Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features Instructions
Transféré par
EmeraldBilbreyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features Instructions
Transféré par
EmeraldBilbreyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
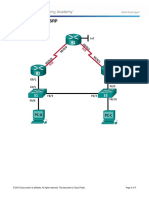
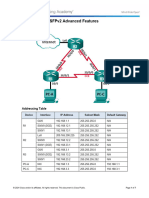
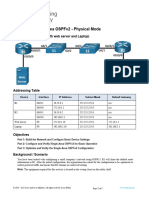
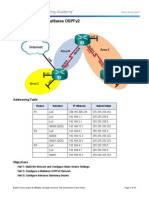
Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features
Topology
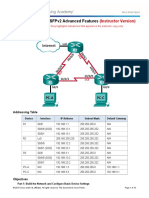
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IPv4 Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
172.16.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.3.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.5
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
172.16.2.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.3.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.9
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/1/0
209.165.200.225
255.255.255.224
N/A
G0/0
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.10.6
255.255.255.252
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.252
N/A
PC1
NIC
172.16.1.2
255.255.255.0
172.16.1.1
PC2
NIC
172.16.2.2
255.255.255.0
172.16.2.1
PC3
NIC
192.168.1.2
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
R1
R2
R3
Objectives
Part 1: Modify OSPF Default Settings
Part 2: Verify Connectivity
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 3
Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features
Scenario
In this activity, OSPF is already configured and all end devices currently have full connectivity. You will modify
the default OSPF routing configuration by changing the hello and dead timers, adjusting the bandwidth of a
link, and enabling OSPF authentication. Then you will verify that full connectivity is restored for all end
devices.
Part 1: Modify OSPF Default Settings
Step 1: Test connectivity between all end devices.
Before modifying the OSPF settings, verify that all PCs can ping the web server and each other.
Step 2: Adjust the hello and dead timers between R1 and R2.
a. Enter the following commands on R1.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 15
R1(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 60
b. After a short period of time, the OSPF connection with R2 will fail. Both sides of the connection need to
have the same timers in order for the adjacency to be maintained. Adjust the timers on R2.
Step 3: Adjust the bandwidth setting on R1.
a. Trace the path between PC1 and the web server located at 64.100.1.2. Notice that the path from PC1 to
64.100.1.2 is routed through R2. OSPF prefers the lower cost path.
b. On the R1 Serial 0/0/0 interface, set the bandwidth to 64 Kb/s. This does not change the actual port
speed, only the metric that the OSPF process on R1 will use to calculate best routes.
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64
c.
Trace the path between PC1 and the web server located at 64.100.1.2. Notice that the path from PC1 to
64.100.1.2 is redirected through R3. OSPF prefers the lower cost path.
Step 4: Enable OSPF authentication on all serial interfaces.
a. Use the following commands to configure authentication between R1 and R2.
Note: The key text R1-R2 is case-sensitive.
R1(config-router)# area 0 authentication message-digest
R1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 R1-R2
b. After the dead interval expires, neighbor adjacency between R1 and R2 will be lost. Repeat the
authentication commands on R2.
c.
Use the following command to configure authentication on R1 for the link it shares with R3.
R1(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 R1-R3
d. Finish the authentication configurations necessary to restore full connectivity. The password for the link
between R2 and R3 is R2-R3.
a. Verify that authentication is working between each router.
