Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fracas
Transféré par
Gerardo Cruz Espinosa100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
253 vues4 pagesf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentf
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
253 vues4 pagesFracas
Transféré par
Gerardo Cruz Espinosaf
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
What is FRACAS?
Failure Reporting Analysis and Corrective Action System (FRACAS) is an
excellent process that can be used to control or eliminate failures. This is
a process in which you identify any reports from your CMMS/EAM or a
specialized Reliability Software that can help you to eliminate, mitigate
or control failures. These reports could include cost variance, Mean Time
between Failure, Mean Time between Repair, dominant failure patterns
in your operation, common threads between failures such as lack of
lubrication (perhaps due to lubricator not using known industry
standards).
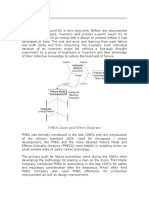
Figure 1 - FRACAS Loop
Seven Steps to a Working Failure Reporting System FRACAS
Youve gotten buy-in from the boss by showing him how much money
the organization can make from a good Failure Reporting Plan (FRACAS).
He said, Great idea! Now go make it happen. How many new ideas
have you seen come and go in your organization? I have seen many
through my career and I am sure you have as well. Failure Reporting
(FRACAS) is something that must be sustainable because it is the
continuous improvement process for your Maintenance Strategies for
each piece of equipment. In this chapter from FRACAS, Failure Reporting
Made Simple book, we are going to offer you a phased approach to
success, one step at a time.
FRACAS Step 1 Determine your end goal.
Know where you are going.
FRACAS Step 2 Create your data collection plan.
What measures will be used?
What data must be collected to create the measures?
How will the data be collected?
How will the data be analyzed?
FRACAS Step 3 Determine organizational roles, goals, and
responsibilities (RACI).
Who collects the data?
Who analyzes the data?
Who takes what action based on analysis results?
FRACAS Step 4 Create the FRACAS Policies and Procedures
Manual.
Create a manual that clearly delineates the items determined in
Steps 1, 2, and 3.
FRACAS Step 5 Develop and execute the FRACAS Training Plan.
Create a Training Plan based on the organizational roles, goals, and
responsibilities determined in Step 3.
FRACAS Step 6 Implement the FRACAS.
Hold required informational meetings.
Begin data collection on highest priority systems.
Analyze data and report results.
Create corrective actions based on results.
FRACAS Step 7 Monitor and adjust.
Monitor data quality and results.
Monitor corrective actions.
Adjust data collection plan and corrective action implementation
plan based on results of monitoring.
FRACAS Benefits
The basic benefit of a comprehensive, closed-loop FRACAS is the
contribution
identification
of
the
and
information
correction
of
that
it
design
contains
for
errors,
part
the
timely
problems,
workmanship defects and /or process errors.
An effective FRACAS results in saving of significant direct costs such as
factory rework, parts/materials crap, or warranty service, and even
greater indirect costs associated with dissatisfied customers.
An effective FRACAS can serve as a major contributor to reliability
growth, efficient maintenance, and continuous process improvement.
Continuous monitoring and tracking of data via the FRACAS provides and
assessment as to whether previous failures trends have been eliminated
through corrective action. In conclusion, the main benefits of an effective
FRACAS process are:
Saving of direct and indirect costs by the proper handling and
investigation of problems followed by appropriate corrective
action.
Visibility of reliability performance problems.
Initiation of continuous reliability improvement process.
Effectiveness of corrective actions controls and linkage to results.
Expedient engineering effort to resolve problems.
