Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 2
Transféré par
KaitlynCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 2
Transféré par
KaitlynDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Quiz on Section 11.3 through 11.8 except 11.
6
11.3 _ Equations in 2 variables: Finding solutions by subtracting in x or y and finding the
other variable. Also, rewrite linear equation in function form-> y= mx + b
11.4 _ Graphs of Linear Equations: Taking solutions found in Section 4.3 and plotting
the solutions as ordered pairs. Then, draw the line through these points(Solutions). Use
an input-output(x-y) table to get points.
11.5 _ Using Intercepts to Graph a Linear Function: A quicker alternative to graphing a
line rather than using a x-y table. Remember, the intercepts are often significant points
in a function. This method does not work if the x and y intercepts are both 0 -> (0,0)
origin is on the graph
11.7 _ Slope-Intercept Form and the Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a line: y= mx +
b; Plot y-intercept and use slope to generate move points on the line through which line
is drawn. If you know only a point on the line and the slope -> y-y1 = m(x-x1).
Sometimes, you only have 2 points to start with -> m= y2 - y1 and then use y-y1 = m(xx1) or y= mx+b!
!
!
!
!
!
x2 - x1
11.8 _ Graphs of Linear Inequalities: Graphs of Linear Inequalities: Graph borderline
y= mx + b. Then if > or < use dashed line, > or < use a solid line. If > or > shade up. If <
or < shade down.
Simple Vocabularies:
Relation- A set of ordered pairs that relates an input to an output
Function- A pairing of each number in a given set with a number in another set
Input- A number in which a function operates
Output- A number produced by evaluating a fraction using a given input
Independent variable: = input value
Dependent variable: = output value
Domain: The set of all input values of a function
Range: The set of all output values of a function
General function notation: F(x) F is the function of x
Function rules: F(x)= mx + y-coordinate where x=0
!
(Type of relation that for each input value there is exactly one output value)
Linear Equation: An equation in which the variables appear in separate terms and each
variable occurs only to the first power. (Function rule)
Linear Function(Function rule): A line on a graph showing the relationship between the
independent variable and dependent variable. * is the function of **
Trend line: shows trend relationship.
Types of trends or relationships(positive, negative, none): positive relationship-3rd
quadrant to 1st quadrant negative relationship- 2nd quadrant to 4th quadrant. no
relationship- no linear relationship then no trend line
Discrete Data- Data that involve a count of items.
Continuous Data- Data where numbers between any two data values have meaning.
Ordered Pair- A pair of numbers (x,y) that can be used to represent a point in a
coordinate plane.
Ratio- A comparison of two numbers using division.
Input- A number on which a unction operates.
Relation- A set of ordered pairs that represents inputs and outputs.
Function- A type of relation that assigns exactly one output value to each input value/ A
pairing of each number in a given set with a number in another set.
Domain- The set of all input values of a function.
Range- The set of all out put values of a function/ The set of matching output values that
makes sense
Scatter Plot- The graph of a collection of ordered pair (x,y), which is a collection of
points in a coordinate plane.
Linear Equation- An equation in which the variables appear in separate terms and each
variable occurs only to the first power.
Slope- The ratio of the vertical change of a non-vertical line to its horizontal change.
Slope- measure of steepness. usually symbolized with the variable m
Rate of change: change in the output/change in the input or change in dependent
variable/ change in dependent variable, delta dep./delta indep.
Equation for rate of change: vertical change/horizontal change = delta(change)
dependent / delta independent = change of dependent variable / change of independent
variable = change in y / change in x
Rise- The vertical change used in finding the slope of a line.
Run- The horizontal change used in finding the slope of a line.
Slopes of vertical lines and horizontal lines: Slope of a vertical line is not possible,
undefined and the slope of a horizontal line is 0, zero.
Slopes of parallel lines and perpendicular lines: Parallel lines have the same slope.
Perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals. {if some lines slope is 2/3
the perpendicular line of that slope would be -3/2. negative reciprocal}
Slope-Intercept Form- The form of a linear equation, such as y= mx + b
Concepts:
-General function notation: F(x) F is a function of x.
