Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrocarbons Usages: Fuel Science and Technology
Transféré par
elsayed amerTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Hydrocarbons Usages: Fuel Science and Technology
Transféré par
elsayed amerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NATURAL GAS ENGINEERING
Hydrocarbons
Usages
Fuel Science And Technology
Presented By : Mosad Dawood
Sublimated To Dr : Hamada Gad
Date : 4 12 2011
Natural Gas Engineering
Fuel Science and Technology
Hydrocarbon Usages
Introduction
The term HYDROCARBONS means organic compounds which contain
only carbon and hydrogen. By using this definition, four classes of
hydrocarbons are included: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and aromatic.
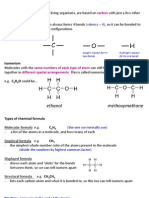
:The simplest compounds containing 2 carbons shown on the LEFT are as follows
Alkanes
SATURATED means
that each carbon is
bonded to four other
atoms through
single covalent
bonds. Hydrogen
atoms usually
occupy all available
bonding positions
after the carbons
have bonded to each
other
PARAFFINS which is
derived from a Latin
word meaning "little
activity", and means
that the compounds
are very unreactive.
Alkenes
Alkynes
UNSATURATED hydrocarbons contain either
double or triple bonds. Since the compound is
unsaturated with respect to hydrogen atoms, the
extra electrons are shared between 2 carbon
atoms forming double or triple bonds.
Alkenes are also called
OLEFINS because they
form oily liquids on
reaction with chlorine
gas.
Alkynes are also
generally known as
ACETYLENES from the
first compound in the
series.
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
Aromatic compounds derive their names from the fact that many of these compounds
in the early days of discovery were grouped because they were oils with fragrant
.odors, hence the name aromatic
The current definition of aromatic compounds includes only those with a benzene
ring, which is a special six carbon ring compound with three alternating double bonds.
This structure imparts unique properties to benzene which are different from other
.ring compounds
Natural Gas Engineering
Fuel Science and Technology
Hydrocarbons are chemical compounds consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen.
They are a subset of organic compounds. Hydrocarbons range from methane, which is
just one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, to polymers such as polystyrene,
which consists of thousands of carbon and hydrogen atoms. As carbon-carbon bonds are
the strongest in all of chemistry, long chains with carbon backbones are extremely
durable, and seem to have a practically unlimited extent.
Hydrocarbons come in a variety of forms. They may be gases (methane and propane),
liquids (hexane and benzene), waxes (paraffin wax), or polymers (polyethylene and
polystyrene). Hydrocarbons can be processed to create plastics.
There are four main types of hydrocarbons: saturated hydrocarbons, consisting of only
single bonds between carbon atoms; unsaturated hydrocarbons, with double or triple
bonds; cycloalkanes, with consist of hydrogen bonded to carbon rings; and aromatic
hydrocarbons, which contain a chemical structure known as an aromatic ring, of which
benzene is the simplest example.
The primary source of hydrocarbons here on Earth is through fossil fuels coal, oil, and
natural gas. These are extracted from the ground in quantities of millions of tons per day,
and are the primary energy source for todays civilization. 85% of all electricity worldwide
is generated by the burning of hydrocarbons, and hydrocarbon fuel is used to propel
practically every mobile machine: cars, trucks, trains, planes, and ships
Natural Gas Engineering
Fuel Science and Technology
The hydrocarbons are the most broadly used organic compounds known, and are quite
literally the driving force of western civilization.
The greatest amounts of hydrocarbons are used as fuel for combustion, particularly in
heating and motor fuel applications.
The primary components of natural gas are methane and ethane.
We are all familiar with the use of propane in gas barbecues, lanterns, and as a fuel
for internal combustion engines and heating systems.
Butane is also a readily available fuel, familiar to everyone in the form of the
pocket lighter.
pentane, the saturated hydrocarbons enter the realm of room-temperature liquids.
