Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra 16
Transféré par
Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Algebra 16
Transféré par
Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CLASES, OPERACIONES, COMPOSICIN E INVERSA DE FUNCIONES
CLASES DE FUNCIONES
1.
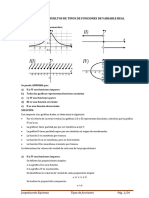
FUNCIN INYECTIVA O UNIVALENTE
Una funcin
f : AB
es inyectiva si a cada elemento del rango le corresponde un
nico elemento del dominio. Es decir:
Si f ( x 1 )=f ( x 2) entonces x 1 x 2 x 1 , x 2 Dom( f )
Si x1 x2 entonces f ( x 1 ) f ( x 2) x 1 , x 2 Dom (f )
Observacion:
f : A B es inyectiva, si para
y B ,! x A / y =f ( x)
1.
Una funcin
2.
En una funcion inyectiva las segundas componentes no se repiten.
3.
Si toda recta paralela al eje
corta a la grfica de
en a lo ms un punto,
dicha grfica ser la representacin de una funcin inyectiva.
2.
FUNCIN SURYECTIVA
Una funcin
f : AB
es suryectiva, si el rango o imagen de
coincide con el
conjunto de llegada B es decir.
Si
Ran ( f )=B entonces f
es una funcin suryectiva.
Observacion:
Una funcin
3.
f : A B es suryectiva, si para
y B , x A /f ( x)= y
FUNCIN BIYECTIVA:
Una funcin
f : A B es biyectiva si f
es a la vez inyectivay suryectiva.
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
149
CEPRU UNSAAC
Ejemplo: Hallar el valor de
ALGEBRA
x 2+ y 2 sabiendo que la funcin f es inyectiva.
2
2
f ={( 5,1 ) , (3,2 ) , ( 2 x y ,1 ) , ( y x , 2 ) ( x , x + y ) }
Solucin: por condicin de inyectividad, si se repite las segundas componentes en dos pares
ordenados estos son iguales, entonces:
3= yx (1)
5=2 x y (2)
De
2
2
2
2
( 1 y (2) x=2; y=1 entonces x + y =(2) +(1) =5
f = { ( 5,1 ) , (3, 2 ) , ( 2 ,5 ) }
OPERACIONES CON FUNCIONES
Sean f y g dos funciones cuyas reglas de correspondencia son
f ( x ) y g ( x ) , entonces:
ADICIN:
f + g={ ( x , y ) / y =( f + g )( x )=f ( x ) + g ( x ) ; x Dom ( f + g )=Dom ( f ) Dom ( g ) }
SUSTRACCIN:
f g= { ( x , y ) / y=( f g ) ( x )=f ( x )g ( x ) ; x Dom ( f g )=Dom ( f ) Dom ( g ) }
MULTIPLICACIN:
f g= {( x , y ) / y=( f g ) ( x )=f ( x ) g ( x ) ; x Dom ( f g )=Dom ( f ) Dom ( g ) }
DIVISIN:
f (x )
f
f
f
={( x , y)/ y=
(x )=
; x Dom
=Dom ( f ) Dom ( g ){x Dom ( g ) / g ( x )=
g
g
g
g(x)
()
()
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
150
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f , g : R R , cuyas reglas de correspondencia son:
Ejemplo: Sean las funciones
f ( x )= 9x y g ( x )=
2
x2
. Hallar f + g y su dominio .
x + 4 x5
2
Solucin:
Dom ( f ) =[3 , 3 ] y Dom ( g )=R{5,1 }
Dom ( f + g ) =Dom ( f ) Dom ( g )=[ 3 ,3 ] { 1 }
y=( f + g ) ( x ) =f ( x )+ g ( x )= 9x +
2
x2
; x Dom ( f +g )=[ 3 ,3 ] { 1 }
x +4 x5
2
COMPOSICION DE FUNCIONES
Sean f y g dos funciones cuyas reglas de correspondencia son
Dom ( f )
f ( x ) y g ( x ) , si x
f ( x ) Dom ( g ) , entonces la composicin de f y g denotado
porg o f existe y se define por:
g o f ={( g o f )(x)=g ( f ( x ) ) ; x Dom ( g o f ) }
Donde:
Dom ( g o f )= { x /x Dom ( f ) f ( x ) Dom ( g ) }
1
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
151
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
Recprocamente:
f o g={(f o g)(x)=f ( g ( x ) ) ; x Dom ( f o g ) }
Donde
Dom ( f o g )= { x /x Dom ( g ) g ( x ) Dom ( f ) }
Propiedades:
( g f ) Existe Ran(f) Dom(g)
1.
