Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SH
Transféré par
Ponnusamy KumarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On Line Resources For Large Group Teaching Learning in Relatively SH
Transféré par
Ponnusamy KumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
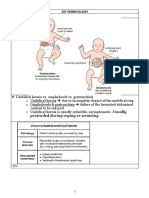
PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
1,2
Ponnusamy
Dr PK_BIOGEN INNO-VISION 2015
1
RN
3
B
Dr Kumar
Ms Jegathambigai1
and Ms Sindhu
Biochemistry & Genetics, International Medical School (IMS) Management & Sciencne University,
1
AIMST University School of Medicine, 08100 Kedah, Malaysia
2
ST Matthews University School of Medicine (SMU), Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, BWI
3
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vellore Institute of technology (VIT) Vellore, India
Abstract
PKU is a inborn error of Phenylalanine (PA) metabolism, the occurrence of PKU varies among ethnic groups and geographic regions 1
worldwide. In the United States, PKU occurs in 1 in 10,000 to 15,000 newborns. Infants with classic PKU are normal at birth but if
untreated show slow development, severe mental retardation, autistic symptoms, and loss of motor control. Children may have pale skin
and white-blonde hair. The neurotoxic effects relate to high levels of PA and not to the phenylketones (PK) from which the name of the
disease derives.
Objective: To delineate the molecular and biochemical basis of PKU, diagnosis and management as well to facilitate
USMLE preparatory Course: BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources for Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively
4
Short Time.
3
Molecular-Biochemical Basis of the Disease /
Disorder: PKU is a metabolic disease
characterizied by accumulation of PA and its
by-products in the blood of fetuses and newborns.
PKU results from a defect in the enzyme
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of White Matter
Pathophysiology
Abnormalities
in
Patients
with
PKU
Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH), such that PA is
of PKU
not converted to Tyrosine. The alternative
Clinical Signs & Symptoms
conversion of PA to PPA causes accumulation of the
PKU &
Neuropathology
latter as a toxin in the CNS, which can lead to
severe mental retardation.
PKU
Phenotype
Klung & Cummings 1997
DEFICIENCY
5
PKU
Musty Odor, Blue Eyes, Microcephaly &
Mental Retardation
Pleotropy of PKU
Dysmorphic Features
in Maternal PKU
Bridge to Pharmacology-Toxicology / Management: Diet low
in Phenylalanine, avoid aspartame, diet important during pregnancy.
6
Contraindications:
Aspartame
(N-aspartyl-phenylalanine
methyl
2
ester), which is widely used as an artificial sweetner, must be strictly
avoided by Phenylketonurics. Women with PKU who become
pregnant must be especially careful about the phenyl alanine level in
Bridge to Genetics / Inheritance: Autosomal recessive their blood so as not to adversely affect neuorologic development in
7
(AR), metabolic genetic disorder, characterized by a
the fetus. Infants born to with phenyl ketonuric mothers without
mutation in the gene for the hepatic enzyme PAH,
metabolic control during pregnency have a high risk of mental
2A
retardation, microcephaly and low birth weight.
rendering it nonfunctional.
Laboratory Diagnosis: Infants are routinely screened a
Behavioural Science / Community Medicine / Ethics: PKU Support
few days after birth for blood PA level as well as urinary Society / Genetic counseling-Prenatal Screening in Chorionic Villi
Sampling / Referral to PKU Specialty Care Centres.
phenyl pyruvic acid and phenyl acetic acids levels.
MCQ: A child with white-blond hair, blue eyes, and
pale complexion is on a special diet in which one of
the essential amino acids is severely restricted. He
has been told to avoid foods artificially sweetened
with aspartame.
9
Ans: A. The child has PKU; aspartame contains
10
phenylalanine. These children may be blond, blue
Dr PK_BIOGEN INNO-VISION 2015. Doc1
eyed, and pale complected because of deficient
References: Kaplan & Google.com melanin production from tyrosine.
