Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Balanced Three-Phase Circuits
Transféré par
Şemsettin karakuşDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Balanced Three-Phase Circuits
Transféré par
Şemsettin karakuşDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
7/7/2014
Chapter 2:
Balanced three-phase circuits
Why dealed with three-phase systems ?
Generation, transmission, and distribution of electrical power are
accomplished by means of three-phase circuits.
It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads.
A three-phase system is usually more economical than an equivalent
single-phase or two-phase system at the same voltage because it uses
less conductor material to transmit electrical power.
Three-phase system was independently invented by Galileo Ferraris,
Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky, and Nikola Tesla in the late 1880s.
1
Three-phase line
Three-phase
voltage
source
Three-phase
load
A basic three-phase circuit
7/7/2014
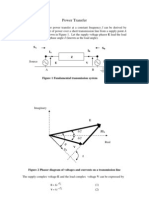
Balanced Three-phase Voltages
They have equal amplitudes.
They have same frequency (50 or 60 Hz).
They are out of phase with each other by exactly 120
Phase sequence is important for paralell operation of three-phase
circuits.
wt*180/
Vm*
variation of instantaneous three-phase voltages wrt time (positive sequence)
Phasor diagram of three-phase voltages
Vc Vm120
Vb Vm120
Va Vm0
Va Vm0
Vb Vm 120
Vc Vm 120
abc (positive sequence)
important property
Va Vb Vc 0
acb (negative sequence)
for balanced operation
7/7/2014
Example: What is the sequence of each of the following set of voltages?
a) Va(t) = 208cos(wt+76) V
Vb(t) = 208cos(wt+316) V
Vc(t) = 208cos(wt-164) V
Va(t) = 208cos(wt+76-76)
Vb(t) = 208cos(wt+316-76)
Vc(t) = 208cos(wt-164-76)
Va(t) = 208cos(wt+0) V
Vb(t) = 208cos(wt+240) V
Vc(t) = 208cos(wt-240) V
b) Va(t) = 4160cos(wt-49) V
Vb(t) = 4160cos(wt-289) V
Vc(t) = 4160cos(wt+191) V
Va(t) = 208cos(wt-49+49)
Vb(t) = 208cos(wt-289+49)
Vc(t) = 208cos(wt+191+49)
Va(t) = 208cos(wt+0) V
Vb(t) = 208cos(wt-240) V
Vc(t) = 208cos(wt+240) V
positive sequence
negative sequence
Types of three-phase voltage sources
Vca(t)
Vc(t)
Vab(t)
Va(t)
Vb(t)
Wye (Y)-connected ideal sources
Vbc(t)
Delta ()-connected ideal sources
7/7/2014
Types of three-phase loads
Wye (Y)-connected load
Delta ()-connected load
If Z1 = Z2 = Z3 => balanced load
7
Four different connection configurations
Three-phase line
Three-phase
voltage
source
Three-phase
load
neutral wire for Y-Y
(optional)
Y Y
Y
Y
7/7/2014
WYE-WYE CIRCUT
VRY VYB VBR VL SOURCE
Vry V yb Vrb VL LOAD Load line-line (line)
VR VY VB V p
Vrn V yn Vbn Vm
Source line-line (line)
voltages
Source phase voltages
VL SOURCE 3V p
voltages
VL LOAD 3Vm
I R I B IY I L I p
Load phase voltages
Line or load phase currents
10
7/7/2014
Real (active) power of the load (Y-connected)
PLOAD 1 ph Vm I p cos
is load power factor angle
PLOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p cos
Since
PLOAD 3 ph 3
Vm
VL LOAD
3
and
I p IL
VL LOAD
I L cos 3VL LOAD I L cos
3
Watts (W)
Real (active) power of the load
11
Reactive power of the load (Y-connected)
QLOAD 1 ph Vm I p sin
is load power factor angle
QLOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p sin
Since
QLOAD 3 ph 3
VL LOAD 3Vm
for Y-connected load
VL LOAD
I p sin 3VL LOAD I p sin
3
Watts (W)
Reactive power of the load
12
7/7/2014
Complex and apparent power of the load (Y-connected)
S LOAD 3 ph PLOAD 3 ph jQLOAD 3 ph
VA
Complex power of the load
S LOAD 3 ph PLOAD 3 ph QLOAD 3 ph
2
Apparent power of the load
S LOAD 1 ph VM I p
VA
Apparent power of the load (1-phase)
S LOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p 3
VA
VL LOAD
IL
3
S LOAD 3 ph 3VL LOAD I L
VA
Apparent power of the load
13
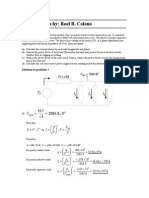
Solution:
14
7/7/2014
(c) KVL => Vry Z Y I R Z Y I Y 0
Vry (12 j 20)9.798 59 (12 j 20)9.798 179 0
Vry (23.3259)9.798 59 (23.3259)9.798 179
Vry 228.490 228.49 120
Vry 228.49 228.49 cos(120) j 228.49 sin(120)
Vry 342.74 j197.88
Vyb=?, Vbr=?