This makes them useful as organic solvents, cleaners, and transport fuels.
Gasoline for internal combustion engines in cars, trucks, tractors, lawnmowers,
and so on, is rated in combustion properties relative to octane. It is in fact a
combination of liquid hydrocarbons ranging from hexanes to decanes.
Slightly larger hydrocarbons are known as kerosene or jet fuel, diesel fuel and
heating oil. Still larger hydrocarbon molecules serve as lubricating oils, and
greases.
Eventually a point is reached at which the materials are solids at room
temperature. These are the waxes. Hydrocarbon molecules larger than those of the
waxes are the heavy greases and the tars commonly used in roofing applications
and highway construction.
Natural Gas Engineering
Fuel Science and Technology
Hydrocarbon oil can be petroleum oil, coal tar, or oil produced from coal,
shale, or peat. These oils will remain in liquid form at 15 degrees Celsius and
have many industrial uses included in the manufacturing of fuel. They can
also be used in a non-liquid state for many other industrial uses, such as in
.plastics
Fuel
Hydrocarbon oil can be processed to make any number of liquid fuels. These
fuels include diesel, petrol, aircraft spirits, as well as heating oils such as
kerosene
Lubricants
Distilled from hydrocarbon oils, lubricants reduce friction between bearing
surfaces. Lubricants include motor oils, greases, and all other grades of
lubricating oil-based stocks
Aerosols
Hydrocarbon oil can also be converted into an aerosol. This oil aerosol is one part
hydrocarbon oil to 200,000 parts air. These aerosols are used like traditional
lubricants but are designed to reduce the consumption of hydrocarbon oils.
Asphalt
When not in liquid form, hydrocarbon oils can be used for other industrial
applications as well. When solidified, these oils can be used in asphalt. They can
also be burned as fuels with little leftover ash residue.
Wax
Another non-liquid form of hydrocarbon oils is wax. In industrial form,
hydrocarbon wax reduces dry friction and can be used to harden other
petroleum-based waxes. Hydrocarbon waxes are also used in cosmetics,
toiletries, and in the automobile industry.
Natural Gas Engineering
Fuel Science and Technology
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SCH 1308Document113 pagesSCH 1308v.monicamohanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 Lesson 1 Composition and Production of FODocument7 pagesTopic 4 Lesson 1 Composition and Production of FOcarltalves1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOrganic ChemistrybethanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum Refining Fourth Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahDocument5 pagesPetroleum Refining Fourth Year DR - Aysar T. JarullahSaad NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryEMMANUEL FESTUSPas encore d'évaluation
- HYDROCARBONS Module3Document22 pagesHYDROCARBONS Module3Mugara Waitega PeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesOrganic ChemistrySayeef MahdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Compound - Part IIDocument4 pagesOrganic Compound - Part IITherese ClairePas encore d'évaluation
- AFL Units 1 To 3 NOLDocument47 pagesAFL Units 1 To 3 NOLpavanranePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec.01 - Unit-II FuelDocument21 pagesLec.01 - Unit-II FuelDr. Kamal Singh RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- MohsinDocument4 pagesMohsinWaqas AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Methane Vs Propane C11!2!09Document11 pagesMethane Vs Propane C11!2!09John WuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3-Carbon CompoundsDocument57 pagesModule 3-Carbon CompoundsJaynarose Castillo Rivera100% (5)
- Hydro-Carbons: Submitted by - Rea AgarwalDocument6 pagesHydro-Carbons: Submitted by - Rea Agarwalrea agarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Petroleum1Document12 pagesCrude Petroleum1AdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment in Advance Chemistry (Hydrocarbons) : Frauline C. Tadle IV-Galileo Mr. Romel Condeza S.Y.: 2010-2011Document7 pagesAssignment in Advance Chemistry (Hydrocarbons) : Frauline C. Tadle IV-Galileo Mr. Romel Condeza S.Y.: 2010-2011Fraul TadlePas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1D'EverandCrude Petroleum analysis handbook: Crude oil Quality control, #1Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry '13Document33 pagesOrganic Chemistry '13Princess KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude OilDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Petroleum/Crude Oilanya de silvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Refining AssignmentDocument19 pagesOil Refining AssignmentKiran ShahzadiPas encore d'évaluation
