Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
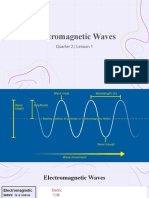
UV Radiation Types & Effects
Transféré par
KhillotheepicTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
UV Radiation Types & Effects
Transféré par
KhillotheepicDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ultraviolet radiation (UV radiation or ultraviolet rays) is a form of energy
traveling through space.
Smaller wavelength = more energy.
electromagnetic radiation that is contained and traveling in little packets
are called photons.
The sun is a major source of ultraviolet rays. 99% of its rays are in the
form of visible light, ultraviolet rays, and infrared rays
ultraviolet rays often carry the unfortunate circumstance of
containing too much energy
The energy contained in ultraviolet rays is very high it can knock electrons
away from the atoms, or cause molecules to split. This can change the
chemical structure of the molecule, which is very harmful to living
organisms, as it can cause cell damage and irregularities by mutating its
genetic code.
UV-C is most energetic and most harmful; UV-A is least energetic and
least harmful.
UV-C rays do not reach the earth's surface because of the ozone layer.
When UV-C rays meet ozone molecules at high layers of the atmosphere,
the energy inside them is enough to break apart the bond of the molecule
and absorb the energy.
UV-B rays have a lower energy level and a longer wavelength than UVC. Their energy is not sufficient enough to split an ozone molecule so
some of them extend down to the earth's surface.
UV-A rays do not have enough energy to break apart the bonds of the
ozone, so UV-A radiation can pass the earth's atmosphere almost
unfiltered.
Researchers know that UV can be damaging to RNA however they found
out that some parts of the molecule act as a protective shield for other
parts. The nitrogenous bases absorb and diffuse UV radiation, protecting
the RNAs pentose-phosphate backbone.
Since double strands can provide more UV protection to the RNA backbone than
single-strands, the scientists suggest that base-pairing may have originated as a trait to
provide greater UV protection.
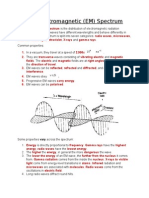
There is another spectrum which is divided into the following 3 regions: near
ultraviolet (NUV), far ultraviolet (FUV), Extreme ultraviolet (EUV)
Classified depending on how energetic the UV radiation is and by its wavelength
Scientists have divided the ultraviolet part of the spectrum into three regions: the near
ultraviolet, the far ultraviolet, and the extreme ultraviolet. The three regions are distinguished
by how energetic the ultraviolet radiation is, and by the "wavelength" of the ultraviolet light,
which is related to energy.
The near ultraviolet, abbreviated NUV, is the light closest to optical or visible light. The
extreme ultraviolet, abbreviated EUV, is the ultraviolet light closest to X-rays, and is the most
energetic of the three types. The far ultraviolet, abbreviated FUV, lies between the near and
extreme ultraviolet regions. It is the least explored of the three regions.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ultraviolet RadiationDocument3 pagesUltraviolet RadiationbirlacementPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Wave and Plasma Structures in the Auroral and Subauroral GeospaceD'EverandNonlinear Wave and Plasma Structures in the Auroral and Subauroral GeospacePas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet: "UV" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See - For Other Uses For "Ultraviolet", SeeDocument2 pagesUltraviolet: "UV" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See - For Other Uses For "Ultraviolet", SeeGemma CanicosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet Light Presentation PDFDocument16 pagesUltraviolet Light Presentation PDFParis ArcillaPas encore d'évaluation
- UvraysDocument14 pagesUvraysReviews Benchmarks & TipsPas encore d'évaluation
- UltravioletDocument17 pagesUltravioletDhanmeet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Visible Light Is One Way Energy Moves AroundDocument2 pagesVisible Light Is One Way Energy Moves AroundNash Gemar Braga EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- UV Radiation Effects and VisibilityDocument9 pagesUV Radiation Effects and VisibilityKevinPas encore d'évaluation
- The electromagnetic spectrum and uses of ultraviolet wavesDocument3 pagesThe electromagnetic spectrum and uses of ultraviolet wavesJhade Kianne Mendoza BarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet LightDocument25 pagesUltraviolet LightHyojin100% (2)
- Lesson 2-Solar RadiationDocument78 pagesLesson 2-Solar RadiationZyra Yvonne MangligotPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic WavesCrisanta GanadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet RaysDocument24 pagesUltraviolet RayschrisshitPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigatory Project in BiologyDocument8 pagesInvestigatory Project in BiologyHarpreet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves General Science LessonDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Waves General Science LessonNarahmie RuadoPas encore d'évaluation
- UltravioletDocument154 pagesUltravioletAnonymous gUjimJKPas encore d'évaluation
- UV Radiation ExplainedDocument24 pagesUV Radiation Explainednishanth naikPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Project On OzoneDocument26 pagesBiology Project On OzoneAkansha Agarwal33% (3)
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumFOODHEALTHPas encore d'évaluation
- Sunscreen Guide Explains Key ConceptsDocument121 pagesSunscreen Guide Explains Key ConceptsRizweta DestinPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigatory Project in BiologyDocument17 pagesInvestigatory Project in Biologyrajath96100% (2)
- BaboDocument13 pagesBaboZezo EdrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet (UV) Light IsDocument1 pageUltraviolet (UV) Light Isparin advaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Responses To Sunlight of Human SkinDocument4 pagesResponses To Sunlight of Human SkinTargetPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Radiation Particle Radiation Acoustic Gravitational Radiation Ionizing Non-IonizingDocument1 pageElectromagnetic Radiation Particle Radiation Acoustic Gravitational Radiation Ionizing Non-IonizingtestaksdfPas encore d'évaluation
