Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bones: A Hard Subject
Transféré par
Maria Dini AdmiratiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bones: A Hard Subject
Transféré par
Maria Dini AdmiratiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
3/23/2009
Bones
A HARD SUBJECT
3/23/2009
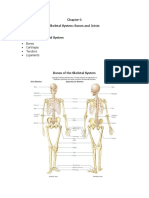
Skeletal System
y 205+ bones
y Associated CT
{ Cartilage
{ Tendons
{ Ligaments
i
{ discs
Functions: Bone
y Maintain body shape
Because of hardness difficult to section
y Must decalcify or grind thin
y Protect internal organs, brain, spinal cord
y System of levers for the muscle system to act upon
y Mineral storage
g Ca2+ and Phosphorus
p
y Blood formation: hematopoiesis
y Surface features for muscle insertions and origins
Bone Anatomy
y Diaphysis
y Metaphysis
y Epiphysis
Proximal/Distal
y Epiphyseal line
y Periosteum
y Compact bone
y Spongy bone
y Articular Cartilage
y Medullary cavity
y Marrow
y Nutrient artery
3/23/2009
Compact/Sp0ngy Bone
SHAPES OF BONES
Long
Short
Flat
Irregular
Sutural
Sesamoid
flat bone
Bone is a connective tissue
sutural bone
y Cells & extracellular matrix
y Matrix is mineralized support & protection
long bone
irregular
bone
y Calcium phosphate in form of hydroxyapatite
crystals
y ~50:50 organic/inorganic
y Can decalcify & tie in knots
sesamoid bone
(patella)
short bone
(carpals)
y Without organic: fragile
3/23/2009
Periosteum covers bones
Endosteum lines bone cavities
y (except at articulations cartilage)
y ~ 1 cell layer thick lining
y Outer fibrous layer
y Osteoprogenitor cells line marrow cavity &
y Inner, cellular layer with osteoprogenitor cells
trabeculae of spongy bone
y Collagen
g fibers from ligaments
g
& tendons g
go into
bone tissue at angle Sharpeys fibers
Bone Marrow
y Red bone marrow where blood cells are made
y As you grow, amount of red marrow doesn't increase
in proportion to bone growth Yellow marrow forms
y Lots o red in sternum, pelvis
A spot of yellow marrow within
Roasted bone marrow
3/23/2009
Mature bone
Compact Bone
y Osteons (Haversion systems): 4-20 lamellae with
central nerve, artery, vein
y Osteocytes trapped in matrix, connected to each
other by canaliculi (processes of osteocytes)
y Sometimes chain of 15
OSTEONS
Canaliculi between Osteocytes
3/23/2009
Osteocytes
Osteocyte with Cytoplasmic Extensions
y Mature bone cells that sit in lacunae
y Gap junctions between osteocytes provide nutrition
(15 cells in a row)
y Maintain bony matrix; long lived cells
y Stimulated by calcitonin (from thyroid); inhibited by
Parathyroid hormone
Osteocytes with Canaliculi
Photomicrograph of dried bone ground very thin.
The lacunae and canaliculi filled with air deflect
the light and appear dark, showing the
communication between these structures
through which nutrients derived from blood
vessels flow.
Compact Bone
y Osteons or Haversian systems.
y Osteons contain blood vessels, lymphatic
vessels, nerves, and osteocytes along with the
calcified matrix.
y Osteons are aligned in the same direction along
lines of stress - Lamellar bone.
y Osteons in spongy (trabecular) bone only in
very thick portions.
Collagen at alternating angles in lamellae
3/23/2009
Compact
Bone
&
Spongy Bone
y Rarely contains osteons.