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument12 pagesHow Oil Refining WorkssubashPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument37 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsGayatri HegdePas encore d'évaluation
- Refining of PetroleumDocument6 pagesRefining of Petroleumzb khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sources of Carbon Compounds: Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesSources of Carbon Compounds: Learning Outcomestrenyce alexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Paper 1 WordDocument7 pagesChemistry Paper 1 WordWAREKARPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 4th QTRDocument3 pagesScience 9 4th QTRClyde Owain Rocafort VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil Presentation - Chemistry 243Document23 pagesCrude Oil Presentation - Chemistry 243Tishonna DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- How Refinery WorksDocument7 pagesHow Refinery WorksmuraliPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrocarbon and Its DerivativesDocument12 pagesHydrocarbon and Its DerivativesReulyn Lardizabal RafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- FUELSDocument35 pagesFUELSJayson DayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Fuels and Earth SciencesDocument6 pages8 Fuels and Earth SciencessophiederryPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahDocument9 pagesChemistry Project: By: Ouail BalahOuail BalahPas encore d'évaluation
- HYDROCARBONS1 Converted 1Document4 pagesHYDROCARBONS1 Converted 1Ajayi DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsChristian Guimmayen ArizoPas encore d'évaluation
- PetroleumDocument8 pagesPetroleumM AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Carbon CompoundsDocument7 pagesThe Carbon CompoundsSean Gabriel LacambraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module FormatDocument18 pagesModule Formatnorlin facultadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 2 Ass - 012632Document11 pagesChem 2 Ass - 012632Natcy DendragonPas encore d'évaluation
- PETROLEUMDocument12 pagesPETROLEUMmadiha fatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal and PetroleumDocument6 pagesCoal and Petroleumsidhantm823Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1, Fuel System 2, Emmision Control System 3, Compostion of FuelsDocument10 pages1, Fuel System 2, Emmision Control System 3, Compostion of FuelsBegna BuzunehPas encore d'évaluation
- This Chapter Includes Data About Petroleum and Corrosion in GeneralDocument25 pagesThis Chapter Includes Data About Petroleum and Corrosion in GeneralFadzli KhirPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter (14) Organic ကျက်စာDocument12 pagesChapter (14) Organic ကျက်စာMoun Lynn SythuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Carbon CompoundsDocument23 pagesModule Carbon CompoundspkrajenpillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Fuel - WikipediaDocument29 pagesLiquid Fuel - WikipediabilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesDocument9 pagesIgcse Separate Sciences Topic C14: Organic Chemistry Revision NotesJamiu Yusuf AsukuPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkanes Are Non-Polar. The C-H Bond Is Weakly Polar, Due To Difference in Electronegativity Between C and H Atoms, However Due ToDocument1 pageAlkanes Are Non-Polar. The C-H Bond Is Weakly Polar, Due To Difference in Electronegativity Between C and H Atoms, However Due ToWilfred PangilinanPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE (v.15) Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesIGCSE (v.15) Organic ChemistryBruce CourtinPas encore d'évaluation
- FEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CDocument134 pagesFEI CSEC Chemistry Handbook Section B - Organic Chemistry and Section CMarques GrantPas encore d'évaluation