Root Cause Analysis
Knowledge base of a history of problems and lessons learned
helping to avoid similar occurrences.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- HALT To HASS To HASADocument177 pagesHALT To HASS To HASAapi-3760998100% (3)
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document16 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Jayson SoguilonPas encore d'évaluation
- Fmea TemplateDocument12 pagesFmea Templatesmtdrkd100% (22)
- Es D Control Program PeriodicDocument8 pagesEs D Control Program Periodicgowtham raju buttiPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Compressor FMEADocument32 pagesAir Compressor FMEAJitu Jena67% (6)
- Scientific American - May 2014Document88 pagesScientific American - May 2014Christopher Brown100% (1)
- Fmea - RCM Machinary PDFDocument0 pageFmea - RCM Machinary PDFpmzabPas encore d'évaluation
- Robustness Valdiation Step by StepDocument36 pagesRobustness Valdiation Step by StepGreenheart OussamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eliminating Defects Through Equipment ReliabilityDocument6 pagesEliminating Defects Through Equipment ReliabilityAriefPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Workbench - IsographDocument1 pageReliability Workbench - IsographsaospiePas encore d'évaluation
- Effective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisD'EverandEffective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Ald Software FmeaDocument2 pagesAld Software FmeaNakkolopPas encore d'évaluation
- Control ChartsDocument19 pagesControl ChartsMichelle GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?Document16 pagesReliability Calculations: What, Why, When & How Do We Benefit From Them?b_shadid8399100% (1)
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad SabriDocument42 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis: Dr. Ir. Muhammad Sabricalvin100% (1)
- E247Document3 pagesE247diego100% (1)
- Process Oriented To FracasDocument9 pagesProcess Oriented To FracasGyogi MitsutaPas encore d'évaluation
- FMEA RCM Course - Foundations of Effective FMEA - RS 470 CourseNotes - Rev9.1Document358 pagesFMEA RCM Course - Foundations of Effective FMEA - RS 470 CourseNotes - Rev9.1gminayas100% (1)
- CMMS computerized maintenance management system The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuideD'EverandCMMS computerized maintenance management system The Ultimate Step-By-Step GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- FMEA Risk ManagementDocument64 pagesFMEA Risk ManagementAbhishek Singh TomarPas encore d'évaluation
- History of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect DiagramDocument8 pagesHistory of FMEA: FMEA Cause and Effect Diagramervikas34Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fracas Illustration1!2!130105114238 Phpapp01Document1 pageFracas Illustration1!2!130105114238 Phpapp01juancgr77Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 FMEA Training - How To DoDocument45 pages02 FMEA Training - How To DoRamkumar PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocument8 pagesA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide On Benchmarking 2014Document36 pagesGuide On Benchmarking 2014erast_dudePas encore d'évaluation
- Family Health Nursing ProcessDocument37 pagesFamily Health Nursing ProcessNeethu Vincent100% (3)
- Questions of Reliability Centered MaintenanceDocument15 pagesQuestions of Reliability Centered Maintenancemariana100% (1)
- Failure Analysis: Basic ConceptsDocument72 pagesFailure Analysis: Basic Conceptsbrucemartin3100% (1)
- FMEADocument23 pagesFMEAtcsPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 FMEA Fourth Edition 2008Document151 pages06 FMEA Fourth Edition 2008白子健Pas encore d'évaluation
- Equipment Criticality AnalysisDocument20 pagesEquipment Criticality AnalysisArmandoPas encore d'évaluation
- SPL Ree FracasDocument1 pageSPL Ree Fracasnicocla94maramPas encore d'évaluation
- TPM Reliability FormulasDocument35 pagesTPM Reliability FormulasjapelePas encore d'évaluation
- Ecss-Q-30-02A Failure Modes, Effect and Criticality Analysis (Fmeca) (7 September 2001)Document52 pagesEcss-Q-30-02A Failure Modes, Effect and Criticality Analysis (Fmeca) (7 September 2001)jgonzalezsanz8914Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Scorecard0127Document9 pagesReliability Scorecard0127partha6789Pas encore d'évaluation
- Primary DataDocument146 pagesPrimary Datashashank reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- SPL Ree FracasDocument1 pageSPL Ree FracasLuz Dary Carvajal Mendoza0% (1)
- IQ FMEA TrainingDocument7 pagesIQ FMEA TrainingKawadasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocument36 pagesFailure Mode Effect AnalysisCharanjeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Centered Asset Mgmet For Power SystemDocument8 pagesReliability Centered Asset Mgmet For Power Systemmilne_christopherPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Blueprint PDFDocument30 pagesReliability Blueprint PDFFabioPaixaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document19 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)recep1100% (1)