-Function rule seems to always have the form f(x) = mx + y-coordinate where x=0
-The slope-intercept form of a linear equation(function form)(rule of a function): y= mx +
b --> Useful when drawing lines when you already know the slope of the line and the y
intercept.
-Concept of dependency- in a function, we will usually say that the output value
depends on the input value. (Y depends on the X)
-If no input values are repeated it means that no x-coordinates are repeated, so it is a
function.
-In the function rule D(t) does not mean you should multiply D times t.
-Trend line= line of best fit
-Slope= Rate of Change
-In a function, there arent always a clear relationship between the input and the output.
-Trend lines are useful for making predictions about data values that are not found in the
original set of data.
-When drawing a trend line draw the trend line so that you roughly have as many points
above the line as below the line. The trend line doesnt have to have at least one point
from the data set on it.
-ways to solve for slope:! m= y2 - y1 and then use y-y1 = m(x-x1) or y= mx
+b ! !
!
!
x2 - x1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (8)
- X y X y M M D : Pre-Calculus QUIZ NO. 1 (Prerequisite Skills)Document2 pagesX y X y M M D : Pre-Calculus QUIZ NO. 1 (Prerequisite Skills)Mikee VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- PreCalculus Quiz #1Document1 pagePreCalculus Quiz #1Ana Marie ValenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 Min QUIZ On Circle Parabola EllipseDocument2 pages30 Min QUIZ On Circle Parabola EllipseLeopold LasetPas encore d'évaluation
- COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Abbottabad: Course Outline - Semester Fall 2019Document4 pagesCOMSATS Institute of Information Technology Abbottabad: Course Outline - Semester Fall 2019Haider AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus Quiz 1Document1 pagePre-Calculus Quiz 1Kim VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Departmental Syllabus For MAT 284, Business Calculus. Spring 2014Document4 pagesDepartmental Syllabus For MAT 284, Business Calculus. Spring 2014Anonymous bZTdTpLPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Banking PrelimsDocument7 pagesBlood Banking PrelimsTriciaLeePas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 2402 Midterm 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesCHEM 2402 Midterm 1 AnswersDaniel Alexander Black100% (1)
- Prelims BitsDocument121 pagesPrelims BitsSaurav SumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Lecture Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Midterm ExamBulajyo Pangngay JolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Erythrocytic DisordersDocument6 pages1 Erythrocytic DisorderschippaiqweqwePas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic and Organic Chemistry Prelims ReviewerDocument33 pagesInorganic and Organic Chemistry Prelims ReviewerMary Ann C RecañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus HomeworkDocument7 pagesPre-Calculus Homeworkapi-205958356Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 - Primary HemostasisDocument4 pagesWeek 3 - Primary HemostasisRubenne Miles ElagasPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 Math Challenge QuizDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Math Challenge QuizScottPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Midterm 3Document16 pages2013 Midterm 3billbyoag123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus Quiz 3Document1 pagePre-Calculus Quiz 3Kim VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus Quiz 3Document2 pagesPre-Calculus Quiz 3Kim VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential CalculusDocument4 pagesDifferential CalculusIsiahTanEdquibanPas encore d'évaluation
- PreCalculus Quiz #1Document1 pagePreCalculus Quiz #1Ana ValenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- CalculusDocument8 pagesCalculusRizwan Iqbal0% (1)
- Chemistry Quiz Grade 7Document4 pagesChemistry Quiz Grade 7menma funPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy Midterm PointersDocument1 pageAnaPhy Midterm PointersAmielsimon NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaphy Lab MidtermsDocument32 pagesAnaphy Lab Midtermsjoseph manansalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Worksheet Redox Reactions 8-9Document4 pages4-Worksheet Redox Reactions 8-9musab8450% (2)