y trabeculae surrounding red marrow spaces
Spongy
Bone:
Spongy bone
Bone is continuously remodeled
y Interstitial lamellae are found between osteons and
are remnants of previous concentric lamellae
Circumferential lamellae
y Inner & outer circumferences of shaft line rings in
Perforating canals (Volkmanns canals)
y Connect osteonal canals to one another
tree
3/23/2009
Blood supply to bone important
y nutrient foramina
Immature Bone
y Develops in fetus
y Doesnt have organized lamella nonlamellar,
woven bone
y Relatively more cells/area
y Stains darker more ground substance
y Adult: tooth sockets,
remodeling
Cells of Bone Tissue
Osteogenic cells:
3/23/2009
Osteoprogenitor cells
y From mesenchymal stem cells
y Resting cell that can transform into osteoblasts
y Found on inside/outside surfaces of bone, line
osteonal canals and blood vessels in bone
y bone-lining cells separate category in text, said to
be from osteoblasts, help osteocytes
y Flattened, elongate nuclei
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
y Synthesize organic components of matrix (collagen,
bone matrix proteins)
y Collagen forms osteoid: strands of spiral fibers that
form matrix not immediately calcified
y Influence deposit of Ca++, PO4
y Active vs. inactive osteoblasts (flat/cuboidal)
y Estrogen, PTH stimulate activity
Photomicrograph of endochondral ossification. In the upper region is a row of
osteoblasts with intense cytoplasmic basophilia, a feature to be expected in cells
synthesizing a glycoprotein (collagen). Note an osteoblast being captured in the bone
matrix (arrow). Between the layer of osteoblasts and the calcified bone matrix is a pale
region made of noncalcified bone matrix called osteoid.
Respond to mechanical stimuli
3/23/2009
Osteocytes discussed earlier
y Mature bone cell enclosed in
bone matrix
y In lacunae, but communicate
with other cells
y Often shrink in preparation
y Quiescent, formative, resorptive?
(M: Marrow cavity, Os: osteoid, CB: calcified bone matrix, C: caniculi, L: lamellae)
Osteoclasts
Eosinophilia lots of lyososomes
y Derived from monocytes; bone resorption
y Large, multinucleated, motile cells
y Secrete enzymes that digest matrix
Osteoclasts
10
3/23/2009
Osteoclast
Bone Resorption Acid first, then enzymes
y Ruffled border
y Clear zone filaments, few other organelles
y Basolateral region exocytosis of digested material
Bone remodeling
y Osteoclasts abundant where bone is changing
y 5-10% bone / year?
{ Vitamin D
{ Nutrition
{ Physical activity
{ Age, hormones
On this image, the
deepest red color
is bone while pink
represents either
fibrocartilage (i.e.,
collagen within
cartilage) or
mineralized
cartilage. The
central clearing
represents
p
the
Remodeling
invasion of bone into calcified cartilage. Osteoblasts are laying down new bone toward
the left of the upper boundary of this cavity. Osteoclasts are removing previouslyformed bone .
Bone Replacing Cartilage
Remodeling Bone
11
3/23/2009
Internal remodeling
X-ray of bone ground to 200 m
y Light = dense (mineralized)
y Interstitial lamellae light
y Bone = dynamic!
Lamellae deposited periphery inward
Physiologic aspects of bone
y Reservoir for calcium
y Blood levels 8.9-10.1 mg/dL
y Parathyroid hormone (from parathyroid of course)
{ Raise blood calcium levels
{ Simulates osteoclasts, osteocytes to resorb bone
{ Tell kidneys to hold on to calcium, absorb more in gut
Skull cavity increases without increasing bone thickness
Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts are at work
y Calcitonin (from thyroid)
{ Lowers elevated blood calcium levels
{ Inhibits osteoclasts
Bone Formation
y 2 Ways to form: Endochondral & intramembranous
y With cartilage model or without
12
3/23/2009
Intramembranous
y 8th week gestation in skull bones
y Skull bones, mandible, clavicle (collarbone)
y Bone forms as small, irregular spicules & trabeculae
y Over time they
y connect and form mature bone
Intramembranous Ossification:
Osteoblasts:
Endochondral Ossification
y Cartilage model
y Cuff of bone forms in midregion bony collar
y Cartilage cells in center swell, secrete calcium
y Calcified cartilage
g inhibits diffusion,, kills cells
y Blood vessels grow in, osteoprogenitor cells move in
13
3/23/2009
Knee of a 6 year old.
Secondary center of ossification in
epiphysis
Leaves cartilage epiphyseal plate
When that cartilage stops growing
bone has reached its max. length
Epiphyseal plate of adolescent (white arrow)
Endochondral Ossification
Endochondral Ossification
Fractures
y Break in the bone
y Simple/Compound (open)
infection
y Single: Horizontal, oblique,
spiral
y Comminuted >2 bone
fragments
14
3/23/2009
Types of Fracture:
Healing in Bone:
1D - Hematoma formation (fibrin mesh)
3D - Inflammation, macrophages remove
debris, Periosteum & endosteum
respond with proliferation of
osteoprogenitor
t
it cells
ll
1W - Soft callus granulation, matrix.
