Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
C D A B C D Biology Assessment Test
Transféré par
ke2Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
C D A B C D Biology Assessment Test
Transféré par
ke2Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BIOLOGY ASSESSMENT
C TEST
their volume/surface area ratio is
Chapter 7
large.
D they never use oxygen.
6. Muscle fatigue is dueDate:
to
Name:
A muscle cramp.
B muscle infection.
high answer
carbon for
dioxide
in muscle.
Instruction: For each of the Questions 1 to 30, choose theCcorrect
each level
question
from the
D
excess
lactic
acid
in
muscle.
four options A, B, C and D.
Class:
1.
The following organisms have a special
respiratory system except
A
B
C
D
2.
A
B
C
D
Provide body support to the soft wall.
Prevent the trachea from collapsing.
Aid inhalation and exhalation.
Filter dust particles from the air.
8.
lactic acid and energy.
ethanol and water.
energy and water.
ethanol and lactic acid.
9.
Red
Purple
Yellow
Orange
Unicellular organisms such as yeast,
amoeba and paramecium have a simple
method of gas exchange because
A
B
their surface area/volume ratio is
large.
their surface area/volume ratio is
small.
Q
Expiration
Photosynthesis
Excretion
Condensation
Absorb oxygen.
Excrete carbon dioxide.
Filter out solid particles.
Direct flow of water.
After maximum expiration, the air left in
the lungs is
A
B
C
D
10.
P
Inspiration
Respiration
Nutrition
Hydrolysis
What is the function of gill rakers?
A
B
C
D
What is the colour of the bicarbonate
indicator when a few drops of
hydrochloric acid is added to it?
A
B
C
D
5.
What processes does P and Q represent?
In anaerobic respiration, glucose is broken
down into
A
B
C
D
4.
fish.
mosquitoes.
paramecium.
frog.
What is the function of the complete rings
of cartilage in the trachea of mammals?
A
B
C
D
3.
7.
tidal volume.
respiratory volume.
residual volume.
expiratory volume.
Which of the following does not respresent
the respiration process?
A
B
C6H12O6 2C3H6O3 + energy
C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2+
energy
C C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 +
energy
D C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
11. The table shows the mechanism of water
intake by fish.
P - Opercular cavity is increased
Q - The base of the mouth is lowered
R - Operculum is closed
S - Mouth opens
T - Water from outside enters the mouth
Which of the following sequence is
correct?
A SQPRT
B SQRP T
C QSPTR
D PQSTR
12.
After an athlete exercises, his blood will
have excess amounts of
A
B
C
D
13.
Which of the following represents X, Y
and Z?
A
heat energy.
light energy.
chemical energy.
mechanical energy.
Yeast fermentation involves the action of
the enzyme
A
B
C
D
15.
lactic acid.
sugar.
ATP.
carbon monoxide.
Energy is lost from the body mostly in the
form of
A
B
C
D
14.
X is the intercostal muscle and Y is the
diaphragm muscle. Z is the effect of the
action of X and Y.
amylase.
lipase.
trypsin.
zymase.
When air enters the nose, it goes through
the respiratory tract. Which of the
following passage way is correct?
Bronchiole bronchus larynx
trachea
B Bronchiole bronchus trachea
larynx
C Trachea bronchiole bronchus
alveolus
D Trachea bronchus bronchiole
alveolus
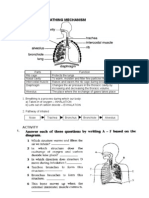
16. The diagram shows a state of breathing in
man.
17.
18.
Y
Diaphragm
muscles
relax
Diaphragm
muscles
contract
Diaphragm
muscles
contract
Diaphragm
muscles
relax
Z
air is
drawn out
air is
drawn in
air is
drawn out
air is
drawn in
In mammals, gaseous exchange takes
place in the
A
B
C
D
X
Intercostal
muscles
relax
Intercostal
muscles
contract
Intercostal
muscles
relax
Intercostal
muscles
contract
tracheae.
bronchioles.
bronchi.
alveoli.
Inhaled air contains
A
B
C
D
5.5 % carbon dioxide.
21 % oxygen.
3.8 % oxygen.
no carbon dioxide.
19.
The diagram shows an experiment to
study the concentration carbon dioxide in
pond water. After 3 hours, the pond water
in each tube was tested with bicarbonate
indicator.
22.
The diagram is a model of a rib cage.
The parts J, K, L and M represents
J
A Sternum Intercostal Vertebral
B
C
Which of these tubes will produce a
yellow colour?
A
B
C
D
20.
21.
J and K only
J, K and L only
J and M only
K, L and M only
The
equation
below
shows
fermentation process by yeast.
Glucose X + carbon dioxide + Y
What does X and Y represent?
