Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 3 - jan2015.PDF (Fluid Mech)
Transféré par
pijechadTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tutorial 3 - jan2015.PDF (Fluid Mech)
Transféré par
pijechadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003)
Chapter 3: Static fluid
TUTORIAL 3
1.
Define Pascals law.
2.
What is difference between gage pressure and absolute pressure?
3.
A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 24 kPa at a location where the
barometric reading is 600 mm Hg. Determine the absolute pressure in the
chamber (Hg = 13,590 kg/m3).
(Ans: 56 kPa)
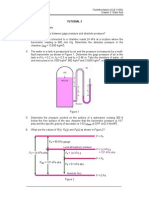
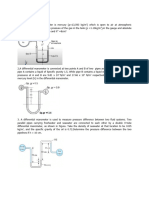
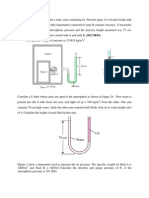
4.
The water in a tank is pressurized by air and the pressure is measured by a multifluid manometer as shown in Figure 1. Determine the gage pressure of air in the
tank is if h1 = 0.2 m, h2 = 0.3 m and h3 = 0.46 m. Take the densities of water, oil
and mercuries to be 1000 kg/m3, 850 kg/m3 and 13,600 kg/m3, respectively.
(Ans:56.9 kPa)
Figure 1
5.
Determine the pressure exerted on the surface of a submarine cruising 300 ft
below the free surface of the sea. Assume that the barometric pressure is 14.7
psia and the specific gravity of sea water is 1.03 (water at 32F is 62.4 lbm/ft3).
(Ans: 149 psia)
Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003)
Chapter 3: Static fluid
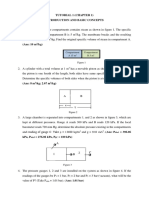
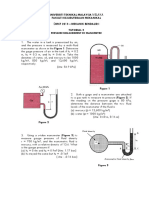
6.
What are the values of P(x), PA(y) and PB(z) as shown in Figure 2?
P = PA
PA = 90 kPa gauge
Local atmospheric pressure
PA = (y) kPa abs
abs
PB = (z) kPa g
P = (x) kPa g
= 101 kPa abs
P = PB
Patm = 101 kPa abs
PB = 51 kPa abs
Absolute Zero
P = 0 Pa
abs
Figure 2
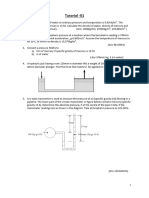
7.
Show that the pressure at point A can be expressed as:
PA = mangh2 Pgh1
Fluid P
Density,
h2
h1
B
Manometric Fluid Density, man
Figure 3
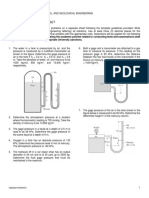
8.
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is measured with a mercury
manometer where hwater = 3.0m and hmercury = 0.43 m. What is the gauge pressure
at the bottom of the tank? (Relative density mercury = 13.56).
(Ans: 27.8 kPa)
Figure 4
Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003)
Chapter 3: Static fluid
9.
A U-tube manometer containing mercury of density 13600 kg/m3 is used to
measure the pressure drop along a horizontal pipe. If the fluid in the pipe has a
relative density of 0.8 and the manometer reading is 0.6m, what is the pressure
difference measured by the manometer?
(Ans: 75.34 kPa)
Figure 5
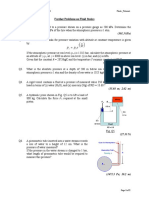
10. Fresh and seawater flowing in parallel horizontal pipelines are connected to each
other by a double U-tube manometer as shown in Figure 6. Determine the
pressure difference between the two pipelines. Take the densities of seawater,
water and mercury to be sea = 1035 kg/m3 and Hg = 13,600 kg/m3.
(Ans: 3.39 kPa)
P1
P2
Figure 6
Fluid Mechanics (CLB 11003)
Chapter 3: Static fluid
11. Determine the pressure difference between points A and B in Figure 7 (SGbenzene =
0.88, SGHg = 13.6, SGkerosene = 0.82, SGwater = 1 and SGair = 0.0118.
(Ans: 10.23 kPa)
Figure 7
12. Define buoyancy.
13. A crane is used to lower weights into a lake for an underwater construction
project. Determine the tension in the rope of the crane due to a 3 ft diameter
spherical steel block (density = 494 lbm/ft3) when it is (a) suspended in the air and
(b) completely immersed in water (density = 62.4 lbm/ft3).
(Ans: a). 6980 lbf. b) 6100 lbf)
14. Consider a large cubic ice block floating in seawater. The specific gravities of ice
and seawater are 0.92 and 1.025, respectively. If a 10 cm high portion of the ice
block extends above the surface of the water, determine the height of the ice
block below the surface.