Vry 395.7630 volts
Solution:
(a) Load phase current:
Ip
1100
1100
4.72 A
Z
12 2 20 2
One-phase average power delivered to the load:
P1 ph Vm I p cos
P1 ph (110)(4.72)(0.512) 265.83W
15
Load power factor angle:
20
59 pf cos 0.515
12
tan 1
Total average power delivered to the load:
P3 ph 3Vm I p cos
P3 ph (3)(110)(4.72)(0.512) 797.49W
or
P3 ph 3VL LOAD I p cos
P3 ph ( 3 )( 3110)(4.72)(0.512) 797.49W
16
7/7/2014
(b)
One-phase reactive power of the load:
Q1 ph Vm I p sin
Q1 ph (110)(4.72)(0.857) 445 var
Total reactive power of the load:
Q3 ph 3Vm I p sin
Q3 ph (3)(110)(4.72)(0.857) 1335 var 1.335k var
or
Q3 ph 3VL LOAD I p sin
Q3 ph ( 3 )( 3110)(4.72)(0.857) 1335 var
This amount of reactive power is consumed (absorbed) by the three-phase load.
Because the load is inductive, i.e., Z = 12+j20
17
(c)
One-phase apparent power of the load:
S1 ph VM I p
S1 ph (110)(4.72) 519.2VA
(d) Power factor
pf cos 0.515 lagging
S3 ph P3 ph jQ3 ph
S3 ph
Total apparent power of the load:
S3 ph 3VM I p
Q3 ph
S3 ph (3)(110)(4.72) 1557.6VA
P3 ph
or
VL LOAD 3 (110) 190.53V
Power triangle of the load
S3 ph 3VL LOAD I p 3 (190.53)(4.72) 1557.6VA
18
7/7/2014
WYE-DELTA CIRCUT
I3
=>Y transformation
I2
Y-
VRY VYB VBR VL SOURCE
Vry V yb Vrb VL LOAD Load line-line (line)
VR VY VB V p
Vry V yb Vrb Vm
Source line-line (line)
voltages
Source phase voltages
VL SOURCE 3V p
voltages
I1 I 2 I 3 I p Load phase currents
I R I B I Y I L 3I p Line currents
Load phase voltages
VL LOAD Vm
19
20
10
7/7/2014
Real (active) power of the load (-connected)
PLOAD 1 ph Vm I p cos
is load power factor angle
PLOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p cos
Since
Vm VL LOAD
PLOAD 3 ph 3VL LOAD
and
Ip
IL
3
IL
cos 3VL LOAD I L cos
3
Watts (W)
Real (active) power of the load
21
Reactive power of the load (-connected)
QLOAD 1 ph Vm I p sin
is load power factor angle
QLOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p sin
Since
Vm VL LOAD
QLOAD 3 ph 3VL LOAD
and
Ip
IL
3
IL
sin 3VL LOAD I L sin
3
VARs
Reactive power of the load
22
11
7/7/2014
Complex and apparent power of the load (-connected)
S LOAD 3 ph PLOAD 3 ph jQLOAD 3 ph
VA
Complex power of the load
S LOAD 3 ph PLOAD 3 ph QLOAD 3 ph
2
VA
Apparent power of the load
S LOAD 1 ph VM I p
VA
Apparent power of the load (1-phase)
S LOAD 3 ph 3Vm I p 3VL LOAD
S LOAD 3 ph 3VL LOAD I L
IL
3
VA
Apparent power of the load
23
24
12
7/7/2014
Solution:
(a)
25
26
13
7/7/2014
Or power factor
pf cos cos 53.13 0.6 lagging
S3 ph P3 ph jQ3 ph
ST
QT
T
Power triangle of the load
27
Y or
IL
Y or
P
VL
Three-phase
voltage
source
+
-
Three-phase
Load
(pf=cos)
Q
The following power equations are valid
regardless of connection type of source (Y or )
regardless of connection type of load (Y or )
P 3VL I L cos
kW
Q 3VL I L sin
kVAR
S P jQ
kVA
28
14
7/7/2014
Power measurement in three-phase circuit using three wattmeter method
Single-phase wattmeter
29
[Ref]: http://ece.mst.edu/media/academic/ece/documents/classexp/ee209labs/Experiment_3_Power_Measurements.pdf
Power measurement in three-phase circuit using two wattmeter method
Single-phase wattmeter
30
[Ref]: http://ece.mst.edu/media/academic/ece/documents/classexp/ee209labs/Experiment_3_Power_Measurements.pdf
15
7/7/2014
Single-phase wattmeter (analog)
Three-phase wattmeter (analog)
Three-phase wattmeter (digital)
display
31
32
16
7/7/2014
33
34
17
7/7/2014
End of Chapter 2
35
18
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 25961 628Document9 pages5 25961 628Belayneh TadessePas encore d'évaluation
- Power System ProblemDocument10 pagesPower System ProblemDanylle Lajera DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- C2-3 PH ckts-S1Document31 pagesC2-3 PH ckts-S1mhmd.akzrPas encore d'évaluation
- 0b Three Phase IOHDocument28 pages0b Three Phase IOHkhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Eca Notes - Final Ver - 22.07.2023 (For Print)Document247 pagesEca Notes - Final Ver - 22.07.2023 (For Print)prem sunderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - 1Document29 pagesChapter 1 - 1Nour Ziad Ibrahim AlkurdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Three-Phase CircuitsDocument40 pagesBalanced Three-Phase CircuitsralucaPas encore d'évaluation
