Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tenses
Transféré par
Vignes KrishnanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tenses
Transféré par
Vignes KrishnanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
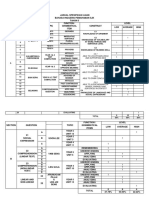
Table of English Tenses
tense
Simple Present
Present Progressive
Simple Past
Affirmative/Negative/Question
A: He speaks.
N: He does not speak.
Q: Does he speak?
A: He is speaking.
N: He is not speaking.
Q: Is he speaking?
A: He spoke.
N: He did not speak.
Q: Did he speak?
Use
action in the present taking
place once, never or several
times
facts
Signal Words
always, every , never,
normally, often, seldom,
sometimes, usually
actions taking place one after if sentences type I (If I
talk, )
another
action set by a timetable or
schedule
action taking place in the
moment of speaking
at the moment, just, just
action taking place only for a now, Listen!, Look!,
now, right now
limited period of time
action arranged for the future
yesterday, 2 minutes
action in the past taking place ago, in 1990, the other
once, never or several times day, last Friday
if sentence type II (If I
actions taking place one after talked, )
another
Table of English Tenses
Past Progressive
Present Perfect Simple
A: He was speaking.
N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking?
A: He has spoken.
N: He has not spoken.
Q: Has he spoken?
action taking place in the
middle of another action
action going on at a certain
time in the past
actions taking place at the
same time
action in the past that is
interrupted by another action
putting emphasis on the result
action that is still going on
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an
influence on the present
action that has taken place
once, never or several times
before the moment of
speaking
when, while, as long as
already, ever, just,
never, not yet, so far, till
now, up to now
Table of English Tenses
Present Perfect Progressive
Past Perfect Simple
A: He has been speaking.
N: He has not been speaking.
Q: Has he been speaking?
A: He had spoken.
N: He had not spoken.
Q: Had he spoken?
A: He had been speaking.
N: He had not been speaking.
Q: Had he been speaking?
all day, for 4 years,
action that recently stopped or since 1993, how long?,
the whole week
is still going on
finished action that influenced
the present
action taking place before a
certain time in the past
Past Perfect Progressive
putting emphasis on the
course or duration (not the
result)
already, just, never, not
sometimes interchangeable
yet, once, until that day
with past perfect progressive if sentence type III (If I
had talked, )
putting emphasis only on the
fact (not the duration)
action taking place before a
certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable
with past perfect simple
putting emphasis on the
duration or course of an
for, since, the whole
day, all day
Table of English Tenses
action
Future I Simple
A: He will speak.
N: He will not speak.
Q: Will he speak?
Future I Simple
(going to)
A: He is going to speak.
N: He is not going to speak.
Q: Is he going to speak?
Future II Simple
A: He will be speaking.
N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking?
A: He will have spoken.
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken?
in a year, next ,
tomorrow
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask
spontaneous decision
her, she will help you.)
assumption: I think,
assumption with regard to the probably, perhaps
future
decision made for the future
in one year, next week,
conclusion with regard to the tomorrow
future
Future I Progressive
action in the future that
cannot be influenced
action that is going on at a
certain time in the future
in one year, next week,
tomorrow
action that is sure to happen in
the near future
action that will be finished at
by Monday, in a week
a certain time in the future
Table of English Tenses
Future II Progressive
A: He will have been speaking.
N: He will not have been
speaking.
Q: Will he have been speaking?
Conditional I Simple
A: He would speak.
N: He would not speak.
Q: Would he speak?
Conditional I Progressive
A: He would be speaking.
N: He would not be speaking.
Q: Would he be speaking?
action taking place before a
certain time in the future
putting emphasis on the
course of an action
action that might take place
action that might take place
putting emphasis on the
course / duration of the action
Conditional II Simple
A: He would have spoken.
N: He would not have spoken.
Q: Would he have spoken?
action that might have taken
place in the past
action that might have taken
place in the past
Conditional II Progressive
A: He would have been
speaking.
N: He would not have been
speaking.