A
Phenylalanine Tyrosine
B
Homogentisate
Valine
Maleylacetoacetate
Leucine
C
D
Methylmalonyl CoA TCA Cycle
E
F
Acetyl-CoA Glutamate
G
Alanine Pyruvate
What you have brought while coming, and what you
are going to take away while going?. The Only Thing
What You Are Going to Take Away is Karma_
Just Educate The Society_Dr P Kumar, BIO-GEN.
PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
Dr Kumar
Pleotropy-Abnormalities Associated with Metab Disorders
*
Ponnusamy
Dr P KUMAR_BIOGEN INNO-VISION 2015
& Dr Jegathambigai RN
Mother: The ONLY Visible GOD I Know
Acknowledgements: Lippincott, Google.com & All On-Line Resources
General Dysmorphisms (abnormality in shape or size), ODOUR.
H & N - CataCNS - Tone, seizures, tense fontanelle.
Resp - Kussmauls, tachypnea. CVS - Myocardial dysfunction.
Abdo HEPATOMEGALY. Skin Jaundice. Cataracts, retinitis pigmentosa.
Family History Helpful to Rule Out IEM.
CONSANGUINITY, ethnicity, inbreeding. Neonatal deaths, fetal losses.
Maternal family history. males - X-linked disorders. All-mitochondrial
DNA is maternally inherited. A positive family history may be helpful!.
Timing of onset of symptoms. After feeds were started?. Response
to therapies.
3
Bridge to Molecular
Biology & Genetics
Bridge to
Behavioural Science
2
Ferric ChlorideTest
Patients With PKU
Bridge to
Genetics
Bridge to ETHICS
Bridge to
Behavioural
Science
Prenatal Screening & Genetic Counselling on PKU
Prenatal Diagnosis of PKU
USMLE STEP 1 Q-1
PKU Biochemistry
Bridge to Genetics
12
1. Which of the metabolites below is a
precursor of tyrosine.
A. L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (dopa).
B. Dopamine.
C. Norepinephrine.
D. Epinephrine.
E. Phenylalanine.
Ans: E.
DIAGNOSIS
Phenylalanine Metabolism
7
6
What Are The Common Signs & Symptoms of Metabolic Diseases in the Neonate?.Acute life
threatening illness. encephalopathy - lethargy, irritability, coma. Vomiting, & respiratory distress.
Seizures, Hypertonia, Hepatomegaly. Hepatic dysfunction / jaundice. Odour, Dysmorphism, failure to
thrive (FTT), Hiccoughs.
15. A new test is developed that can non-radioactively label compounds in the human body. As a physician with a back-ground In the
new field of metabolomics, you assess a 21-year-old with classical phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine is fed with a label in the phenyl
ring. In the urine, in which of the following compounds would you expect to find the greatest amount of label?.
A. Tyrosine.
B. Tryptophan.
C. Epinephrine.
D. Phenylketone.
E. Acetate. Answer: D. Phenylketonutria (PKU) is a defect in phenylalanine hydroxylase, resulting in a block in the conversion of p
Henylalanine to tyrosine. Phenylalanine accumulates in in both disorders and to converted to phenylketones. Tyrosine is the product
whose formation is blocked, and epinephrine, a product of tyrosine, would not be made or labelled. Acetate and tryptophan are very
far downstream from tyrosine.
PKU &
Neuroscience
10
11
USMLE STEP 1 Q-2
Epidemiology
USMLE STEP 1 MCQ
Note & Disclaimer: The content in this e-Cognitive Concept Map on BIO-GEN is
based on the knowledge that I acquired studying regular reference books and On-Line
Learning Resources in Google, PUBMed ect., and after years of teaching biochemistryGenetics to Medical and Allied Health Science students in PBL Based Integrated Med
Curriculum. The sourvce of the figures, animation used in this Map is mentioned where
ever applicable, and they are used purely for teaching Biochemistry-Genetics to
audience and no monetary benefit intended out of it. If copyright owner of the figures
used in this Map do not agree with this disclaimer, they are welcome to contact me about
it and, I will delete their content and source from my presentation. Thanking You!.