- Em SpectrumDocument24 pagesEm SpectrumFender CoomstonePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Project On Ultraviolet RaysDocument14 pagesBiology Project On Ultraviolet Raysokesh27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uv RaysDocument1 pageUv RaysChloe de RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet Radiation: Distribution and Variability: Article OutlineDocument280 pagesUltraviolet Radiation: Distribution and Variability: Article OutlineTaher El NoamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sia83 3notesDocument5 pagesSia83 3notesAmaechi ZalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Radiation: The Classical and Quantum DescriptionDocument256 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation: The Classical and Quantum DescriptionMpaphi Map'z Dambe100% (1)
- The Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentDocument30 pagesThe Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentJhunner Buan100% (1)
- الإشعاع - WikipediaDocument80 pagesالإشعاع - WikipediaA.M.B M.B.M.EPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2Lee DabinPas encore d'évaluation
- Dalaodao InfographicDocument1 pageDalaodao InfographicLizalyn DalaodaoPas encore d'évaluation
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Information Search (Physics)Document1 pageInformation Search (Physics)Jay-Jay Kaigetsu SalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Copy 2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesCopy 2nd QuarterLiwayway MadaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Document (6 Sci Presentation)Document5 pagesDocument (6 Sci Presentation)Ivan UmaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyDocument42 pagesRadiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyChristine Marielle Claroniño ApoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5. The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pages5. The Electromagnetic SpectrumTomas Aquino DiquitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 Research PresentationDocument13 pagesScience10 Research PresentationIvan UmaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet Radiation and The Eye - An Epidemiologic StudyDocument52 pagesUltraviolet Radiation and The Eye - An Epidemiologic StudyMaria Gerber RozaPas encore d'évaluation
- What is Visible Light? Understanding the Spectrum of Light WavesDocument9 pagesWhat is Visible Light? Understanding the Spectrum of Light WavesJF BatucalPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Reading PassageDocument2 pagesWaves Reading PassagedavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 5 Physics 10 UV ScriptDocument3 pagesGroup 5 Physics 10 UV ScriptEmilrie RogeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Ge321 Lec2.1Document18 pagesGe321 Lec2.1Hazel Jane Vega UyPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Things Have Color: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ExplainedDocument5 pagesWhy Things Have Color: The Electromagnetic Spectrum Explainedbinyang lalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Radiation of The High Alps: Mario BlumthalerDocument11 pagesSolar Radiation of The High Alps: Mario BlumthalerDale Francis ClapanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultra VVI - 20231119 - 124804 - 0000Document30 pagesUltra VVI - 20231119 - 124804 - 0000chechecabral76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-2-Solar Thermal EnergyDocument15 pagesUnit-2-Solar Thermal EnergyDr. Navneet Kumar PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- YesDocument7 pagesYesforgamingandschoolpurposesonlyPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is RadiationDocument17 pagesWhat Is RadiationaljonPas encore d'évaluation
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceseradillajoshgabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultraviolet Radiation Group 5Document30 pagesUltraviolet Radiation Group 5Blessie Zyren BasinangPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Bilat 123Document2 pagesApplication Bilat 123qroww birdPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 ReviewerDocument6 pagesGrade 10 ReviewerDino M PangilinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDocument20 pagesWireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Effects of Radiation On HumansDocument10 pagesEffects of Radiation On Humanshirenpatel_universalPas encore d'évaluation
- Harmony and CounterpointDocument1 pageHarmony and CounterpointKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- Music: Elements of Harmony and CounterpointDocument1 pageMusic: Elements of Harmony and CounterpointKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- Absorption Spectra of Nickel: CobaltDocument24 pagesAbsorption Spectra of Nickel: CobaltKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- G.B.Pergolesi - Siciliana For Flute and Piano (Basso Continuo)Document4 pagesG.B.Pergolesi - Siciliana For Flute and Piano (Basso Continuo)Fabio Falsini100% (2)
- The World and Going TruthDocument1 pageThe World and Going TruthKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- Let It SnowDocument5 pagesLet It SnowKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- The world: its place and our viewDocument1 pageThe world: its place and our viewKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ultra AbsorptionDocument8 pagesThe Ultra AbsorptionKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- Se Tu M'amiDocument4 pagesSe Tu M'amiSharon Eilisen100% (1)
- The Sugar Plum FairygDocument3 pagesThe Sugar Plum FairygKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- GHGHHGGHGHGHHHHHHHHHHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGHHHHH Gfds FDSG SFD Gfds Fs DGDocument1 pageGHGHHGGHGHGHHHHHHHHHHGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGHHHHH Gfds FDSG SFD Gfds Fs DGKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- JVM Back-UpDocument1 pageJVM Back-UpKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerpointrubricDocument1 pagePowerpointrubricapi-237801056Pas encore d'évaluation
