Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Opnet-Cds 08 32
Transféré par
solbahiaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Opnet-Cds 08 32
Transféré par
solbahiaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
JJ
CDS
Network Simulation
Chapter 2: OPNET
A Tool for Discrete Event Simulation (DES)
2: OPNET
Prof. Dr. Jrgen Jasperneite
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Lecture Objectives
Learn how OPNET can be used for
Application troubleshooting
Network planning and design
Operational validation
Understand and be able to explain the value of OPNET
Get a hands-on learning experience and learn various
OPNET features
CDS
JJ
OPNET
OPtimised Network Engineering Tools
OPNET for short
http://www.opnet.com/
2: OPNET
General-purpose tool for discrete event simulations
Object-oriented design
The simulator can be used for:
traffic modeling of telecommunication networks
protocol modeling
modeling queueing networks
modeling multiprocessors and other distributed hardware systems
validating hardware architectures
evaluating performance aspects of complex software systems
. . . modeling any other system where the discrete event approach
is suitable.
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Where is OPNET
in the world of simulation tools?
There are a lot of network simulation tools available:
Non-commercial:
SMURPH www.cs.ualberta.ca/~pawel/SMURPH/smurph.html
NS www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/
NetSim++
OMNET++ www.omnetpp.org
.....
Commercial:
COMNET III
OPNET www.opnet.com -> state of the art
...
Here we use the academic version IT Guru !
CDS
JJ
The Virtual Network Environment (VNE)
Troubleshooting
Identify problems faster
Operational Validation
Reduce costly mistakes
2: OPNET
Traffic,
Topology, and
Configurations
Planning
Improve price /
performance
Virtual Network Environment
Replicates the behavior of your entire network,
including its routers, switches, servers, protocols,
and individual applications
C DS
JJ
Examples of Problems Solved
IT Guru can be used to
Identify problems
Increasing traffic loads by 20% causes unacceptable FTP
response times
If the Chicago router fails, the Seattle router becomes
overloaded
The link between Seattle and Portland averages 10% utilization
2: OPNET
Pinpoint causes
The FTP server is not fast enough
More traffic than expected is being routed through Seattle
Test solutions
Where is the best location for a new server?
Which router configuration will give the best performance?
Create/import topology/configuration
Create traffic
Choose statistics
Run simulation
View results
Duplicate or create new scenario
Publish results
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Discrete Event Simulation Workflow
C DS
JJ
DES Example: Technology Migration
Problem: Voiceover-IP applications
choppy
2: OPNET
Cause: Voice packet
delay variation
Potential solution:
Understand the
effect of adding IP
QoS
Iterate
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
DES Example: Protocol Behavior
Problem: Large file transfers
too slow
Upgrading from T1 (1.544
Mbps) to T3 (44.7 Mbps) links
is costly, and more
importantly, does not help
Cause: TCP is throttling
throughput
Solution: Modify TCP window
size
Cost: $0
Capture traffic
Import packet trace file(s)
Visualize application behavior
Diagnose problems
Explore potential solutions
Document application analysis
Import into IT Guru for analysis
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
ACE Workflow
10
ACE: Application Characterization Environment
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Summary
IT Guru can predicts performance of infrastructure by
aiding in
Application analysis
Application deployments
Capacity planning
Technology migration
Understanding protocol behavior
Identifying network configuration errors
Failure analysis
Device change management
C DS
JJ
11
2: OPNET
Workflow (not limited to IT Guru)
12
JJ
IT Guru Workflow
Projects and Scenarios
CDS
Startup Wizard
Building Topologies
2: OPNET
Creating Topologies
Network Object
Model Libraries
LAN and Cloud Objects
Object Attributes
Model Architecture
Subnets
Creating Traffic
Choosing Statistics
Viewing Results
13
C DS
JJ
Project Editor and Topologies
Project Editor
Networks are modeled and created in this editor
The first step is to specify project and scenario names and select
how to create the topology
2: OPNET
Topology can be created or imported from
14
Empty Scenario - built manually
ACE traffic file
Device Configuration files
Circuit Switched Text files
ATM Text files
XML
CDS
JJ
Projects and Scenarios
A scenario is a snapshot of the entire network
configuration, topology,
and traffic
Baseline Scenario
Baseline Scenario
With Doubled Traffic
Capacity Planning Project
2: OPNET
Scenario With
Upgraded Links
15
JJ
IT Guru Workflow
Projects and Scenarios
C DS
Startup Wizard
Building Topologies
2: OPNET
16
Creating Topologies
Network Object
Model Libraries
LAN and Cloud Objects
Object Attributes
Model Architecture
Subnets
Creating Traffic
Choosing Statistics
Viewing Results
Organized set of network objects
Defines
Node location
Connectivity
Configuration
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
What Is a Topology?
