Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Teodas HPLC
Transféré par
natinlala0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
65 vues4 pageskghyug
Titre original
teodas HPLC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentkghyug
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
65 vues4 pagesTeodas HPLC
Transféré par
natinlalakghyug
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Kepedasan merupakan salah satu indikator mutu cabai merah yang
dicerminkan oleh kandungan capsaicin. Capsaicin adalah senyawa utama
capsaicinoid yang terdapat dalam buah cabai dari tanaman genus Capsicum.
Cabai mengandung 0,1 sampai 1,5% capsaicin tergantung dari jenis cabai
dan varietasnya serta kondisi lingkungan tempat tumbuhnya (Edmond dkk.,
1983). Senyawa capsaicinoid terdiri dari capsaicin, dihydrocapsaicin,
nordihydrocapsaicin, homodihydrocapsaicin, homocapsaicin, dan vanillyl
pelargonamide (Edmond dkk., 1983; Govindarajan, 1985; Todd dkk., 1997).
Capsaicin merupakan komponen terbesar yaitu sebesar 69% dari total
capsaicinoid diikuti dihydrocapsaicin sebesar 22%. Kandungan homocapsaicin
dan homodihydro capsaicin terdapat dalam konsentrasi sangat kecil (Andrew,
1979; Govindarajan, 1985). Oleh karena itu rasa pedas pada cabai
diidentikkan dengan capsaicin.
Cabai mengandung senyawa aktif capsaicin dengan rumus kimia
C18H27NO3. Senyawa capsaicin memiliki kelarutan rendah dalam air tetapi
larut dalam lemak, dan mudah rusak oleh proses oksidasi. Capsaicin terdiri
dari unit vanil amin dengan asam dekanoat yang mempunyai ikatan rangkap
pada rantai bagian asam (Andrew, 1979).
Derajat kepedasan cabai diukur dengan satuan Scoville. Skala scoville
mengukur konsenstrasi capsaicin dalam cabai. Terdapat beberapa tingkat
kepedasan cabai atau scoville rating yang berkisar antara 0 sampai
16.000.000 SHU (Scoville Heat Unit). Sebagai contoh bell pepper (termasuk
juga paprika) mempunyai skala scoville 0 (nol), ini berarti bell pepper tidak
pedas sama sekali karena tidak mempunyai zat capsaicin (Todd dkk., 1997).
Namun cabai rawait (Thai pepper atau birds eye pepper) atau jika di
Malaysia sering disebut chili padi mempunyai skala scoville 50.000 hingga
100.000 SHU.
Selama penyimpanan akan terjadi degradasi mutu cabai merah giling seperti
degradasi capsaicin, penurunan vitamin C, perubahan warna. Degradasi
capsaicin meningkat seiring dengan peningkatan temperatur (Ahmed dkk.,
2000 dan Ahmed dkk., 2002). Proses pemanasan pada pengolahan puree
cabai merah yang dilakukan exhausting pada suhu 82C selama 10 menit
dapat memperpanjang masa simpan produk 2 hingga 3 bulan (Renate, 2004).
Kehilangan nilai gizi juga terjadi pada penyimpanan yang terlalu lama,
terutama pada kondisi suhu kamar atau suhu panas. Pertumbuhan jamur
dapat dikurangi dengan menurunkan suhu tetapi jamur juga kurang aktif di
ruang yang tidak lembab atau ruangan yang kering.
