Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cyclone Design
Transféré par
Kartika RizqimaulidaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cyclone Design
Transféré par
Kartika RizqimaulidaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
1 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering
Print version ISSN 0104-6632
Braz. J. Chem. Eng. vol.17 n.4-7 So Paulo Dec. 2000
Services on Demand
Article
ReadCube
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322000000400010
Article in xml format
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS AND
DESIGN OF SMALL DIAMETER
CYCLONES
Article references
How to cite this article
Curriculum ScienTI
Automatic translation
Send this article by e-mail
M.R.T. Halasz 1 and G. Massarani 2*
1
PEQ/COPPE/UFRJ, 2 PEQ/COPPE/UFRJ
C.P.68502, CEP 21945-970, Rio de Janeiro - RJ, Brazil
Phone: +55 21 590-2241, Fax: +55 21 590-7135
E-mail: gmassa@peq.coppe.ufrj.br
Indicators
Cited by SciELO
Access statistics
Related links
(Received: September 20, 1999 ; Accepted: April 6, 2000)
Share
More
More
Permalink
Abstract - In this work, the effect of the configuration on the
collection efficiency and pressure drop in small diameter cyclones is
evaluated based on neural networks (Functional Link Networks). The
experiences were conducted at LSP/COPPE Laboratory in a Stairmand high efficiency prototype (Dc
= 5 cm) with variable overflow diameter. Three different configurations were tested, and it is
possible to observe a significant increase in the collection efficiency with the reduction of the
overflow diameter.
Keywords: small diameter cyclone, neural networks, radioactive wastes.
INTRODUCTION
This work stands for one of the development steps of an efficient gas treatment system, involving high
performance small diameter cyclones with a high separation efficiency, for treatment of gases from radioactive
waste incineration.
Annually a great amount of radioactive waste is generated, originated in nuclear power plants, radioisotope
applications in industry, teaching and research institutions, hospitals, etc. [Raduan, 1993]. A traditional way of
treating those wastes is using incineration, which is able to reduce the amount of waste for the safe disposal in
fillings or storage facilities. The incineration process generates gases, ashes and vapors that must be treated
before disposing. In general, the first step of such treatment is accomplished using cyclones, responsible for the
removal of part of the particle solids.
The cyclones are solid-gas separators that use the same principle as the centrifuges, i.e., sedimentation by
centrifugal field, and have been used in industry since the beginning of this century [Dirgo, 1985]. The cyclones
present as main features the extreme versatility, low operational and maintenance costs, easy construction and
installation [Leith and Licht, 1972].
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
2 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
The cyclone collection efficiency is directly affected by the cylindrical section diameter. The decrease in this
parameter causes an immediate increase in the centrifugal field intensity formed inside the cyclone, increasing
the separation efficiency. Small diameter cyclones are defined as the cyclones with diameter smaller than 5.0
cm, that can be used in the separation of small particles (smaller than 10mm) with high separation efficiency.
Small diameter cyclones can be used for treating radioactive wastes, due to their better ability to separate
smaller particles than the traditional cyclones [Bttner, 1986 and Kim and Lee, 1990].
In this work a FLN (Functional Link Network) neural network was used for obtaining a model capable of
describing the particle collection efficiency. The ortogonal estimator procedue of Billings et al. (1988) was used
as implemented by Henrique and Lima (1996). The Matlab package was used for carrying out the computations.
In the literature it is possible to find a multitude of experimental data for cyclones with body diameter in the
range of 20 to 100 cm. The experimental data used in this work, however, are related to small diameter
cyclones with body diameter in the range of 1 to 5 cm. These data were obtained from Bttner (1986), Kim and
Lee (1990) and Griffiths and Boysan (1992).
It is possible to build a model, using neural networks, that is able to predict the separation efficiency of small
diameter cyclones with a good degree of confidence. In this work a neural network (Functional Link Network)
was used, trained with literature data and validated using experimental results obtained for small diameter
cyclones with the high efficiency Stairmand configuration. The equation obtained is presented below. In a
detailed analysis (Figure 1) it can be noted that the separation efficiency tends to increase with a decrease in
the overflow diameter (keeping the other parameters constant).