17
C DS
JJ
Creating a Topology
Topologies can be built manually or imported
To build manually:
Choose appropriate node and link objects
Position nodes and links
Set node and link attributes
2: OPNET
To import:
18
Use third-party software to gather topology information
Import into IT Guru
Fine-tune and verify the model
Create Model Assistant file to streamline future imports
CDS
JJ
Subnets
Organizes network components
Represents actual network physical constructs
No behavioral aspects
Stationary, mobile or satellite
2: OPNET
3 Subnet Types
19
JJ
Choosing Network Objects
Object Palettes
C DS
A catalog of different network devices
Utility objects
Simplify the setup and configuration of network model
Standard models
Generic network devices
Vendor models
Vender specific network devices
LAN objects
2: OPNET
A network object that represents a LAN entity
Cloud objects
Represents a cluster of routers or ISP
Attributes
20
Device inputs that control its behavior
CDS
JJ
Network Domain: Network Objects
Network models consist of nodes, links and subnets
Nodes represent network devices and groups of devices
Servers, workstations, routers, etc.
LAN nodes, IP clouds, etc.
Links represent point-to-point and bus links
Icons assist the user in quickly locating the correct nodes and links
Vendor models are distinguished by a specific color and logo for each
company
Vendor Devices
2: OPNET
Generic Devices
21
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Subnets
23
Contain segments of the network
Add hierarchy to model
Provide geographical and logical organization
Not related to IP subnets
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Device Models
The Standard Model Library comprises the majority of
objects
Routers
Switches
Hubs
Workstations
Servers
Firewalls
Load Balancers
Printers
Graphical conventions for network objects
Models represent both hardware and software full
protocol stacks are modeled
24
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Cloud Models
27
Cloud models represent backbone networks
Helpful for modeling packet transmission through an external network
or ISP
Clouds have attributes such as Latency and Packet Loss Ratio
ATM and Frame Relay clouds support PVCs through the network
CDS
JJ
Object Attributes
Object attributes control device behavior.
All objects have attributes.
2: OPNET
Right-click
28
C DS
JJ
Model Architecture
Within each IT Guru model is a full
protocol stack
Each protocol is modeled individually
to simulate exactly the protocols
specified behavior
All models are thoroughly tested for
high fidelity
Demo:
2: OPNET
29
Explore Model Architecture with OPNET
Modeler
CDS
JJ
Node Domain
Basic building blocks (modules) include processors,
queues, and transceivers
Processors are fully programmable via their process model
Queues also buffer and manage data packets
Transceivers are node interfaces
Interfaces between modules
Packet streams
Statistic wires
2: OPNET
Stat Wire
Receiver
Packet Stream
Queues
Transmitters
Processor
30
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Process Domain
31
Process model components
State transition diagrams
Blocks of C code
OPNET Kernel Procedures (KPs)
State variables
Temporary variables
A process is an instance of a process model
Processes can dynamically create child processes
Processes can respond to interrupts
JJ
Background Maps
2: OPNET
CDS
TIFF, MIFF (MapInfo), and
GEOTIFF image maps can
be imported, as shown
below
Map backgrounds add
geographical context and make
models easy to interpret
32
JJ
IT Guru Workflow
Projects and Scenarios
C DS
Startup Wizard
Building Topologies
2: OPNET
33
Creating Topologies
Network Object
Model Libraries
LAN and Cloud Objects
Object Attributes
Model Architecture
Subnets
Creating Traffic
Choosing Statistics
Viewing Results
To represent a person using e-mail and downloading files:
Edit Application Config node to support email and FTP
Define the level of use or use a predefined level
Define a user in the Profile Config node that uses the email and FTP
applications you just configured
Set the client to support the user profile you just created
Set the server to support the email and FTP applications
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Common Networked Applications
35