- Optimizing Spare Parts ManagementDocument36 pagesOptimizing Spare Parts ManagementBartolomeu SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apis Iq Fmea ManualDocument42 pagesApis Iq Fmea ManualRambir KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- IRQB Guideline-4 RAMS LCC-Rev.01 Final-DraftDocument15 pagesIRQB Guideline-4 RAMS LCC-Rev.01 Final-DraftRagul VinothPas encore d'évaluation
- Research II: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Interpretation of DataDocument18 pagesResearch II: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Interpretation of DataTrexia Singson100% (1)
- RCM II Decision Diagram - v2Document2 pagesRCM II Decision Diagram - v2Javier Gutierrez100% (1)
- 203 LSS Gbo - FmeaDocument47 pages203 LSS Gbo - FmeaRocker byPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 - Estimating ReliabilityDocument34 pages2015 - Estimating ReliabilityLuis Eduardo VielmaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIAG FMEA Manual The BenchmarkDocument2 pagesAIAG FMEA Manual The BenchmarkUmer Al-FaisalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cre Insert 2012 PDFDocument12 pagesCre Insert 2012 PDFsachinumaryePas encore d'évaluation
- Condition-Based Fault Tree AnalysisDocument11 pagesCondition-Based Fault Tree AnalysisDamir Kapidzic100% (1)
- Test FixtureDocument6 pagesTest FixtureSiti Maryam KazimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cause Mapping Investigation Template - GeneralDocument20 pagesCause Mapping Investigation Template - GeneralMickloSoberanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6878 Ed 01Document20 pages6878 Ed 01Gurwinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluating FMEA, FMECA and FMEDADocument6 pagesEvaluating FMEA, FMECA and FMEDAZakaria RadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Quad Torc 23/05/2015Document3 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Quad Torc 23/05/2015Vishnu RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Use Fmea To Reduce The Size of Your Quality ToolboxDocument4 pagesHow To Use Fmea To Reduce The Size of Your Quality ToolboxJosé Esqueda Leyva100% (2)
- Questions Being Addressed by This SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesQuestions Being Addressed by This SpreadsheetLuciano Marcelo OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- CS-25 Amendment 11 - AMC 25.1309Document30 pagesCS-25 Amendment 11 - AMC 25.1309leopoldor_5100% (1)
- A Two-Stage Failure Mode and Effect Analysis of Offshore Wind Turbines - 2020Document24 pagesA Two-Stage Failure Mode and Effect Analysis of Offshore Wind Turbines - 2020johnPas encore d'évaluation
- B Maxx Bm4-F-Enc-Xx Enc-Xx: EnglishDocument104 pagesB Maxx Bm4-F-Enc-Xx Enc-Xx: EnglishAung Naing OoPas encore d'évaluation
- Silo - Tips - Use Cases of Guard I o Modules Bipolar Output and Sourcing OutputDocument16 pagesSilo - Tips - Use Cases of Guard I o Modules Bipolar Output and Sourcing OutputGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BNI00HM 286464 enDocument2 pagesDatasheet BNI00HM 286464 enGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BNS01KT 155691 enDocument2 pagesDatasheet BNS01KT 155691 enGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 Macx MCR VacDocument2 pages00 Macx MCR VacGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- m07580919 00000000 0en PDFDocument66 pagesm07580919 00000000 0en PDFGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BNS00JH 182505 enDocument3 pagesDatasheet BNS00JH 182505 enGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BES01MM 122083 enDocument2 pagesDatasheet BES01MM 122083 enGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- PU 47 MachineAccessControlDocument1 pagePU 47 MachineAccessControlGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BMF00ERDocument2 pagesDatasheet BMF00ERGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual BNI005ADocument42 pagesManual BNI005AGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet BID000TDocument1 pageDatasheet BID000TGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- If5898 00 - en UsDocument3 pagesIf5898 00 - en UsGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asset Management Discussion DocumentDocument5 pagesAsset Management Discussion DocumentGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- MasterCAM - X4 - Beginner Training Tutorial - SampleDocument53 pagesMasterCAM - X4 - Beginner Training Tutorial - SampleRafael Donadio100% (1)
- Brochure Btl's AmetekDocument86 pagesBrochure Btl's AmetekGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- RevisionsDocument17 pagesRevisionsMoises MezaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Ext - For. Prob. 4Document32 pages4 Ext - For. Prob. 4Gerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Loco ChonDocument1 pageLoco ChonGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide For Exam Cultura InglesaDocument5 pagesGuide For Exam Cultura InglesaGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- NuevoDocumento 3Document1 pageNuevoDocumento 3Gerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCAMX4 QuickStartDocument144 pagesMCAMX4 QuickStartGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- RP MFG Introduction 1Document12 pagesRP MFG Introduction 1Gerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- MasterCAM - X4 - Beginner Training Tutorial - SampleDocument53 pagesMasterCAM - X4 - Beginner Training Tutorial - SampleRafael Donadio100% (1)