2.
gf fg
3.
(g f) h = g (f h)
4.
! Funcin identidad I tal que
f I=f
If=f
5.
(f +g) h = f h + g h
6.
(f .g) h = (f h ).(g h)
7.
Dom ( g f ) Dom ( f )
8.
Ran ( g f ) Ran ( g )
9.
funcin f.
Si f y g son funciones inyectivas entonces g f es una funcin inyectiva.
Ejemplo: Sean las funciones
f , g : R R , cuyas reglas de correspondencia son:
f ( x )= 4 + x ; x [ 2 ,6 ]
2
g ( x ) =x +2 ; x [1 ,3 ] . Hallar f o g y su dominio .
Solucin:
152
Dom ( f ) =[ 2 , 6 ] y Dom ( g )= [1 ,3 ]
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
Dom ( f o g )= { x /x Dom ( g ) g ( x ) Dom ( f ) }
x [1 ,3 ] x 2 +2 [ 2 ,6 ]
2
1 x 3 2 x + 2 6
2
1 x 3 0 x 4
1 x 3 0 x 2 4
1 x 32 x 2
x Dom ( f o g )=x [ 1 , 2 ] Entonces:
(f o g)(x)=f ( g ( x ) ) =f ( x 2 +2 )= 4+ x 2 +2= x 2+ 6 ; x [ 1 , 2 ]
FUNCIN INVERSA
Sea f una funcin cuya regla de correspondencia es:
f ={ ( x , y ) / y =f ( x ); x Dom (f ) } Si "f " es inyectiva entonces la funcin inversa de f
existe y esta dado por:
f 1 ={( y , x ) / x=f 1 ( y); x Dom( f ) }
Propiedades: sean f , g ,I funciones inyectivas, entonces:
f 1 ) = Ran (f)
1.
Dom (
2.
Ran (
3.
(g f)-1 =
4.
) = Dom (f)
f 1 = I
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
153
CEPRU UNSAAC
5.
6.
ALGEBRA
f = I
f 1 ) -1 = f
Ejemplo: Seaf(x) = 2x 3
Despejar x en funcin de y,
Es decir : x=
y +3
2
Luego a x se cambia por f(x)-1 y a y se cambia por x.
Entonces: f 1 ( x )=
x+ 3
2
EJERCICIOS
G= {( 4,3 ) ; ( 2,2 ) ; ( 3,3 ) ;(6,1) } ,
1) Dadas las funciones.
f ={( x , y ) R 2 / y = 16x } y
calcular la suma de los elementos
1
g= ( x , y ) R2 / y= 2
x 16
del rango de:
el dominio de la funcin,
f g ,
es:
Rpta.:
,4 4 , 16 ]
2) Dadas las funciones:
F={ ( 3,1 ) ; (2,3 ) ; ( 0,0 ) ;(4,5) }
F +2 G .
Rpta.: 51.
3) Dadas las funciones:
f ( x )=2 x ,
x0 .
g( x)={(2,4);(0,2) ;(2,3);(1,5);
( 4,2 ) ;(1,3)} , hallar la suma
de los elementos del rango de
f 23 g .
Rpta.: 4.
4) Dadas las funciones:
154
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f (x)=3 x +2, x 3,6
g= { (1,3 ) ; ( 2,7 ) ; ( 3,9 ) ; ( 7,12 ) , ( 0,10 ) }
f (x)=4 x +k
g(x)=2 xk . Hallar el valor de
k , si se cumple que:
, determinar el nmero de
elementos del
7) Si
Ran(f + g) .
Rpta.: 4.
( fog ) ( x ) + ( 2k ) =( fog ) ( x ) ( f g ) (x)
.
Rpta.: 2.
5) Dadas las funciones:
g= { (1,1 ) ; ( 2,2 ) ; (3,3 ) ; ( 4,4 ) , ( 5,5 ) }
8) La inversa de la siguiente funcin:
f ( x )= 5x (|x5|+1+ x ) , es:
f ={ ( x ,1 ) / x N 1< x<5 } ,
Rpta.:
determinar el valor de:
[(
g
f + g ) + fg ( gf ) (x) ,
f
con respecto al mayor valor de
x .
180x 2
, x [ 0 , + .
