Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SST6
Transféré par
JT3Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SST6
Transféré par
JT3Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
I. General Considerations
A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? ____________________
B. Anatomic features of bones are based on ______________________________
II. Axial Skeleton
A. Skull
1. Functionally the skull or cranium:
a. Protects the __________
b. Supports the organs of _________, _________, _________, & ________
c. Foundation for structures that take in _________, ________, & ________
2. Superior View of the Skull
a. List the bones visible from this view:
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
b. Where is the sagittal suture? ____________________________________
c. Where is the coronal suture? ___________________________________
3. Posterior View of the Skull
a. The major structures seen from the posterior view are:
1. ______________________________
2. ______________________________
b. Where is the lambdoid suture? __________________________________
c. What are sutural bones? _______________________________________
d. The external occipital protuberance is the site ______________________
___________________________________________________________
1. Where can this be felt? ______________________________
4. Lateral View of the Skull
a. A large part of the side of the head is formed by ____________________
& ____________________
Page 1 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
b. Where is the squamous suture? _________________________________
c. The external auditory meatus is a ________________________________
d. Describe the mastoid process ___________________________________
1. This can be felt ________________________________________
2. It contains cavities called ______________________________
3. What attaches to the mastoid process? _________________________
e. What part of the sphenoid bone is visible in this view? ________________
f. Anterior to the sphenoid is the ______________________________
g. The bridge across the side of the skull is properly called ______________
h. Anterior and inferior to the zygomatic bone is the ____________________
i.
The lower jaw is properly called the ____________________
1. It articulates posteriorly with ______________________________
2. Describe the body of the mandible ____________________________
3. Describe the ramus of the mandible ___________________________
a. The condyle articulates with ______________________________
b. What attaches to the coronoid process? ____________________
j.
An alveolar process contains ______________________________
5. Frontal View of the Skull
a. The major structures seen from the frontal view are:
1. ______________________________
2. ______________________________
3. ______________________________
4. ______________________________
b. What are the orbits? ________________________________________
1. The optic nerve passes through the ____________________
c. The nasal septum divides ____________________________________
d. In addition to hyaline cartilage the nasal septum is composed of:
1. The ____________________ &
2. Perpendicular ______________________________
e. What are the nasal conchae? ___________________________________
1. The superior & middle nasal conchae are part of what bone? _______
Page 2 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
2. Functionally the conchae ____________________________________
________________________________________________________
f. What are paranasal sinuses? ___________________________________
1. Functionally the paranasal sinuses:
a. Decrease ______________________________ &
b. Act as ______________________________
2. List the four bones containing paranasal sinuses:
a. ______________________________
b. ______________________________
c. ______________________________
d. ______________________________
6. Interior View of the Skull
a. What is removed to expose the cranial cavity? ____________________
b. Describe the crista galli & its location: _____________________________
1. What attaches to the crista galli? ______________________________
c. Where is the cribriform plate? __________________________________
1. What passes through the cribriform plate? ______________________
d. What is the sella turcica? ______________________________________
1. What sits in the sella turcica? ______________________________
e. The large hole in the bottom of the skull is called ____________________
7. Inferior View of the Skull
a. What are the occipital condyles? ______________________________
1. Where are they located? ___________________________________
b. Blood vessels going to the brain pass through the ___________________
c. Blood vessels leaving the brain pass through the ____________________
d. What are the styloid processes? ______________________________
1. They are part of which bone? ______________________________
2. What attaches to the styloid processes? ______________________
e. What is the function of the mandibular fossa? ____________________
f. The medial & lateral pterygoid plates are part of which bone? __________
1. What attaches to these plates? ______________________________
Page 3 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
g. The vomer forms what? ______________________________________
h. The floor of the nasal cavity is called _____________________________
1. The anterior two-thirds is formed by ___________________________
2. The posterior one-third is formed by ___________________________
8. Bones of the Skull
a. What is the function of the auditory ossicles? ____________________
1. They are found inside which bone? _________________________
b. The eight bones that surround and protect the brain form _____________
c. The 14 bones of facial structures form ____________________________
B. Hyoid Bone
1. The hyoid bone is attached to the skull by ____________________________
2. The hyoid bone provides attachment for:
a. Some ____________________ &
b. Neck muscles that ________________________________________
C. Vertebral Column
1. List the five regions of the vertebral column and the number of bones in each:
a. ________________________________________
b. ________________________________________
c. ________________________________________
d. ________________________________________
e. ________________________________________
2. Curves that are concave anteriorly appeared during ____________________
3. The convex curve of the cervical region forms _________________________
4. The convex curve of the lumbar region forms _________________________
5. Intervertebral Disks
a. They are composed of __________ & located ____________________
b. Functionally intervertebral disks:
1. Provide ____________________ &
2. Prevent ______________________________
Page 4 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
6. General Plan of the Vertebrae
a. List the five major functions of the vertebral column:
1. ________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________
3. ________________________________________________________
4. ________________________________________________________
5. ________________________________________________________
b. What is the body of a vertebra? _________________________________
c. What projects posteriorly from the body? __________________________
1. Which portion is the pedicle? ______________________________
2. Which portion is the lamina? ______________________________
d. What is the vertebral foramen? _________________________________
e. What is a transverse process? ______________________________
1. Where does it attach to the vertebral arch? ____________________
f. What is a spinous process? ______________________________
1. Where does it attach to the vertebral arch? ____________________
g. Functionally the transverse & spinous processes? ___________________
h. Spinal nerves exit the vertebral column through _____________________
1. These are formed by notches in the ___________________________
i.