2
13
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- UW Notes - 9 - Gastero-Intestinal ArrangedDocument61 pagesUW Notes - 9 - Gastero-Intestinal ArrangedMohammed SadoonPas encore d'évaluation
- HY Endocrine UsmleDocument22 pagesHY Endocrine UsmleNakhal JararPas encore d'évaluation
- NeurologyDocument22 pagesNeurologyEnrique ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- UW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesDocument41 pagesUW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsDocument1 pageDisease Pathognomonic Sign: Muddy Brown CastsRafey AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- April v1.1 2022Document188 pagesApril v1.1 2022Mamado IdrisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospitals That Offer ObservershipsDocument6 pagesHospitals That Offer ObservershipsNisarg DavePas encore d'évaluation
- Practice GI QuestionsDocument14 pagesPractice GI QuestionsJenna DantPas encore d'évaluation
- INI-CET 2020 ALL Solutions FULL-MergedDocument119 pagesINI-CET 2020 ALL Solutions FULL-MergedDr ajay purushottamPas encore d'évaluation
- HY MSK - AnatomyDocument88 pagesHY MSK - AnatomyHumna Younis100% (1)
- 5 Days To Step 1Document4 pages5 Days To Step 1Deborah PetersPas encore d'évaluation
- A11 - Pediatrics Main Handout Oct 2022 Karmina Marie Dela Fuente 2Document107 pagesA11 - Pediatrics Main Handout Oct 2022 Karmina Marie Dela Fuente 2karminadelafuente94Pas encore d'évaluation
- REMS Obgyn Shelf Notes Dec 2021Document53 pagesREMS Obgyn Shelf Notes Dec 2021Swarna BanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology & Oncology. Anatomy 56Document60 pagesHematology & Oncology. Anatomy 56Heran TeferiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Genetics USMLE Practice Questions (2 of 4)Document13 pagesBiochem Genetics USMLE Practice Questions (2 of 4)MedSchoolStuff100% (2)
- Pediatric Nursing Practice TestDocument10 pagesPediatric Nursing Practice TestEthel Gretchen Casalla71% (7)
- 17 July RecallsDocument5 pages17 July RecallsDelaPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Step 2: Clinical Knowledge (CK)Document7 pagesUSMLE Step 2: Clinical Knowledge (CK)Нваневу СильванусPas encore d'évaluation
- Cns PathologyDocument18 pagesCns Pathologysunnyorange8Pas encore d'évaluation
- CV - Dr. Atif Ashraf (Physician)Document6 pagesCV - Dr. Atif Ashraf (Physician)dratifashrafPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET PG MOCK TEST MergedDocument103 pagesNEET PG MOCK TEST MergedShaik AmjadPas encore d'évaluation
- McKenzie Vs WilliamsDocument38 pagesMcKenzie Vs Williamstonhamil100% (2)
- Dengue Nov2019Document87 pagesDengue Nov2019Marie Razel Lopez100% (1)
- "Cephalometrics Is The Language in Which The Poetry of Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Is Written" - Cecil SteinerDocument97 pages"Cephalometrics Is The Language in Which The Poetry of Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Is Written" - Cecil Steinersanjay100% (1)
- Distinguishing TRALI and TACODocument6 pagesDistinguishing TRALI and TACOl1o2stPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report Multispeciality HospitalDocument13 pagesProject Report Multispeciality HospitalChetan Kabra87% (15)
- DR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDocument1 pageDR Kumar Ponnusamy Biochemistry-Genetics USMLE Preparatory Course BIOGEN Reusable On-Line Resources For Large Group Teaching-Learning in Relatively Short TimeDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- Nbme 13Document10 pagesNbme 13jettyvikasPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry UW NotesDocument38 pagesBiochemistry UW NotesAnonymous lLiWgjFiPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE Review Q&As On Phenylketonuria (PKU) - DR P KumarDocument4 pagesUSMLE Review Q&As On Phenylketonuria (PKU) - DR P KumarDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (1)
- First Aid Step 1 2017 Sample RevisionsDocument9 pagesFirst Aid Step 1 2017 Sample RevisionsFirst Aid/USMLE-Rx100% (2)