Q: Would he have been
speaking?
puts emphasis on the course /
duration of the action
for , the last couple of
hours, all day long
if sentences type II
(If I were you, I would
go home.)
if sentences type III
(If I had seen that, I
would have helped.)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Importance of GreetingsDocument2 pagesThe Importance of GreetingsVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Clever KingDocument2 pagesThe Clever KingVignes Krishnan100% (1)
- Have N HasDocument2 pagesHave N HasVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsu B.Inggeris SJK Tahun 6 2019Document3 pagesJsu B.Inggeris SJK Tahun 6 2019Vignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- PN - HJ Sapiah BT HJ Saphi: Kerian District Education ChiefDocument1 pagePN - HJ Sapiah BT HJ Saphi: Kerian District Education ChiefVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2017: Jadual Spesifikasi Ujian Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman SJK Tahun 5Document3 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2017: Jadual Spesifikasi Ujian Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman SJK Tahun 5Vignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- English Language Camp: Section B (15 Marks)Document3 pagesEnglish Language Camp: Section B (15 Marks)Vignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- FridayDocument2 pagesFridayVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tamil Sol VilakkamDocument97 pagesTamil Sol VilakkamVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- JS 2015 TaskDocument1 pageJS 2015 TaskVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Directorate: Name Position Email Phone FaxDocument2 pagesDirectorate: Name Position Email Phone FaxVignes KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 2nd. Guide. Pedagogy of English in Preschool CourseDocument5 pages2nd. Guide. Pedagogy of English in Preschool CoursewendyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dakota Grammar Texts and EthnographyDocument284 pagesDakota Grammar Texts and EthnographyalexandreqPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 10 Tips For InterpretersDocument1 pageTop 10 Tips For InterpretersTrung KiênPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4Document2 pagesUnit 4api-377848238Pas encore d'évaluation
- Demonstrative Pronouns Lesson PlanDocument1 pageDemonstrative Pronouns Lesson PlanJay Pras33% (3)
- Hortatory ExpositionDocument2 pagesHortatory ExpositionJohnson fidelisPas encore d'évaluation
- English ReviewerDocument10 pagesEnglish ReviewerKyla PrincipePas encore d'évaluation
- Micro Pragmatics by Anmar Ahmed Context As The Basic Extension in LinguisticsDocument14 pagesMicro Pragmatics by Anmar Ahmed Context As The Basic Extension in Linguisticsanmar ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Turn-Taking in ConversationDocument4 pagesTurn-Taking in ConversationIonela LunguPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-Translation MethodsDocument9 pagesChapter 3-Translation MethodsThảo PhạmPas encore d'évaluation
- Western Bicutan National High School: Division of Taguig City and PaterosDocument1 pageWestern Bicutan National High School: Division of Taguig City and PaterosYanyan EducPas encore d'évaluation
- WVHCHFCDocument22 pagesWVHCHFCFahad RashdiPas encore d'évaluation
- A An WorksheetDocument1 pageA An WorksheetEncarna Garcia MéndezPas encore d'évaluation
- ESL Unit PlanDocument11 pagesESL Unit PlanMeghannPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Participle Word FindDocument1 pagePast Participle Word FindAsmidar HashimPas encore d'évaluation
- Resident Expert Assignment: Presentation RequirementsDocument5 pagesResident Expert Assignment: Presentation RequirementsAllison BallardPas encore d'évaluation
- Lbs 330 - Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesLbs 330 - Lesson Planapi-268943289Pas encore d'évaluation
- Peer-Editing Checklist PDFDocument1 pagePeer-Editing Checklist PDFAlvaro TrejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Swahili Tense AspectDocument326 pagesSwahili Tense Aspectnikolakr8526Pas encore d'évaluation
- AQA ENG1H W MS Jan13 PDFDocument16 pagesAQA ENG1H W MS Jan13 PDFMoulee GPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical: Iso/Iec TR 15285Document30 pagesTechnical: Iso/Iec TR 15285ramesh2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Anticipated Problems and Possible SolutionsDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Anticipated Problems and Possible SolutionsbettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Noun ClauseDocument15 pagesNoun ClauseVina ErfinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Exam in Oral CommunicationDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam in Oral CommunicationHao Li MinPas encore d'évaluation
- How Brand Communication Works: Key PointsDocument20 pagesHow Brand Communication Works: Key PointsAstha PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- An Etymological Dictionary of The Gaelic LanguageDocument487 pagesAn Etymological Dictionary of The Gaelic Languagetiby_olimp100% (4)
- English Has Two Basic Intonation PatternsDocument1 pageEnglish Has Two Basic Intonation Patternszulu22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Peer ReviewDocument2 pagesSpeech Peer ReviewC Derick VarnPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice in EnglishDocument4 pagesPassive Voice in EnglishRatri BerlianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adverbs - Types, Formation, Comparison PDFDocument6 pagesAdverbs - Types, Formation, Comparison PDFrodrigo100% (1)