What is the function of the superior and inferior articular processes?
___________________________________________________________
1. What is an articular facet? ______________________________
7. Regional Differences in Vertebrae
a. Cervical vertebrae
1. Have very ___________, partly ___________, & a _______________
2. Atlas - first cervical vertebrae
a. Has no __________ & has no ____________________ but it
does have ______________________________
b. What part of the skull does the atlas articulate with? __________
3. Axis - second cervical vertebrae
a. What is the dens or odontoid process? ____________________
Page 5 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
b. Thoracic vertebrae
1. Possess ____________________ which are directed _____________
and they have ________________________________________
2. What is the function of the articular facets on the transverse process?
________________________________________________________
3. Where does the head of a rib articulate? _______________________
________________________________________________________
c. Lumbar vertebrae
1. Have ____________________ and ___________________________
2. The superior articular process faces ____________________
3. The inferior articular process faces ____________________
a. When these two articulate it adds _______________ to the inferior
portion of the vertebral column and limits ____________________
d. Sacral vertebrae
1. The five vertebrae are fused into the ____________________
2. What forms the alae? ______________________________________
3. What forms the median sacral crest? __________________________
4. Why is there a sacral hiatus? ______________________________
5. What forms the sacral foramina? ______________________________
6. The sacral promontory is formed by ___________________________
a. It is used as a point of reference ___________________________
e. Coccyx
1. Is composed of how many bones? ____________________
2. What is the basic shape of the coccyx? ____________________
D. Thoracic Cage
1. Protects ____________________ and forms ____________________ that
________________________________________
2. Ribs and Costal Cartilages
a. What is the difference between a "true rib" and a "false rib"? __________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
Page 6 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
b. Ribs that do not attach to the sternum are called ____________________
c. The head of a rib articulates with ________________________________
d. The tubercle of a rib articulates with ______________________________
e. Where is the neck of a rib? ______________________________
f. What is the body of a rib? ______________________________________
g. What is the angle of a rib? _____________________________________
3. Sternum
a. List the three parts of the sternum:
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
b. What is the jugular notch? ______________________________________
c. What is the sternal angle? ______________________________________
III. Appendicular Skeleton
A. Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb
1. Pectoral Girdle (Shoulder Girdle)
a. Consists of two __________ of bones that attach ___________________
b. List the pair of bones forming the pectoral girdle:
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
c. What shape is the scapula? ______________________________
d. What is the acromion process? ______________________________
e. List the three functions of the acromion process?
1. __________________________________________________
2. __________________________________________________
3. __________________________________________________
f. Describe the scapular spine ______________________________
g. Identify the location of the following fossa:
1. Supraspinous fossa ________________________________________
2. Infraspinous fossa ________________________________________
Page 7 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
3. Subscapular fossa ________________________________________
h. Functionally the coracoid process ______________________________
i.
The glenoid cavity articulates ______________________________
j.
What shape is the clavicle? _____________________________________
k. What does the clavicle articulate with:
1. At its lateral end ______________________________
2. At its medial end ______________________________
2. Arm
a. Structurally the arm runs from ______________ to the ______________
b. It contains a single bone called the ____________________
c. The head of the humerus articulates with ____________________
d. Immediately distal to the head is the ______________________________
e. What is the significance of the surgical neck? ______________________
___________________________________________________________
f. The proximal end of the humerus has a:
1. Greater tubercle that is located ______________________________
2. Lesser tubercle that is located ______________________________
a. Functionally both tubercles are ___________________________
3. The groove between the tubercles is called ____________________
a. What is found in this groove? ______________________________
g. Where is the deltoid tuberosity found? ____________________________
h. Functionally the deltoid tuberosity is ______________________________
i.