36
9) Dada la siguiente funcin:
f ( x )=4 xx ; x [ 0,1 ] . Hallar
f .
la funcin inversa de
Rpta.: 2.
Rpta.:
(2 4x ) .
6) Sean las funciones:
f ={ ( 1,5 ) ; ( 10,7 ) ; ( 2,4 ) ; ( 3,1 ) }
,
f : R R /f (x )=
g= {( x , y ) R x R/ y=x 2 +1, x [ 5,8 ] }
Hallar:
10) Sean las funciones:
Dom(gof ) .
1
x +n ,
2
g :R R/ g( x )=( n1) x1 ,
y sea la funcin compuesta definida
por:
1
( g1 of ) ( x )=8 x +12
Determinar el valor de
a .
Rpta.: 5.
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
155
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f
f x 2 3x 2
11) Dadas las funciones
y
definidas por:
f 6,8 ; 4, 7 ; 0,1 ; 3, 5 ; 7, 4
14) Si
real
de la funcin
Rpta:11
x 31
9
Rpta:
, es:
12) Dadas la funciones
tales que
x 1, 7
con
x 2,
con
son
8
3
g of
7
5
biyectivas , tales que
;
8
2
2
g 1
f 1
9
5
9
. Hallar
Rpta:3/7
. Hallar
f og
16) Dadas
las
funciones
g 5,1 , 6, 2 , 3, 1 , 1,3 , 2,1
el rango de la funcin
16,36
Rpta:
13) Dadas las funciones.
f 1, 0 ; 3, 3 ; 1, 4 ; 2,1
3, 4 ; 4, 6 ; 1, 2
Hallar
R( g h gh )
5,7
Rpta:
h
Hallar
una funcin
g hof
h 1,1 ; 1,1 , 2, 2
g 1, 6 ; 2, 2 ; 3, 4
tal que
17) Sean
las
funciones
f 1, 0 ; 2,3 , 1, 3 , 4,1
y
g 1, 2 , 3, 4 ; 2,1 ; 4,1
.
f og
156
15) Si las funciones
f
Rpta:
es una funcin
el valor de
, es:
La suma de los elementos del rango
f g
g x 2x 1
entonces
f 1 f 1 x 1
g x x 3
f x x 1
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
Hallar
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f og 1,3 , 3,1 , 2, 0 , 4, 0
Rpta:
2, 1 , 4, 5 , 7, 5
.
f x x 1
18) Sean
g x x 1
, el
f .g
23) Dadas las funciones
f : / f x 3x 2
Rpta:
f x 5x 2 2 x 1
.
Hallar
g : / g x 2x 2
of
y
, entonces
x
, es:
4
5 ,
3x 4
2
Rpta:
Rpta:
f x
2x 1
3x 1
20) Si
f x
. Hallar la inversa de
Hallar la suma de la elementos del
F 2 3G
rango de
Rpta:59
Rpta:
y
21) Dada la funcin real
hallar la inversa
23 x 2
Rpta:
f
24) Dadas las funciones
F 3, 2 , 0, 0 , 2, 4 , 3,1 , 4,3
G 2, 0 , 3, 4 , 4, 7 , 6, 2
x 1
3x 2
22) Si
2, 3 , 4,1 , 7,1
Rpta:
rango de
, es.
1,
19) Si
Df I Rf
Hallar
f og
x3
2
8
,
25) Dadas las funciones
f x x3 5 x 1 x 4, 2
,
g x 3 x 7 x 0, 7
definidas
por
son dos funciones
f x x2 4
Hallar
Rpta:
,
f g x
x 0, 2
x3 2 x 8
,
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
157
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f x x 2x 3
x 3, 2
26) Si
g x 5 3x
Dom g o f
,
x 1, 4
,
y
.
30) Sean la funciones:
f {( 4,1), (3,1), (2,4), (1,4)}
,y
Hallar
g {(1,1), (4,3), (5,2), (0,4)}
La suma de los elementos del
1 2 , 2
f g
Rpta:
rango de la funcin
Rpta. 5
f*
27) Hallar
si
x 1
f x , y x / y
x 1
f ( x ) 5 x 3,
Hallar la regla de correspondencia
f g
x 1
1 x
de
f g
Rpta:
Rpta (
28) Dadas las funcione:
f {(2,3), (1,6), (4,2), (6,8)}
y
g {( 0,2), (1,3), (4,1), (6,0), (9,8)}
f
f g
g
El rango de
y
g ( x ) 2 x 3, con x 2, 4]
2
funciones.
dominio de (
Rpta [2,6]
29) Dada las funciones:
f ( x) 2 x ; x 0
Determinar
el
gf
, es:
Rpta.