Kondisi proses terhadap parameter kinetika dapat dinyatakan dengan
pendekatan model kinetika maupun model matematis seperti bentuk linier,
eksponensial maupun hiperbola. Suhu merupakan faktor yang berpengaruh
terhadap perubahan produk pangan. Semakin tinggi suhu penyimpanan
maka laju reaksi sebagai senyawa kimia akan semakin cepat.. Untuk
menentukan kecepatan reaksi kimia bahan pangan dalam kaitannya dengan
perubahan s
(AGRITECH, Vol. 34, No. 3, Agustus 2014
MODEL KINETIKA DEGRADASI CAPSAICIN CABAI MERAH GILING PADA
BERBAGAI KONDISI SUHU PENYIMPANAN
Kinetic Model of Capsaicin Degradation on Red Chilli Paste at Various Storage
Temperature
Dharia Renate1, Filli Pratama2, Kiki Yuliati2, Gatot Priyanto2 )
The major capsaicinoids present in most varieties of the chili are capsaicin
(tran-8-methyl-N-vanillyl- 6-nonenamide)and dihydrocapsaicin (8-methyl- Nvanillylnonanamide). In addition, other minor ones are also found such as
nordihydrocapsaicin, and dihydrocapsaicin. Capsaicin has been used in
neurological research to stimulate sensory nerves and also to treat bladder
inflammation. It is also found in topical ointments used for arthritis and
neuralgia (Kaale et al., 2002), and exerts its effect on the sensory nerves by
interacting with the vanilloid receptor, promoting the release of substance P
as well as other cytokines (Surh et al., 2005).The determination of
*Corresponding author.
Email: pandyagh@rediffmail.com
All Rights Reserved
capsaicinoids in chili peppers, topical cream (Kaale et al., 2002), self-defense
weapons (Reilly et al., 2001a) and aerosol defense sprays (Spicer and
Almirall, 2005) has been of increasing interest for many reasons.
Chilli punge
high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method has replaced the
organoleptic method since the HPLC method is considered the most reliable
and accurate method for determining both the amount of capsaicin and
pungency in chili samples. HPLC is currently the most popular and reliable
technique for the analysis of capsaicinoids. The technique has been mainly
associated with UV absorption detection. Reversed phase-HPLC separation of
capsaicinoids in some chili varieties was achieved using UV-Visible detector
method. The linearity range of calibration curve was 0.0 to 200 ug/ml
Validation was carried out by establishing the repeatability and Limits of
detection (LOD/MDL) and Limit of quantitation (LOQ). The optimized
conditions were applied for the determination of capsaicinoids in varieties of
the chili samples.
In this work, reverse phase HPLC was used. The application of HPLC methods
allows one to obtain a sensitivity and selectivity gain over other conventional
methods. The aim of this study was to develop and validate an LC method for
determining capsaicin in chilli samples determined in less than 20 min after
extraction.
International Food Research Journal 21(3): 1137-1142 (2014) Journal
homepage: http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my
Study of quality control and uncertainty in estimation of capsaicinoids
content and pungency in real chili samples using RP HPLC
Mukund Nagarnaik, Anil Dhakulkar and *Girish Pandya.. 2014
Capsanthin is the most important carotenoid pigment in red pepper (Kim et
al. 2002). It has different properties such as antioxidant and
immunoenhancing activities (Rhim et al. 2011; Topuz et al. 2011). Capsaicin
(8-methyl- N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide) is the main pungency compound
isolated from red pepper (Othman et al.
2011). As a spicy by-product, it affects the quality of capsanthin extracted
from hot red pepper. In fact, capsaicin is also used to treat pain and
inflammation associated with various diseases (Shakhidoyatov et al. 2001;
Zhang et al. 2008; Kim et al. 2009).
Capsanthin and capsaicin are usually extracted using conventional organic
solvents and then iso- lated from the crude extract. This multistep process
has some disadvantages such as high consumption of energy, inefficiency,
and need of large amounts of a solvent. Although supercritical carbon dioxide
(SC-CO2) extraction, a new method, can be used to extract capsanthin and
capsaicin (Uquiche et
al. 2004; Kwon et al. 2011), it has no advantage in the extraction of some
polar components, such as capsanthin and capsaicin, because carbon dioxide
is a weak polar solvent. In addition, SC-CO2 extraction has stringent
equipment requirements.
The salting-out extraction (SOE) system composed of short-chain alcohol,
hydrophobic organic solvents, inorganic salt, and water is a novel method
used to separate active constituents from fermentation broth or natural plant
(Liu et al. 2010; Dai et al.