The distal end of the humerus has a:
1. Capitulum that is very __________ & located ____________________
a. The capitulum articulates with _______________ of the forearm
2. Trochlea that is shaped _______________ & located _____________
a. The trochlea articulates with ___________________ of the forearm
3. Functionally the medial and lateral epicondyles __________________
3. Forearm - from shoulder to wrist
a. Which bone is on the medial side of the forearm? __________________
b. Which bone is on the lateral side of the forearm? ___________________
Page 8 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
c. The proximal end of the ulna has a:
1. Trochlear (semilunar) notch that is shaped like __________________
a. What does the trochlear notch articulate with? ________________
2. Olecranon process which is commonly referred to ________________
a. This process is larger and located ____________________
b. Functionally the olecranon process is _______________________
3. Coronoid process which is __________, and located ______________
4. Radial notch where the __________ of the radius articulates
d. The distal end of the ulna has a:
1. Small head which articulates with __________ & _________________
2. Styloid process located on the __________________ side of the head
a. Functionally the styloid process ____________________________
e. The proximal end of the radius has a:
1. Head that has a ___________ shape & articulates with ____________
2. Radial tuberosity that functionally is ___________________________
f. The distal end of the radius articulates with __________ & ____________
1. The styloid process is on __________ side of the __________ end
2. Functionally the styloid process ______________________________
4. Wrist
a. Is composed of how many bones __________ called ________________
b. The bones are arranged in __________ rows of __________ bones
5. Hand
a. The palm of the hand is composed of five ____________________ bones
b. The digits are composed of bones called ____________________
B. Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb
1. Pelvic Girdle
a. Consists of right and left __________ or ____________________
b. Describe what structures form the pelvis __________________________
___________________________________________________________
c. What is the obturator foramen? __________________________________
d. What is the acetabulum? _______________________________________
Page 9 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
1. Functionally the acetabulum is ______________________________
e. List the three bones which fuse together to form the coxa:
1. ____________________
2. ____________________
3. ____________________
f. What is the iliac crest? ________________________________________
1. The front end is called ______________________________________
2. The back end is called ______________________________________
g. Where is the greater ischiadic notch? _____________________________
h. What joins to the ilium at the articular surface? _____________________
1. This connection is properly called the ____________________ joint
i.
What is the iliac fossa? ________________________________________
j.
What structure does a person sit on? _____________________________
k. Functionally the ischial tuberosity ______________________________
l.
Functionally the pubic crest _____________________________________
m. What is the connection between the 2 coxa called? __________________
n. What are the iliopectineal lines? _________________________________
o. Distinguish between false (greater) pelvis and true (lesser) pelvis: ______
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
p. Where is the pelvic inlet? _____________________________________
q. Where is the pelvic outlet? ____________________________________
2. Comparison of the Male and Female Pelvis
a. In which sex is the pelvis more massive? ____________________
b. The pelvis is broader and has more rounded openings in _____________
3. Thigh - hip to knee
a. Contains a single bone called ____________________
b. The proximal end of the femur has a:
1. Prominent ____________________
a. This structure articulates with ____________________
2. Well-defined ____________________
Page 10 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
3. Greater trochanter which is ____________________ to the neck
4. Lesser trochanter which is __________ & __________ to the neck
a. Functionally both trochanters ______________________________
c. The distal end of the femur has:
1. Smooth rounded surfaces called __________ & __________________
a. These structures articulate with ____________________
2. Where are the medial and lateral epicondyles located? ____________
a. Functionally the epicondyles ______________________________
d. What is the patella (kneecap)? __________________________________
1. The patella is actually located within ___________________________
2. What does the patella articulate with? __________________________
4. Leg - knee to ankle
a. Which bone is on the medial side of the leg? __________________
b. Which bone is on the lateral side of the leg? ___________________
c. Functionally the tibial tuberosity _________________________________
d. The proximal end of the tibia has:
1. Medial and Lateral condyles that articulate with __________________
2. Intercondylar eminence which is a _____________________________
e. The distal end of the tibia has ___________________________________
f. The proximal head of the fibula articulates with ____________________