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
3 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
(1)
where
(2)
It is worth to note that the equation is a function of operational conditions [flow (Q), diameter of the particle to
be separated (dp) and ratio between fluid viscosity and particle density (m/rs)], the equipment characteristic
relations [(a/D), (b/D), (De/D), (H/D), (h/D), (B/D), (S/D)] and cylindrical section diameter, D. The
limit values for the parameters are reported in Table 1.
The pressure drop is an essential parameter in the design of cyclone systems that allows to evaluate the blower
specifications. Equation 3 represents one expression that can be used to calculate this parameter.
(3)
where NH is a dimensionless parameter and depends on the cyclone proportions, that by Shephered and Lapple
(1939) is equivalent to:
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
4 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
(4)
According to Figure 2, that represents Equation 3, it can be observed that the decrease in the overflow diameter
(keeping other parameters constant) leads to an increase in the pressure drop in the cyclone.
Usually the methodology to determine the equations and design parameters for cyclones is semi-empirical and
well known for some configurations. The equations for the design of a high efficiency Stairmand cyclone can be
written according to the methodology proposed by Massarani (1991).
(5)
where K = 0.041
(6)
where
(7)
(8)
D* is the cut diameter of the equipment, i.e., the diameter of the particle that is separated with 50% efficiency,
K is the dimensionless constant that considers the cyclone geometry, DP is the pressure drop between the feed
and the overflow, v is the velocity at the cylindrical section of the cyclone, r is the fluid density b is a
dimensionless constant, which depends on the cyclone configuration, is the global collection efficiency and
h(dp) is the grade collection efficiency.
In this work the collection efficiency is evaluated for three different cyclone configurations, resulting from the
variation of the diameter of the high efficiency Stairmand cyclone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
5 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
The experimental system presented in Figure 3 was assembled using a high efficiency Stairmand cyclone with 5
cm diameter. Three different outlet diameters were adapted to this cyclone (De = 2.50, 2.35 and 2.25 cm). The
feed inlet diameter could not be altered, because this section was fixed to the cylindrical section. A dust bunker
was adapted to equipment underflow outlet, in order to collect the particle material. One-inch diameter piping
was connected to the cyclone overflow outlet and to the blower suction inlet. An expansion tank was connected
to the piping, between the blower and the cyclone, in order to avoid the retention of small particles in the
rotameter.
The feed system is composed of two parts: one feed bin of 30 cm height and 8 cm of cylindrical section
diameter, and a rotating disk of 20 cm diameter. The feed bin outlet is attached to a vibrator, which facilitates
the particle flow from the feed bin. The rotating disk is used to guide the particles to the cyclone inlet.
In this work a gas-solid system was investigated. The solid materials studies are described in Table 2. The
material present physical properties similar to the ashes resulting from the radioactive waste incineration (rs =
3.0g/cm3 and dpmean = 20mm). It could be observed that 40 wt% of the sand and 30 wt% of the neodymium
carbonate particles have diameter smaller than 10 mm. It was possible to adjust the particle distribution of
every condition studied using the Rosin-Rammler-Bennet (RRB) model, described by the following equation.
(9)
where X is the mass fraction of particles with diameter smaller than D; D and m are model parameters, which
represent the diameter correspondent to X=0.632 and to the dispersion, respectively.
The particle distribution was determined using the Malvern Masterizer X equipment and the solid density
presented in Table 2 was determined using classic picnometry.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Experiments using three different configurations of the small diameter cyclone were carried out. The first
configuration (1) was the high efficiency Stairmand cyclone with De/Dc = 0.50, the second (2) and the third
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
6 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
(3) were variations of the high efficiency Stairmand cyclone with De/Dc = 0.47 and De/Dc = 0.45, respectively.
When the collection efficiency is high, it could not be observed almost any differences between the particle
distribution curves of the feed and the underflow. This leads to imprecision in the cut diameter determination
and consequently in the determination of the design parameters, following the methodology described by
Massarani (1991) (Eq. 5, 7 and 8), which considers the grade collection efficiency. In this case, it is possible to
use the strategy proposed by Yuan (1996), where the design is based only on the global collection efficiency.
The global efficiency obtained with the three different configurations studied can be observed in Figures 4 and
5. The experimental results correspond to the predicted by the neural network, showing that when the overflow
diameter is decreased, the collection efficiency increases. However, it could be noted by the experimental
results that this increase is more significant when configurations (1) and (2) rather than when configurations
(2) and (3) are compared.