)(x).
33) Sean
,y
g {( 2,4), (0,2), (2,3), (1,5), ( 4,2), ( 1,3)}
f x 2 x2 4 x 3
y
1, 2 , 0, 7 , 1, 3 ,
2f
Hallar la suma de los elementos
f 2 3g
158
)(x)=15x-2
f ( x ) x 4, con x [2, 6]
32) Si
Son
{5,11}
del rango de
Rpta. 4
g ( x) 3x 1
31) Si
.
f*
, es:
3g
Hallar
86 8 5
Rpta.
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
3,10 ,
5, 20
CEPRU UNSAAC
ALGEBRA
f
g
34) Sean las funciones
f x x2 2 x 4
a)
y
g x x2 4x 3
. Hallar
f
g
b)
y su dominio
Rpta:
f
1
2
2, , 1, ,
g
5
3
a)
a)
y su dominio
g
f
b)
Rpta.
f
g
D f / g 2, 1, 2
y su dominio
D f / g 2 7, 2 7
b)
2, 0
b)
Dg / f 2, 1,1
g
3
2,5 , 1, , 1, 0
f
2
x2 2x 4
x2 4x 3
a)
g
f
y su dominio
g
f
x2 4x 3
x2 2x 4
Dg / f 1 5,1 5
35) Sean las funciones
f
2,1 , 1, 4 , 1,5 ,
2, 0 ,
2,5 , 1, 6 , 1, 0 ,
2, 5 ,
3, 0 , 4,10
3, 0 , 5, 20
Hallar
CENTRO DE ESTUDIOS PREUNIVERSITARIO
159
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sol SM 2019-I (Pre) tiFDD15Ar3Kw PDFDocument29 pagesSol SM 2019-I (Pre) tiFDD15Ar3Kw PDFzerkPas encore d'évaluation
- El Paradigma Cuantitativo y El Paradigma CualitativoDocument4 pagesEl Paradigma Cuantitativo y El Paradigma CualitativoJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- (A) Sicuani - PoDocument4 pages(A) Sicuani - PoJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- (Po) Razon y ProporcioDocument5 pages(Po) Razon y ProporcioJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- ManualaimacionlectoraDocument96 pagesManualaimacionlectoraLiz Yesenia Cahuaya InofuentePas encore d'évaluation
- (Po) EstadisticaDocument3 pages(Po) EstadisticaJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil SucesionesDocument6 pagesCírculo Sil SucesionesJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Conamat7 1er AñoDocument4 pagesCírculo Conamat7 1er AñoJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Boletin 1º MARZODocument196 pagesBoletin 1º MARZOjobregon-2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Géneros Periodísticos ManuelDocument3 pagesGéneros Periodísticos ManuelJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Olimpiadas Nivel I 2015Document8 pagesProblemas Olimpiadas Nivel I 2015Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- MODIFICACIÒN DEL LIBRO IV. (Downloaded With 1stbrowser)Document7 pagesMODIFICACIÒN DEL LIBRO IV. (Downloaded With 1stbrowser)Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas Plan Tea Dos en Diversas Partes Del MundoDocument4 pagesProblemas Plan Tea Dos en Diversas Partes Del MundoluisangeluniPas encore d'évaluation
- Criptoaritmética1 PrinstonDocument5 pagesCriptoaritmética1 PrinstonJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Conamat6 1er AñoDocument3 pagesCírculo Conamat6 1er AñoJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil ProbabilidadesDocument7 pagesCírculo Sil ProbabilidadesJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil Series y SumatoriasDocument5 pagesCírculo Sil Series y SumatoriasJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil Combinatoria1Document12 pagesCírculo Sil Combinatoria1Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil Edades1Document12 pagesCírculo Sil Edades1Jorge Luis Chumberiza Manzo100% (1)
- Círculo - Sil - Factorial de Un NúmeroDocument5 pagesCírculo - Sil - Factorial de Un NúmeroJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aritmética Pre DivisibilidadDocument3 pagesAritmética Pre DivisibilidadJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aritmética Pre Números PrimosDocument2 pagesAritmética Pre Números PrimosJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aritmética Pre 2sDocument3 pagesAritmética Pre 2sJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Sil Números DecimalesDocument2 pagesCírculo Sil Números DecimalesJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Círculo Numeración1 2015Document3 pagesCírculo Numeración1 2015Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Modulo 04Document22 pagesModulo 04Jorge Delgado ParionaPas encore d'évaluation
- NUMERACIÓN Preu 2016Document3 pagesNUMERACIÓN Preu 2016Jorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Estrella de MarDocument1 pageEstrella de MarJorge Luis Chumberiza ManzoPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULO - 01 Resolucion de Problemas para DocentesDocument14 pagesMODULO - 01 Resolucion de Problemas para Docentes20071614Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seis Visiones de La Pedagogía en El Siglo XXIDocument5 pagesSeis Visiones de La Pedagogía en El Siglo XXIJorge Luis Chumberiza Manzo50% (2)
