Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Form 4 Ujian Ogos
Transféré par
jesunathan44@yahoo.com0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
97 vues3 pagesphysics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentphysics
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
97 vues3 pagesForm 4 Ujian Ogos
Transféré par
jesunathan44@yahoo.comphysics
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
1
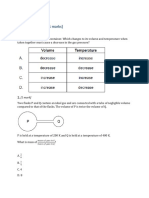
Which of the following is true?
A The unit of heat is o C
B Heat is a form of energy
C Heat flows from a cold substance to a hot substance.
Heat and temperature are
A forms of energy
B
scalar quantities
C measured in the same S.I.units
D measured by the same instrument.
0 oC is equivalent to
A - 273 K B -173 K C 100 K
D 273 K E 373 K
An earth-monitoring satellite falls into the earths atmosphere
at a high velocity and reaches at the sea surface with a high
temperature. After a while the temperature of the satellite is
same as the temperature of the sea water. This is caused by
A The heat released by the satellite
B The heat absorbed by the sea water
C The satellite is cooled by the sea water
D The satellite and the sea water are in thermal equlibrium
The diagram shows a metal sphere P at 80oC is immersed in
a cooler liquid Q.
Thermal equilibrium is reached when
A temperature of P = temperature of Q
B mass of Q displaced = mass of P
C volume of Q = volume of P
D specific heat capacity of P = specific heat capacity of Q
6
The diagram shows two copper blocks, L and M, touching
each other. The initial temperatures of L and M are 50 oC
and 30 oC respectively.
Which statement is correct when L and M are at thermal
equilibrium?
A Temperature of L is higher than M
B The quantity of heat in L is the same as in M
C Rate of change in temperature of L is bigger than that
of M
D Net rate of heat flow between L and M is zero
7
Which relationship between T1 , T2 and T is true?
A T1 > T2 > T
B
T2 > T1 > T
C T1 > T > T2
D
T2 > T > T1
8
Which principle is used in a Mercury thermometer?
A Principle of conservation of temperature
B Principle of conservation of energy
C Principle of thermal equilibrium
D Principle of the forces in equilibrium
Regarding to the fixed points in the Celsius scale of a
mercury thermometer , which of the following is true?
Lower fixed point Upper fixed point
A the freezing point the boiling point
of mercury
of mercury
B the boiling point
the freezing point
of mercury
of mercury
C the freezing point the boiling point
of water
of water
D the boiling point
the freezing point
of water
of water
10
The lengths of the mercury column in a thermometer at the
ice point and the steam point are 5 cm and 25 cm
respectively. When the thermometer is placed in a liquid ,
the length of the mercury column is 12 cm. What is the
temperature of the liquid?
A 30 o C B 35 o C C 55 o C D 70 o C E 85o C
11
The lengths of the mercury thread in a thermometer are 8
cm and 20 cm respectively at 0oC and 100oC. What is the
length of the thread when the thermometer is placed in a
substance at -25oC.
A 4 cm B 5 cm C 10 cm D 12 cm E 16 cm
12
The diagram shows a thermometer.
A
B
C
D
Which modification will increase the sensitivity of
the thermometer?
Using a longer capillary tube
Using a bulb with a thicker wall
Using a glass stem with a thicker wall
Using a narrower bore of capillary tube
13
Heat energy is supplied at the same rate to 0.4 kg of
substance P and 0.4 kg of substance Q in similar containers.
The temperature of substance P rises faster.
This is because the substance P
A is less dense than substance Q
B is more dense than substance Q
C evaporates less readily than substance Q
D has a smaller specific heat capacity than substance Q
14
The diagram shows solid blocks M and N of equal mass,
which are being heated. The initial temperature of M and N is
the same and heated by the same amount of energy.
The diagram shows object A and object B are of
temperatures T1 and T2. The heat flows from A to B until the
thermal equilibrium is reached at a temperature T.
19
When 0.6 kg water of 40o C is mixed with 0.4 kg water of
90o C, what is the final temperature of the mixture?