- UW Notes - 3 - MicrobiologyDocument45 pagesUW Notes - 3 - MicrobiologyKimberly KanemitsuPas encore d'évaluation
- NBME 16 FlashreviewDocument27 pagesNBME 16 Flashreviewilse torresPas encore d'évaluation
- A-Define: (10 Degrees) Total Marks 150Document4 pagesA-Define: (10 Degrees) Total Marks 150khaled mohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Blueprints - Radiology PDFDocument134 pagesBlueprints - Radiology PDFBenny KMPas encore d'évaluation
- Errata 2018 First Aid For The Usmle Step 1 Pub 6-1-18Document5 pagesErrata 2018 First Aid For The Usmle Step 1 Pub 6-1-18AmitShettyPas encore d'évaluation
- UVA QuestionsDocument61 pagesUVA QuestionsjhhjjhPas encore d'évaluation
- NeurologyDocument14 pagesNeurologyMedSchoolStuffPas encore d'évaluation
- Block 13 Patho SlidesDocument62 pagesBlock 13 Patho SlidesLennon Ponta-oyPas encore d'évaluation
- Professional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Document25 pagesProfessional Skills Review Central Nervous System (CNS)Noora AlmuailiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 pageExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Neonatal Disease-Bi GuangliangDocument43 pagesIntroduction of Neonatal Disease-Bi GuangliangsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Final USMLE ScheduleDocument7 pagesFinal USMLE Schedulerobert_bahnsen100% (1)
- 1 Q PDFDocument32 pages1 Q PDFAhmad DamatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Renal Buzzword ChartDocument6 pages2 Renal Buzzword ChartTyler KingPas encore d'évaluation
- QuizletDocument104 pagesQuizletS.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesWriting Multiple Choice Questionsbrokenwings4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goljan Errata SheetDocument11 pagesGoljan Errata SheetVishala MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Aid: Usmle Mnemonics: o o o o oDocument25 pagesSecond Aid: Usmle Mnemonics: o o o o oAnthony LPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneticsDocument54 pagesGeneticsmarwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hy EndoDocument20 pagesHy EndoNaresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Contact Privacy Policy Sitemap Terms of Service Advertisement Submit ArticleDocument10 pagesHome Contact Privacy Policy Sitemap Terms of Service Advertisement Submit ArticlesquidblitzPas encore d'évaluation
- For 350 MbbsDocument48 pagesFor 350 MbbsNAYAB HASSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Workbook of BiochemDocument22 pagesWorkbook of BiochemMedStudent MedStudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Mcqs Made EasyDocument62 pagesPathology Mcqs Made EasygyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical StudentsDocument1 pageRetinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical StudentsPonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Erpm 1Document33 pagesErpm 1Nivethitha NarayanasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- STEP 1 CluesDocument3 pagesSTEP 1 CluesRaji NaamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument34 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiaAmir MuhrizPas encore d'évaluation
- COVERAGE For USMLEDocument1 pageCOVERAGE For USMLEJemarey de RamaPas encore d'évaluation
- 224 in Step 1 To 263 in Step 2CK Write-Up - Step2Document2 pages224 in Step 1 To 263 in Step 2CK Write-Up - Step2lashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics TestDocument62 pagesGenetics TestGabby Becerra-Steck100% (1)
- NEW UMHS Clinical Student HandbookDocument25 pagesNEW UMHS Clinical Student HandbookAmit TamboliPas encore d'évaluation
- Passing The Boards Can USMLE and Orthopaedic PDFDocument5 pagesPassing The Boards Can USMLE and Orthopaedic PDFICH KhuyPas encore d'évaluation