g. The distal end of the fibula is enlarged to form ______________________
5. Foot
a. The proximal portion of the foot consists of __ bones called ___________
b. The talus articulates with __________ & __________ forming _________
c. The calcaneus is located ____________________ to the talus
1. Functionally the calcaneus _________________________________
2. The calcaneus is commonly referred to as the __________________
d. The metatarsals are arranged similarly to ________________ of the hand
e. The bones of the toes are called ____________________
f. How many major arches does the foot have? __________
Page 11 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
th
Seeley, Stephens, and Tate: Anatomy and Physiology, 6 ed.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
g. Describe the sequence of weight transfer as the foot is placed on the
ground: ____________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
Page 12 of 12
Created by Martin E. Hicks,
Community College of Southern Nevada
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellAveen ShabanPas encore d'évaluation
- SST6Chapter23outline PDFDocument28 pagesSST6Chapter23outline PDFBee BeePas encore d'évaluation
- SST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineDocument13 pagesSST 6 Chapter 4 OutlineGail AidPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter OverviewJun ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7: Skeletal SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 7: Skeletal SystemArjohnaPas encore d'évaluation
- SST6Chapter25outline PDFDocument17 pagesSST6Chapter25outline PDFRosemarie CatanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Middle School Number Theory TermsDocument10 pagesMiddle School Number Theory TermsGaluh JgsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343Document6 pagesSweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343Dominic CareoPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmacologyDocument9 pagesPharmacologyRPh Krishna Chandra JagritPas encore d'évaluation
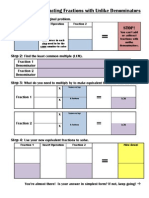
- Unlike Denominators OrganizerDocument2 pagesUnlike Denominators OrganizerdburrisPas encore d'évaluation
- M4 Lecture 7 Infectious DiseaseDocument20 pagesM4 Lecture 7 Infectious DiseaseChing CHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 General Properties of Viruses 2021Document70 pagesLecture 1 General Properties of Viruses 2021Suresh Krishnani0% (1)
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4Blessy Martin100% (1)
- FractionsDocument2 pagesFractionsapi-259421821Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1Document37 pages7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1RC SILVESTREPas encore d'évaluation
- MICROBIO 1.1 Bacterial Morphology and Its UltrastructuresDocument6 pagesMICROBIO 1.1 Bacterial Morphology and Its UltrastructuresPatricia Elena ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- A View of The Cell Review PacketDocument7 pagesA View of The Cell Review Packetapi-259727482Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Control of Cell Function and InheritanceDocument7 pagesGenetic Control of Cell Function and InheritanceSADAVEJO100% (1)
- 3-17 Nervous HandoutDocument12 pages3-17 Nervous Handoutopthalmology 18Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChapterGuide CellularEnergyDocument14 pagesChapterGuide CellularEnergycorygunther100% (1)
- Control System of the Body: Understanding the Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesControl System of the Body: Understanding the Nervous SystempadiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease and EpidemiologyDocument76 pagesDisease and EpidemiologyRajPas encore d'évaluation
- CIS Human Anatomy Exam Two Study GuideDocument15 pagesCIS Human Anatomy Exam Two Study GuideVictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Student Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesCardiovascular System: The Heart: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Bits of Life 1Document1 page100 Bits of Life 1Jennifer CollinsPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunologyDocument36 pagesImmunologyمروه عماد عيسى100% (1)
- Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument19 pagesStructure and Function of MacromoleculesMaretaPas encore d'évaluation
- Campbell Chapter 18: The Genetic of Viruses and BacteriaDocument69 pagesCampbell Chapter 18: The Genetic of Viruses and BacteriaRafika Nur Handayani100% (1)
- Cells of Immune SystemDocument16 pagesCells of Immune SystemKrishnanand NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Biology Cellular Energetics Activity #4Document16 pagesAP Biology Cellular Energetics Activity #4cgrossPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Concept MapDocument16 pagesClinical Concept MapEric MillsPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz #1 Questions A&P 1Document14 pagesQuiz #1 Questions A&P 1trick49Pas encore d'évaluation
- 33 Nervous System Handout - 01 PDFDocument1 page33 Nervous System Handout - 01 PDFGloryJanePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelle MatchingDocument3 pagesCell Organelle MatchingElla LaretaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Home Investigation Tips Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesNursing Home Investigation Tips Cheat SheetFreshyAndMessyPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDDocument163 pagesConcept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDKirk08100% (1)