A 55o C B 60o C C 65o C D 70o C E 75o C
20
0.5 kg liquid M at 40o C is mixed with 2 kg liquid N at 25o
C. The mixture is stirred . What is the maximum temperature
reached by the mixture? ( specific heat capacity of liquid M =
8.4 x 103 J kg -1o C-1) ( specific heat capacity of liquid N =
4.2 x 103 J kg -1 o C-1 )
A 28o C B 30o C C 32.5o C D 34.5o C E 38.5o C
21
A beaker is filled with 2 kg of water at 30 o C . A plumbum
sphere of mass 1.5 kg at 90o C is placed in the beaker. The
final temperature reached by the water and the sphere are
31.5o C .What is the specific heat capacity of plumbum?
( specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 x 103 J kg -1 o C-1,
A 144 J kg -1 o C-1 B 568 J kg -1oC-1 C1425 J kg -1 o C-1
D 2070J kg-1oC-1
E 3020 J kg-1oC-1
22
A 240 V, 2 kW electric heater is immersed in 6 kg of a
liquid and switched on for 5 minutes.What is the rise in
temperature of the liquid?( specific heat capacity of the liquid
= 4.2 x 103 J kg -1 o C-1 )
A 5 o C B 10 o C C 15 o C D 18 o C
E 24 o C
23
A 800 watt kettle holds 0.5 kg of water at 30 o C. It is turned
on until the water boils. What is the time taken to boil the
water? (specific heat capacity = 4.2 x 103 J kg -1oC-1)
A 76 s B 168 s C 184 s D 340 s E 520 s
24
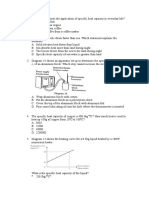
The diagram shows the temperature time graph of a liquid .
The liquid is heated by using a 0.4 kW heater . The mass of
the liquid is 0.2 kg .
It observed that M is hot faster than N. This observation is
due to the difference in
A density B melting point
C latent heat of fusion
D specific heat capacity
15
16
The diagrams show four types of metal block of the same
mass being heated using the same quantity of heat for 10
minutes. Which metal block shows the highest increase in
the temperature?
The diagrams represent two beakers contain liquid W and
liquid X respectively. Each liquids receiving the same heat
energy Q.
Which statement about W and X is correct?
A The specific heat capacity of W is half the
specific heat capacity X.
B The specific heat capacity of W is twice the
specific heat capacity X.
C The specific heat capacity of W is same as the specific
heat capacity X.
17
What is the energy released by a metal block of mass 5.0 kg
when it is cooled from 30o C to 20 o C. (specific heat capacity
of the metal = 500 J kg-1o C -1)
A 1.25 x 104 J B 2.5 x 104 JC
5.0 x 104 J
D 6.25 x 104 J E 8.85 x 104 J
18
3 200 J of energy is absorbed by a copper block of mass 0.1
kg when it is heated from 30o C to 110 o C. What is the
specific heat capacity of copper?
A 200 J kg-1 o C -1 B 400 J kg-1 o C-1 C 800 J kg-1 o C -1
D 1000Jkg-1oC -1 E 2000Jkg-1oC -1
What is the specific heat capacity of the liquid?
A 1000J kg -1 o C-1 B 2000 J kg -1o C-1 C 3000 J kg -1 o C-1
D 4000 J kg -1 o C-1
E 5000 J kg -1 o C-1
25 A metal block is dropped from a height of 82 m. What is
the rise in the temperature of the metal block after it hits the
ground?( specific heat capacity of the metal block = 410
J kg -1oC-1 )
A 0.5 o C B 1.0 o C C 2.0 o C D 4.0 o C E 8.0 o C
26
An Asteroid of mass 500 kg travellling in atmosphere with
a velocity 2000 m s-1 . The temperature of the Asteroid rises
by 10000oC. What is the specific heat capacity of the
Asteroid ?
A 100 J kg -1 o C-1 B 200 J kg -1oC-1 C 400 J kg -1 o C-1
D 1000Jkg -1oC-1 E 2000J kg -1o C-1
27
Which of the following is true?
Specific heat capacity of
cooking utensil
A
B
C
D
high
low
high
low
Specific heat of
the handle of the
cooking utensil
high
high
low
low
28
A substance changes from a liquid state to a solid state. This
process is called
A fusion B sublimation C vaporization
D solidification
29
A liquid naphthalene begin to solidify.Which of the following
is true?