- EeImpQuesUnit3 PDFDocument21 pagesEeImpQuesUnit3 PDFpadmajasivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuits 2 LaboratoryDocument22 pagesCircuits 2 Laboratorypabloaguirre4293Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECE252 Lesson 13BDocument6 pagesECE252 Lesson 13BPhillip ChirongwePas encore d'évaluation
- Uniti Three PhasecircuitsDocument22 pagesUniti Three PhasecircuitsHarishReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Polyphase CircuitsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Polyphase CircuitsNidhija PillayPas encore d'évaluation
- L-7 Ece-495 595Document63 pagesL-7 Ece-495 595Nathan HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- Steady State Voltage Stability Enhancement of Power System by Proper Placement of Facts DevicesDocument19 pagesSteady State Voltage Stability Enhancement of Power System by Proper Placement of Facts DevicesVenkatesh PeruthambiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee366 Chap 5 2Document28 pagesEe366 Chap 5 2Michael Adu-boahenPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Systems L 3: EctureDocument23 pagesPower Systems L 3: EctureAmit DostPas encore d'évaluation
- SolvedDocument36 pagesSolvedJatin hemwani73% (30)
- BEF 23803 - Lecture 4 - Unbalanced Three - Phase CircuitsDocument41 pagesBEF 23803 - Lecture 4 - Unbalanced Three - Phase CircuitsJames LiewPas encore d'évaluation
- K13 T1 SolDocument4 pagesK13 T1 SolPriya Veer0% (1)
- Topic - Three-Phase Diode Rectifiers (Compatibility Mode)Document33 pagesTopic - Three-Phase Diode Rectifiers (Compatibility Mode)raadawad100% (1)
- Novel, Switch, Z-Source Three-Phase InverterDocument6 pagesNovel, Switch, Z-Source Three-Phase InverterJanjanam PraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Wattmeter Solved PRoblems-Paliza, JoshuaDocument11 pagesWattmeter Solved PRoblems-Paliza, Joshuajoshua palizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Unbalanced Polyphase Systems 1 23 13Document36 pagesBalanced Unbalanced Polyphase Systems 1 23 13Wyatt C. Lewis67% (3)
- PolyphaseDocument11 pagesPolyphasejoshua palizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Base (Reference) PaperDocument7 pagesBase (Reference) Papermphaniteja2012Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes 2Document25 pagesLecture Notes 2Sandesh ChinchrekarPas encore d'évaluation
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureDocument52 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureSreenath MPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13Document29 pagesLecture 13Andrew GoulderPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase NetworksDocument12 pagesThree Phase NetworksA-Jay N. GalizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Power Circuits: Lecture Notes: EEE Instructor: Dr. U D DwivediDocument39 pagesThree-Phase Power Circuits: Lecture Notes: EEE Instructor: Dr. U D Dwivedieche120014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Balanced Three-Phase CircuitsDocument40 pagesBalanced Three-Phase CircuitsMB CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Balanced FaultsDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Balanced FaultspecsppPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2: Three-Phase SystemDocument30 pagesLecture 2: Three-Phase SystemAddi KhattakPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric FundamentalDocument31 pagesElectric FundamentalKein Huat ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-2 - 3 Phase System To Part 3Document40 pagesChapter 1-2 - 3 Phase System To Part 3Hanis SyafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Transformers: ExperimentDocument8 pagesThree-Phase Transformers: ExperimentKoti ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- 001 Pow SystemDocument3 pages001 Pow SystemGian GarducePas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity & Magnetism Electricity & Magnetism: FE ReviewDocument41 pagesElectricity & Magnetism Electricity & Magnetism: FE Reviewsamir_ssh7151Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Three Phase Y-Y ConnectionDocument25 pages12 Three Phase Y-Y ConnectionAbdullah NaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- PFC Nptel PDFDocument50 pagesPFC Nptel PDFJagdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Phase Ac Problems With SolutionDocument12 pages3 Phase Ac Problems With SolutionKim FetalverPas encore d'évaluation