- Seiko RT3200Document4 pagesSeiko RT3200Gerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- New York CityDocument6 pagesNew York CityGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document34 pagesChapter 1Gerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-ToE-C945-111 - Service Manual Motoman K6S K10SDocument36 pages02-ToE-C945-111 - Service Manual Motoman K6S K10SBayron López CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Oscar NominationsDocument1 page2013 Oscar NominationsGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rudarski Radovi 3-4 2017Document207 pagesRudarski Radovi 3-4 2017dusan1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Standard: Methods of Physical Tests For Foundry Sands (Document30 pagesIndian Standard: Methods of Physical Tests For Foundry Sands (akhil_rao_13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tute Exercises PDFDocument141 pagesTute Exercises PDFViviennePas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation ReflectionDocument5 pagesPresentation Reflectionembry44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Law - VII SemDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Law - VII SemShivam SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Gym Ball Adalah Sebuah Alat Bantu Olahraga Yang Banyak Kita Temui Di Pusat Kebugaran. Alat IniDocument10 pagesGym Ball Adalah Sebuah Alat Bantu Olahraga Yang Banyak Kita Temui Di Pusat Kebugaran. Alat IniRizky AwaliyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Diorama PDF LplanDocument6 pagesDiorama PDF Lplanapi-223177421Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iim Bangalore HRC BrochureDocument4 pagesIim Bangalore HRC BrochureIgit Sarang Placement CellPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Engineers Produce Specifications ForDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineers Produce Specifications FormeeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diatom Test A Golden Standard Test in Drowning CasesDocument1 pageDiatom Test A Golden Standard Test in Drowning CasesRevathy RPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Community Partnership ResourceDocument7 pagesFinal Community Partnership Resourceapi-315848490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Analysis of Icici Bank: A Research Project OnDocument155 pagesFundamental Analysis of Icici Bank: A Research Project Onanunaykumar7847Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scrutinizing Data Collection Methods WlingiDocument27 pagesScrutinizing Data Collection Methods WlingiMegeon SeongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 Artificial Mouth Opening Fosters Anoxic ConditionsDocument7 pages2009 Artificial Mouth Opening Fosters Anoxic ConditionsMartha LetchingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment in Undergraduate Medical Education - Guidance 0815 - PDF 56439668Document30 pagesAssessment in Undergraduate Medical Education - Guidance 0815 - PDF 56439668Dr Jaspreet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions For Authors Ambio 2017 11Document10 pagesInstructions For Authors Ambio 2017 11PrasetyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Methods in Taxation Ethics: Developing The Defining Issues Test (DIT) For A Tax-Specific ScenarioDocument20 pagesResearch Methods in Taxation Ethics: Developing The Defining Issues Test (DIT) For A Tax-Specific ScenarioDulcianeFortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cover Letter - South Dakoda UniversityDocument1 pageCover Letter - South Dakoda UniversitySisir MahantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument14 pagesRandom Variables and Probability DistributionAyesha Thahanie LucmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phillips-Perron Test Statistic: 0.9990 I (0) - 12.62137 0.0000 I (1) - 1.686543 0.7533 I (0) - 12.76035 0.0000 IDocument6 pagesPhillips-Perron Test Statistic: 0.9990 I (0) - 12.62137 0.0000 I (1) - 1.686543 0.7533 I (0) - 12.76035 0.0000 IXed XamzPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Programs and Their Dimensions : &even N. BrennerDocument9 pagesEthics Programs and Their Dimensions : &even N. BrennerBilalAshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Pr2 Ai FinalpaperDocument28 pagesPr2 Ai FinalpaperJustin EsguerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages From 1 Unit One Moh 2022Document11 pagesPages From 1 Unit One Moh 2022api-239415320Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3: Performance AssessmentDocument91 pagesLesson 3: Performance AssessmentNICHOLE DIANNE DIME. DIAZPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 - The Translation of Metaphors in Selected Political Speeches (1988 - 1999) of King Hussein of Jordan FR (3730)Document355 pages2016 - The Translation of Metaphors in Selected Political Speeches (1988 - 1999) of King Hussein of Jordan FR (3730)Amani AwniPas encore d'évaluation