A Temperature decreases B Temperature increases
C Heat is absorbed
D Heat is released
30
31
The latent heat is released when
A liquid changes to steam B solid changes to steam
C steam change to liquid
The specific latent heat of fusion of ice is the quantity of
energy required to
A change 1 kg of ice from ice to water with 1o C rise in
temperature
B change 1 kg of ice from water to steam without a
change in temperature
C change 1 kg of ice from water to steam with 1o C rise
in temperature
D change 1 kg of ice from ice to water without a change
in temperature
35
0.4 kg of water at 100o C. What is the quantity of heat
required to change the water to steam at 100oC? [ Specific
latent heat of vaporisation of water =2.3x106 Jkg-1 ]
A 9.2 x102 J B 9.2 x105 J C 9.2 x106 J
D 9.2 x108 J E 9.2 x1010 J
36
What is the quantity of heat released to change 0.3 kg of
water at 0o C to ice at 0o C ?[ specific latent heat of fusion
of ice = 3.3 x105 J kg -1 ]
A 9.9 x102 J B 9.9 x104 J C 9.9 x106 J
D 9.9 x108 J E 9.9 x1010 J
37
What is the quantity of heat required to change 0.02 kg of
ice at 0o C to water at 40o C ?[ specific heat capacity of
water = 4.2 x 103 J kg-1 o C-1 specific latent heat of fusion
of ice = 3.34 x105 J kg -1 ]
A 3 320 J B 3 360 J C 6 680 J D 10 040 J
E 267 200 J
38
A 2 000 W electric heater is used to change 2 kg of water at
100o C to steam. What is the time tken to change the water
to steam? [ Specific latent heat of vaporisation of water
=2.26 x106 Jkg-1 ]
A 590 s B 1540 s C 2260 s D 3280 s E 4070 s
39
A 500 W electric heater is used to heat 0.1 kg of a liquid
to its boiling point. The liquid is allowed to boil in 3 minutes
again until the mass of liquid becomes 0.06 kg. What is
the specific latent heat of vaporisation of the liquid?
A 4.75 x106J kg-1 B 3.85 x106J kg-1 C 2.25 x106J kg-1
D 1.15 x106J kg-1 E 1.45 x106J kg-1
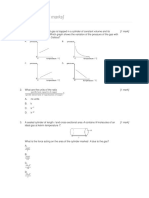
The graph shows the cooling curve of a substance.
Which of the following is true?
A At section WX the average kinetic energy of the
substance molecules decreases
B At section XY heat is not released
C At section YZ the substance exits in the
solid and liquid states
33
34
The graph shows the heating curve of a substance.
At which stage is the substance in a solid and liquid state at
the same time?
A PQ
B QR
C RS
D ST
32
The heat absorbed during the process is called
A specific heat capacity of vapour
B specific heat capacity of liquid
C latent heat of vaporisation
D latent heat of fusion
The diagram shows a process in which water is changed to
steam.
40 A steam burn is more damaging than a burn from boiling
water at the same temperature. It is because
A the water boils and released heat to surroundings
B the steam has a higher temperature than the boiling
water
C the heat released from condensing steam.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Document4 pages2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Raistlin Chan Ching KitPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermometry: T/s T/KDocument9 pagesThermometry: T/s T/KJing Yu VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- TranscriptDocument29 pagesTranscriptNurAfifah OsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sDocument9 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sPavithiran50% (2)
- (183 Marks) : (1 Mark)Document33 pages(183 Marks) : (1 Mark)Yu SunPas encore d'évaluation
- TDocument12 pagesTholdonpainendsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFDocument21 pagesHasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFIrnawati KarubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 3 - RevisionDocument33 pagesTopic 3 - RevisionYu Seung KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Exercise 5Document26 pagesPhysics Exercise 5Law Jing SeePas encore d'évaluation
- Phyf4 Chap4Document71 pagesPhyf4 Chap4Mohd AzlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Revision: (147 Marks)Document31 pagesThermal Revision: (147 Marks)Irnawati KarubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lesson Note SS2 2nd Term 2022 - 1Document103 pagesPhysics Lesson Note SS2 2nd Term 2022 - 1isaac bakare100% (7)
- Atomic PhysicsDocument31 pagesAtomic PhysicsOnur YavuzcetinPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Exercise 3Document19 pagesPhysics Exercise 3Law Jing SeePas encore d'évaluation
- A2 53a ThermalenergyDocument39 pagesA2 53a ThermalenergyHany ElGezawyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 - Thermal - 2020 QuestionsDocument5 pages3.1 - Thermal - 2020 QuestionsHelen TarekePas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Contact and Thermal Equilibrium. Two Objects Are inDocument40 pagesThermal Contact and Thermal Equilibrium. Two Objects Are in11 AniketPas encore d'évaluation
- 73 1st Long Problem Set BDocument13 pages73 1st Long Problem Set BRicardo Jose BracamontePas encore d'évaluation