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument13 pagesHow Oil Refining WorksHerman_ms2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- OF Fuel: by Varun Pratap SinghDocument58 pagesOF Fuel: by Varun Pratap Singhduy.ho188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of AlkanesDocument2 pagesApplications of AlkanesAira Jane SembranPas encore d'évaluation
- On Average, Crude Oils Are Made ofDocument19 pagesOn Average, Crude Oils Are Made ofbalajiupesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument6 pages4 Carbon and Its CompoundsRounak BasuPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Organic ChemistryChemistryKlipz98% (40)
- Attachment 3 PDFDocument12 pagesAttachment 3 PDFEricha Palaypay EmpaynadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Students SlidesDocument124 pagesStudents SlidesAadhavan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةDocument234 pagesOil Refinary Dr Adndn 2016-مهمةHmid AljbrePas encore d'évaluation
- MCB 410Document33 pagesMCB 410oluwaleye victorPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Compounds in OUR Daily Life: Sheeny Pawal X-C R.No.:42Document24 pagesCarbon Compounds in OUR Daily Life: Sheeny Pawal X-C R.No.:42Sneha ParwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting and Tracking The Value of Injection Wellwork For Wets .Document7 pagesPredicting and Tracking The Value of Injection Wellwork For Wets .elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil Refining ProcessDocument8 pagesCrude Oil Refining Processpapasky0% (1)
- Syed Jilani - Experimental Study of Formation Damage in Horizontal Wells PDFDocument222 pagesSyed Jilani - Experimental Study of Formation Damage in Horizontal Wells PDFelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Engineering: Reda Esp System ComponentsDocument4 pagesApplication Engineering: Reda Esp System Componentselsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Trends in Petroleum RefiningDocument2 pagesRecent Trends in Petroleum Refiningelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Petroleum Refining ProcessesDocument5 pagesHandbook of Petroleum Refining Processeselsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Schlum TBG Punch SummaryDocument1 pageSchlum TBG Punch Summaryelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Refining Crude Oil: Step 1 - SeparationDocument24 pagesRefining Crude Oil: Step 1 - Separationho-faPas encore d'évaluation
- Refining Crude OilDocument24 pagesRefining Crude Oilelsayed amer100% (1)
- Crude Oil Refining - Separators, Extractors,...Document24 pagesCrude Oil Refining - Separators, Extractors,...elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum RefiningDocument4 pagesPetroleum Refiningkvsangeeth100% (1)
- Personal Data::: Mohammed Ahmed Zakariya Ahmed 13/10/1980Document4 pagesPersonal Data::: Mohammed Ahmed Zakariya Ahmed 13/10/1980elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Petroleum Refining ProcessesDocument5 pagesHandbook of Petroleum Refining Processeselsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Avail The Medical Service Ver2Document2 pagesHow To Avail The Medical Service Ver2elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Well MonitoringDocument1 pageWell Monitoringelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Remibursement Asoap Form: Symptom(s) As Described by Patient (Chief Complaint)Document1 pageRemibursement Asoap Form: Symptom(s) As Described by Patient (Chief Complaint)elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Complition AccessoriesDocument1 pageComplition Accessorieselsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Rig Floor ChicksanDocument1 pageRig Floor Chicksanelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1007-DISQ-0-P-PH-48450 Rev1Document1 page1007-DISQ-0-P-PH-48450 Rev1elsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.0 Utilities: Onspec Engineering Solutions Disouq Field Development Project Process Datasheet Fuel Gas PackageDocument1 page5.0 Utilities: Onspec Engineering Solutions Disouq Field Development Project Process Datasheet Fuel Gas Packageelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Number: 1007 1007-DISQ-0-P-DP-48122-Rev.3 1 of 5 Contract File ReferenceDocument1 pageNumber: 1007 1007-DISQ-0-P-DP-48122-Rev.3 1 of 5 Contract File Referenceelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Number: 1007 1007-DISQ-0-P-DP-48122-Rev.3 1 of 5 Contract File ReferenceDocument1 pageNumber: 1007 1007-DISQ-0-P-DP-48122-Rev.3 1 of 5 Contract File Referenceelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Onspec Engineering Solutions Disouq Field Development Project Process Datasheet Fuel Gas PackageDocument1 pageOnspec Engineering Solutions Disouq Field Development Project Process Datasheet Fuel Gas Packageelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Log SheetDocument1 pagePlant Log Sheetelsayed amerPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Grade12Document454 pagesScience Grade12Nurfaizura Saala RizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum PropertiesDocument28 pagesPetroleum PropertiesRathish RagooPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge O Level Chemistry Syllabus 2010Document23 pagesCambridge O Level Chemistry Syllabus 2010mohammad_islam_9Pas encore d'évaluation
- TariqLNG - Technology SelectionDocument4 pagesTariqLNG - Technology SelectionAndrey KrPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrochemical Standards (PDFDrive)Document68 pagesPetrochemical Standards (PDFDrive)fatimahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsDocument53 pagesReaction of Alkenes and Alkynes For StudentsGlen MangaliPas encore d'évaluation
- enviroFlu-HC Manual 20100325 EnglishDocument31 pagesenviroFlu-HC Manual 20100325 EnglishABMOHEPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework Booklet (4, S)Document55 pagesHomework Booklet (4, S)VarshLokPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Experiments In: Bachelor of Science in CriminologyDocument8 pagesLaboratory Experiments In: Bachelor of Science in CriminologyJonas BoadillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet NamingDocument2 pagesWorksheet NamingKristoff Avila0% (1)
- Astm UopDocument5 pagesAstm UopHamid Heidari50% (2)
- Chapter 15 Fuels and LubricantsDocument48 pagesChapter 15 Fuels and LubricantsJinky Mae PobrezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Demonstration Teaching (Lesson Plan)Document10 pagesFinal Demonstration Teaching (Lesson Plan)jaychrist12350% (2)
- 10th Carbon and Its Compounds Solved Question and 1 Practice Paper PDFDocument2 pages10th Carbon and Its Compounds Solved Question and 1 Practice Paper PDFRatan Kunwar VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Foundations of BiochemistryDocument28 pagesUnit 1 - Foundations of BiochemistryJoselitz Reyes TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum and Hydrocarbon Microbiology PDFDocument22 pagesPetroleum and Hydrocarbon Microbiology PDFJen Yanez100% (5)
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument37 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsGayatri HegdePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Document6 pagesChemistry Notes (Organic Chem)Teo Jia Ming NickolasPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D1319 - Jtvo9242Document7 pagesASTM D1319 - Jtvo9242Nayth Andres GalazPas encore d'évaluation
- WACKER AF 21 en 2020.07.01Document3 pagesWACKER AF 21 en 2020.07.01UtpalPas encore d'évaluation
- Org ChemDocument172 pagesOrg ChemMikaila Denise LoanzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Alkanes PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Alkanes PDFSITI NUR ALISSA BINTI AHMAD RASMANPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrocarbons-and-Alkanes-worksheet HOMEWORKDocument3 pagesHydrocarbons-and-Alkanes-worksheet HOMEWORKTeena SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- FIITJEE Big Bang 2016 Paper 2 Class 8 Sample PDFDocument13 pagesFIITJEE Big Bang 2016 Paper 2 Class 8 Sample PDFPushpa Pal50% (2)
- Well-Site Formation Evaluation by Analysis of Hydrocarbon Ratios G.H. FerrieDocument12 pagesWell-Site Formation Evaluation by Analysis of Hydrocarbon Ratios G.H. Ferriec_b_umashankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen Plant Safety PrinciplesDocument10 pagesOxygen Plant Safety Principleshwang2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Continuous Waste Tire AnalysisDocument49 pagesContinuous Waste Tire Analysis202040336Pas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes - Difference BetweenDocument7 pagesDifference Between Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes - Difference BetweenAjit KalelPas encore d'évaluation
- Impacts On Marine Ecology 2016Document56 pagesImpacts On Marine Ecology 2016Kalyani C ChendilPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument44 pagesOrganic ChemistryKushashwa Ravi ShrimaliPas encore d'évaluation