Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
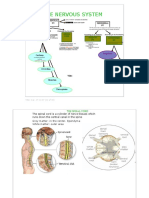
Brachial Plexus
Transféré par
Kaesha Alex Thomas0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesBrachial Plexus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentBrachial Plexus
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesBrachial Plexus
Transféré par
Kaesha Alex ThomasBrachial Plexus
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Brachial Plexus
10/03/2014
Upper limb is going to be supplied by the brachial plexus.
Mixed nerves, sensory and motor innervations.
Innervation to the joints proprioception (joint sense information)
Sympathetic fibers from the cervical ganglion will serve the function
of sweating.
C5,6 pick up sticks, C7,8 lay them straight.
Abduction and adduction of fingers is done by T1.
PAd- Palma interossii will adduct
DAbRoots are from C5 to T1 (VENTRAL RAMI)
Dorsal branch supplies the erector spinae.
Dorsal horn of spinal cord contain primarily the sensory neurons
that are going to be involved with the ascending tracks of the spinal cord.
Lower motor neurons????
Roots of the brachial plexus are located between scalenous anterior and
scalenous medius. Scalenous anterior is covered by prevertebral fascia
and lying on it are two important arteries suprascapular and transverse
cervical.
Brachial plexus is wrapped in an axillary sheath formed from prevertebral
fascia.
Trunks are located in the posterior triangle of the neck boundaries are
posterior boarder sternocleidomastoid (anterior), anterior boarder
trapezius (posterior), base is clavicle and the roof deep cervical/investing
fascia covered by skin. In the triangle is the spinal root of the
accessory nerve which supplies the trapezius. It arises from C1- C5,
ascends from the foramen magnum and leads to the jugular foramen in
the skull. It passes through the middle third of the sternoclastoid so If it is
damaged there will be problems with lateral rotation of the scapula.
Trapezius and serratus anterior laterally rotate the scapula so if these are
damaged there will be a problem in abducting. Dorsal scapular nerve
supplies the rhomboids. Levator scapulae is supplied from C1-C4.
Erbs point can end up with erbs palsy.
Divisions of the brachial plexus are located retroclavicularly (behind the
clavicle). They are such that each trunk is going to supply an anterior and
posterior division.
3 posterior posterior chords. Gives rise to radial nerve (supplies the
extensors and triceps) and axillary nerve (supplies the deltoid muscle and
teres minor). Deltoid cannot adduct.
Pec major and lattisimus dorsi are the two powerful ADDUCTORS.
Lateral and medial roots of the median nerve.
Ulnar nerve (C8,T1)- main function is to supply the intrinsic muscles of
the hand.
Medial side of the arm right down to the medial epicondyle is supplied by
the intercostaobrachial nerve.
Suprascapular nerve is below suprascapular artery in the suprascapular
notch.
Omohyoid artery???
SECOND PART OF AXILLARY ARTERY- Named according to the SECOND
part of the axillary artery the will be lateral is lateral, posterior will be
posterior and the medial will be medial.
FIRST PART OF AXULLARY ARTERY- First part however lateral and poster
is LATERAL and the medial chord is POSTERIOR.
Branches of axillary artery is SALSA.
Axillary artery begins on the outer boarder of the first rib.
Inner boarder of scalenous anterior is where subclavian artery begins.
Axilly ends on the lower boarder of the teres major in relation to the fifth
rib.
Subclavian vein is in front of scalenous anterior and the artery is behind
it. THE VEIN IS OUTSIDE THE ARTERY IS WITHIN THE AXILLARY SHEATH.
THE FIRST RIB IS ALWAYS IN THE EXAM.
Apex of axilla cervicoaxillary tunnel
Frenic nerve 345 keeps you alive
567 long thoracic nerve to serratus anterior.
678 nerve to lattisimus dorsi.
Radial and median nerve takes all.
Lower subscapular supplies the teres major and subscapularis.
Lateral pectoral nerve will pierce the clavi-pectoral fasica lympatics,
thyrocervical and cephalic vein.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Clinical Neuroanatomy: Stephen G. Waxman, MD, PHDDocument12 pagesClinical Neuroanatomy: Stephen G. Waxman, MD, PHDandiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Heubner ArteryDocument1 pageHeubner Arterytiririca1901Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothalamus, Limbic System, and Memory RegulationDocument71 pagesHypothalamus, Limbic System, and Memory RegulationvinodksahuPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyyDocument15 pagesBiologyyBrittany Tuyet SotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke Syndromes and Lacunar Infarcts ExplainedDocument2 pagesStroke Syndromes and Lacunar Infarcts ExplainedRyan TownsendPas encore d'évaluation
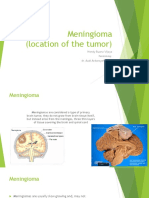
- MeningiomaDocument7 pagesMeningiomadrhendyjuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Nerve Injuries - Medical ApplicationsDocument103 pagesPeripheral Nerve Injuries - Medical ApplicationsJune Epe100% (1)
- Lab3 Human Anatomy 1 YearDocument51 pagesLab3 Human Anatomy 1 Yearnatheer ayedPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysioEx Exercise 6 Activity 2Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 6 Activity 2MARILYN MARIANA HERNANDEZ MENDOZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology of the Central Nervous System: Neurodegenerative Diseases and CNS TumorsDocument67 pagesPathology of the Central Nervous System: Neurodegenerative Diseases and CNS TumorsLIEBERKHUNPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Brachial Plexus Injuries in PeadsDocument30 pagesPresentation Brachial Plexus Injuries in Peadskashmala afzalPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuron DefinitionDocument6 pagesNeuron Definitionapi-357540357Pas encore d'évaluation
- 03 The Spinal Cord and The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument7 pages03 The Spinal Cord and The Peripheral Nervous SystemAlejandro González MoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesRevised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireivanPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ 23 Physio AnswersDocument8 pagesMCQ 23 Physio AnswersJulyhathul Kuraishi100% (1)
- (Radiology Illustrated) In-One Kim (Eds.) - Radiology Illustrated - Pediatric Radiology-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2014) PDFDocument1 077 pages(Radiology Illustrated) In-One Kim (Eds.) - Radiology Illustrated - Pediatric Radiology-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2014) PDFpatricia dascaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System Functions and DivisionsDocument19 pagesNervous System Functions and DivisionsTran9716Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hemiplegia LectureDocument37 pagesHemiplegia LectureRancesh FamoPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Can Be Very BadDocument37 pagesBlood Can Be Very BadPhil SingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas 2nd Edition by Adel AfifiDocument1 079 pagesFunctional Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas 2nd Edition by Adel AfifiPaola Andrea Martínez PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisiologi Genitourinary SystemDocument14 pagesFisiologi Genitourinary SystemPandu Dian WicaksonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology Lecture 8 - Nervous TissueDocument21 pagesZoology Lecture 8 - Nervous TissueNi Ki TaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Tecnico IDocument7 pagesIngles Tecnico IDamian MaferiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Brain and Spinal Cord: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemDocument64 pagesThe Brain and Spinal Cord: Anatomy and Functions of the Central Nervous SystemMaymay MustradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Sensations and ResponsesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Sensations and Responsessajith kumar VariathPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal ShockDocument82 pagesSpinal ShockPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- U Michigan Written Practice Quiz Brain and MeningesDocument3 pagesU Michigan Written Practice Quiz Brain and MeningesJublant JimmiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Phy Psy Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesBio-Phy Psy Lecture NotesakanePas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Cranial Nerves: Functions and LocationsDocument3 pages12 Cranial Nerves: Functions and LocationsPam ZingapanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFPas encore d'évaluation