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Common Networked Applications
37
Includes various network
applications with predefined load levels
View and edit these settings
by selecting a predefined
load and then selecting
Edit
Custom
Off, Edit
Database
Off, Low Load, Medium Load, High Load, Edit
Off, Low Load, Medium Load, High Load, Edit
FTP
Off, Low Load, Medium Load, High Load, Edit
HTTP
Off, Light Browsing, Heavy Browsing, Searching,
Image Browsing, Edit
Off, Text File, B/W Images, Color Prints, Edit
Remote Login
Off, Low Load, Medium Load, High Load, Edit
Video Conferencing
Off, Low Resolution Video, High Resolution Video,
VCR Quality Video, Edit
Voice
Off, PCM Quality Speech, PCM Quality and Silence
Suppressed, Low Quality Speech, Low Quality and
Silence Suppressed, IP Telephony, IP Telephony and
Silence Suppressed, GSM Quality Speech, GSM
Quality and Silence Suppressed, Edit
JJ
IT Guru Workflow
Projects and Scenarios
CDS
Startup Wizard
Building Topologies
2: OPNET
Creating Topologies
Network Object
Model Libraries
LAN and Cloud Objects
Object Attributes
Model Architecture
Subnets
Creating Traffic
Choosing Statistics
Viewing Results
40
C DS
JJ
Choosing Statistics
Before running a simulation, choose statistics that will help
answer your questions about the network
Also choose statistics that will validate your network model
and ensure its accuracy
After running the simulation, view graphs for those
statistics you chose
Four types of statistics are available
2: OPNET
- Global Statistics
- Node Statistics
- Link Statistics
41
CDS
JJ
Choosing Statistics Global Statistics
Represents values for all nodes in the network
Use global statistics to look at overall performance of
applications or protocols
Example: End-to-End Delay for all HTTP web page
downloads
To collect global statistics
2: OPNET
DES / Choose Individual Statistics /
Global Statistics
42
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Choosing Statistics Node Statistics
43
Information specific to each individual node
Examples: End-to-End Delay for all HTTP web page
downloads from a particular workstation or server CPU
utilization for each server
Collect node statistics on all
relevant nodes at once or
on individual nodes
To collect a statistic on all nodes,
use:
DES / Choose Individual Statistics /
Node Statistics
For a specific node: Right-click
on the node, Choose
Individual Statistics
Similar to Node Statistics
Statistics of point-to-point or
bus links such as throughput,
utilization, packet loss ratio,
and queuing delay
To collect a statistic on all links:
DES / Choose Individual
Statistics / Link Statistics
To collect a statistic on a
specific link: Right-click the link,
Choose Individual Statistics
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Choosing Statistics Link Statistics
44
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Configuring and Running Simulations
45
Name
Description
Duration
Duration of simulation, in
simulated time
Seed
Random number
generation seed
Values Per
Statistic
Number of values to be
collected for each statistic
Run
Execute the simulation for
this scenario
JJ
IT Guru Workflow
Projects and Scenarios
CDS
Startup Wizard
Building Topologies
2: OPNET
Creating Topologies
Network Object
Model Libraries
LAN and Cloud Objects
Object Attributes
Model Architecture
Subnets
Creating Traffic
Choosing Statistics
Viewing Results
46
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Plotting Results
49
Sometimes it might be useful to view multiple results at once
Multiple graphs can be displayed within the same graph panel in a
stacked or overlaid format
2: OPNET
CDS
JJ
Applying Filters to Results
Variety of mathematical filters can be applied to results data
As Is filter is the default and represents the raw data (as if there is
no filter)
Average filter is
commonly used to plot the
running sample mean of the
raw results data
You can view filtered traces
in a new graph panel, or add
traces to existing graph
panels
50
2: OPNET
C DS
JJ
Comparing Results Between Scenarios
52
Comparing Results automatically selects and presents the
corresponding results from all other scenarios
CDS
JJ
Summary IT Guru
DES:
Simulates precise protocol effects for capacity planning, tuning protocol
behavior, response time engineering, technology migration, QoS, etc.