- % Quiz Complex 2014Document2 pages% Quiz Complex 2014KhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- % DC Voltage Ex Ex SolutionDocument2 pages% DC Voltage Ex Ex SolutionKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- The Oscilloscope: For The Measurement of Voltage: AC and DCDocument16 pagesThe Oscilloscope: For The Measurement of Voltage: AC and DCKhillotheepicPas encore d'évaluation
- Qdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateDocument178 pagesQdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateFarzana BatoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Image Processing System AbstractDocument4 pagesDigital Image Processing System AbstractTelika RamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Citizen Journalism Practice in Nigeria: Trends, Concerns, and BelievabilityDocument30 pagesCitizen Journalism Practice in Nigeria: Trends, Concerns, and BelievabilityJonathan Bishop100% (3)
- A&P Book - Aeronautical Charts and CompassDocument17 pagesA&P Book - Aeronautical Charts and CompassHarry NuryantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Damplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Document5 pagesDamplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Vikram MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Political SubjectDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Political SubjectlukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding PerformanceDocument65 pagesUnderstanding PerformanceClaudia AfinekPas encore d'évaluation
- Escaping The Digital Dark AgeDocument5 pagesEscaping The Digital Dark AgeKarlos lacallePas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Reason Why I Like DoraemonDocument2 pages2 Reason Why I Like Doraemonpriyanka shafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrDocument4 pagesThe Confidence Myth and What It Means To Your Career: by Tara MohrdargeniPas encore d'évaluation
- LLRP PROTOCOLDocument19 pagesLLRP PROTOCOLRafo ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of K-Pop Music On The Academic PDocument29 pagesImpact of K-Pop Music On The Academic Pdave tayron paggao100% (1)
- HA200Document4 pagesHA200Adam OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Herschel 10027757Document83 pagesHerschel 10027757jurebiePas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Characterization 3 LoggingDocument47 pagesReservoir Characterization 3 LoggingMohamed AbdallahiPas encore d'évaluation
- AufEx4 02 02Document28 pagesAufEx4 02 02BSED SCIENCE 1APas encore d'évaluation
- Textual Equivalence-CohesionDocument39 pagesTextual Equivalence-CohesionTaufikPas encore d'évaluation
- Political Philosophy of J S MillDocument9 pagesPolitical Philosophy of J S MillRajkumar SunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Audit of Organizational Communication NetworksDocument17 pagesAudit of Organizational Communication NetworksLissette ObleaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Year-Industrial Training Letter SampleDocument3 pages3rd Year-Industrial Training Letter SampleSai GowthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Write Hello in The PDFDocument95 pagesWrite Hello in The PDFraghupulishettiPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDocument8 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDipteemaya BiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Newsletter April.Document4 pagesNewsletter April.J_Hevicon4246Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Cultural Diversity Phenomenon in Organisations and Different Approaches For Effective Cultural Diversity Management - A Literary Review PDFDocument21 pagesThe Cultural Diversity Phenomenon in Organisations and Different Approaches For Effective Cultural Diversity Management - A Literary Review PDFeugene123Pas encore d'évaluation
- 015-Using Tables in ANSYSDocument4 pages015-Using Tables in ANSYSmerlin1112255Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution To Information TheoryDocument164 pagesSolution To Information Theorynbj_133% (3)
- Biologicalisation - Biological Transformation in ManufacturingDocument32 pagesBiologicalisation - Biological Transformation in ManufacturingGuillermo AvilesPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical PartsDocument25 pagesANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical Partsgiaphongn100% (5)
- Digital Citizenship RubricDocument1 pageDigital Citizenship Rubricapi-300964436Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bangla Web AddressDocument5 pagesBangla Web Addressapi-3864412100% (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseD'EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowD'EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (48)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingD'EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessD'EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismD'EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceD'EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidD'EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayD'EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (125)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesD'EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2193)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishD'EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsD'EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (94)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterD'EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (409)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeD'EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifePas encore d'évaluation
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)D'EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (155)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityD'EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (380)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldD'EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsD'EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (57)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceD'EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityD'EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (76)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishD'EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationD'EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseD'EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsD'EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)