(Ans: 87.6 cm)
Figure 8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3M Syafiq SamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 - BMCF 2223 (Manometer)Document4 pagesTutorial 3 - BMCF 2223 (Manometer)Muhamad Syazwan100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 Pressure and Pressure MeasurementDocument8 pagesTutorial 2 Pressure and Pressure MeasurementeijamPas encore d'évaluation
- 4HOMEWORKDocument6 pages4HOMEWORKBlue SkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Work Practice Sheet:: ManometersDocument2 pagesClass Work Practice Sheet:: ManometersAli Al AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4challamjPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Concepts and DefinitionsDocument3 pagesIntroductory Concepts and Definitionsisrael moizo dintsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDocument15 pagesUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadPas encore d'évaluation
- Scribd Download - Com Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersDocument6 pagesScribd Download - Com Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersRomil ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Thermodynamics (Tutorial 1) PDFDocument4 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (Tutorial 1) PDFSahil AcharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFAnson NaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 01Document3 pagesTutorial 01shain begumPas encore d'évaluation
- Further Problems On Fluid StaticsDocument2 pagesFurther Problems On Fluid StaticsCool DouglasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sikkerarv - DK Fluids PDFDocument84 pagesSikkerarv - DK Fluids PDFJoymi Claire100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 2 Problems and AnswersAlex LakePas encore d'évaluation
- Adama Science and Technology University School of Civil Engineering and Architecture Department of Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesAdama Science and Technology University School of Civil Engineering and Architecture Department of Civil EngineeringAmanuel TkPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids 2Document7 pagesFluids 2Ryan CanteraPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesSolved Problems Fluid MechanicsGashaw Minaye100% (2)
- Ejercicios TermodinamicaDocument11 pagesEjercicios TermodinamicaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- CIV2040S Problem Set - 1 - Pressure and Its MeasurementDocument6 pagesCIV2040S Problem Set - 1 - Pressure and Its MeasurementMark JacobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid StaticDocument2 pagesFluid StaticAditi SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Concepts Definition and Basic PrinciplesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Concepts Definition and Basic PrinciplesEyron EyronPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Document4 pagesAssignment I SKPU1123 1213 2Rajab AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3Document14 pagesTutorial 3HAJAR KHALIDPas encore d'évaluation
- First Quiz in Module 1 and 2Document6 pagesFirst Quiz in Module 1 and 2Emmanuel MaalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet 2Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet 2oginoweijPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet StaticsDocument4 pagesSheet StaticsMohamed Tally0% (1)
- Practice Solving Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesPractice Solving Fluid MechanicsJan HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Example 3Document3 pagesExample 3sharanbiet0% (1)
- Tutorial 2 Fluid StaticDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 Fluid StaticAiman HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- FLUMECH New Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesFLUMECH New Practice ProblemsMLNDG boysPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 SolutionDocument6 pagesHW2 SolutionHamzaJehadPas encore d'évaluation
- Homeworks 1-10 PDFDocument95 pagesHomeworks 1-10 PDFWendy LinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce 371 Homework 2Document2 pagesCe 371 Homework 2Anonymous xtFoefqNPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 GD StudentsDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 GD Studentsgokuler137Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Sheet 1Document6 pagesProblem Sheet 1Abdul WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo 27 45 1 29Document18 pagesThermo 27 45 1 29Danerys Targaryan0% (1)
- KKKR1243 Tutorial I 20212022Document3 pagesKKKR1243 Tutorial I 20212022atiqa aqila01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 - DMCF 2213 (Manometer)Document4 pagesTutorial 3 - DMCF 2213 (Manometer)shazwani zamriPas encore d'évaluation
- BME2303 Tutorial 2Document6 pagesBME2303 Tutorial 2Zarif IzzatPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture Week 8 Quiz 2 QuestionsDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture Week 8 Quiz 2 QuestionsJake CanlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Malindu WickramasinghePas encore d'évaluation
- 181ctdcha2 Tutorial 1aDocument4 pages181ctdcha2 Tutorial 1aESTHER TSAKANE MONKWEPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 1 PDFDocument4 pagesHomework 1 PDFعلي علي صالح انقعPas encore d'évaluation
- Escanear 0001Document3 pagesEscanear 0001estereotipoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce142p-2 Cw05 - Problem Set (Cw2)Document3 pagesCe142p-2 Cw05 - Problem Set (Cw2)Keroro SeighartPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Ch1 ProblemDocument5 pagesTutorial Ch1 ProblemKiat HauPas encore d'évaluation