R1# show ip ospf interface
Message digest authentication enabled
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 3
Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features
Part 2: Verify Connectivity
Verify all PCs can ping the web server and each other.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- WorkLearning ContractDocument2 pagesWorkLearning ContractEmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationD'EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityD'EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 2 3 4Document6 pages5 2 3 4SamuelAbateSimmonsPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFDocument14 pages5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov100% (12)
- Munications For Railway Applications K5t8u Iji8fDocument135 pagesMunications For Railway Applications K5t8u Iji8fAlfrecron Oneone100% (1)
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- 10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features ELEISER HEBER ZELAYA CONDORIDocument8 pages10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features ELEISER HEBER ZELAYA CONDORIHeber Eleiser Zelaya Condori100% (2)
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMDocument12 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMرافد البركي75% (12)
- Drive Test Parameters SummaryDocument29 pagesDrive Test Parameters SummaryCharles WeberPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGDocument5 pages7.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Basic EIGRP With IPv4 Instructions IGkarenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyDocument8 pagesChapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using The AS - PATH Attribute: TopologyMeliko ianPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)Document38 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access (Filled)true0soul80% (5)
- 3G Networks: Chapter SummaryDocument22 pages3G Networks: Chapter SummaryYodi HermawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - 5 - OSPFDocument10 pagesLab - 5 - OSPFLipp00 M0MA100% (1)
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- 5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features Instructions IGDocument3 pages5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features Instructions IGIvanco Dario Covaria RondonPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Featuressebastian ruizPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesCarlos Beltran0% (1)
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument3 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesSean VillacortaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modify OSPF Settings and Verify ConnectivityDocument3 pagesModify OSPF Settings and Verify ConnectivityLizardo Hilario Hinostroza GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument11 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriquePas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument10 pages4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMDocument6 pages3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMElectronica EdwinPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocument7 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Document8 pages2.6.6-Packet-Tracer - 19030313Dante CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- HRRPDocument7 pagesHRRPJavier CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pagesLab 3 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF Advanced FeaturesWING KIN LEUNGPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet TracerDocument3 pages8.2.2.7 Cisco Packet Tracerjstring69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring OSPF Brandon&KatieDocument8 pagesConfiguring OSPF Brandon&KatieLuis GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationDocument3 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationLayla KettlewellPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationDocument3 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationjohnathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationDocument5 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authenticationjbon lagoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pages10.1.3.5 Lab Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesjohnathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMDocument7 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMANDRESSRCOPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorDocument26 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorHuanChiHuaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMDocument3 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMElectronica EdwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyHarrison Hayes100% (1)
- Lab 2. OSPF Configuration Lab: M C Tiêu (Learning Objectives)Document5 pagesLab 2. OSPF Configuration Lab: M C Tiêu (Learning Objectives)Dat LCPas encore d'évaluation
- Practica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument9 pagesPractica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesOctavio KuriPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2Document7 pages5.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2joleszaz JenciPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features - ILMDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features - ILMSergio TejedorPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument2 pages9.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure OSPF Advanced Featuresmarcelo tanimucaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pages10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesdboPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure Multiarea OSPFv2 with MD5 AuthenticationDocument8 pagesConfigure Multiarea OSPFv2 with MD5 AuthenticationChinen momoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 - Skills ActivityDocument11 pagesWeek 5 - Skills ActivitykonowePas encore d'évaluation
- Configure Single-Area OSPFv2Document12 pagesConfigure Single-Area OSPFv2Mohammed AkeelPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument9 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesJozeph Abod67% (3)
- Lab 3.2a - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - 2.3.2.6Document3 pagesLab 3.2a - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - 2.3.2.6MR APas encore d'évaluation
