Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Film Language
Transféré par
Edit Lukács0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
25 vues3 pagesThis document discusses various camera techniques used in filmmaking, including different types of camera movements and shots. It describes how the camera can pivot from side to side or up and down. It also discusses different types of camera movements like pans, tilts, tracks, dollies, booms, and hand-held shots. Additionally, it outlines specialized shot types like establishing shots, master shots, point-of-view shots, cutaways, inserts, two-shots, follow shots, and reaction shots. Finally, it covers composite shots created through techniques like mattes, dissolves, and wipes.
Description originale:
The Film Language - handout
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses various camera techniques used in filmmaking, including different types of camera movements and shots. It describes how the camera can pivot from side to side or up and down. It also discusses different types of camera movements like pans, tilts, tracks, dollies, booms, and hand-held shots. Additionally, it outlines specialized shot types like establishing shots, master shots, point-of-view shots, cutaways, inserts, two-shots, follow shots, and reaction shots. Finally, it covers composite shots created through techniques like mattes, dissolves, and wipes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
25 vues3 pagesThe Film Language
Transféré par
Edit LukácsThis document discusses various camera techniques used in filmmaking, including different types of camera movements and shots. It describes how the camera can pivot from side to side or up and down. It also discusses different types of camera movements like pans, tilts, tracks, dollies, booms, and hand-held shots. Additionally, it outlines specialized shot types like establishing shots, master shots, point-of-view shots, cutaways, inserts, two-shots, follow shots, and reaction shots. Finally, it covers composite shots created through techniques like mattes, dissolves, and wipes.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
The film language
Handout
Part 2
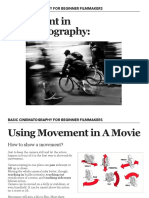
Pivoting and Moving the Camera
Camera can be moved: forward, backward, to the side
Camera pivots: from right to the left, from low to high angle
Camera can sweep through the air
Camera stays where it is
Pivoting and Zooming
Movement in two ways: 1.) horizontal or vertical axis
2.) using a zoom lens
Forward and backward zooms introduce only apparent movements
Pan or panamic shot:
o camera pivots on a vertical axis and turns in a horizontal plane
o swivels from side to side
o 360 spot: the camera rotates in a complete circle
o swish pan: a rapid pan renders the image as streacks
o the pan can survey a wide, horizontal field of view or swing from one
subject to another within a more limited field
o From Here To Eternity (1953) symbolic pan
Tilt ir tilting shot
o camera pivots on a horizontal axis and moves in a vertical plane
Moving Camera Shots
the operator or the camera platform will move from one location to another
the most common moving camera shots are hand-held, track, dolly and crane
shots
pan and tilt is also considered a camera movement, but of a different way
Hand-held shot
o perfectly smooth
o instability of the normal hand-held shot introduces a desireable jerkiness, a
feeling of informality, or the impression of impromptu shoting under
realistic conditions
o The War Game chaos of food riot instable shot
Track or trucking shot
o Camera platform moves along rails that are very like a pair of railroad
tracks
o Used as a generic term for any forward, backward, lateral or curving
camera movement executed on the ground (regardless of wheter the camera
platform has rubber wheels (dolly) or moves on steel rails)
o the term adverts to the use of a moving car or a wheelchair
Dolly shot
o Involves more intricate movements than the average track shot
o The Conformist (1971 B. Bertolucci) dance scene: the camera crosses
the dance floor and seems to dance itself
Boom or crane shot
o Camera is mounted on a large, cantilevered boom or arm that is itself
attached to a vehicle called a crane
o The system is balanced for grace and smoothness
o Aerial shot: the camera support actually leaves the ground (helicopter)
o Young and Innocent
Specialized Functions and Characteristics
Some shots are identified by the specialized functions they play in a film or by
other unique characteristics
These functions: establishing shot, the master shot, the POV shot, the cutaway,
the insert, the two-shot, the follow shot, the reaction shot, the matte shot, the