It is possible to note from Figure 6 that the pressure drop increases with the flow rate increase, as expected. In
this case the equation 3 is very good to describe the pressure drop.
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
7 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
CONCLUSIONS
It was confirmed through the Neural Network prediction and by the equation proposed by Shephered and Lapple
(1939) that the decrease in the overflow diameter of small cyclones leads to an increase in the pressure drop
and in the collection efficiency. The experimental results show that below a certain ratio (De/Dc), the increase in
the collection efficiency is small when compared to the increase in the pressure drop.
NOMENCLATURE
a
cyclone inlet height [L]
cyclone inlet width [L]
cyclone lower (dust) outlet diameter [L]
dp
diameter of the particle to be separated [L]
cylindrical section diameter [L]
Dc
cylindrical section diameter [L]
De
cyclone outlet diameter [L]
D*
cut diameter of the equipment [L]
diameter correspondent to X=0.632 [L]
cyclone cylinder height [L]
cyclone height [L]
dimensionless constant [-]
model RRB dispersion [-]
NH
dimensionless parameter [-]
flow rate [L3/q ]
cyclone gas outlet pipe length [L]
velocity at the cylindrical section of the cyclone [L/q ]
vi
inlet velocity [L/q ]
mass fraction of particles with diameter smaller than D [-]
dimensionless constant [-]
DP
pressure drop between the feed and the overflow [M/Lq 2]
global collection efficiency [-]
h(dp)
grade collection efficiency [-]
fluid viscosity [M/Lq ]
fluid density [M/L3]
rs
particle density [M/L3]
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
22/09/2014 16:14
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering - Performance analysis and d...
8 of 8
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-66322...
This work is part of the project entitled "Modelagem, Simulao e Controle de Processos Qumicos", FAPERJ
number E-26/150.970/99. Halasz would also like to acknowledge CNEN for the scholarship.
REFERENCES
Billings, S.A., Chen, S., Korenberg, M.J., Identification of MIMO non-linear systems using a forward-regression
orthogonal estimator, I.J. Control, V. 49, p. 2157 2189, (1989).
[ Links ]
Bttner, H., Investigation on Particle Collection in Small Cyclones, J. Aerosol Science, V. 17, No. 3, p.537-541,
Great Britain, (1986).
[ Links ]
Dirgo, J. and Leith, D., Cyclone Collection Efficiency: Comparison of Experimental Results with Theoretical
Predictions, Aerosol Science and Technology, V. 4, Elsevier Science Publishing Co, (1985).
[ Links ]
Griffiths, W.D. and Boysan, F. , An Assessment of the Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to
Model the Performance of a Range of Small Sampling Cyclones, J. Aerossol Science, V. 23, Suppl. 1, p.
S587-S590, Pergamon Press Ltd., (1992).
[ Links ]
Henrique, H.M. and Lima, E.L., Model structure determination in neural network models, accept for publication
in Chemical Engineering Science, RR/1999/000858, (1996).
[ Links ]
Kim, J.C. and Lee, K.W., Experimental Study of Particle Collection by Small Cyclones, Aerosol Science and
Technology, V. 12, Elsevier Science Publishing Co, p.1003-1015, (1990).
[ Links ]
Leith, D. and Licht, W., The Collection Efficiency of Cyclone Type Particle Collectors a New Theoretical
Approach, A. I.Ch. E. Symposium Series 68, p.196 - 206, (1972).
[ Links ]
Massarani, G., "Projeto e Anlise de Desempenho de Ciclones e Hidrociclones II" Revista Brasileira de
Engenharia, V. 8, No. 2, p.86, (1991).
[ Links ]
Raduan, R.N. and RzyskI, B.M., Instalao de Repositrios de Subsuperfcie para Rejeitos Radioativos Requisitos
para Avaliao de Impacto Ambiental, Anais do Simpsio Sobre Engenharia Nuclear e Meio Ambiente, Seo
Latino Americana da American Nuclear Society, Rio de Janeiro, p. IV - 35 IV 43, (1993).