- ECEN 2633 Chapter 11Document6 pagesECEN 2633 Chapter 11Akira ZamudioPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdul Wahab LAB 6 EMDocument8 pagesAbdul Wahab LAB 6 EMFahad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase TransformersDocument8 pages03 EM3 Sample QA 3-Phase Transformersbinu_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- PE Lect7.CompressedDocument18 pagesPE Lect7.CompressedWuri Adining BagaskaraPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Power Tut Qns PDFDocument26 pagesAC Power Tut Qns PDFAlex LakePas encore d'évaluation
- ESO 203A: Introduction To Electrical Engineering (2014-15 Second Semester) Assignment # 6 SolutionDocument7 pagesESO 203A: Introduction To Electrical Engineering (2014-15 Second Semester) Assignment # 6 SolutionTejasv RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - Power Transfer0Document9 pagesLecture 2 - Power Transfer012onn1ePas encore d'évaluation
- L3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 1 PDFDocument18 pagesL3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 1 PDFAhmad WahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Delta-Connected Balanced LoadDocument12 pagesThree-Phase Delta-Connected Balanced LoadNitin BathamPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution of Tutorial Sheet No. 5 EE - 101: Electrical Science Spring Semester 2009 - 10Document10 pagesSolution of Tutorial Sheet No. 5 EE - 101: Electrical Science Spring Semester 2009 - 10DeepanjanMajheePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap12Document42 pagesChap12deskaug1Pas encore d'évaluation
- PS-II Lab ManualDocument69 pagesPS-II Lab ManualChilla DivyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 19EE10076 Machinelab Expt1Document11 pages19EE10076 Machinelab Expt1temp tempPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase SystemsDocument42 pagesThree Phase SystemsMahesh PushpakumaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Output Speed vs. Input Voltage: Experıment 6 Characterıstıc of A Permanent Magnet DC MotorDocument8 pagesMotor Output Speed vs. Input Voltage: Experıment 6 Characterıstıc of A Permanent Magnet DC MotorŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment #9 Tuning An Analog Pid Controller: Aim of The ExperimentDocument7 pagesExperiment #9 Tuning An Analog Pid Controller: Aim of The ExperimentŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE 352 ACS Lab Report CoverDocument1 pageEEE 352 ACS Lab Report CoverŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Controlled Systems 1) Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesLight Controlled Systems 1) Aim of The ExperimentŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics and Stability of Open Loop and Closed Loop Systems 1.aim of The ExperimentDocument14 pagesCharacteristics and Stability of Open Loop and Closed Loop Systems 1.aim of The ExperimentŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Carrier Transport: 3.1 Drift and DiffusionDocument1 pageCarrier Transport: 3.1 Drift and DiffusionŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Electron Energy Bands: 2.1 FundamentalsDocument1 pageElectron Energy Bands: 2.1 FundamentalsŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- AELE.3505 Control Theory 2: Class Test (10% of The Final Grade)Document2 pagesAELE.3505 Control Theory 2: Class Test (10% of The Final Grade)Şemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document37 pagesChapter 9Şemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- ZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class TestDocument2 pagesZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class TestŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- ZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class TestDocument3 pagesZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class TestŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- ZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class Test (10% of The Final Grade)Document2 pagesZITE 3203 Control Theory 2: Class Test (10% of The Final Grade)Şemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- C++ Ders7 - StreamsDocument19 pagesC++ Ders7 - StreamsŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- C++ Ders8 - DizinlerDocument25 pagesC++ Ders8 - DizinlerŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Lab 3: - Control Structures: SelectionDocument1 pageProgramming Lab 3: - Control Structures: SelectionŞemsettin karakuşPas encore d'évaluation