- Biomedical Engg Project SolveDocument10 pagesBiomedical Engg Project Solveasif0% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Midterm 1epox+mech+keyDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Midterm 1epox+mech+keyNorma Leticia RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4Document117 pagesUnit 4Soc Sci0% (1)
- Prelim Exam Schedule 1st Sem 2021 2022Document2 pagesPrelim Exam Schedule 1st Sem 2021 2022Carylle FontanillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Solution Manual - Chapter 3Document22 pagesGenetics Solution Manual - Chapter 3amarka01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus ABDocument32 pagesCalculus ABaw awPas encore d'évaluation
- HH Model Documentation PDFDocument21 pagesHH Model Documentation PDFSamuel LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- C3 Chapter 5 Modulus and TransformationsDocument55 pagesC3 Chapter 5 Modulus and TransformationsDaLilSPPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 9 Harmonic and Fibonacci SequencesDocument2 pagesDay 9 Harmonic and Fibonacci Sequencessummer victoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 GED Quiz1 Real Number Quiz QUEXDocument4 pages1 GED Quiz1 Real Number Quiz QUEXtognibenePas encore d'évaluation
- The Normal DistributionDocument33 pagesThe Normal DistributionEdmar AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra II Chapter 3.1-3.3 QuizDocument1 pageAlgebra II Chapter 3.1-3.3 QuiztentingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton'S Law of Motion: ForceDocument2 pagesNewton'S Law of Motion: ForceJohanna AlumbroPas encore d'évaluation
- STAT Module 4Document10 pagesSTAT Module 4Jayson CabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris Course Curiculum Design and Instructional PlanDocument6 pagesUniversiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris Course Curiculum Design and Instructional PlanMuzammer MansorPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1 To Prelims: Hehehe AnonymousDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 To Prelims: Hehehe AnonymousLoving AngelPas encore d'évaluation
- PreCalculus Advanced Course Expectations, 2017-2018Document10 pagesPreCalculus Advanced Course Expectations, 2017-2018samjshahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Ultimatum Math Quiz Series OneDocument2 pages1st Ultimatum Math Quiz Series Onehec chumpi100% (1)
- ECE633F09 HW5solutionsDocument9 pagesECE633F09 HW5solutionsJoe SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- L20 Maxima Minima ProblemDocument20 pagesL20 Maxima Minima ProblemKaren Dela TorrePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.02 Physiology Trans - Muscle PhysiologyDocument10 pages1.02 Physiology Trans - Muscle PhysiologyMineTagraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsBittu100% (1)
- IB Chem, Topic 10, Organic Quiz 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesIB Chem, Topic 10, Organic Quiz 1 ReviewJulie VuPas encore d'évaluation
- Think-Pair-Share Activity 1: Extend On A Separate Graph Represent y 3Document1 pageThink-Pair-Share Activity 1: Extend On A Separate Graph Represent y 3Antwayne Youcantstopmaprogress HardiePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Midterm ExamDocument19 pagesBiology Midterm ExamC Bala DiwakeshPas encore d'évaluation
- SCH 3U Final Exam: Practice: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesSCH 3U Final Exam: Practice: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question소피아Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Biology Final Exam ReviewDocument1 pageAP Biology Final Exam Reviewrobertclee1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- IMP Video ConceptDocument56 pagesIMP Video ConceptParthJainPas encore d'évaluation
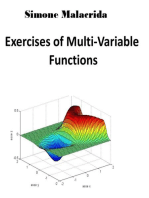
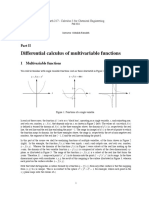
- Differential Multivariate CalculusDocument42 pagesDifferential Multivariate CalculusjwfostePas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Probability Distribution and Z TableDocument4 pagesNormal Probability Distribution and Z TableAnimeliciousPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Quiz Biology 3200Document1 pageLaboratory Quiz Biology 3200rodneyperuPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra MidtermDocument5 pagesLinear Algebra MidtermAndre McAuslin PinsonaultPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 1Document2 pagesPre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 1KaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 1Document2 pagesPre-Algebra Ch.11 Quiz 1KaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2Document2 pagesPre-Algebra Ch. 8 Quiz 2KaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Algebra Ch. 9 Quiz 1Document2 pagesPre-Algebra Ch. 9 Quiz 1KaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Rome and ChristianityDocument1 pageRome and ChristianityKaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Vocab For Grade 8Document1 page12 Vocab For Grade 8KaitlynPas encore d'évaluation