ACE:
Application performance troubleshooting: visualize performance,
diagnose problems, explore solutions
Traffic,
Topology, and
Configuration
DES
MVI, VNES, GUI
Virtual Network
Environment
Application Trace
Sniffer, OPNET Application Capture Agent, etc.
54
ACE
Graphs, web reports,
charts, for all timevarying network
performance metrics
(e.g., app response time,
queue depths,
convergence time,
protocol behavior, etc.)
Application Visualization,
Diagnosis, Analysis,
Protocol Decodes
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ESP 12F ESP8266 Module Connection TestDocument8 pagesESP 12F ESP8266 Module Connection TestsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Split Core Current Transformer: CR3100 SeriesDocument1 pageSplit Core Current Transformer: CR3100 SeriessolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- BoardMountPressureSensor ABP2SeriesDatasheet IssueCDocument39 pagesBoardMountPressureSensor ABP2SeriesDatasheet IssueCsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Specification: Front View Side View Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageProduct Specification: Front View Side View Schematic DiagramsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- dht11 & dht22Document15 pagesdht11 & dht22fasfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computing Energy Industrial Medical Transportation: ApplicationsDocument5 pagesComputing Energy Industrial Medical Transportation: ApplicationssolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Sensing Rises To The Challenges of Advanced Embedded SystemsDocument6 pagesCurrent Sensing Rises To The Challenges of Advanced Embedded SystemssolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Invest in High Performance Green Buildings PDFDocument24 pagesWhy Invest in High Performance Green Buildings PDFMohammed AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mca1101-Xx-5: High Accuracy Current Sensor Ic With 1.5Mhz 3Db Bandwidth and Isolation 5A, 20A, 50A, 5V, Fixed GainDocument14 pagesMca1101-Xx-5: High Accuracy Current Sensor Ic With 1.5Mhz 3Db Bandwidth and Isolation 5A, 20A, 50A, 5V, Fixed GainsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- HighByte Presentation HarringtonDocument5 pagesHighByte Presentation HarringtonsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rastreador ATU-620 v4Document2 pagesRastreador ATU-620 v4solbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microgrids TADocument7 pagesMicrogrids TAsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- OX200 User Manual: Bluetooth Indicator Heart Rate (PR) Pulse BarDocument2 pagesOX200 User Manual: Bluetooth Indicator Heart Rate (PR) Pulse BarsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Shelf: Brief DescriptionDocument7 pagesLight Shelf: Brief DescriptionsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Preliminary Study On Internal Light Shelf System Applying IT TechnologyDocument4 pagesA Preliminary Study On Internal Light Shelf System Applying IT TechnologysolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Nanostation M2Document15 pagesDatasheet Nanostation M2André LungarezePas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Transfer System (ATS) Explained in Details PDFDocument5 pagesAutomatic Transfer System (ATS) Explained in Details PDFsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Why We Forget and How To RememberDocument6 pagesWhy We Forget and How To RememberTope Georges-Emmanuel100% (1)
- ATS Operational RequirementsDocument7 pagesATS Operational RequirementssolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To IoT PDFDocument94 pagesIntroduction To IoT PDFsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current Sensors Replace Inductive Sensor Sand SwitchesDocument8 pagesEddy Current Sensors Replace Inductive Sensor Sand SwitchessolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Six Steps of Humidification Design: Step 1: Review Building ConstructionDocument8 pagesThe Six Steps of Humidification Design: Step 1: Review Building ConstructionsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network SegregationDocument13 pagesNetwork SegregationsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- DrayTek White Paper Router Security Best PracticeDocument24 pagesDrayTek White Paper Router Security Best PracticesolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seven Properties of Highly Secure DevicesDocument10 pagesSeven Properties of Highly Secure DevicessolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tool Box Training - How To Torque Electrical ConnectionsDocument2 pagesTool Box Training - How To Torque Electrical ConnectionssolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration Essentials Ebook PDFDocument64 pagesCalibration Essentials Ebook PDFsolbahia100% (1)