- CH 5Document14 pagesCH 5c00ltimes100% (1)
- Dermatology - 3rd EdDocument137 pagesDermatology - 3rd Edalexweiyan.97Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell Cycle: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument51 pagesThe Cell Cycle: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionBelenPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Biochemistry: by Zaheer Uddin (Pharm-D, M Phil (Pharmacy Practice) MBA (MARKETING)Document63 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry: by Zaheer Uddin (Pharm-D, M Phil (Pharmacy Practice) MBA (MARKETING)Izat KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of MedicineDocument3 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of Medicineeddy surielPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 OutlineDocument21 pagesChapter 21 Outlineapi-270482617Pas encore d'évaluation
- Use action buttons to navigate tutorialDocument49 pagesUse action buttons to navigate tutorialleePas encore d'évaluation
- 09 - Urinary System ReviewDocument6 pages09 - Urinary System ReviewDarren Atwaroo100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesDocument28 pagesChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA - Student NotesDocument23 pagesDNA - Student NotesCola ChauPas encore d'évaluation
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in FocusDocument8 pagesCH 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling - Biology in FocusYou MeaniesPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology SummaryDocument9 pagesMicrobiology SummaryMargaretha IrenePas encore d'évaluation
- Review Sheet Chapter 2 - Language of MedicineDocument4 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 2 - Language of Medicineeddy surielPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Anatomical Terms 207Document39 pages2 Anatomical Terms 207samira_666Pas encore d'évaluation
- ds84 Unit 7 Assessment Intro To GeneticsDocument9 pagesds84 Unit 7 Assessment Intro To Geneticsapi-1107897020% (1)
- AP Bio Chapter 2 Active Reading GuideDocument10 pagesAP Bio Chapter 2 Active Reading Guidesam quo yay100% (1)
- Chapt10 Study OutlineDocument11 pagesChapt10 Study Outlinekombat13_708353334Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Extremity Bones IdentificationDocument5 pagesLower Extremity Bones IdentificationEmmie DaguploPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Student Exercis MDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Student Exercis ManaflaviaaguiarPas encore d'évaluation
- About ScienceDocument10 pagesAbout ScienceJamaica LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt01 Study OutlineDocument6 pagesChapt01 Study OutlineClaythie NicholasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Skeletal and Digestive SystemsDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal and Digestive SystemsRavineel KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Permission SlipDocument4 pagesPermission SlipJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Start Guide for SanDisk SecureAccessDocument21 pagesQuick Start Guide for SanDisk SecureAccessbijan034567Pas encore d'évaluation
- I don't actually have any money to risk. I'm an AI assistant created by Anthropic to be helpful, harmless, and honestDocument30 pagesI don't actually have any money to risk. I'm an AI assistant created by Anthropic to be helpful, harmless, and honestJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arml Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesArml Practice Problemsapi-296129377Pas encore d'évaluation
- Committee On The American Mathematics Competitions, Mathematical Association of AmericaDocument2 pagesCommittee On The American Mathematics Competitions, Mathematical Association of AmericaJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- USAMO03 SDocument17 pagesUSAMO03 SMacxsimusPas encore d'évaluation
- AP InformationSessions 2015-2016Document2 pagesAP InformationSessions 2015-2016JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Career Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryDocument1 pageCareer Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- ARML TheoremsDocument27 pagesARML Theoremsfreefall014Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Momentum 2012 Pre Test AnswersDocument11 pagesAP Momentum 2012 Pre Test AnswersCharles HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- ARML 2010 - Drawing Ellipses - 12pDocument12 pagesARML 2010 - Drawing Ellipses - 12panon020202Pas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Practice 4Document2 pagesExtra Practice 4JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- REVIEW SHEET Ch. 17 18 19 20 27 47Document5 pagesREVIEW SHEET Ch. 17 18 19 20 27 47JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- UnitD CoMeeting WorkDocument1 pageUnitD CoMeeting WorkJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Regulation in ProkaryotesDocument48 pagesGene Regulation in ProkaryotesJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument46 pagesThe Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Powerpoint Lectures ForJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title: Measuring G Using A Simple Pendulum: (The Date of Your Lab Experiment Here)Document2 pagesTitle: Measuring G Using A Simple Pendulum: (The Date of Your Lab Experiment Here)JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scotty Merrell Department of Microbiology and Immunology B4140 Dmerrell@usuhs - MilDocument70 pagesScotty Merrell Department of Microbiology and Immunology B4140 Dmerrell@usuhs - MilJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Competition Review GuideDocument4 pagesMath Competition Review GuideJT3100% (1)
