Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
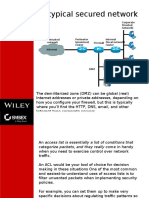
Anatomy of An Access List
Transféré par
boardstDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anatomy of An Access List
Transféré par
boardstDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Infrastructure
address signifies that the whole
source address in the filter should be
ignored. Technically, it doesnt matter what you use as the IP source address here, because it will be ignored.
The all 0s mask on the destination
address means that you want to
the destination address, thus denying
access to all packets that are not permitted because of the previous rule.
numbers because they are backwardcompatible with previous IOS versions.
Turning It On Once you have your access list set up, you must apply it to
the interface before it becomes effective. Just as you would for any change
to an interface configuration, you will
E n d t h e l i s t w i t h a s t a t e m e n t t h a t d e n i e s e v e r y t h i n g.
have to enter config mode and desapply the entire address. If you list with a statement that denies ignate the interface where you want to
wanted to deny access to all ad- everything. This helps you keep track apply the filter. At this point, the list of
dresses on the 130.120.110 network, of the end of the list:
access list statements is referred to as a
you would use a mask of 0.0.0.255. access-list 101 deny ip 0.0.0.0 group. The command to apply access
The 255 in this case means ignore the 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
list 101 to incoming packets on an inlast octet of the address when looking
Of course, if you want to begin terface is: ip access-group 101 in
for a matching packet.
your list by denying specific packets
As soon as you enter this command,
Allowing access only to HTTP on a and you want to allow everything else, the access list will immediately take efhost Here, we permit access only to you would use the same statement fect. Its helpful to start a continuous
the HTTP port on the host and deny with a permit instead of a deny. An ping in another window to a host on
all other access to the host. This re- easier way to state this is to use the the other side of the interface that
quires two lines:
following syntax:
youre filtering to monitor its accessibilaccess-list 101 permit tcp 0.0.0.0 access-list 101 deny ip any any
ity while applying the list. Save your
255.255.255.255 130.120.110.100 0.0.0.0
This statement functions exactly changes with a write memory and a
eq 80
the same as the previous one, and write network if youre backing your
access-list 101 deny ip 0.0.0.0 later versions of the IOS will translate configurations up on a TFTP server.
255.255.255.255 130.120.110.100 0.0.0.0
the longer version into this shorter
You can use the show config
The first statement matches any version when you display it.
command to see which access groups
packet with 130.120.110.100 as the
When you display the list, you may are associated with particular interdestination IP address and with a TCP find that some of the TCP and UDP port faces. This command also will list all of
port equal to 80. The second rule ap- numbers have been changed to a ver- the access list statements at the end.
plies a match to all IP packets with bose description. We prefer to enter An easier way to look at the access lists
Tying Up Loose Ends Although all unmatched packets are dropped by default, its still a good idea to end the
Anatomy Of An Access List
List No.
Rule
access-list xxx
permit or
deny
Pattern Definition
IP or ICMP
(100-199)
TCP or UDP
3
Source
IP address
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Source
Destination
Destination
eq=equal
IP address
IP address
IP address
gt=greater than
mask
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
mask
lt=less than
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx neq=not equal
255=ignore
0=apply
5
1) Every extended access list has a number from 100 to 199, which identifies the list
in two places. When building the list, every line must be labeled with the same
access list number. When you apply the list to an interface on the router, you
must reference it by the same number. Version 11.2 of the IOS allows you to use
a name for the list instead of a number.
255=ignore
0=apply
7
TCP or UDP
destination
port no.
5) Every IP source address in the list must have a mask. The mask lets you determine
how much of the preceding IP address to apply to the filter. In most cases, you will
simply want to put a 255 corresponding to every octet in the IP address that you
want to ignore, and 0 for every octet that you want the packet match to apply to.
6) Every line in the list must have a destination address.
2) A permit or deny rule has to be applied to every line or statement on
the list.
3) If you are only filtering on IP address, you will specify IP (or ICMP for pings and
trace routes) as the protocol. This means that only the IP address is considered for
a match. If you are also filtering on UDP or TCP port, you must specify TCP or UDP.
