cooler V2.
Obtain a sample of Ethanol Water mixture from the Reboiler through the Sampling Port and test its
composition using Refractometer.
Turn on the main power control switch.
Turn on the power switch of the heater.
Switch on electrical supply (green heater on button).
Set heater controller HC.4 to maximum setting. (About 200 V)
Allow a period of 15 minutes for the equipment to maintain thermal equilibrium with surroundings.
Observed the temperature readings of all Temperature Indicator (TI). Record the temperature
reading every 5 minutes (from Time 0 onwards).
When distillate liquid is seen to flow through RI.A1, reduce the heat input and set HC.4 to roughly
150V.
During this period observe HC.4.
The unit is now ready to be used for an experiment.
4.4 Experiment: Operation under Partial Reflux Condition
Ensure that the valve for Reflux Ratio RCV 1 adjustment is opened.
Adjust both valve for Reflux Ratio RCV 1 and valve below Product Cooler V2 so that both readings
on R1 and R2 provide a Reflux Ratio of 1.0 for the operation.
Wait for about 15 minutes until the flow rate shown by R1 and the temperature readings at the top
and bottom of the columns are steady. (Refer to instructor / technician).
Collect samples from the Reboiler and the overhead from the Sampling Port for every 5 minutes.
Observe the Temperature of the Reboiler TI4. If the temperature is already 90C, reduce the current
of the Reboiler to between 150V to 160V.
Observe the flow rate at R1. Adjust the valve for Reflux Ratio adjustment to ensure that the
Reflux Ratio is maintained at 1.0.
The concentration of the samples drawn is measured using the Refractive Index method.
Continue record the reading of temperatures for every 5 minutes.
Readings are recorded in the provided table of results.
4.5 General Shut Down Procedures
Adjust heater controller HC.4 to minimum setting.
Switch off electrical supply (red heater off button).
Turn off the power switch of the Reboiler.
Turn off the main power control switch.
Do not drain the hot liquid from the Reboiler. If necessary, the liquid within the system could be
drained only when the liquid is already cooled.
Allow the Cooling Water to run for some time (Ask Lecturer / Technician).
Separation Technology CKD 20103/EXP2A/Jan2015
5. Results (Please attach this part in your report)
Standard Refractive Index (RI):
Ethanol :______________
Water : _______________
Table 1
% v/v Ethanol
Time
(Min)
TI 1
TI
1A
RI Value
Table 2
Temperature Readings ( C )
TI
TI 2
TI
TI
TI 4
1B
2A
2B
TI 5
TI 6
RI
Top
Product
RI
Bottom
Product
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
105
110
115
120
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Malaysian Institute of Chemical and Bioengineering TechnologyDocument2 pagesMalaysian Institute of Chemical and Bioengineering TechnologyAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Collection PointDocument19 pagesWaste Collection PointAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- REPOT EditedDocument51 pagesREPOT EditedAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document38 pagesChapter 4Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Document13 pagesIndividual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Document4 pagesCurrent Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- RESULT and Discussion.Document4 pagesRESULT and Discussion.Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Catalyst Characters On The Photocatalytic Activity and Process of Nio Nanoparticles in The Degradation of Methylene BlueDocument7 pagesEffects of Catalyst Characters On The Photocatalytic Activity and Process of Nio Nanoparticles in The Degradation of Methylene BlueAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Document13 pagesIndividual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Graph HeatDocument5 pagesGraph HeatAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Catalytic Oxidation of SO To SO: Apodaca, 2012Document9 pages1.1 Catalytic Oxidation of SO To SO: Apodaca, 2012Farah Talib Al-sudaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 2 Principles of ProgrammingDocument1 pageExercise 2 Principles of ProgrammingAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Report Equipment DesignDocument2 pagesReport Equipment DesignAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment ESPDocument8 pagesExperiment ESPAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Report Cover Page (50%)Document1 pageLaboratory Report Cover Page (50%)Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Justification: Why Double Contact Process Is Most Suitable For Sulfuric Acid ProductionDocument1 pageJustification: Why Double Contact Process Is Most Suitable For Sulfuric Acid ProductionAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- RBDDocument2 pagesRBDAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Document4 pagesCurrent Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Document4 pagesCurrent Technologist Challenges and Achievements: What Do You Think?Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods / Procedures: List of ChemicalsDocument3 pagesMethods / Procedures: List of ChemicalsAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Technology Tool Paper Final PDFDocument18 pagesWater Technology Tool Paper Final PDFAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Document13 pagesIndividual Assignment A1 Engineering Technologist in Society Clb40002Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Inside The Wind TurbineDocument1 pageInside The Wind TurbineAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- SafetyDocument1 pageSafetyAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- CPB 30103 Biochemical Engineering (July)Document8 pagesCPB 30103 Biochemical Engineering (July)Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- (C) Laboratory Report SubmissionDocument2 pages(C) Laboratory Report SubmissionAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 TUTORIAL 3 Hazard IdentificationDocument3 pages3 TUTORIAL 3 Hazard IdentificationAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 1Document12 pagesExp 1Anonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- SafetyDocument1 pageSafetyAnonymous T7vjZG4otPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Advanced Plastic Testing Technologies PDFDocument20 pagesAdvanced Plastic Testing Technologies PDFManoj BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual: Ozone ModuleDocument7 pagesManual: Ozone ModuleCamilo Acosta APas encore d'évaluation
- Ocean Tides SEDocument3 pagesOcean Tides SEKeni RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- CPVC Price List March 06-12-2022Document10 pagesCPVC Price List March 06-12-2022dec industriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes: Introduction To Condensed Matter TheoryDocument154 pagesLecture Notes: Introduction To Condensed Matter Theory谭志阳Pas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Recommendation Conclusion WeldingDocument2 pagesDiscussion Recommendation Conclusion Weldingzarif73% (15)
- Chapter 2: Earth in SpaceDocument75 pagesChapter 2: Earth in SpaceKen AguilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reif F Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFDocument668 pagesReif F Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFVeerareddy Vippala85% (123)
- Utilizare VAS 6096Document6 pagesUtilizare VAS 6096georgescuriosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing Failures, Causes & Remidies 25.02.08Document66 pagesBearing Failures, Causes & Remidies 25.02.08Sonali Priyadarshini100% (2)
- Unclassified Ad Number Limitation Changes TODocument36 pagesUnclassified Ad Number Limitation Changes TORuben's OscarPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Equipment DesignDocument21 pagesProcess Equipment DesignAsila Ahmed0% (1)
- Tensile Test Expreriment (Lab Report) .Document4 pagesTensile Test Expreriment (Lab Report) .ضياء بن احمد الكباريPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Answer SchemeDocument4 pagesPhysics Answer SchemeBENNY LAU XUE ZHENG MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Friction and Pile DesignDocument7 pagesSkin Friction and Pile DesignNaveen RPas encore d'évaluation
- FEM Question Bank PDFDocument23 pagesFEM Question Bank PDFedla rajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 43 Heat Pumps1Document92 pagesUnit 43 Heat Pumps1hvactrg1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tabel PenmanDocument3 pagesTabel PenmanYuli Ana Fransisca SantanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemie Ingenieur Technik Volume 73 Issue 6 2001 (Doi 10.1002/1522-2640 (200106) 73:6-605::aid-Cite6054444-3.0.Co 2-g) Görge Baltin Heinz Köser Klaus-Peter Wendlandt - Reactive DesorDocument1 pageChemie Ingenieur Technik Volume 73 Issue 6 2001 (Doi 10.1002/1522-2640 (200106) 73:6-605::aid-Cite6054444-3.0.Co 2-g) Görge Baltin Heinz Köser Klaus-Peter Wendlandt - Reactive Desorlili purwasihPas encore d'évaluation
- Heavy-Duty Lubricant: FeaturesDocument2 pagesHeavy-Duty Lubricant: Featuresarjun vsPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamic Database of Multi-Component MG Alloys and Its Application To Solidification and Heat TreatmentDocument16 pagesThermodynamic Database of Multi-Component MG Alloys and Its Application To Solidification and Heat Treatmentmridzuan69Pas encore d'évaluation
- D86 - 19 PDFDocument29 pagesD86 - 19 PDFGuillermo ZapataPas encore d'évaluation
- Crashworthiness Optimization Design of Thin Walled Tube Filled With Re Entrant Triangles HoneycombsDocument13 pagesCrashworthiness Optimization Design of Thin Walled Tube Filled With Re Entrant Triangles Honeycombsash ketchumPas encore d'évaluation
- Julian Schwinger Selected Papers On Quantum Electrodynamics 1958 PDFDocument443 pagesJulian Schwinger Selected Papers On Quantum Electrodynamics 1958 PDFLav100% (6)
- Experiment 3: Determination of Lead in Anchovies by Cold Vapour Generation Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocument31 pagesExperiment 3: Determination of Lead in Anchovies by Cold Vapour Generation Atomic Absorption SpectrometrymanurihimalshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Standard: Guide For Lateral Dynamic Load Test On PilesDocument21 pagesIndian Standard: Guide For Lateral Dynamic Load Test On PilesSubodh SontakkePas encore d'évaluation
- Tamura Solder Paste GP 216 HF 17Document5 pagesTamura Solder Paste GP 216 HF 17luthfiPas encore d'évaluation
- CADE Technologybrochure AccumulatorsDocument24 pagesCADE Technologybrochure AccumulatorsJose francisco Lazo castroPas encore d'évaluation
- Connection DesignDocument33 pagesConnection Designjesus curielPas encore d'évaluation