[ Links ]
Shepherd, C.B. and Lapple, C.E., Flow Pattern and Pressure Drop in Cyclone Dust Collectors, Ind. Eng. Chem., V.
31, No. 8, p. 972-984, (1939).
[ Links ]
Yuan, H., Thew, M.T. and Rickwood, D., Separations of Yeast with Hydrocyclones, Hydrocyclones96, p.135-149,
London, (1996).
[ Links ]
*To whom correspondence should be addressed
Associao Brasileira de Engenharia Qumica
Rua Lbero Badar, 152 , 11. and.
01008-903 So Paulo SP Brazil
Tel.: +55 11 3107-8747
Fax.: +55 11 3104-4649
Fax: +55 11 3104-4649
rgiudici@usp.br
22/09/2014 16:14
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Assignment (Air Pollution)Document7 pagesAssignment (Air Pollution)Durga Prasad Murmu0% (1)
- Venturi Scrubber ProjectDocument1 pageVenturi Scrubber ProjectChristopher LloydPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD Analysis of A Cyclone Separator-Project ReportDocument17 pagesCFD Analysis of A Cyclone Separator-Project ReportRavichandran SrinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Brian JR Geoffroy CHNG 3012 Part II PDFDocument103 pagesBrian JR Geoffroy CHNG 3012 Part II PDFjanelle ramdahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Union Engineering PDFDocument25 pagesUnion Engineering PDFCristian ParaschivPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 Metallic Glasses, Dr. T. HufnagelDocument30 pages22 Metallic Glasses, Dr. T. HufnagelSam AkinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lys Ark Rusten 2010Document26 pagesLys Ark Rusten 2010mbsahgPas encore d'évaluation
- Fig 1.1 Typical Particle Size: Bvcoeri Nashik (B.E. Mechanical) 1Document54 pagesFig 1.1 Typical Particle Size: Bvcoeri Nashik (B.E. Mechanical) 1shailesh pansarePas encore d'évaluation
- Accepted Manuscript: Chemical Engineering and ProcessingDocument26 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Chemical Engineering and ProcessingMorgen GumpPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclone CalculationDocument151 pagesCyclone CalculationBANGGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalog Foxboro Pneumatic Instruments 03-11Document88 pagesCatalog Foxboro Pneumatic Instruments 03-11Chu Tùng100% (1)
- Design of Separation Equipment of Heterogeneous MixDocument32 pagesDesign of Separation Equipment of Heterogeneous Mixbakhtyar21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ciclones Modelamiento FlujoDocument97 pagesCiclones Modelamiento Flujodaraos3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sand Filtration Units150Document3 pagesSand Filtration Units150Smriti PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity SettlingDocument10 pagesGravity SettlingNithinKallayil100% (1)
- Assignment On Environmental Consequences of Fossil FuelDocument25 pagesAssignment On Environmental Consequences of Fossil FuelMozakkir AzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Clariflocculator: Description Unit Input Calculated Range Value Value 54000 Mim M 492 M MDocument6 pagesClariflocculator: Description Unit Input Calculated Range Value Value 54000 Mim M 492 M MAnonymous EKxXjqyVHPas encore d'évaluation
- CHE572 Chapter 7 Gas CycloneDocument23 pagesCHE572 Chapter 7 Gas CycloneMuhd FahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- GPSX - Techref 01Document372 pagesGPSX - Techref 01felixPas encore d'évaluation
- Volume 3 Section 2 Process Requirements-FINAL 10062010Document63 pagesVolume 3 Section 2 Process Requirements-FINAL 10062010Pavle DimitrijevicPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Introduction To Air Pollution and Control: Primary PollutantsDocument26 pagesI. Introduction To Air Pollution and Control: Primary PollutantsMoves JaggerPas encore d'évaluation
- Resin Regeneration CalculationDocument3 pagesResin Regeneration CalculationJORGE CAICEDOPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Multiphase Desander Technology To Oil and Gas ProductionDocument19 pagesApplication of Multiphase Desander Technology To Oil and Gas ProductionJose Rodrigo Salguero DuranPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystallization Theory For Practice IntroductionDocument12 pagesCrystallization Theory For Practice IntroductiontroitrangPas encore d'évaluation
- PlantDocument2 pagesPlantSohail HanifPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Aktif DesignDocument21 pagesCarbon Aktif Designnurrahman.auliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor Loss Coefficients in Pipes and Tubes ComponentsDocument2 pagesMinor Loss Coefficients in Pipes and Tubes ComponentsSurendra ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- OtherDocument20 pagesOtherVineet Chaudhary100% (1)