- PG Notes 3Document29 pagesPG Notes 3Eliza SparkPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 - Pku (BSN 1-A)Document11 pagesGroup 4 - Pku (BSN 1-A)oluanah13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spider Model E-Cognitive Concept Map - Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy, Siddarth Srigkul & DR Jegathambigai RN - BIO-GEN PEARLS 2016Document2 pagesSpider Model E-Cognitive Concept Map - Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy, Siddarth Srigkul & DR Jegathambigai RN - BIO-GEN PEARLS 2016Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - Case of The Week - USMLE Genetics - All About Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy & DR Jegathambigai RNDocument2 pagesCognitive Concept Map - Case of The Week - USMLE Genetics - All About Cystic Fibrosis (CF) - DR Kumar Ponnusamy & DR Jegathambigai RNPonnusamy KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicineDocument1 pageCognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicinePonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicineDocument1 pageCognitive Concept Map - Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout - DR P Kumar & Senthilkumar Rajasekaran - ST Matthew's Uni School of MedicinePonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Document1 pageCognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Cognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Document1 pageCognitive Concept Map - XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM - DR P Kumar, Et Al, 2015Ponnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Retinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical StudentsDocument1 pageRetinoblastoma Cognitive Concept Map - DR Kumar Ponnusamy and DR Jegathambigai RN - Problem Based Learning (PBL) For Large Groups Medical StudentsPonnusamy Kumar100% (1)
- Carti DermatoDocument29 pagesCarti Dermatosepis10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ankle XraysDocument43 pagesAnkle XraysKastiaji HendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Endometriosis Classification An UpdateDocument8 pagesEndometriosis Classification An UpdateZurya UdayanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Otomycosis Due To Aspergillus Niger With Tolnaftate PDFDocument3 pagesTreatment of Otomycosis Due To Aspergillus Niger With Tolnaftate PDFMei Risanti SiraitPas encore d'évaluation
- P Harm Cheat SheetsDocument13 pagesP Harm Cheat SheetsAhmad Syafaat SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Splints (Compatibility Mode)Document14 pagesSplints (Compatibility Mode)wese87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Examination: Textbook of OrthodonticsDocument3 pagesFunctional Examination: Textbook of OrthodonticsndranPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal MicrobiologyDocument36 pagesRenal MicrobiologyHayelom MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Raptor AnesthesiaDocument13 pagesRaptor AnesthesiaRaj Nath100% (1)
- Beleta WoundDocument18 pagesBeleta WoundahmadhsnPas encore d'évaluation
- PortfolioDocument11 pagesPortfolioSherry IgnacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Burns AlgorithmDocument10 pagesBurns AlgorithmAmmaarah IsaacsPas encore d'évaluation
- Article - CVD Cardiac Arrest - Bls AclsDocument2 pagesArticle - CVD Cardiac Arrest - Bls AclsAkhosh SomarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Levetiracetam EpilepsiaDocument6 pagesLevetiracetam EpilepsiaAndresPimentelAlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- BARCDocument6 pagesBARCMohaideen SubairePas encore d'évaluation
- HomeopathyDocument18 pagesHomeopathypksharma75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Melomed Pregnancy JournalDocument24 pagesMelomed Pregnancy JournalCelvin SohilaitPas encore d'évaluation
- IG Bio Case StudyDocument2 pagesIG Bio Case StudyMikaela SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Staff ListDocument2 pagesHospital Staff ListOsheen KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Anophthalmos in Benin CityDocument3 pagesCongenital Anophthalmos in Benin CityLjubomirErdoglijaPas encore d'évaluation
- PGIMER Chandigarh Assistant Professor NotificationDocument23 pagesPGIMER Chandigarh Assistant Professor NotificationBaldhariPas encore d'évaluation