2011). Recently, aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) and three-liquid-phase
system (TLPS) have been used to extract and isolate effective components
from natural products such as anthocyanins from mulberry (Wu et al. 2011),
geniposide from garde- nia fruit (Pan et al. 2002), piceid, resveratrol, and
emodine from Polygonum cuspidatum (Wang et al.
2008), and salvianolic acid B from the crude extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Zhi
et al. 2006). This method has many advantages such as low solvent requirement, low cost, low equipment requirements, and short extraction time.
Vol. 32, 2014, No. 1: 109114 Czech J. Food Sci.
This study aims to establish TLPS with hydrophilic and hydrophobic organic
solvents and inorganic salt aqueous solution as well as to extract capsanthin
and capsaicin from red pepper in a single step. A fast extraction and
separation method of capsanthin and capsaicin was realised by analysing the
distribution of capsanthin and capsaicin in different phases.
(Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No.
21266028, and by the Technology Innovation Program of Xinjiang Bingtuan,
Project No. 2012CB015.
Three-liquid-phase Extraction and Separation
of Capsanthin and Capsaicin from Capsicum annum L.
Yan-Yan DANG1,2, Hua ZHANG1 and Zhi-Long XIU1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2 Kelompok 5 Koefisien Partisi-1Document18 pages2 Kelompok 5 Koefisien Partisi-1Lupita Churry Aini0% (1)
- Teknik Asas Pembiakan Hibrid Ikan Keli Thailand (Clarias sp.)D'EverandTeknik Asas Pembiakan Hibrid Ikan Keli Thailand (Clarias sp.)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Draft Artikel Riset Wening GalihDocument34 pagesDraft Artikel Riset Wening GalihWening GalihPas encore d'évaluation
- Pengaruh Jenis Kemasan Dan Cara Penyimpanan Terhadap Mutu Minuman Kunyit Asam (Curcuma Domestica Val. - Tamarindus Indica L.)Document8 pagesPengaruh Jenis Kemasan Dan Cara Penyimpanan Terhadap Mutu Minuman Kunyit Asam (Curcuma Domestica Val. - Tamarindus Indica L.)Yunita Siti MardhiyyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bakhtra Et Al, 2017Document9 pagesBakhtra Et Al, 2017Meliani AinunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Praktikum Teklab PascapanenDocument26 pagesLaporan Praktikum Teklab PascapanenDiana Puspita Sari SariPas encore d'évaluation
- KOR-METUJIDocument8 pagesKOR-METUJIRahmawati YuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Admin, 3 (2) 6 Ainul Yahya RevDocument7 pagesAdmin, 3 (2) 6 Ainul Yahya RevindiyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 14.I1.0167 Aloysius Ladaywa - BAB IVDocument7 pages14.I1.0167 Aloysius Ladaywa - BAB IVMirna DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Fitolimia 2Document13 pagesJurnal Fitolimia 2inayah100% (1)
- Jurnal JSKD 01 1 1Document9 pagesJurnal JSKD 01 1 1yuliana rizqiawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Identifikasi Bahan Kimia Obat dalam Jamu Pegal LinuDocument12 pagesIdentifikasi Bahan Kimia Obat dalam Jamu Pegal LinuLerika PrihtiantiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lada Hitam Hal 1, 3Document3 pagesLada Hitam Hal 1, 3Vicha Fatanah0% (1)
- Artikel B.indonesia-2 LobakDocument11 pagesArtikel B.indonesia-2 Lobakmaximiliaus hayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Pengolahan Dan Bioteknologi Hasil PerikananDocument15 pagesJurnal Pengolahan Dan Bioteknologi Hasil PerikananLeonardo SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- PENGARUH PENAMBAHAN KITOSAN SEBAGAI PENGAWET ALAMI PADA PEMBUATAN SIRUP BUAH NAGA (Hylocereus Polyrhizus)Document11 pagesPENGARUH PENAMBAHAN KITOSAN SEBAGAI PENGAWET ALAMI PADA PEMBUATAN SIRUP BUAH NAGA (Hylocereus Polyrhizus)Indra SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah 1Document15 pagesMakalah 1Anonymous C4huq0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fullpapers Bikf490875a769full PDFDocument9 pagesFullpapers Bikf490875a769full PDFIndra KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Riana ZulfaDocument9 pagesRiana ZulfaKiswan SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kumpulan AbstrakDocument43 pagesKumpulan AbstrakYuda PangestuPas encore d'évaluation