- Taller Examen FinalDocument9 pagesTaller Examen FinalHumberto TapiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Avanzado 02aDocument119 pagesControl Avanzado 02aKaty LisbethPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetismo PRUEBA 1Document11 pagesElectromagnetismo PRUEBA 1EIEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 3 - CalculoDocument12 pagesTarea 3 - CalculoErika DimasPas encore d'évaluation
- Oihane SyllabusDocument6 pagesOihane SyllabusdarkbalderPas encore d'évaluation
- Aporte 3 - Tarea 4 - Grupo Grupo - 5Document43 pagesAporte 3 - Tarea 4 - Grupo Grupo - 5DEIVI MARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario - Ecuaciones Diferenciales PDFDocument3 pagesFormulario - Ecuaciones Diferenciales PDFAcosta JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplicacion de VectoresDocument5 pagesMultiplicacion de VectoresEliana Korina CabanillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Contenido Programático Cálculo Integral, 2020-03Document3 pagesContenido Programático Cálculo Integral, 2020-03Laura Estefan Gómez AmayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practica Calificada de AlgebraDocument2 pagesPractica Calificada de Algebracontador jeremy semestre 2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Funciones Parcial 2Document6 pagesFunciones Parcial 2Cynthia CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía Didáctica 3 Métodos de Factorización DiferentesDocument15 pagesGuía Didáctica 3 Métodos de Factorización DiferentesKirzy A MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- TEMA 4.3 - Tipos de Funciones-1Document24 pagesTEMA 4.3 - Tipos de Funciones-1Erick GuallpaPas encore d'évaluation
- F 01 Vectores PDFDocument3 pagesF 01 Vectores PDFSergioSaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Filemd9249-2023-10-26 09-54-25Document20 pagesFilemd9249-2023-10-26 09-54-25Astrid CLPas encore d'évaluation
- Ficha Mat Ib-IV-Derivadas IV Bimestre 2022Document73 pagesFicha Mat Ib-IV-Derivadas IV Bimestre 2022Johan TraversoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostico Pedagógico - Fase 2Document11 pagesDiagnostico Pedagógico - Fase 2kelly fernanda cortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad 1 MatricesDocument4 pagesActividad 1 MatricesJesus ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cálculo Del Tiempo de Carga de Un CapacitorDocument9 pagesCálculo Del Tiempo de Carga de Un CapacitorDalmiro Nina MorodiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformada ZDocument35 pagesTransformada ZSteven Mauricio ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra PDFDocument5 pagesAlgebra PDFOnier2 Hernandez2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solución de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en MATLABDocument2 pagesSolución de Ecuaciones Diferenciales en MATLABJuan Carlos Torres HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Teorema de Green, Stokes y de La Divergencia y Su Aplicación en La Física.Document8 pagesTeorema de Green, Stokes y de La Divergencia y Su Aplicación en La Física.Carlos Ivan VilladiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Normalidad MultivarianteDocument21 pagesNormalidad MultivarianteErick BarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Modulo Calculo Integral I 2010Document240 pagesModulo Calculo Integral I 2010Dubier Quinchoa0% (1)
- Seminario de Algebra IDocument6 pagesSeminario de Algebra IFrank Alex VillalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios de MateDocument50 pagesEjercicios de MateJhasmany FtPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulario Reglas de DerivacionDocument2 pagesFormulario Reglas de DerivacionGianpier Pier FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Matematico II - Armando VeneroDocument353 pagesAnalisis Matematico II - Armando VeneroKevin Joseph Martinez RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Influencia. La psicología de la persuasiónD'EverandInfluencia. La psicología de la persuasiónÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (14)
- Recupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaD'EverandRecupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (6)
- Resetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazD'EverandResetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (196)
- ¿Por qué mis padres no me aman?: Empezando a sanarD'Everand¿Por qué mis padres no me aman?: Empezando a sanarÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (33)
- Psicología oscura: Una guía esencial de persuasión, manipulación, engaño, control mental, negociación, conducta humana, PNL y guerra psicológicaD'EverandPsicología oscura: Una guía esencial de persuasión, manipulación, engaño, control mental, negociación, conducta humana, PNL y guerra psicológicaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (766)
- Cómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaD'EverandCómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Teoría polivagal práctica y terapiaD'EverandTeoría polivagal práctica y terapiaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Yo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)D'EverandYo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (7)
- Tu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaD'EverandTu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Pequeño elogio de la fuga del mundo: De Petrarca a Pascal QuignardD'EverandPequeño elogio de la fuga del mundo: De Petrarca a Pascal QuignardÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (64)
- Terapia cognitivo-conductual (TCC) y terapia dialéctico-conductual (TDC): Cómo la TCC, la TDC y la ACT pueden ayudarle a superar la ansiedad, la depresión, y los TOCSD'EverandTerapia cognitivo-conductual (TCC) y terapia dialéctico-conductual (TDC): Cómo la TCC, la TDC y la ACT pueden ayudarle a superar la ansiedad, la depresión, y los TOCSÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- El poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaD'EverandEl poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (16)
- La violencia invisible: Identificar, entender y superar la violencia psicológica que sufrimos (y ejercemos) en nuestra vida cotidianaD'EverandLa violencia invisible: Identificar, entender y superar la violencia psicológica que sufrimos (y ejercemos) en nuestra vida cotidianaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Disciplina Mental: Técnicas infalibles para lograr todo lo que te propones y eliminar la pereza y la procrastinación de tu vida para siempreD'EverandDisciplina Mental: Técnicas infalibles para lograr todo lo que te propones y eliminar la pereza y la procrastinación de tu vida para siempreÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- No desperdicies tus emociones: Cómo lo que sientes te acerca a Dios y le da gloriaD'EverandNo desperdicies tus emociones: Cómo lo que sientes te acerca a Dios y le da gloriaÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (12)
- Terapia cognitiva: Conceptos básicos y profundizaciónD'EverandTerapia cognitiva: Conceptos básicos y profundizaciónÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Una mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosD'EverandUna mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (142)
- Cómo Decir No Sin Sentirte Culpable: Aprende a poner límites en tu vida y a ser respetado sin ofender ni ser ofendidoD'EverandCómo Decir No Sin Sentirte Culpable: Aprende a poner límites en tu vida y a ser respetado sin ofender ni ser ofendidoÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- El chico a quien criaron como perro: Y otras historias del cuaderno de un psiquiatra infantilD'EverandEl chico a quien criaron como perro: Y otras historias del cuaderno de un psiquiatra infantilÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (271)
- Resumen de Pensar rápido pensar despacio de Daniel KahnemanD'EverandResumen de Pensar rápido pensar despacio de Daniel KahnemanÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (64)
- Suicidología: Prevención, tratamiento psicológico e investigación de procesos suicidasD'EverandSuicidología: Prevención, tratamiento psicológico e investigación de procesos suicidasÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (7)
- Libro de Trabajo DE LA TERAPIA DE ACEPTACIÓN Y COMPROMISO (ACT). UNA GUÍA COMPLETA PARA CAMBIAR EL MINDFULNESS Y RECUPERARSE DE LA ANSIEDAD, LA DEPRESIÓN, LOS ATAQUES DE PÁNICO Y LA IRAD'EverandLibro de Trabajo DE LA TERAPIA DE ACEPTACIÓN Y COMPROMISO (ACT). UNA GUÍA COMPLETA PARA CAMBIAR EL MINDFULNESS Y RECUPERARSE DE LA ANSIEDAD, LA DEPRESIÓN, LOS ATAQUES DE PÁNICO Y LA IRAÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (26)
- Autismo: guía para padres sobre el trastorno del espectro autista En españolD'EverandAutismo: guía para padres sobre el trastorno del espectro autista En españolÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Lee a las personas como un libro: Cómo analizar, entender y predecir las emociones, los pensamientos, las intenciones y los comportamientos de las personasD'EverandLee a las personas como un libro: Cómo analizar, entender y predecir las emociones, los pensamientos, las intenciones y los comportamientos de las personasÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)