A Lactic acid + energy
B Ethanol + energy
C Fatty acid and oxygen
D Ethanol + lactic acid
muscles
Vertebral Intercostal
column
muscles
Sternum
Rib
D Vertebral
Rib
column
23.
24.
Rib
Sternum
Vertebral Intercostal
column
muscles
Intercostal Sternum
muscles
Amoeba and other unicellular organisms
carry out gaseous exchange through the
A
B
C
D
the
column
Rib
vacuole.
ectoplasm.
plasma membrane.
cell wall.
The diagram shows a food web
When green plants are exposed to strong
sunlight, no carbon dioxide is released to
the atmosphere. This shows that
A
B
C
D
carbon dioxide from respiration is
absorbed for photosynthesis.
the rate of respiration is faster than
the rate of photosynthesis.
the carbon dioxide released from
respiration dissolves in water to
become carbonic acid.
the carbon dioxide from respiration is
oxidized.
Which organism is a tertiary consumer?
A
B
C
D
Rats
Pigeons
Snakes
Eagles
25.
Oxygen is transported in the blood in the
form of
A
B
C
D
26.
28.
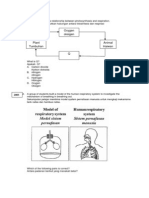
The diagram is a model of the lungs.
haemoglobin.
oxyhaemoglobin.
liquid oxygen.
potassium oxide.
This experiment was set up to study
respiration.
Which of the following is true about the
condition shown above?
A
B
C
D
After an hour, what would be the colour of
the bicarbonate indicator solution in the
boiling tubes K, L and M?
A
B
C
D
27.
K
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Purple
L
Yellow
Red
Yellow
Purple
M
Purple
Yellow
Red
Yellow
Which of the following takes place during
anaerobic respiration in animals?
A
B
C
D
Ethanol is produced.
Carbon dioxide is produced.
Heat energy is used.
Glucose is used.
29.
Carbon dioxide that is absorbed into the
cell, will combine with water to form
A
B
C
D
30.
Air is drawn into the balloon.
The gas jar contracts to push the air
out.
The volume of the balloon increases
slowly.
The pressure in the gas jar is higher
than the atmospheric pressure.
carbolic acid.
carbonic acid.
hydrogen carbonate acid.
carboxylic acid.
Energy for the contraction of muscles can
be obtained from
A
B
C
D
glycogen that is stored in the muscles.
fats in adipose tissues.
glucose in the muscles.
adenosine triphosphate in the
muscles.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Margaret Moore Bob Tschannen-Moran Erika JacksonDocument201 pagesMargaret Moore Bob Tschannen-Moran Erika JacksonBella100% (18)
- Ebook PDF Currens Math For Meds Dosages and Solutions 11th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Currens Math For Meds Dosages and Solutions 11th Edition PDFcecil.slocum194100% (27)
- Diagnostic Test in Science 9Document6 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 9John BG93% (15)
- A Case-Based Guide To Clinical Endocrinology (October 23, 2015) - (1493920588) - (Springer)Document434 pagesA Case-Based Guide To Clinical Endocrinology (October 23, 2015) - (1493920588) - (Springer)AbdulraHman KhalEd100% (2)
- SUMMATIVE TEST-SCIENCE 9 (Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration)Document3 pagesSUMMATIVE TEST-SCIENCE 9 (Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration)lavenia acdal100% (1)
- Grade 9 Science ExamDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Science Examjenefer100% (2)
- Heavy Equipment Operator Testing and CertificationDocument7 pagesHeavy Equipment Operator Testing and CertificationJaffer Rizvi0% (1)
- Life Processes Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesLife Processes Test QuestionsUtkarsh VaishnavPas encore d'évaluation
- Mt. Zion Christian College End of Term Two Examinations 2010Document18 pagesMt. Zion Christian College End of Term Two Examinations 2010joseph kunikinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 Biology Form 5Document11 pagesPaper 1 Biology Form 5GerlJerlPas encore d'évaluation
- 1ST Grade 9Document4 pages1ST Grade 9Randolf CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Municipality of TERNATE Science ClassDocument4 pagesMunicipality of TERNATE Science ClassMaria Elaine Feranil33% (3)
- Biology F4Chapter 6 (Ver1)Document4 pagesBiology F4Chapter 6 (Ver1)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansDocument19 pagesPaper 2 Biology 1996 Paper 2+ansapi-3812894100% (1)
- Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (40 Marks)Document17 pagesSection A: Multiple Choice Questions (40 Marks)Syafiq AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade+10+ +Biology+Revision+Question+ +part+2Document20 pagesGrade+10+ +Biology+Revision+Question+ +part+2MoghanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Document99 pagesUlangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Norizan DarawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quizlet-style multiple choice science examDocument14 pagesQuizlet-style multiple choice science examraysklinePas encore d'évaluation
- 5090 w03 QP 1Document20 pages5090 w03 QP 1mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration CoppDocument50 pagesRespiration CoppsyamaladevinPas encore d'évaluation
- Dharumavantha School Examinations: First Term 2009 Grade 10Document15 pagesDharumavantha School Examinations: First Term 2009 Grade 10afoo1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory - 2 - WsDocument5 pagesRespiratory - 2 - WsRatna PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Gajah Berang, Melaka: Sulit Science Paper 1 1 HourDocument11 pagesSMK Gajah Berang, Melaka: Sulit Science Paper 1 1 HourYanti FarhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- #8 Midterm @assmentDocument12 pages#8 Midterm @assmentTijani Basit AbiodunPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterDocument6 pages1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterJessa Lynn E. AcalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ST4 Biology F4Document14 pagesST4 Biology F4Najiha AlHabsyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology MCQs on RespirationDocument10 pagesBiology MCQs on RespirationKeelah BennPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ and theory questions on plant and human transport systemsDocument8 pagesMCQ and theory questions on plant and human transport systemsVipin DasPas encore d'évaluation