- Villa VeronicaDocument12 pagesVilla Veronicacj fontzPas encore d'évaluation
- mc96 97 01feb - PsDocument182 pagesmc96 97 01feb - PsMohammed Rizwan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareDocument8 pagesHealth Problem Family Nusing Problem Goals of Care Objectives of CareMyrshaida IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Adventure Shorts Volume 1 (5e)Document20 pagesAdventure Shorts Volume 1 (5e)admiralpumpkin100% (5)
- 2.2 Push and Pull Sources of InnovationDocument16 pages2.2 Push and Pull Sources of Innovationbclarke113Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Reported Speech - T16-6 PracticeDocument3 pages5 Reported Speech - T16-6 Practice39 - 11A11 Hoàng Ái TúPas encore d'évaluation
- Spoken KashmiriDocument120 pagesSpoken KashmiriGourav AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook PDF The Irony of Democracy An Uncommon Introduction To American Politics 17th Edition PDFDocument42 pagesEbook PDF The Irony of Democracy An Uncommon Introduction To American Politics 17th Edition PDFscott.stokley449100% (39)
- Phonetic Sounds (Vowel Sounds and Consonant Sounds)Document48 pagesPhonetic Sounds (Vowel Sounds and Consonant Sounds)Jayson Donor Zabala100% (1)
- 3a Ela Day 3Document5 pages3a Ela Day 3api-373496210Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hyrons College Philippines Inc. Sto. Niño, Tukuran, Zamboanga Del Sur SEC. No.: CN200931518 Tel. No.: 945 - 0158Document5 pagesHyrons College Philippines Inc. Sto. Niño, Tukuran, Zamboanga Del Sur SEC. No.: CN200931518 Tel. No.: 945 - 0158Mashelet Villezas VallePas encore d'évaluation
- 1820 Celestial EventDocument8 pages1820 Celestial EventDoor Of ElPas encore d'évaluation
- PCA Power StatusDocument10 pagesPCA Power Statussanju_81Pas encore d'évaluation
- 89 Robinson V MirallesDocument1 page89 Robinson V MirallesMartin AlfonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Educ 323 - The Teacher and School Curriculum: Course DescriptionDocument16 pagesEduc 323 - The Teacher and School Curriculum: Course DescriptionCherry Lyn GaciasPas encore d'évaluation
- Finlatics Investment Banking Experience ProgramDocument4 pagesFinlatics Investment Banking Experience ProgramSameer BheriPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Social CapitalDocument17 pagesBuilding Social CapitalMuhammad RonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics - FinalsDocument18 pagesEthics - Finalsannie lalangPas encore d'évaluation
- All New Keys DictionaryDocument7 pagesAll New Keys DictionaryvishntPas encore d'évaluation
- Scanned - National Learning CampDocument2 pagesScanned - National Learning CampJOHN JORICO JARABAPas encore d'évaluation
- Conspicuous Consumption-A Literature ReviewDocument15 pagesConspicuous Consumption-A Literature Reviewlieu_hyacinthPas encore d'évaluation
- Introducing Identity - SummaryDocument4 pagesIntroducing Identity - SummarylkuasPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesReaction PaperPatrick Ramos80% (15)
- ABHI Network List As On 30-06-2023Document3 401 pagesABHI Network List As On 30-06-20233uifbcsktPas encore d'évaluation
- Computerized Dynamic Posturography (CDP)Document2 pagesComputerized Dynamic Posturography (CDP)eldescribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation of % Slip in Mill During Rolling by Ajmal (10.09.2014)Document15 pagesCalculation of % Slip in Mill During Rolling by Ajmal (10.09.2014)Rakesh Karan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is ForexDocument8 pagesWhat Is ForexnurzuriatyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chat GPT DAN and Other JailbreaksDocument11 pagesChat GPT DAN and Other JailbreaksNezaket Sule ErturkPas encore d'évaluation
- AUTONICSDocument344 pagesAUTONICSjunaedi francePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2: Osmosis Lab Data: Student Name: Nguyen Duc MinhDocument2 pagesLesson 2: Osmosis Lab Data: Student Name: Nguyen Duc MinhMinh Nguyen DucPas encore d'évaluation