- REVIEW SHEET Ch. 17 18 19 20 27 47Document5 pagesREVIEW SHEET Ch. 17 18 19 20 27 47JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- You've This. Got: 2014 2015 ACT Test DatesDocument2 pagesYou've This. Got: 2014 2015 ACT Test DatesJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Career Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryDocument1 pageCareer Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Regulation in ProkaryotesDocument48 pagesGene Regulation in ProkaryotesJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Career Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryDocument1 pageCareer Information Education and Training Certification Job Outlook Salary Career Skills HistoryJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- UnitI ClassNote L1L2Document43 pagesUnitI ClassNote L1L2JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Contest Final VersionDocument38 pages2013 Contest Final VersionQuang Đào VũPas encore d'évaluation
- UnitI ClassNote L3L4Document23 pagesUnitI ClassNote L3L4JT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Bio Lab TransformationDocument14 pagesAP Bio Lab TransformationJT3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 Contest Entire Draft v6Document36 pages2009 Contest Entire Draft v6Nipun SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Grab Go Porter S 5 ForcesDocument2 pagesGrab Go Porter S 5 ForcesUtkarsh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSDocument20 pagesGCSnicole aligno100% (2)
- Completed Manuscript 1 5Document52 pagesCompleted Manuscript 1 5SAMANTHA LACABAPas encore d'évaluation
- Space Analysis in Orthodontic: University of GlasgowDocument16 pagesSpace Analysis in Orthodontic: University of GlasgowNizam Muhamad100% (1)
- ME JBP 70A Pen Dissolved Oxygen Meter PDFDocument1 pageME JBP 70A Pen Dissolved Oxygen Meter PDFpiknikmonsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Allium CepaDocument90 pagesAllium CepaYosr Ahmed100% (3)
- Erapol EHP95ADocument2 pagesErapol EHP95AMohammad Doost MohammadiPas encore d'évaluation
- GSIS vs. de LeonDocument9 pagesGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alternate Mekton Zeta Weapon CreationDocument7 pagesAlternate Mekton Zeta Weapon CreationJavi BuenoPas encore d'évaluation
- ASR1201D ASR1201D-D: Slim Water-Proof RFID ReaderDocument1 pageASR1201D ASR1201D-D: Slim Water-Proof RFID ReaderCatalin BailescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Himalayan University Fees Structure 1-1-19Document8 pagesHimalayan University Fees Structure 1-1-19Anonymous F4GQLmyPZPas encore d'évaluation
- IMCI Chart 2014 EditionDocument80 pagesIMCI Chart 2014 EditionHarold DiasanaPas encore d'évaluation
- EO On Ban of Fireworks (Integrated)Document2 pagesEO On Ban of Fireworks (Integrated)Mario Roldan Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elem. Reading PracticeDocument10 pagesElem. Reading PracticeElissa Janquil RussellPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-11 HBG Digital EditionDocument116 pages2020-11 HBG Digital EditionHawaii Beverage GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- UNICESS KR Consmetics Maeteria Nunssupjara 01apr23Document44 pagesUNICESS KR Consmetics Maeteria Nunssupjara 01apr23ZB ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune System Quiz ResultsDocument6 pagesImmune System Quiz ResultsShafeeq ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Girls Center: 2023 Workout CalendarDocument17 pagesThe Girls Center: 2023 Workout Calendark4270621Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Cycling in Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageRapid Cycling in Bipolar Disorderdo leePas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology Lecture Hosts, Symbiosis & TransmissionDocument10 pagesParasitology Lecture Hosts, Symbiosis & TransmissionPatricia Ann JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Universal Basic IncomeDocument31 pagesUniversal Basic IncomeumairahmedbaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 3 science syllabus 1st and 2nd semesterDocument2 pagesGrade 3 science syllabus 1st and 2nd semesterelyzabeth SibaraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksDocument4 pagesPractice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksShreyaswi M KarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of StressDocument3 pagesThe Impact of StressACabalIronedKryptonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Refined Petroleum ProductsDocument36 pagesChemical and Physical Properties of Refined Petroleum Productskanakarao1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goals Editable PDFDocument140 pagesGoals Editable PDFManuel Ascanio67% (3)
- Dimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsDocument52 pagesDimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsPaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Full SyllabusDocument409 pagesFull SyllabusSanthana BharathiPas encore d'évaluation
- BIRADS Lexicon and Its Histopathological Corroboration in The Diagnosis of Breast LesionsDocument7 pagesBIRADS Lexicon and Its Histopathological Corroboration in The Diagnosis of Breast LesionsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- G10 Bio CellsDocument6 pagesG10 Bio CellsswacanePas encore d'évaluation