- Set2ans 12Document6 pagesSet2ans 12footballtrack_21Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW1 9Document6 pagesHW1 9Eduardo VCPas encore d'évaluation
- C3 QuestionnairesDocument2 pagesC3 QuestionnairesCharlie SumagaysayPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction)Document10 pagesAssignment 1 (Chapter 1: Introduction)Ragh AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument4 pagesFMvishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Problems For Week IIIDocument1 pageTutorial Problems For Week IIIShiva YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad 1 Mecanica FLuidosDocument5 pagesActividad 1 Mecanica FLuidosAngel HCastPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 2 QDocument3 pagesChap 2 QnurudinsatharPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 - DMCF 2223 (Manometer)Document4 pagesTutorial 3 - DMCF 2223 (Manometer)zul hilmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 123Document13 pages123Cheska FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp3 Star-Delta ConnectionDocument9 pagesExp3 Star-Delta Connectionpijechad0% (2)
- Exp1 Punya Result HeheDocument8 pagesExp1 Punya Result HehepijechadPas encore d'évaluation
- CLB 10603 Microbial Technology Lesson Plan Jan 2016Document6 pagesCLB 10603 Microbial Technology Lesson Plan Jan 2016pijechadPas encore d'évaluation
- Results (Air Flow Convection)Document3 pagesResults (Air Flow Convection)pijechadPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Saponification of SoapDocument3 pagesDiscussion Saponification of Soappijechad0% (1)
- Generalized Compressibility ChartDocument4 pagesGeneralized Compressibility ChartpijechadPas encore d'évaluation
- Argon PDFDocument18 pagesArgon PDFPavan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Write Up On PumpsDocument74 pagesWrite Up On PumpsGopal Reddy100% (1)
- Refrigeration (Kylteknik) : 2. Vapour-Compression Refrigeration ProcessesDocument36 pagesRefrigeration (Kylteknik) : 2. Vapour-Compression Refrigeration ProcessesiJeng RalluPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Chemistry - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024Document1 pageSurface Chemistry - Mind Maps - Lakshya JEE 2024SAMRIDH SAHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Press Carbg and High Press QNCHGDocument56 pagesLow Press Carbg and High Press QNCHGskluxPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Water R0 - 220830Document29 pagesChemistry of Water R0 - 220830Kelly Roxelle De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Foaming in Fractionation ColumnsDocument7 pagesFoaming in Fractionation ColumnsAnonymous v5uipH100% (1)
- Characterization of A Black ...Document78 pagesCharacterization of A Black ...Watcher InstancePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 123Document9 pagesLab Report 123Falcon Tech0% (1)
- Crude Oil ProcessingDocument19 pagesCrude Oil ProcessingYinka OlatunjiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Anesthesia - Vaporizers (64 94)Document31 pages3 Anesthesia - Vaporizers (64 94)racut_khansatra100% (1)
- EBARA Reference DataDocument6 pagesEBARA Reference DataMarcelo Peretti100% (1)
- Full Text 01Document118 pagesFull Text 01paolita788Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Meters in Incompressible FlowDocument13 pagesFluid Meters in Incompressible FlowStephen Mirdo100% (2)
- 09-05-Sulzer-Key To Success in Ethylene Plant-VFDocument23 pages09-05-Sulzer-Key To Success in Ethylene Plant-VFnktiah1207Pas encore d'évaluation
- AMACS Multipocket Vane WebDocument1 pageAMACS Multipocket Vane WebadrianioantomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument40 pagesChapter 4-Simple Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systemm_alodat614450% (2)
- Unit Operation and ProcessDocument20 pagesUnit Operation and ProcessHaseebPas encore d'évaluation
- EHB en 7-Sizing PDFDocument83 pagesEHB en 7-Sizing PDFChristopher Kenneth ChoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jitorres - Regression To Experimental PVT DataDocument9 pagesJitorres - Regression To Experimental PVT DataOskr OvallePas encore d'évaluation
- Standard AtmosphereDocument39 pagesStandard Atmosphereravi gautamPas encore d'évaluation
- G12 Chemistry Answer KeyDocument22 pagesG12 Chemistry Answer KeyDaniel Monclear CatiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Got Water How The Water Cycle WorksDocument3 pagesGot Water How The Water Cycle Worksapi-528795360Pas encore d'évaluation
- SHS Sy2021-2022 Q3law W1-2 General-Chemistry-ValidatedDocument8 pagesSHS Sy2021-2022 Q3law W1-2 General-Chemistry-Validatedjohnrobertdeocampo84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics 1.EE 2A Stem Midterms. LM 1Document11 pagesThermodynamics 1.EE 2A Stem Midterms. LM 1mery9jean9lasamPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet-Sources of Water - Water Cycle - Where Is The Water StoredDocument2 pagesWorksheet-Sources of Water - Water Cycle - Where Is The Water StoredEeshaalPas encore d'évaluation
- Powder Production Techniques: AtomizationDocument13 pagesPowder Production Techniques: AtomizationVasantha SudasinghaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cause Effect Diag PDFDocument28 pagesCause Effect Diag PDFabderrahmanePas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Plant - 2Document63 pagesGas Plant - 2viettanctPas encore d'évaluation
- Ideal Gas LawDocument21 pagesIdeal Gas Lawjervis GrajoPas encore d'évaluation