- STANDARISASIDocument10 pagesSTANDARISASIAnisah MahardianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Residu PestisidaDocument7 pagesAnalisis Residu PestisidaYodeadetPas encore d'évaluation
- ANTIOKSIDAN BAWANG MERAHDocument12 pagesANTIOKSIDAN BAWANG MERAHEva Apriliyana RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- ChindyMeliana - 1041711028 - TUGAS REVIEW JURNAL PRAKTIK TSBADocument3 pagesChindyMeliana - 1041711028 - TUGAS REVIEW JURNAL PRAKTIK TSBAchindy melianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 2. Laprak ToksikDocument15 pagesKelompok 2. Laprak ToksikEzzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 1 - Analisis 3 JurnalDocument36 pagesKelompok 1 - Analisis 3 JurnalMiniatur IniPas encore d'évaluation
- Standardisasi AdasDocument4 pagesStandardisasi AdasrahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Black GarlicDocument11 pagesTugas Black GarlicArifin HidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 SMDocument13 pages1 SMmarioPas encore d'évaluation
- ANALISIS KADAR BKODocument11 pagesANALISIS KADAR BKOSalep 69 Anti miskinPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis Ester Asam SinamatDocument7 pagesSintesis Ester Asam Sinamatdewi nurhasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Polaritas FlavonoidDocument7 pagesPolaritas FlavonoidSukma NaimPas encore d'évaluation
- 1824-1828 Irma AntasionastiDocument5 pages1824-1828 Irma AntasionastiFina AnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 2 - A - Validasi MetodeDocument38 pagesKelompok 2 - A - Validasi Metodesofyan novrizalPas encore d'évaluation
- EKSTRAK KAENPFERIADocument66 pagesEKSTRAK KAENPFERIAFirda Andi0% (1)
- Analisis Kadar Asam UratDocument10 pagesAnalisis Kadar Asam Uratssundari65580Pas encore d'évaluation
- 391 849 1 PBDocument8 pages391 849 1 PBWisuda 2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Metode PemisahanDocument19 pagesMakalah Metode PemisahanArie Ifans ApotekerPas encore d'évaluation
- ANALISIS PONCEAU 4RDocument9 pagesANALISIS PONCEAU 4REmilia GintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Jamu TradisionalDocument8 pagesJamu TradisionalSitti SartinahPas encore d'évaluation
- JURNAL JaheDocument11 pagesJURNAL JaheFurqoni Nurul UmmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lapsem Bio 1Document10 pagesLapsem Bio 1PSF Mila Mayanti KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- GAMBARAN PARASETAMOLDocument12 pagesGAMBARAN PARASETAMOLRizha ameyliaPas encore d'évaluation
- 61 318 1 PBDocument6 pages61 318 1 PBGita Perdani DamayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Metode EkstraksiDocument11 pagesAnalisis Metode EkstraksiSeptebi Eko PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Farmakognosi DAUN GEDIDocument13 pagesJurnal Farmakognosi DAUN GEDIcecePas encore d'évaluation
- LA ODE RONI SETIAWAN - O1A117028-MAKALAH Standarisasi EkstrakDocument15 pagesLA ODE RONI SETIAWAN - O1A117028-MAKALAH Standarisasi EkstrakLaode Roni Setiawan RamePas encore d'évaluation
- 2632 - Laporan MAI Perc.3Document22 pages2632 - Laporan MAI Perc.3SundariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Ku 1Document10 pagesTugas Ku 1Randi Putra Falesa SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- JurnalDocument9 pagesJurnalIlham nandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Praktikum Aot 1 ProdukDocument17 pagesLaporan Praktikum Aot 1 Produkliza fauziahPas encore d'évaluation