- Branch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019Document46 pagesBranch & Category Wise Opening & Closing Rank of JEE (Main) 2019soni dwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- GCGM PDFDocument11 pagesGCGM PDFMiguel Angel Martin100% (1)
- Ofsaai Ic 72 E22351 01Document312 pagesOfsaai Ic 72 E22351 01Mohamed AbrarPas encore d'évaluation
- High School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Document6 pagesHigh School Department PAASCU Accredited Academic Year 2017 - 2018Kevin T. OnaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Cause List 2.1.2023Document4 pagesCause List 2.1.2023あいうえおかきくけこPas encore d'évaluation
- High School Physics Rutherford Atom Lesson 27Document4 pagesHigh School Physics Rutherford Atom Lesson 27John JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- HTML Editor 8Document13 pagesHTML Editor 8Guru PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfa Laval Aalborg Os Tci Marine BoilerDocument2 pagesAlfa Laval Aalborg Os Tci Marine Boilera.lobanov2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- To Word AkheebDocument31 pagesTo Word AkheebDavid Raju GollapudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kimberly Jimenez Resume 10Document2 pagesKimberly Jimenez Resume 10kimberlymjPas encore d'évaluation
- Chrysler Dodge Ram Jeep Drive Cycle InformationDocument2 pagesChrysler Dodge Ram Jeep Drive Cycle InformationslpkthPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticDocument10 pagesSelf-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticAyeshia FréyPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of AyurvedaDocument9 pagesFaculty of AyurvedaKirankumar MutnaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Bo Sanchez-Turtle Always Wins Bo SanchezDocument31 pagesBo Sanchez-Turtle Always Wins Bo SanchezCristy Louela Pagapular88% (8)
- 04 DosimetryDocument104 pages04 DosimetryEdmond ChiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart English 2 PDFDocument44 pagesSmart English 2 PDFmishhuana90% (21)
- The Names of Allah and Their ReflectionsDocument98 pagesThe Names of Allah and Their ReflectionsSuleyman HldPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Information2009 2010Document4 pagesCourse Information2009 2010shihabnittPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Process Piping - Part 1 General Piping Design PDFDocument33 pagesLiquid Process Piping - Part 1 General Piping Design PDFnitin guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Citadel Securities Australia Pty LTD - Company DetailsDocument5 pagesCitadel Securities Australia Pty LTD - Company DetailsBrendan OswaldPas encore d'évaluation
- State of The Art in Research On MicrogridsDocument36 pagesState of The Art in Research On MicrogridsDulal MannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges Affecting Devolution PDFDocument94 pagesChallenges Affecting Devolution PDFELIJAH M. OMBEOPas encore d'évaluation
- Учебный предметDocument2 pagesУчебный предметorang shabdizPas encore d'évaluation
- Orange County Sheriff's Office SeaWorld Death Investigative ReportDocument43 pagesOrange County Sheriff's Office SeaWorld Death Investigative ReportWESH2News100% (1)
- Jungbluth Main Catalogue-LanacDocument60 pagesJungbluth Main Catalogue-LanacMilenkoBogdanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire OriginalDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire OriginalJAGATHESANPas encore d'évaluation
- GENTLENESSDocument4 pagesGENTLENESSAprylleCourtneyMayeMauyaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookDocument16 pages50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookSai DhanushPas encore d'évaluation
- Dell Inspiron 5547 15Document7 pagesDell Inspiron 5547 15Kiti HowaitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science: BiologyDocument22 pagesScience: BiologyMike RollidePas encore d'évaluation