- DAHUA-Digital Villa VTO User's ManualDocument39 pagesDAHUA-Digital Villa VTO User's ManualsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- LG AireAcond 20multi20v20ii20outdoors202008 PDFDocument33 pagesLG AireAcond 20multi20v20ii20outdoors202008 PDFsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Backup, Standby, and Emergency Power For High-PerformDocument3 pagesDesigning Backup, Standby, and Emergency Power For High-PerformsolbahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- So NetDocument110 pagesSo NetRaj_Jai03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial PassengerDocument15 pagesArtificial Passengerakinsoji ayomidePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 The Future of InformationDocument19 pagesChapter 13 The Future of InformationKhairul bariahPas encore d'évaluation
- Men 4210 QigDocument13 pagesMen 4210 QigVivek Kumar RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceic3006 Lecture 5Document88 pagesCeic3006 Lecture 5sarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - Overview of C#Document31 pagesModule 2 - Overview of C#api-19796528Pas encore d'évaluation
- VOL 2 SEC 3 1 - SCOPE OF WORKS Rev 2 PDFDocument189 pagesVOL 2 SEC 3 1 - SCOPE OF WORKS Rev 2 PDFsivaguruk250% (2)
- 02 - Shadowrun - Gear ListDocument26 pages02 - Shadowrun - Gear ListDiss onancePas encore d'évaluation
- 7 ITIL 4 FN GlossaryDocument9 pages7 ITIL 4 FN Glossarypavithra chinniPas encore d'évaluation
- M Information Systems 3rd Edition Baltzan Test Bank DownloadDocument172 pagesM Information Systems 3rd Edition Baltzan Test Bank DownloadJoyce Leonard100% (17)
- Kgisl Selected Students ListDocument4 pagesKgisl Selected Students ListNishanthPas encore d'évaluation
- PLM Case StudyDocument4 pagesPLM Case StudyMANOJPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Rotary Cutoff ValveDocument4 pages2012 Rotary Cutoff ValveZikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Ags20 Series Universal Aggregation PlatformDocument7 pagesAgs20 Series Universal Aggregation PlatformGonzalo FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Streetcar Final PaperDocument21 pagesDC Streetcar Final PaperElissa SilvermanPas encore d'évaluation
- 120scmapi PDFDocument1 680 pages120scmapi PDFSasidhar Bhagavan SunkaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CMN OIL FREE COMPRESSOR - CompressedDocument4 pagesCMN OIL FREE COMPRESSOR - CompressedAriantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat Forklift v160b Operation Maintenance ManualDocument9 pagesCat Forklift v160b Operation Maintenance Manualxycedfsf100% (34)
- Data Communications and Networks (IT-213) : Spring 2021Document9 pagesData Communications and Networks (IT-213) : Spring 2021sso640238Pas encore d'évaluation
- Using The ETDR Word Template: Masters Theses and ReportsDocument22 pagesUsing The ETDR Word Template: Masters Theses and ReportsdineshsirasatPas encore d'évaluation
- EK Gladiator 80 Spec SheetDocument1 pageEK Gladiator 80 Spec SheetRafael JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Radar System Using Rduino PDFDocument4 pagesRadar System Using Rduino PDFYasser Auliya PPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Microphones : IndexDocument6 pagesDynamic Microphones : IndexJuan Gabriel NiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1fm S4hana2021 BPD en MXDocument67 pages1fm S4hana2021 BPD en MXEnrique MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Project MajorDocument2 pagesProject MajorHarshPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Analysis of Efficient and Low Complexity MIMO-OFDM Using STBC and V-BLASTDocument66 pagesPerformance Analysis of Efficient and Low Complexity MIMO-OFDM Using STBC and V-BLASTDheeksha ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- CHM 11-3 SyllabusDocument6 pagesCHM 11-3 SyllabusruthraquinoPas encore d'évaluation
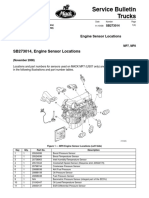
- SB 273 014 Engine Sensor Locations Nov 19 2008 1 PDFDocument4 pagesSB 273 014 Engine Sensor Locations Nov 19 2008 1 PDFImade EmadePas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Robotics in Healthcare and Medical DevicesDocument1 pageApplications of Robotics in Healthcare and Medical Devicesrowena salapiPas encore d'évaluation
- A DSL For Collaborative Business ProcessDocument6 pagesA DSL For Collaborative Business ProcesskenPas encore d'évaluation