4) Every line in the list must have a source address.
Required
Optional
7) Every IP destination address in the list must have a mask. See 5 above.
8) This applies to the TCP or UDP port that you are filtering on. In most cases, you will
use the eq, which means equals. This gives you the ability to permit or deny TCP or
UDP ports equal to the port specified. There are cases, however, where you will want
to apply a range of port numbers, which is where the gt, greater than, or lt, less than,
will come in handy.
9) If you have defined the pattern as a TCP or UDP packet, you will have to
have an associated port number.
118 Network Computing April 15, 1998 www.NetworkComputing.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ACL StructureDocument1 pageACL Structurecbrzana100% (1)
- Access Lists ExDocument6 pagesAccess Lists ExSameer BasilPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Document54 pagesCisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Paul100% (2)
- Access Control Lists OverviewDocument6 pagesAccess Control Lists OverviewdondegPas encore d'évaluation
- Configure Extended Access ListsDocument7 pagesConfigure Extended Access Listsrial_ganeshPas encore d'évaluation
- More Access Control Lists: Eumed - GrnetDocument29 pagesMore Access Control Lists: Eumed - GrnetErwin HidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Packet Tracer Activity Extended Acls: Standard ACLDocument2 pagesCCNA Packet Tracer Activity Extended Acls: Standard ACLGhana KumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control ListDocument6 pagesAccess Control ListVishesh MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Access List TutorialDocument5 pagesAccess List TutorialGustavo Muñoz SuroPas encore d'évaluation
- FreeccnalabDocument2 pagesFreeccnalabfranco.pinotti8354Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ex 20 EACLDocument4 pagesEx 20 EACLDileep DamodaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control List (ACL)Document37 pagesAccess Control List (ACL)Nikhil Patel50% (2)
- Access Control ListsDocument11 pagesAccess Control ListsSudhir MaherwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab # 12: Access Control List Access Control ListDocument9 pagesLab # 12: Access Control List Access Control ListMudassir ZiaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Presentation - ACLDocument58 pagesCCNA Presentation - ACLArslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control ListsDocument12 pagesAccess Control ListsJavier Alexander CastellanosPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control Lists - : Access Control Lists (Acls) Can Be Used For Two Purposes On Cisco DevicesDocument17 pagesAccess Control Lists - : Access Control Lists (Acls) Can Be Used For Two Purposes On Cisco DevicesmukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals Cisco 2Document33 pagesFinals Cisco 2eun mun kangPas encore d'évaluation
- Access ListDocument43 pagesAccess ListghanshyamPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA ACL Cheat Sheet UpdatedDocument3 pagesCCNA ACL Cheat Sheet Updatedbitta.ayelePas encore d'évaluation
- Eth103: Basic Switch Router Configuration & Maintenance Access Control Lists (Acls)Document16 pagesEth103: Basic Switch Router Configuration & Maintenance Access Control Lists (Acls)Vivek11Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP de Uso General ACL de La Configuración: ContenidoDocument12 pagesIP de Uso General ACL de La Configuración: ContenidoTriana Humpire SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- PF: Network Address Translation (NAT)Document8 pagesPF: Network Address Translation (NAT)HrishiPas encore d'évaluation
- DisplayFilters - The Wireshark WikiDocument3 pagesDisplayFilters - The Wireshark WikiAKUEPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic IPv4 Access Control ListsDocument21 pagesBasic IPv4 Access Control ListsdeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4:implementing Firewall TechnologiesDocument115 pagesChapter 4:implementing Firewall TechnologiesRyanb378Pas encore d'évaluation