- CEC2170 Environmental Engineering I Unit IV Air Pollution ControlDocument10 pagesCEC2170 Environmental Engineering I Unit IV Air Pollution ControlNeeraj Raushan KanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Flow MetersDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Flow MeterssethuraghulPas encore d'évaluation
- Paddle FlocculatorsDocument12 pagesPaddle FlocculatorsBinyam KebedePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiments and Modeling of Bubble Column Dehumidifier PerformanceDocument11 pagesExperiments and Modeling of Bubble Column Dehumidifier PerformanceAl-Kawthari As-SunniPas encore d'évaluation
- PH Control Using CO2Document38 pagesPH Control Using CO2Bob SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Stream FiltrationDocument8 pagesSide Stream FiltrationAhmed WagihPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclone SeparatorDocument15 pagesCyclone Separatorhadimarvi100% (3)
- Lecture37 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture37 PDFNico Aumento Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 0331-CAL-ING-014-010-0001 - R0 - HVAC System - Hydraulic - Calculation - Report PDFDocument302 pages0331-CAL-ING-014-010-0001 - R0 - HVAC System - Hydraulic - Calculation - Report PDFOleg ShkolnikPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Zawia Faculty of Oil & Gas Engineering: Mud FiltrationDocument5 pagesUniversity of Zawia Faculty of Oil & Gas Engineering: Mud Filtrationايمن القنونيPas encore d'évaluation
- Specific Energy Consumption of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) For SewageDocument14 pagesSpecific Energy Consumption of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) For Sewagesulihah12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Stockyard Storm Water TreatmentDocument23 pagesCoal Stockyard Storm Water TreatmentRajaram Jayaraman100% (1)
- Bubble Column Humidification Dehumidification Desalination SystemDocument67 pagesBubble Column Humidification Dehumidification Desalination SystemAnnjoe MathewsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Water System - 44-64 PDFDocument21 pages2 - Water System - 44-64 PDFAniesh MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment On Packed Bed Column - Mass TransferDocument15 pagesExperiment On Packed Bed Column - Mass TransferAllyana Marie TiemsimPas encore d'évaluation
- Scale Up of Paddle DryerDocument4 pagesScale Up of Paddle DryerRavindra V. Lakhapati100% (1)
- Eurox Cross Flow ScrubberDocument8 pagesEurox Cross Flow ScrubberRobin LayogPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane Nitrogen GeneratorsDocument2 pagesMembrane Nitrogen GeneratorsRoozbeh PPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Pollution ControlDocument35 pagesAir Pollution ControlPraveen YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Co2 Degasifier To Adjust The PHDocument2 pagesCo2 Degasifier To Adjust The PHGhuna UcihaPas encore d'évaluation
- ProMinent Operating Instructions Meta HM-HKDocument20 pagesProMinent Operating Instructions Meta HM-HKivan_shterevPas encore d'évaluation
- Constant Pressure FiltrationDocument2 pagesConstant Pressure FiltrationHarjasa AdhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thickeners: It Pays To Talk To A SpecialistDocument8 pagesThickeners: It Pays To Talk To A SpecialistKumardasNsPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Desander: Unit Wt. 1064 Tons/cu.mDocument4 pagesDesign of Desander: Unit Wt. 1064 Tons/cu.mChris Angelo G CaadlawonPas encore d'évaluation
- Svi 5Document5 pagesSvi 5Kapil GhongadePas encore d'évaluation
- Article JAS Cyclone Revised R2 PDFDocument24 pagesArticle JAS Cyclone Revised R2 PDFAinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yyzzzz Scaling Parameters For PFBC Cyclone Separator Sistems AnalysisDocument17 pagesYyzzzz Scaling Parameters For PFBC Cyclone Separator Sistems AnalysisJosé Pedro Casagrande TrentínPas encore d'évaluation