- Lab5 2Document7 pagesLab5 2pzydf6wjxvPas encore d'évaluation
- Mpls l3vpn Option A B C IosDocument25 pagesMpls l3vpn Option A B C IosMojtaba SeifPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.4.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring GRE - ILM AndreaDocument10 pages3.4.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring GRE - ILM Andreaandrea villaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2Document2 pages2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2-- JokerPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.3.8 LabDocument10 pages6.2.3.8 LabAutumn TillmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Document10 pages6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic EIGRP For IPv4Ana DianaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing UpdatesDocument20 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing UpdatesErid RocaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess NetworkDocument6 pages5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Networkرافد البركيPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure OSPF MD5 AuthenticationDocument2 pagesConfigure OSPF MD5 AuthenticationJUAN MAURICIO QUEZADA JAMASMIEPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingD'EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To Chapter Review QuestionsDocument48 pagesAnswers To Chapter Review QuestionsEmeraldBilbrey100% (1)
- Answers To Review QuestionsDocument46 pagesAnswers To Review QuestionsKimverlie Abastar0% (1)
- Random DatesDocument2 pagesRandom DatesEmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Datebase Mangement HW HelpDocument11 pagesDatebase Mangement HW HelpChadSheppersonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1.1.5 Packet Tracer - Examining A Redundant Design InstructionsDocument3 pages2.1.1.5 Packet Tracer - Examining A Redundant Design InstructionsEmeraldBilbrey0% (4)
- Sikandar Ccna Notes LibreDocument193 pagesSikandar Ccna Notes LibreEmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Little Man Little Man Little Man Little Man Little ManDocument1 pageLittle Man Little Man Little Man Little Man Little ManEmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Whatigetatmy Scentsy Party Whatigetatmy Scentsy Party: Hostess 5' Reasons Chart Hostess 5' Reasons ChartDocument2 pagesWhatigetatmy Scentsy Party Whatigetatmy Scentsy Party: Hostess 5' Reasons Chart Hostess 5' Reasons ChartEmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- pb100561 1Document7 pagespb100561 1EmeraldBilbreyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument11 pages1.3.1.3 Lab - Mapping The InternetHugoSantaellaSr100% (1)
- CATALOGODocument84 pagesCATALOGOestefanyespinoza_fcaPas encore d'évaluation
- WELLPRO Module MODBUS RTU SETUPDocument1 pageWELLPRO Module MODBUS RTU SETUPOscar SantellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.the WiMAX TechnologyDocument8 pages1.the WiMAX TechnologyMedin JazvinPas encore d'évaluation
- MPQ-ODV065R15B18J - DS - 1-0-1 Ong NuocDocument1 pageMPQ-ODV065R15B18J - DS - 1-0-1 Ong NuocJair CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- History and Logos of Adult Swim in RomaniaDocument2 pagesHistory and Logos of Adult Swim in RomaniaAndrei Augustin DogaruPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 24 Cat.5e: Category 6A UTP Cable Part Number:PROCAT6ADocument3 pages00 24 Cat.5e: Category 6A UTP Cable Part Number:PROCAT6ABonier Yesid Garcia CantilloPas encore d'évaluation
- CM1000ManualE OldDocument116 pagesCM1000ManualE OldGreg WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- How Nokia Went From Dominance to Downfall in SmartphonesDocument6 pagesHow Nokia Went From Dominance to Downfall in SmartphonesAfiq de Winner0% (1)
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version) PDFDocument2 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version) PDFAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile BankingDocument11 pagesMobile Bankingsuresh aPas encore d'évaluation
- New Radio Station List (Name)Document4 pagesNew Radio Station List (Name)Kavindu H. PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE Feature Study - SWITCHDocument14 pagesLTE Feature Study - SWITCHosmannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Commnication Sec III CH 2Document92 pagesCommnication Sec III CH 2Naresh Dhanda100% (2)
- Analysys Mason Polystar Whitepaper On VoLTE FINAL 1Document13 pagesAnalysys Mason Polystar Whitepaper On VoLTE FINAL 1jrashevPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Based RobotDocument232 pagesGSM Based RobotTanvi KhuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Video Fundamentals: Signal Processing For Digital TVDocument86 pagesVideo Fundamentals: Signal Processing For Digital TVAndrewWerdnaPas encore d'évaluation
- KPN NX 308 XXX Us En00.00 00Document35 pagesKPN NX 308 XXX Us En00.00 00VantedPas encore d'évaluation
- HCA Mini Coax CatalogDocument5 pagesHCA Mini Coax Catalogمحيي الدين الكميشىPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae Clive Wilton: Current Address: Mobile: Languages Spoken: EducationDocument12 pagesCurriculum Vitae Clive Wilton: Current Address: Mobile: Languages Spoken: Educationmoueed8Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5G Rds-Hq2-Test-Ibs0342 - CDDDocument19 pages5G Rds-Hq2-Test-Ibs0342 - CDDKausik RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Impulse Response and Multipath EffectsDocument13 pagesChannel Impulse Response and Multipath EffectsNguyễn ThắngPas encore d'évaluation
- Fieldbus Technology Industrial AutomationDocument70 pagesFieldbus Technology Industrial AutomationAndrePas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To IGRPDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To IGRPAnonymous cRxoHJ32QvPas encore d'évaluation
- 920 Imagine Router Datasheet Iss04Document2 pages920 Imagine Router Datasheet Iss04Asep Dani SuhermanPas encore d'évaluation
- SBNHH-1D45C Product SpecificationsDocument4 pagesSBNHH-1D45C Product SpecificationsMauricioPas encore d'évaluation
- P02 - Procedure For Handling The RBS External & Internal AlarmsDocument3 pagesP02 - Procedure For Handling The RBS External & Internal AlarmsMangata AcaronarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Apr-11 Sprint MMBS Installation Guide1Document67 pages5-Apr-11 Sprint MMBS Installation Guide1jgh954067% (3)