- N.S.S.S Biology Midterm ExamDocument7 pagesN.S.S.S Biology Midterm ExamAlice MAGOBAPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledLyshanya HymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerDocument6 pagesRespiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerRatna PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 5090 w12 QP 12Document20 pages5090 w12 QP 12mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHaider AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Umta Uace Guide Bio1 GuideDocument18 pagesUmta Uace Guide Bio1 Guidejordanmulumba34Pas encore d'évaluation
- LongmanBiologyforCSECWebQuestions PDFDocument22 pagesLongmanBiologyforCSECWebQuestions PDFRonikePas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCEDocument6 pagesSCIENCEHARSH MESHRAMPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarter Exam BiologyDocument4 pages1st Quarter Exam BiologyElpi Ferrer100% (2)
- Modul 1Document28 pagesModul 1Irrinna Shakinah100% (1)
- 5090 w03 QP 1Document20 pages5090 w03 QP 1wilsky05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)Document7 pagesUnit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)usbdetailsPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration & Gas Exchange MCQ QPDocument25 pagesRespiration & Gas Exchange MCQ QPVivehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Organ Stimulus DetectedDocument12 pagesSensory Organ Stimulus DetectedSiti NazirahPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.1 Set 1 Paper 1Document19 pages6.1 Set 1 Paper 1ning jyePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsAsad YaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge AS Level Biology: Transport (Animals)Document15 pagesCambridge AS Level Biology: Transport (Animals)mjPas encore d'évaluation
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDocument3 pagesSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions 1 PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesPractice Questions 1 Photosynthesis사나Pas encore d'évaluation
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHaider AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber SanchisPas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Exam PP1 Science Double AwardDocument20 pagesMock Exam PP1 Science Double AwardRorisang Lebakeng100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test in Science 9Document6 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 9Peter Jay CorrosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio O P1 Nov 06Document12 pagesBio O P1 Nov 06Prince AsherPas encore d'évaluation
- First Quarter Summative Test in Science 9Document3 pagesFirst Quarter Summative Test in Science 9NurshahadahPas encore d'évaluation
- S4 Biology Exam Graphs Show Athlete Gas ExchangeDocument8 pagesS4 Biology Exam Graphs Show Athlete Gas ExchangeSsenteza FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- SS1 Biology Revison Questions Summer Term 2022Document27 pagesSS1 Biology Revison Questions Summer Term 2022Abimbola Brodie-MendsPas encore d'évaluation
- Human RespirationDocument9 pagesHuman RespirationMona MohtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Monthly Test Feb 2009Document11 pagesMonthly Test Feb 2009ajeyraPas encore d'évaluation
- PH 1 8FLC Ipa GenapDocument5 pagesPH 1 8FLC Ipa GenapNurtri NunuPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizGusthe Jebb AzarconPas encore d'évaluation
- תרגול - ביולוגיה לתלמידיםDocument5 pagesתרגול - ביולוגיה לתלמידיםdodbenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 42 Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 42 Study QuestionsGabriel FreschPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Paper 2 QuestionDocument11 pagesPhysics Paper 2 Questionke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kertas 1 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2007 - SoalanDocument15 pagesKertas 1 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2007 - Soalanke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Add-Maths ProjectDocument14 pagesAdd-Maths Projectke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Add-Maths ProjectDocument14 pagesAdd-Maths Projectke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and DDocument4 pagesName: Date: Class: Instruction: For Each of The Questions 1 To 30, Choose The Correct Answer For Each Question From The Four Options A, B, C and Dke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Subjective (Transport of Plants)Document1 pageBiology Subjective (Transport of Plants)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fizik Esei Bab 2 QP2Ch1&2BDocument5 pagesFizik Esei Bab 2 QP2Ch1&2Bzarinah22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Poster SSMDocument1 pagePoster SSMke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Past Year QuestionsDocument4 pagesPast Year Questionske2Pas encore d'évaluation