- Kimia Farmasi AnalisisDocument4 pagesKimia Farmasi AnalisisFauzi Akbar NugrahadiPas encore d'évaluation
- ADKARDocument20 pagesADKARGalih SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Artikel Etri Puji RahayuDocument11 pagesArtikel Etri Puji Rahayuroni setiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- HPLCDocument10 pagesHPLCNesti Jetmaira SembiringPas encore d'évaluation
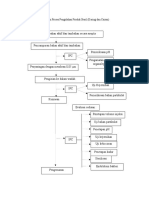
- Rangkaian Proses Pengolahan Produk SterilDocument4 pagesRangkaian Proses Pengolahan Produk SterilnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Lingkungan Kecamatan PadalarangDocument2 pagesAnalisis Lingkungan Kecamatan PadalarangnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- DafpuuuuuuuuuuusDocument4 pagesDafpuuuuuuuuuuusnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Farmakokinetika KlinikDocument17 pagesFarmakokinetika KlinikAmalia AlfiPas encore d'évaluation
- Systane Eye Drops...Document3 pagesSystane Eye Drops...natinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital - 123885-S09009fk-Pengetahuan Ibu-Literatur PDFDocument17 pagesDigital - 123885-S09009fk-Pengetahuan Ibu-Literatur PDFjastin_sinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 - 224diagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Meningitis BakterialisDocument5 pages06 - 224diagnosis Dan Tatalaksana Meningitis BakterialisZeewy DeiruyoPas encore d'évaluation
- ORKITIS PAROTITISDocument5 pagesORKITIS PAROTITISHadimerto UndangPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 - 217CPD - Farmakogenomik Dan Terapi KankerDocument4 pages06 - 217CPD - Farmakogenomik Dan Terapi KankerMuh Akbar BaharPas encore d'évaluation
- ValidasiiDocument3 pagesValidasiinatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jantung KoronerDocument11 pagesJantung KoronerEdwin F. Freecss WoworPas encore d'évaluation
- Pengaruh Konseling Terhadap Kepatuhan Pasien TBC ParuDocument6 pagesPengaruh Konseling Terhadap Kepatuhan Pasien TBC ParunatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISPADocument70 pagesISPAAbdul Zulhairu100% (4)
- Polimorfisme Gen insl3 dan lgr8 sebagai Faktor Risiko KriptorkismusDocument220 pagesPolimorfisme Gen insl3 dan lgr8 sebagai Faktor Risiko KriptorkismusnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- HIpertensiDocument4 pagesHIpertensinatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Bed GranulatorDocument3 pagesFluid Bed GranulatornatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- PERILAKUDocument14 pagesPERILAKUnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spektroskopi InframerahDocument2 pagesSpektroskopi InframerahnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asam Urat - HipertensiDocument4 pagesAsam Urat - HipertensinatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 9Document8 pages2009 9Rista FitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelestarian Tanaman ObatDocument5 pagesKelestarian Tanaman ObatnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antidiare ..Document1 pageAntidiare ..natinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- HipertensiDocument21 pagesHipertensiArief SatriyoPas encore d'évaluation
- ReuploadDocument9 pagesReuploadnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- A8 - B Ringkasan Kajian Air BersihDocument6 pagesA8 - B Ringkasan Kajian Air BersihRepiyanto TariganPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis IsoniazidDocument27 pagesAnalisis IsoniazidnatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prevent and Treat Dehydration BAHASADocument3 pagesHow To Prevent and Treat Dehydration BAHASASebo IrengPas encore d'évaluation
- Latar Belakang Revisi SambilotoDocument2 pagesLatar Belakang Revisi SambilotonatinlalaPas encore d'évaluation