- Z AIAAJournal2007Document5 pagesZ AIAAJournal2007engma3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Response Surface Methodology For Modeling and Optimization of The Cyclone SeparatorDocument20 pagesApplication of Response Surface Methodology For Modeling and Optimization of The Cyclone SeparatorBayu Pramana PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD Modeling and Multi-Objective Optimization of CycloneDocument25 pagesCFD Modeling and Multi-Objective Optimization of CycloneArunPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclonic Dryer 2Document15 pagesCyclonic Dryer 2andresmendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of The Cyclone Fractional Efficiency Curves: Lwang@cora - Tamu.edu C-Parnell@tamu - Edu Bw-Shaw@tamu - EduDocument14 pagesStudy of The Cyclone Fractional Efficiency Curves: Lwang@cora - Tamu.edu C-Parnell@tamu - Edu Bw-Shaw@tamu - Edubabak mirPas encore d'évaluation
- Polution ModelDocument8 pagesPolution ModelDede Si Engghe SurengghePas encore d'évaluation
- COBEM-2017-0764 Numerical and Experimental Analysis For Performance Improvement of An Admission Restrictor For A Formula-Sae VehicleDocument8 pagesCOBEM-2017-0764 Numerical and Experimental Analysis For Performance Improvement of An Admission Restrictor For A Formula-Sae VehicleLetícia CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Optimization of The Methanolto-Olefin Process Part IDocument12 pagesDesign and Optimization of The Methanolto-Olefin Process Part IForcus onPas encore d'évaluation
- SEDEMENTATIONDocument13 pagesSEDEMENTATIONNatan SolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbine OperationDocument30 pagesTurbine OperationGanesh Dasara100% (2)
- Diametros de Drill PipeDocument3 pagesDiametros de Drill PipeDaniel AlarconPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On IoclDocument39 pagesPresentation On IoclRashmi AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Nalco Document For High Pressue Boiler ChemistryDocument79 pagesGood Nalco Document For High Pressue Boiler ChemistryJayanath Nuwan Sameera100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument184 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFctguyoungPas encore d'évaluation
- University of The West Indies, St. Augustine.: FacultyDocument8 pagesUniversity of The West Indies, St. Augustine.: FacultyCharlotte BPas encore d'évaluation
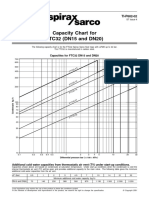
- FTC32 Ti P602 02 enDocument1 pageFTC32 Ti P602 02 enErce KoyunbabaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, LubricationDocument43 pagesThe Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, Lubricationحسين مهديPas encore d'évaluation
- Bernolii EquationDocument5 pagesBernolii EquationEsra BelhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Incomp Comp CombustionDocument3 pagesIncomp Comp CombustionAbby SevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent HeatTransfer L01 Introduction PDFDocument50 pagesFluent HeatTransfer L01 Introduction PDFHoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 WearDocument23 pagesModule 5 WearrohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant RO 26 TPHDocument13 pagesPlant RO 26 TPHveroniu ricaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Work ReviewDocument15 pagesProject Work ReviewManish VankudrePas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Constructin of SewerDocument94 pagesDesign of Constructin of SewerHanRo MaharjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Manual LWWCSC120Document41 pagesTechnical Manual LWWCSC120Julian ArizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biofiltration As An Air Pollution Control Technology For Volatile Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesBiofiltration As An Air Pollution Control Technology For Volatile Organic CompoundsGangadhar. GPas encore d'évaluation
- Sop For Cleaning of Ss Water Transfer PipeDocument3 pagesSop For Cleaning of Ss Water Transfer PipeSolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- RLT 01 GuidelineDocument24 pagesRLT 01 GuidelineBruno GuedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Reynolds NumberDocument8 pagesReynolds NumberpaoloasequiaPas encore d'évaluation
- PR-3Document1 pagePR-3Fernanda QuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Scale UpDocument109 pagesScale UpΟδυσσεας ΚοψιδαςPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystallization in TernaryDocument14 pagesCrystallization in TernaryArie TarunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturi Scrubber Theory & ExperimentDocument6 pagesVenturi Scrubber Theory & ExperimentTian Fung Wang100% (1)
- Actuated Ball Valve 357 A - BDKDocument3 pagesActuated Ball Valve 357 A - BDKfarhanakhtar ansariPas encore d'évaluation