3-6W - Callus ossification, woven bone
8+W - Re-modeling absorb/deposit,
strength, lamellate.
Healing in Bone:
Stages of wound healing
Resolution/ Remodeling
Vessel regression, Collagen remodeling
Proliferation
Reepithelialization, Angiogenesis, Fibrogenesis,
Inflammation
PMNs, Macrophages, Lymphocytes
Hemostasis
Fibrin clot, platelet
deposition
1D 3D
1wk
6wk
8wk
Time after injury
Healing in Bone:
Bone healing: Callus
15
3/23/2009
Broken hip really femur
Osteoporosis
16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Alveolar BoneDocument81 pagesAlveolar BoneLavanya KalapalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone-LDocument34 pagesBone-LurjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam A-3Document11 pagesExam A-3yapues87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 HumanAnat&Fisio - 6 Agustus 2012Document17 pagesWeek 1 HumanAnat&Fisio - 6 Agustus 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteopetrosis (Marble Bones, Albers-Schönberg Disease) DefinitionDocument9 pagesOsteopetrosis (Marble Bones, Albers-Schönberg Disease) DefinitionRustin Dale EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (1) An Introduction To The Skeletal Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry of Bone (Assignment)Document7 pagesBiochemistry of Bone (Assignment)haseeb ShafaatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureDocument70 pagesChapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Skeletal StructureStefanie Henry100% (1)
- Lec 3 2010 02 6Document8 pagesLec 3 2010 02 6Ras WhoknowsmePas encore d'évaluation
- Bones and Cartilage Structure, Development, and FunctionDocument18 pagesBones and Cartilage Structure, Development, and FunctionMandeep DhillonPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual 1stevenbrownxockdjatwe100% (17)
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3Rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3Rd Edition Booth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (16)
- Orthopedic NursingDocument237 pagesOrthopedic Nursingɹǝʍdןnos100% (24)
- Bone and CartilageDocument9 pagesBone and Cartilageindnboi23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy 4Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesHuman Anatomy 4Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdora.ivy892100% (15)
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1donnawugnwsjrzcxt100% (20)
- Functions of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesFunctions of The Musculoskeletal SystemLinda XuePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bones and Skeletal Tissues Skeletal CartilagesDocument7 pagesBones and Skeletal Tissues Skeletal CartilagesChelsey ReaumePas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Skeletal System HandoutDocument8 pages2 Skeletal System Handoutapi-302873465Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Main Functions of BonesDocument9 pagesThe Main Functions of BonesabbaslafePas encore d'évaluation
- BoneDocument33 pagesBoneNihal BilalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Skeletal System The Skeletal System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document16 pagesThe Skeletal System The Skeletal System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Olympiad 2020 Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesScience Olympiad 2020 Cheat SheetLisa RetbergPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteoglycans, Whose Main Glycosaminoglycans Are Chondroitin-4-Sulfate and Chondroitin-6Document14 pagesProteoglycans, Whose Main Glycosaminoglycans Are Chondroitin-4-Sulfate and Chondroitin-6Joseph Enoch ElisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone TissueDocument46 pagesBone TissueFiraol DiribaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Document37 pagesChapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Sav Oli100% (1)
- General Osteology: DefinitionsDocument45 pagesGeneral Osteology: DefinitionsAndreeaPas encore d'évaluation
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument123 pagesSkeletal SystemFernando DisuPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument75 pagesPower Point Presentation SKELETAL SYSTEMaprillianlozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2: Bones and Cartilage Structure and Types 0F Bones and Cartilage Ossification Bone Growth and ResorptionDocument75 pagesUnit 2: Bones and Cartilage Structure and Types 0F Bones and Cartilage Ossification Bone Growth and Resorptionsourya jyoti dashPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Document36 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument104 pagesSkeletal Systemsyafi zulPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Bone: Presented By: Tinaye Blessing Nyamuda IDocument12 pagesHistology of Bone: Presented By: Tinaye Blessing Nyamuda Imr_cool3858Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bone HistologyDocument56 pagesBone HistologyNaveed AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 1516 Bone Tissue and Skeletal SystemDocument28 pagesLec 1516 Bone Tissue and Skeletal SystemonegaonnwePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 10 and 6Document25 pagesCh. 10 and 6Bammary88909Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Tissue Structure and FunctionDocument36 pagesBone Tissue Structure and FunctionKhdhir M. SalemPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 06 Lecture OutlineDocument6 pagesCH 06 Lecture OutlineTameka HedgepethPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 6 AnaphyDocument8 pagesChap 6 AnaphyNicholle VelosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano Gold Therapy for Bone CancerDocument29 pagesNano Gold Therapy for Bone CancerIshkruti WaghmarePas encore d'évaluation