- Specific Heat CapacityDocument7 pagesSpecific Heat Capacitykeeesh4100% (1)
- Change in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500Document7 pagesChange in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500Ziauddin TaposhPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Thermo (2016)Document7 pagesIB Thermo (2016)Hiroki Nose100% (1)
- Soalan Heat 2 QualitiDocument10 pagesSoalan Heat 2 QualitiShahrir DoralimPas encore d'évaluation
- 73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersDocument12 pages73 Summer 1st LE Set A With AnswersNikkei Pfeiffer TadiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Document5 pagesLesson 4.1 (Smtai 09) .Ilman MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 73 1st Ps 1say14-15Document15 pagesPhys 73 1st Ps 1say14-15Marco ConopioPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Yixiang TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Item 0 20181223050211203Document10 pagesItem 0 20181223050211203DeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Probset 1bDocument12 pagesProbset 1bRegina Marie MaximoPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat CapacitiesDocument9 pagesHeat Capacitiesanwar9602020Pas encore d'évaluation
- WDocument4 pagesWkenenathPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: (Chapter 4) HEAT: (4.2) Specific Heat Capacity Highlight: (30 Minutes)Document7 pagesTopic: (Chapter 4) HEAT: (4.2) Specific Heat Capacity Highlight: (30 Minutes)RusnizaARPas encore d'évaluation
- HKDSE Phy 1A A2 - AllDocument8 pagesHKDSE Phy 1A A2 - Alljackson wongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 18Document94 pagesChap 18noscribdyoucantPas encore d'évaluation
- Icse X Calorimetry Question BankDocument9 pagesIcse X Calorimetry Question BankanimeshtechnosPas encore d'évaluation
- BB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatDocument7 pagesBB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatAh Tiang100% (4)
- 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat Capacity BaruDocument23 pages4.2 Understanding Specific Heat Capacity BarureanizaPas encore d'évaluation
- BB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatDocument7 pagesBB101 Engineering Science Chapter 6 Temperature and HeatMollel TajiriPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 18Document4 pagesCH 18ian jheferPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Revision MC TestDocument28 pagesHeat Revision MC TestCiv NortubPas encore d'évaluation
- PHY 111, Principles of Physics I: C F 32 K 273.15 M TDocument3 pagesPHY 111, Principles of Physics I: C F 32 K 273.15 M TTanjim IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Calorimetry ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesCalorimetry Thermodynamicssanits591Pas encore d'évaluation
- F3 1st ExamDocument10 pagesF3 1st ExamSharon WongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019 1st Sec80Document8 pages2019 1st Sec80Aboahmed Ali0% (1)
- 4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01Document14 pages4 0heat 130415001626 Phpapp01sherlyn may lolPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Phys DC ESQ B 231118 135653Document25 pagesIb Phys DC ESQ B 231118 135653sammeaan khanPas encore d'évaluation
- F.3 Heat NoteDocument12 pagesF.3 Heat Noteskywalker_handsomePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1Document6 pagesChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1maxime namaPas encore d'évaluation
- Igcse Physics MCDocument5 pagesIgcse Physics MCayeayePas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire For Elimination RoundDocument7 pagesQuestionnaire For Elimination RoundJV CustodioPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Exam ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesMidterm Exam ThermodynamicsRoselyn BenavidezPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 73 PS 1 - OriginalDocument13 pagesPhysics 73 PS 1 - OriginalJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsD'EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Inertia Mass ExperimentDocument1 pageInertia Mass Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Ohms Law ExperimentDocument1 pageOhms Law Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- U and V ExperimentDocument2 pagesU and V Experimentjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic Gate 2Document7 pagesLogic Gate 2jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay Force and MotionDocument6 pagesEssay Force and Motionjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Force EsaiDocument8 pagesForce Esaijesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- (9.7.17) Gallery Walk (Environment), 4ODocument4 pages(9.7.17) Gallery Walk (Environment), 4Ojesunathan44@yahoo.com100% (1)