composite and the superimposition or double exposure
Shots have slow, fast and normal motion
Establishing shot
o introduces the location where the action will take place
o long shot
Master shot
o overview of a scene that is capable of taking in all of its major action
o full or long shot
o master shot: more particularized views
Insert
o shot of an unmoving object that is cut into a scene or sequence
Two-shot
o view of two people
Follow or following shot
o the camera moves in order to keep a moving subject in view
o follow-focus: art of keeping the moving subject in focus
Reaction shot
o shows peoples reaction to sg
Reverse or reverse-angle shot
o reverses the field of view, usually by an angle between 120 and 160
(180 or 360 reverse is not unheard of)
o shot/reverse shot: used for conversations between people who are facing
each other
o over-the-shoulder shot: view over one persons shoulder to the face
Matte Shots and Composites
Mask or matte card
o produces an image of certain desired shape
Matte shot:
o part of the frame has been blocked out
o single image created through the sequential use of a matte and a countermatte
o shots can be conbined into a single image without overlap
o travelling matte: opaque pattern that changes shape with every frame
composite
o a shot that has been composed from material in several different shots or
pre-print materials
o composite print: has both sound and picture
dissolve: one image melts into another that comes to replace it, is produced by
superimposing a fade-out over a fade-in
wipe:
o one image displaces another without any fading or overlap (both are
onscreen at the same time)
o wipe line: two images point of conjunction
o horizontal wipe: the line moves from screen right to left, or the reverse
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Film GlossaryDocument9 pagesFilm GlossaryNandi ChinniPas encore d'évaluation
- CINEMATIC TECHNIQUES Shortened List For VocabDocument5 pagesCINEMATIC TECHNIQUES Shortened List For VocabMitesh TakePas encore d'évaluation
- Film Studies: The Shot: CinematographyDocument87 pagesFilm Studies: The Shot: CinematographyCynthia ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Film TechniquesDocument5 pagesFilm TechniquesmatthewshuPas encore d'évaluation
- Film AnalysisDocument2 pagesFilm AnalysispicboyPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Directional ContinuityDocument44 pages10 Directional ContinuitykbhattrapistPas encore d'évaluation
- Movement, Shots, and Angles: Rhetorical Analysis of MediaDocument28 pagesMovement, Shots, and Angles: Rhetorical Analysis of MediamarvenmorrebasinangPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of Film TermsDocument7 pagesGlossary of Film TermsJuan Carlos ArrayanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera MovementsDocument1 pageCamera Movementsapi-263848576Pas encore d'évaluation
- Area 1 - Film FormDocument140 pagesArea 1 - Film FormJoseph ChildsPas encore d'évaluation
- CinematographyDocument51 pagesCinematographypranavPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of Film TermsDocument4 pagesGlossary of Film TermsElena LeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Technical Film Terms: Action, Establishing Shot, Shot/reverse ShotDocument3 pagesSome Technical Film Terms: Action, Establishing Shot, Shot/reverse ShotunirailsPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera MovementsDocument10 pagesCamera Movementsunnati.srivastava2510Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bordwell Thompson Film TermsDocument3 pagesBordwell Thompson Film Termslokaminta89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Movement EquipmentDocument18 pagesCamera Movement EquipmentBhåvøöķWadhwa100% (1)
- Movie Terminology GlossaryDocument14 pagesMovie Terminology GlossaryMary SingletonPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera SupportDocument26 pagesCamera Supportdmsngc55njPas encore d'évaluation
- Shot DesignDocument6 pagesShot Designartimpresro9108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Directional ContinuityDocument22 pagesDirectional ContinuityZishan MuzeebPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Angles, Movement & FramingDocument17 pagesCamera Angles, Movement & FraminggraveneyjlfPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera MovementsDocument10 pagesCamera MovementsRumpa MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Camera ShotsDocument4 pagesCamera ShotsChia TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Movements and Angles: Media Studies Pixx Productions Ayan MagudiaDocument4 pagesCamera Movements and Angles: Media Studies Pixx Productions Ayan MagudiaDATProudctionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Studies NotesDocument4 pagesFilm Studies NotesNancy JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cinematography RulesDocument2 pagesCinematography Rulesapi-265004995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Large Format (4x5) Camera Operating Guide - Help WikiDocument5 pagesLarge Format (4x5) Camera Operating Guide - Help WikiFFenton100% (1)