- 451L Summary PDFDocument16 pages451L Summary PDFAnthony AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- All About Access Control Lists PDFDocument25 pagesAll About Access Control Lists PDFSupriyo SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACL and SecurityDocument15 pagesACL and Securityatul1988Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices ACLDocument9 pagesExercices ACLPapa NiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Plane ProtectionDocument104 pagesManagement Plane ProtectionIvan MachuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Linux Iptables Firewall Configuration: Prince - KenshiDocument8 pagesLinux Iptables Firewall Configuration: Prince - KenshiMohith VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers FullDocument16 pagesCCNA 4 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 4 Exam Answers Fullabdel6qui6onez6jaimePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Document3 pagesCisco Access Control Lists (ACL)Arslan SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 94Document4 pagesLab 94Os MayutelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1 5 3 PDFDocument4 pagesLab 1 5 3 PDFSan SokvisalPas encore d'évaluation
- R1 (Config) #Access-List 100 ? Deny Specify Packets To Reject Permit Specify Packets To Forward Remark Access List Entry CommentDocument11 pagesR1 (Config) #Access-List 100 ? Deny Specify Packets To Reject Permit Specify Packets To Forward Remark Access List Entry Commentrichard akpagniPas encore d'évaluation
- UCCN1004 - Lect7 - ACL and Packet FilteringDocument40 pagesUCCN1004 - Lect7 - ACL and Packet FilteringVickRam RaViPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA4CH5SGDocument4 pagesCCNA4CH5SGAustin LivengoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Filtros WiresharkDocument8 pagesFiltros WiresharkalafbhmgPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec.10 11 PDFDocument25 pagesLec.10 11 PDFHaider majedPas encore d'évaluation
- Access ListDocument18 pagesAccess ListRishika JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Re Sequencing ACL EntriesDocument2 pagesRe Sequencing ACL Entriesasapot2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Iptables Tutorial For BeginnersDocument4 pagesIptables Tutorial For BeginnerssaidpmkPas encore d'évaluation
- IP Access Control List SecurityDocument20 pagesIP Access Control List SecurityGorib ManushPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Access ListDocument7 pages8 Access ListChis LebroPas encore d'évaluation
- IP Traffic Management With Access ListsDocument51 pagesIP Traffic Management With Access ListsAbdul MajeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Troubleshooting by Sniffing Packets (Packet Capture)Document5 pagesAdvanced Troubleshooting by Sniffing Packets (Packet Capture)CristiPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control Lists: Advanced Systems Administration CourseDocument21 pagesAccess Control Lists: Advanced Systems Administration CourseKarthik GunasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Simulator QuestionsDocument54 pagesCCNA Simulator Questionscreature1990Pas encore d'évaluation
- NETVÆRK NotesDocument8 pagesNETVÆRK NotesDuxie DoogiePas encore d'évaluation
- Information About Access ListsDocument4 pagesInformation About Access ListsJoseph FleischfresserPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer SheetDocument8 pagesAnswer SheetChris McoolPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA4 V 4.0 Exam Chapter 5 ACLsDocument5 pagesCCNA4 V 4.0 Exam Chapter 5 ACLsrobeitorPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1D'EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Starting Guide for Postfix Mail Server Configuration Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusD'EverandStarting Guide for Postfix Mail Server Configuration Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusD'EverandConfiguration of Postfix Mail Server Supporting Anti Spam and Anti VirusPas encore d'évaluation
- MFJ Catalog 2019Document148 pagesMFJ Catalog 2019boardstPas encore d'évaluation
- Winlink Legality Concerns: Part 97 - Interfering (Qrming) Existing QsosDocument4 pagesWinlink Legality Concerns: Part 97 - Interfering (Qrming) Existing QsosboardstPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo Parts Suitable JLGDocument160 pagesCatalogo Parts Suitable JLGboardst100% (4)
- Ts440s Repair FaqDocument17 pagesTs440s Repair FaqboardstPas encore d'évaluation
- How To 3D Scan With SkanectDocument13 pagesHow To 3D Scan With SkanectMahmut AydinPas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar 31 Adjustable Speed Drive Controllers Installation ManualDocument130 pagesAltivar 31 Adjustable Speed Drive Controllers Installation Manualboardst100% (1)