- MatterDocument4 pagesMatterke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- BioF5CH10 (Ver1)Document4 pagesBioF5CH10 (Ver1)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Most Interesting Character in Catch Us If You CanDocument25 pagesMost Interesting Character in Catch Us If You Canke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: MarkahDocument4 pagesBiology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: Markahke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 13 IntegrationDocument16 pagesModul 13 Integrationhasnitajb0% (1)
- Kertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2007 - SoalanDocument15 pagesKertas 2 Pep Akhir Tahun Ting 4 Terengganu 2007 - Soalanke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- A B C D Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: MarkahDocument4 pagesA B C D Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: Markahke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- A B C D Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: MarkahDocument4 pagesA B C D Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: Markahke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- BioF4CH7 (Ver2)Document5 pagesBioF4CH7 (Ver2)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: MarkahDocument4 pagesBiology: Nama Pelajar: Kelas: Markahke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1.3 Terms in A.PDocument3 pages1.1.3 Terms in A.PChet ShowPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Biology Test 4 ReviewDocument6 pagesSMK Biology Test 4 Reviewke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.6 (Practical Textbook Page 113)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.6 (Practical Textbook Page 113)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.11 (Practical Textbook Page 119)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.11 (Practical Textbook Page 119)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.8 (Practical Textbook Page 115)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.8 (Practical Textbook Page 115)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.5 (Practical Textbook Page 111)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Activity 8.5 (Practical Textbook Page 111)ke2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.3 (Practical Textbook Page 108)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 8.3 (Practical Textbook Page 108)ke2100% (1)
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- XxssDocument13 pagesXxssfkhunc07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Appendicitis in Adults: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDocument37 pagesAcute Appendicitis in Adults: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDaniela MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- Enquiry ReportDocument4 pagesEnquiry ReportMeena Koushal0% (1)
- Lplpo Sub Unit Des-JanDocument33 pagesLplpo Sub Unit Des-JanDiasTikaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnupanaDocument60 pagesAnupanaVaidya Nur50% (4)
- Beta Blockers: Selective and Non-Selective TypesDocument22 pagesBeta Blockers: Selective and Non-Selective TypesJewelyn ConolPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 2012 EditionDocument215 pagesChapter 11 2012 EditionLuis Soriano MitraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDinesh Babu PugalenthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Barthel IndexDocument2 pagesBarthel Indexgania100% (1)
- CDS - MMS Protocols A-Z - Yummy - Doctor Holistic Health EducationDocument23 pagesCDS - MMS Protocols A-Z - Yummy - Doctor Holistic Health Educationbagus918Pas encore d'évaluation
- L1095852 R5 QF-TB Gold Plus BCT IFDocument12 pagesL1095852 R5 QF-TB Gold Plus BCT IFTuấn Minh PhùngPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersDocument149 pagesAdvances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersjprewittdiazPas encore d'évaluation
- September 15, 2016Document20 pagesSeptember 15, 2016CassiePas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Document16 pagesAtlas de Acupuntura (Ingles)Medicina Tradicional China - Grupo LePas encore d'évaluation
- Caliber - L: Expandable Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion DeviceDocument6 pagesCaliber - L: Expandable Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion DeviceBobPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology All Case Studies PDFDocument54 pagesPsychology All Case Studies PDFArmeen AmirPas encore d'évaluation
- Try Out Paket BDocument13 pagesTry Out Paket BDian Purnama Dp'TmPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Room InstrumentsDocument2 pagesEmergency Room InstrumentsEduardo AnerdezPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-Lead ECG Placement GuideDocument9 pages12-Lead ECG Placement GuideFalusi Blessing OlaidePas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric PulmonologyDocument250 pagesPediatric Pulmonologyshankargoudachildicu100% (4)
- Hypnosis, Past Lives and NLPDocument8 pagesHypnosis, Past Lives and NLPZiad Cassim (anti-Sufi)100% (1)
- Robin Williams Case of Acute Depression Leading To Suicide From Point of View of AstrologyDocument5 pagesRobin Williams Case of Acute Depression Leading To Suicide From Point of View of AstrologyJatinder Sandhu100% (1)
- Narcotic Drugs: Opium Herion Codeine Tramadol MorphineDocument9 pagesNarcotic Drugs: Opium Herion Codeine Tramadol MorphineSyed renobaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument20 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmPortia Rose RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayurveda Today IndexDocument15 pagesAyurveda Today IndexrajrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4intestinal NematodesDocument41 pagesChapter 4intestinal Nematodesdeneke100% (1)