- Bone and Cartilage TissueDocument33 pagesBone and Cartilage TissueGIANG ĐẶNG DUY TRÚCPas encore d'évaluation
- ALVEOLAR BoneDocument72 pagesALVEOLAR BoneArchana50% (2)
- Cartilage and Bone Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesCartilage and Bone Structure and FunctionRehab OmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone TissueDocument66 pagesBone TissueFunikawati Baldiyah100% (1)
- Hydroxyapatite Crystals Structural Components of Bone MatrixDocument4 pagesHydroxyapatite Crystals Structural Components of Bone MatrixhahaayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone HistologyDocument50 pagesBone HistologyMajd HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy 5Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesHuman Anatomy 5Th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJenniferWhitebctr100% (8)
- ANAT 215 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesANAT 215 Lecture Notesjchyeung20Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401Document18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Musculoskeletal System Chap 6 - 2401slyfoxkittyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Skeletal Sys.Document89 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal Sys.Adriane Basa100% (1)
- Skeletal Tissue2005Document40 pagesSkeletal Tissue2005ewijayapalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 pagesChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal SystemDocument200 pagesSkeletal SystemJB AriasdcPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionD'EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesD'EverandSkeletal System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacologic Aspect of GI Tract Disease 2012Document51 pagesPharmacologic Aspect of GI Tract Disease 2012Silvestri PurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Histology - 16 Januari 2013Document68 pagesWeek 1 Histology - 16 Januari 2013Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Histology - 16 Januari 2013Document68 pagesWeek 1 Histology - 16 Januari 2013Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pledisuraealse - 30 Oktober 2012Document57 pagesPledisuraealse - 30 Oktober 2012Silvestri PurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2 GenerativeBoneDisease - 13 Agustus 2012Document25 pagesWeek 2 GenerativeBoneDisease - 13 Agustus 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2 SpesificInfectionoftheLung - 5 November 2012Document41 pagesWeek 2 SpesificInfectionoftheLung - 5 November 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- BITHV - 9 November 2012Document22 pagesBITHV - 9 November 2012Silvestri PurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pledisuraealse - 30 Oktober 2012Document57 pagesPledisuraealse - 30 Oktober 2012Silvestri PurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2 Hemopthysis - 9 November 2012Document30 pagesWeek 2 Hemopthysis - 9 November 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2 BTMC - 6 November 2012Document63 pagesWeek 2 BTMC - 6 November 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rwes SpirystaetorymDocument44 pagesRwes SpirystaetorymSilvestri PurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 MeadiastinumTumor - 20 November 2012Document40 pagesWeek 4 MeadiastinumTumor - 20 November 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- ArthritisDocument42 pagesArthritisRaj Staple VersesPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 ARDS - 27 November 2012Document54 pagesWeek 5 ARDS - 27 November 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 BackBoneAnatomy - 3 September 2012Document20 pagesWeek 4 BackBoneAnatomy - 3 September 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument56 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Joint Diseases GuideDocument19 pagesInflammatory Joint Diseases GuideMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle Structure and TypesDocument21 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structure and TypesMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rangkuman Week 3 (PBL) - RADocument27 pagesRangkuman Week 3 (PBL) - RAMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rangkuman Week 4 (PBL) - OsteoporosisDocument38 pagesRangkuman Week 4 (PBL) - OsteoporosisMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal Muscle Structure and TypesDocument21 pagesSkeletal Muscle Structure and TypesMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rangkuman Week 5 (PBL) - OsteomyelitisDocument9 pagesRangkuman Week 5 (PBL) - OsteomyelitisMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- ArthritisDocument42 pagesArthritisRaj Staple VersesPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012Document16 pagesWeek 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Joint Diseases GuideDocument19 pagesInflammatory Joint Diseases GuideMaria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012Document16 pagesWeek 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012week 4 MetabolicBoneDisease - 3 September 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 SportInMedicine - 30 Agustus 2012Document47 pagesWeek 3 SportInMedicine - 30 Agustus 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiPas encore d'évaluation
- NoseDocument50 pagesNosejanePas encore d'évaluation
- WHO Guidelines For OsteoporosisDocument206 pagesWHO Guidelines For Osteoporosisscribdandrealeoni100% (1)
- Best Aid To Orthopedics PDFDocument586 pagesBest Aid To Orthopedics PDFDNDTPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Dieu Duong Tien TienDocument64 pagesTest Dieu Duong Tien TienPhạm Quỳnh TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Key 2012183Document8 pagesBone Key 2012183Jesus MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument63 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrelatermotifef4oq100% (10)
- OsteoinmunologíaDocument19 pagesOsteoinmunologíaKate RodasPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Midterm ReviewerDocument14 pagesAnaphy Midterm ReviewerCarmela Jane SonzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Special TopicsDocument8 pagesSpecial Topicskatherine ruizPas encore d'évaluation
- Articulo MelcherDocument8 pagesArticulo MelcherLuisHerreraLópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomecanica en Anomalias VerticalesDocument296 pagesBiomecanica en Anomalias VerticalesLisbethPas encore d'évaluation
- GSOE Research News 2018-19Document8 pagesGSOE Research News 2018-19CCNY CommunicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Matrix HypothesisDocument16 pagesFunctional Matrix HypothesisUddyot ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ar 3595Document54 pagesAr 3595suryasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Session #14 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document8 pagesSession #14 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G IPas encore d'évaluation
- Perio Ortho Inter Relationship 10278 - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFDocument7 pagesPerio Ortho Inter Relationship 10278 - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFSofia Zaematul ArifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone and Cartilage PDFDocument50 pagesBone and Cartilage PDFalviraPas encore d'évaluation
- Histo Trans 1.4 - Cartilage and BoneDocument6 pagesHisto Trans 1.4 - Cartilage and BonePim AramPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP'S)Document7 pagesBone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP'S)dileep9002392Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1the Functional Matrix Hypothesis 1 Moss PDFDocument4 pages1the Functional Matrix Hypothesis 1 Moss PDFNievecillaNeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1donnawugnwsjrzcxt100% (20)
- Skeletal System 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of BonesDocument5 pagesSkeletal System 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of Boneslabibah mahmudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Osteoporosis: Submitted To: Dr. Divya Vohra Submitted By: Sharique Raza M.pharm Jamia HamdardDocument38 pagesPresentation On Osteoporosis: Submitted To: Dr. Divya Vohra Submitted By: Sharique Raza M.pharm Jamia Hamdardsri susantiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Medication Related Osteonecrosis of The Jaw - Otto SvenDocument216 pagesMedication Related Osteonecrosis of The Jaw - Otto SvenNicoPaullierPas encore d'évaluation
- ISSA Corrective ExerciseDocument268 pagesISSA Corrective ExerciseSalman Khan100% (2)
- Pathology of Bone: Functions, Cells, Development and DiseasesDocument95 pagesPathology of Bone: Functions, Cells, Development and DiseasesabdillahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano Gold Therapy for Bone CancerDocument29 pagesNano Gold Therapy for Bone CancerIshkruti WaghmarePas encore d'évaluation
- Bone and Cartilage Histology GuideDocument43 pagesBone and Cartilage Histology GuideMila AnriyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteoporosisDocument47 pagesOsteoporosisSasha VaidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Avascular Necrosis of The Foot and Ankle Volume 24, Issue 1Document177 pagesAvascular Necrosis of The Foot and Ankle Volume 24, Issue 1汪汪汪100% (1)
- Body Mechanics and PositioningDocument32 pagesBody Mechanics and PositioningMiraSaniPas encore d'évaluation