- Film TerminologyDocument4 pagesFilm TerminologyHenrique TavaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Movements and AnglesDocument4 pagesCamera Movements and AnglesnirajmagudiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Filming Techniques and Conventions: 1. Production - Shooting Your VideoDocument4 pagesBasic Filming Techniques and Conventions: 1. Production - Shooting Your VideoTacomtt7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shots AnglesDocument23 pagesShots AnglesMarJohnAlibayoPas encore d'évaluation
- MovementDocument9 pagesMovementapi-488762480Pas encore d'évaluation
- 180 Degree RuleDocument5 pages180 Degree RuleKhent ApduhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Camera Movements and Perspective: By: Raymund Rex D. DimaandalDocument17 pagesBasic Camera Movements and Perspective: By: Raymund Rex D. Dimaandalsiobhan margaretPas encore d'évaluation
- Calumet 4x5Document3 pagesCalumet 4x5PVLLCHURCHPas encore d'évaluation
- 30-Degree Rule: Film EditingDocument14 pages30-Degree Rule: Film EditingBhavana SubramaniyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Date: - Class: - Camera Shots, Angles, and Movement Terms and ExamplesDocument4 pagesName: - Date: - Class: - Camera Shots, Angles, and Movement Terms and ExamplesbrisongerPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera MovementsDocument5 pagesCamera MovementsAditya DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Movements 2022Document3 pagesCamera Movements 2022david.olmedobPas encore d'évaluation
- Drone MovementsDocument11 pagesDrone Movementsmanoj kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of Film TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary of Film TermsNandi ChinniPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Shots and Editng SkilsDocument3 pagesCamera Shots and Editng SkilsdamoncoatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of EditingDocument4 pagesPrinciples of EditingRockySharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera TechniquesDocument6 pagesCamera Techniquesapi-344476126Pas encore d'évaluation
- BlankDocument2 pagesBlankFromencia Dalayan AntipordaPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Shots, Angle, MovementDocument30 pagesCamera Shots, Angle, Movementsakshimann2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Large Format FocussingDocument10 pagesLarge Format FocussingSandeep Sakpal100% (2)
- Summary of Chapter TwoDocument5 pagesSummary of Chapter Twomahirwecynhtia1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Language of Film PCDocument102 pagesLanguage of Film PCVanessa_Rendon_5816Pas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary For AsDocument7 pagesGlossary For AsRichardStratfordTukePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CameraDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Camerahusen abduPas encore d'évaluation
- The 9 Classic Camera MovesDocument2 pagesThe 9 Classic Camera MovesFirman SyahPas encore d'évaluation
- TerminologyDocument4 pagesTerminologyapi-310201216Pas encore d'évaluation
- Camera MovementsDocument3 pagesCamera MovementsuahproductionsPas encore d'évaluation
- CinematographyDocument41 pagesCinematographyVajje MBAPas encore d'évaluation
- Typesofcameraangles-161216093843 2Document16 pagesTypesofcameraangles-161216093843 2Yesha Shah CherubsPas encore d'évaluation
- Animation GlossaryDocument5 pagesAnimation GlossarypudelhsdPas encore d'évaluation
- Camera Angles (Part 2)Document26 pagesCamera Angles (Part 2)Zishan MuzeebPas encore d'évaluation
- The Slave Rebellion of 1791Document2 pagesThe Slave Rebellion of 1791Edit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Poe and PhrenologyDocument2 pagesPoe and PhrenologyEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Vocabulary - Project: 1. Crossword With Picture CardsDocument3 pagesTeaching Vocabulary - Project: 1. Crossword With Picture CardsEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Screen Adaptations of Pride and PrejudiceDocument2 pagesScreen Adaptations of Pride and PrejudiceEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Australian EnglishDocument3 pagesAustralian EnglishEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- English Classroom Observation: An AnalysisDocument5 pagesEnglish Classroom Observation: An AnalysisEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Class:: First Day at School - Revision of The Story, Practice Lesson Polite Requests 1Document3 pagesSubject: Class:: First Day at School - Revision of The Story, Practice Lesson Polite Requests 1Edit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Class:: Time - Practice: What's The Time? It'sDocument3 pagesSubject: Class:: Time - Practice: What's The Time? It'sEdit LukácsPas encore d'évaluation