- MRSM Past Years Form 4Document39 pagesMRSM Past Years Form 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Paper 2 Esai 2010Document30 pagesSeminar Paper 2 Esai 2010jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- (9.4.17) Cause and EffectDocument3 pages(9.4.17) Cause and Effectjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3Document30 pagesPaper 3jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Nota Padat ForceDocument22 pagesNota Padat Forcejesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Interference of Wave 1Document4 pagesInterference of Wave 1jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)Document2 pagesCathode Ray Oscilloscope (Cro)jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Nota PadatDocument13 pagesNota Padatjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Esay Section B@C Ting 4Document4 pagesEsay Section B@C Ting 4jesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Fun FactsDocument2 pagesChemistry Fun FactsBabitha MonteiroPas encore d'évaluation
- CLO - Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesCLO - Fluid Mechanicstooba IshfaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Improved Steam Condenser Gas Removal SystemDocument7 pagesImproved Steam Condenser Gas Removal Systemtfernandes.x18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Pressurization SystemDocument78 pagesAircraft Pressurization Systemsai prasad100% (4)
- Brief Introduction To Superconductivity PDFDocument69 pagesBrief Introduction To Superconductivity PDFAbdur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Banana Cold Storage: Chapter 2: Related LiteratureDocument8 pagesBanana Cold Storage: Chapter 2: Related LiteratureVelaPas encore d'évaluation
- MM311 LAB 3 FinalDocument7 pagesMM311 LAB 3 FinaldipanshilPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On PhotoconductivityDocument6 pagesReview On PhotoconductivitySumon DebnathPas encore d'évaluation
- IChemE Online Poster CompetitionDocument1 pageIChemE Online Poster CompetitionBilly HughPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemsheets AS 1057 Group 2 Physical PrperrtiesDocument1 pageChemsheets AS 1057 Group 2 Physical PrperrtiesYusuf AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Fluid StaticsDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Fluid StaticsSoban Malik100% (1)
- Product Water Pump DatasheetDocument3 pagesProduct Water Pump DatasheetMoubarakAtitoMohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 NS PDFDocument31 pagesUnit 1 NS PDFAbhijeeth NagarajPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Room-Temperature Organic and Molecular MagnetsDocument2 pagesA Review of Room-Temperature Organic and Molecular MagnetsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- MO 201 Magnetic Material 2023Document44 pagesMO 201 Magnetic Material 2023RashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity Flow, SubmergenceDocument7 pagesGravity Flow, Submergenceflashkickerazar0% (1)
- R For MAT-02-Task Agreement 2013: ReferenceDocument31 pagesR For MAT-02-Task Agreement 2013: ReferenceMauricio García CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10Document25 pages10aytajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - Pump SelectionDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Pump SelectionZakariya MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2211379722008154 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2211379722008154 MainArunPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Falling Film Evaporators in The Food Industry DesignDocument4 pages1 Falling Film Evaporators in The Food Industry DesignIvan Ruben Capuñay IzquierdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Manhours & Method Statement - Pump ManualDocument5 pagesManhours & Method Statement - Pump ManualbecpavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex B (Informative) - Control Valve Sizing Flow Charts: - 41 - ISA-75.01.01-2007 (IEC 60534-2-1 Mod)Document3 pagesAnnex B (Informative) - Control Valve Sizing Flow Charts: - 41 - ISA-75.01.01-2007 (IEC 60534-2-1 Mod)Abhishek Kumar SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Oil Gas Mechanical Refrigeration enDocument2 pagesBrochure Oil Gas Mechanical Refrigeration enRafraf EzdinePas encore d'évaluation
- 08 - Section-3 Three Phase SeparationDocument19 pages08 - Section-3 Three Phase SeparationOladayo Siyanbola100% (1)
- Fractional DistillationDocument5 pagesFractional DistillationLê LộcPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of Production of Liquefied Methane - The Component of Rocket PropellantDocument8 pagesThe Process of Production of Liquefied Methane - The Component of Rocket Propellantmercy giftPas encore d'évaluation
- MA3006 Tutorials (7 To 10) AnswersDocument12 pagesMA3006 Tutorials (7 To 10) AnswersWilliam LuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Separator: Calculation SheetDocument10 pagesTest Separator: Calculation SheetAffian WidjanarkoPas encore d'évaluation