- The Objective of These Question Is To Help You Reading The Book and Focus On Important Topics in Chapter 5Document3 pagesThe Objective of These Question Is To Help You Reading The Book and Focus On Important Topics in Chapter 5Abdul Rahman AL-MoghrabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum With Unity Pro: TCP/IP Configuration User ManualDocument76 pagesQuantum With Unity Pro: TCP/IP Configuration User ManualcamiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Albicom Cenovnik 20050923Document15 pagesAlbicom Cenovnik 20050923Zoki BatinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lan WanDocument7 pagesLan WanMuhammed YousafPas encore d'évaluation
- 6700 Security Gateway DatasheetDocument5 pages6700 Security Gateway DatasheetElivy LPas encore d'évaluation
- HDLCDocument2 pagesHDLCAditya KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Illustra PRO Gen4 Outdoor PTZ Data Sheet V4Document5 pagesIllustra PRO Gen4 Outdoor PTZ Data Sheet V4unstrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Ericsson RedBack Smart Edge 800 DatasheetDocument6 pagesEricsson RedBack Smart Edge 800 DatasheetMannus PavlusPas encore d'évaluation
- SSL CheckerDocument2 pagesSSL CheckerLifalakhe MaganganePas encore d'évaluation
- B. Chain DstnatDocument23 pagesB. Chain DstnatAinun NaimPas encore d'évaluation
- Default GatewayDocument3 pagesDefault Gatewayyuva razPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity School of Business: BBA, Semester 1Document38 pagesAmity School of Business: BBA, Semester 1Geetika Jain GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Process-to-Process Delivery: Udp, TCP, and SCTPDocument89 pagesProcess-to-Process Delivery: Udp, TCP, and SCTPprashantvlsiPas encore d'évaluation
- VPN 0de34747507907ed9Document8 pagesVPN 0de34747507907ed9Johan PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Woldia, Faculty of TechnologyDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Woldia, Faculty of Technologydagnu muluPas encore d'évaluation
- Source Routing BridgesDocument9 pagesSource Routing BridgesKaushal FaujdarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2.8 Packet Tracer - Investigate A VLAN ImplementationDocument2 pages3.2.8 Packet Tracer - Investigate A VLAN ImplementationGillian Balais DoblePas encore d'évaluation
- C79000-G8976-1554 ROS v5.7 RSG2488 ConfigurationManualDocument486 pagesC79000-G8976-1554 ROS v5.7 RSG2488 ConfigurationManualivan.melnikov.arPas encore d'évaluation
- Eu 19 Yazdanmehr Mobile Network Hacking IP Edition 2Document24 pagesEu 19 Yazdanmehr Mobile Network Hacking IP Edition 2THE No NAMEPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Protocol X 25 PDFDocument2 pagesCommunication Protocol X 25 PDFKennethPas encore d'évaluation
- Using HP Auto Port Aggregation APADocument206 pagesUsing HP Auto Port Aggregation APAWalter LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Iptv Over PonDocument5 pagesIptv Over Ponchaidar_lakarePas encore d'évaluation
- 10.6.12 Lab - Use TFTP, Flash, and USB To Manage Configuration Files - ILMDocument17 pages10.6.12 Lab - Use TFTP, Flash, and USB To Manage Configuration Files - ILMMuhammad SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Symantec SSL Visibility Appliance: Data SheetDocument6 pagesSymantec SSL Visibility Appliance: Data SheetDebojit GoswamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Address: Iran Hormozgan Kish Island Mojtamae Bankha Centre Mellat Bank Branch Of: 44172Document12 pagesBank Address: Iran Hormozgan Kish Island Mojtamae Bankha Centre Mellat Bank Branch Of: 44172mantanha066Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.1.2 Packet Tracer - Connect IoT Devices To A Registration Server PDFDocument7 pages6.2.1.2 Packet Tracer - Connect IoT Devices To A Registration Server PDFAngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Introduction To The StealthWatch System Rev1Document32 pagesTechnical Introduction To The StealthWatch System Rev1Faizan HyderPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab4 - Packet TracerDocument2 pagesLab4 - Packet TracerIenei Csongor AttilaPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.2.7 Lab - View Network Device MAC AddressesDocument8 pages7.2.7 Lab - View Network Device MAC Addresseskrishnveer12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mn00268e v12 WEB LCT ALCplus2e - 1.9 - Enh User Manual PDFDocument548 pagesMn00268e v12 WEB LCT ALCplus2e - 1.9 - Enh User Manual PDFBuzduga IonutPas encore d'évaluation