- Fo Transfer ProcedureDocument8 pagesFo Transfer ProcedureadityasahayPas encore d'évaluation
- CM Bu9000 Eng Bushings 3Document36 pagesCM Bu9000 Eng Bushings 3ing.dmanriq27100% (1)
- LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxDocument56 pagesLINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxFalley FasterPas encore d'évaluation
- Library: Astrology and WisdomDocument13 pagesLibrary: Astrology and Wisdomalimuhammedkhan2115Pas encore d'évaluation
- Camouflage Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCamouflage Lesson Planapi-344569443Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marxism and The Oppression of Women Lise VogelDocument259 pagesMarxism and The Oppression of Women Lise VogelMoises SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Cycle Rickshaw For School ChildrenDocument23 pagesDesign of Cycle Rickshaw For School ChildrenAditya GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical CodingDocument5 pagesMedical CodingBernard Paul GuintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Dewa Inspection CommentsDocument2 pagesSample Dewa Inspection Commentsrmtaqui100% (1)
- Neuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleDocument5 pagesNeuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleRaquel DuartePas encore d'évaluation
- 5 160 1 PBDocument13 pages5 160 1 PBLotkomoaidone Harahu TukambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tyba S4 Syntax PDFDocument107 pagesTyba S4 Syntax PDFIndahPas encore d'évaluation
- Sop ExcelDocument104 pagesSop ExcelRizky C. AriestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument3 pagesConceptual Frameworkprodiejigs36Pas encore d'évaluation
- BMS of Dubai International AirportDocument4 pagesBMS of Dubai International AirportJomari Carl Rafal MansuetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Problems Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheet For KidsDocument2 pagesHealth Problems Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheet For KidsTarisubhPas encore d'évaluation
- JMO 2023 (7, 8) Question PaperDocument2 pagesJMO 2023 (7, 8) Question PaperSuryanshu BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument413 pagesUntitledjgj38j90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Equipment in The NICUDocument7 pagesEquipment in The NICUGheDine PeracionPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionDocument62 pagesLecture 1 - Reinforced Concrete - IntroductionChristopher PaladioPas encore d'évaluation
- EU - Guidance On GMP For Food Contact Plastic Materials and Articles (60p)Document60 pagesEU - Guidance On GMP For Food Contact Plastic Materials and Articles (60p)Kram NawkPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Psychology Core Concepts 7th Edition Zimbardo Test Bank PDFDocument13 pagesDwnload Full Psychology Core Concepts 7th Edition Zimbardo Test Bank PDFcomfortdehm1350100% (7)
- The Latent Phase of LaborDocument8 pagesThe Latent Phase of LaborLoisana Meztli Figueroa PreciadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Famous Bombers of The Second World War - 1st SeriesDocument142 pagesFamous Bombers of The Second World War - 1st Seriesgunfighter29100% (1)
- Wet Chemical Pre E PresentationDocument310 pagesWet Chemical Pre E PresentationEdwardAlexanderGarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Vapor Permeability of Polypropylene: Fusion Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesWater Vapor Permeability of Polypropylene: Fusion Science and TechnologyBobPas encore d'évaluation
- T 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationDocument3 pagesT 1246784488 17108574 Street Lighting Control Based On LonWorks Power Line CommunicationsryogaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ield Methods: A Typical Field Mapping Camp in The 1950sDocument4 pagesIeld Methods: A Typical Field Mapping Camp in The 1950sshivam soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Document310 pagesAir Force To 32-1-101 Army TM 9 243 Navy m6290 Aj Man 1010 Marine Corp TM 10209 101 Technical Manual Use and Care of Hand Tools and Measuring Tools 14Michael SmallPas encore d'évaluation