Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rigid Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Compounds
Transféré par
hashemTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rigid Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Compounds
Transféré par
hashemDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pars Ethylene Kish Co.
Designation: D1784 11
Standard Specification for
Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and
Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Compounds1
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
sh
.c
om
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1784; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon () indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1.4 The text of this specification references notes and
footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and
footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be
considered as requirements of this specification.
1.5 Rigid PVC recycle plastics meeting the requirements of
this specification may be used in some applications. Refer to
the specific requirements in the materials and manufacture
section of the applicable product standard.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.7 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification: This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
en
e-
ki
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers rigid PVC and CPVC compounds intended for general purpose use in extruded or molded
formincluding pressure piping applications and nonpressure
piping applicationscomposed of poly(vinyl chloride), chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride), or vinyl chloride copolymers
containing at least 80 % vinyl chloride, and the necessary
compounding ingredients. The compounding ingredients shall
be permitted to consist of lubricants, stabilizers, non-poly(vinyl
chloride) resin modifiers, pigments, and inorganic fillers.
th
yl
NOTE 1Selection of specific compounds for particular end uses or
applications requires consideration of other characteristics such as thermal
properties, optical properties, weather resistance, etc. Specific requirements and test methods for these properties should be by mutual
agreement between the purchaser and the seller.
NOTE 2Selection of compounds for pressure piping applications
requires consideration of material stress ratings that are required for
determining pressure ratings, but are not addressed in this specification.
Requirements for long-term material stress ratings in accordance with
recognized stress rating standards, such as HDB in accordance with Test
Method D2837 for pressure piping, should be included in specifications
for pressure piping products or systems.
NOTE 3The list of compounding ingredients in 1.1 is not meant to be
an exhaustive list of allowable compound ingredients. In addition to the
compounding ingredients listed, others may also be used. The list of
compounding ingredients in 1.1 does not imply that every ingredient listed
is a required ingredient. Some compounds may not contain all the
ingredients listed in 1.1.
se
NOTE 4This specification is similar in content (but not technically
equivalent) to ISO 1163-1:1985 and ISO 1163-2:1980.
.p
ar
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:2
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
Impact Resistance of Plastics
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D635 Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and
Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
Plastics
D3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
D2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design Basis
for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis
Provided by : www.spic.ir
w
w
1.2 For applications involving special chemical resistance
see Classification D5260.
1.3 The requirements in this specification are intended for
the quality control of compounds used to manufacture finished
products. These properties are based on data obtained using
standard test specimens tested under specified conditions. They
are not directly applicable to finished products. See the
applicable ASTM standards for requirements for finished
products.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published May 2011. Originally
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D1784 08. DOI:
10.1520/D1784-11.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standards Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
(+98 - 21) 88 20 20 60
www.parsethylene-kish.com
Copyright. ASTM International. 100 Barr Harbour Dr. P.O. box C700 West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania 19428-2959, United States
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Nov 1 03:05:06 EDT 2011
Downloaded/printed by
Pars Ethylene Kish Co.
D1784 11
5.2 Further definition, as may be required for the following,
shall be on the basis of agreement between the purchaser and
the seller:
5.2.1 Physical form and particle size (see 6.1),
5.2.2 Contamination level (see 6.2),
5.2.3 Color (see 6.3),
5.2.4 Other supplementary definition if necessary, and
5.2.5 Inspection (see 12.1).
for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
D5260 Classification for Chemical Resistance of Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Homopolymer and Copolymer Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC)
Compounds
2.2 ISO Standards:3
ISO 1163-1:1985
ISO 1163-2:1980
sh
.c
om
6. Materials and Manufacture
6.1 Materials supplied under this specification shall be PVC
and CPVC compounds in the form of cubes, granules, freeflowing powder blends, or compacted powder blends.
6.2 Materials shall be of uniform composition and size and
shall be free of foreign matter to such level of contamination as
may be agreed upon between the purchaser and the seller.
6.3 Color and transparency or opacity of molded or extruded articles formed under the conditions recommended by
the seller shall be comparable within commercial match
tolerances to the color and transparency or opacity of standard
molded or extruded samples of the same thickness supplied in
advance by the seller of the material.
3. Terminology
3.1 DefinitionsDefinitions are in accordance with Terminology D883 and abbreviations with Terminology D1600
unless otherwise indicated.
e-
ki
4. Classification
4.1 Means for selecting and identifying rigid PVC and
CPVC compounds are provided in Table 1. The properties
enumerated in Table 1 and the tests defined are expected to
provide identification of the compounds selected. They are not
necessarily suitable for direct application in design because of
differences in shape of part, size, loading, environmental
conditions, etc.
4.2 Classes are designated by the cell number for each
property in the order in which they are listed in Table 1.
en
7. Physical Requirements Physical Requirements
7.1 Test values for specimens of the material prepared as
specified in Section 9 and tested in accordance with Section 10
shall conform to the requirements given in Table 1 for the class
selected.
yl
NOTE 5The manner in which selected materials are identified by this
classification system is illustrated by a Class 12454 rigid PVC compound
having the following requirements (see Table 1). The two-digit cell limits
10 and 11 are rarely used, only for special high-temperature grades of
CPVC compound:
th
9. Conformance Testing
9.1 The minimum properties identified by the class designations in Table 1 specified in the purchase order (see 5.1) shall
be verified by the tests described in Section 11.
9.2 Conformance with this specification shall be determined
with one set of test results. If there are multiple test results, the
average value for all test samples shall be used to determine
conformance.
9.3 If the average test value produces values below the
minimum property values of the Class designation in Table 1,
the material does not conform to this specification.
ar
Property and Minimum Value:
Izod
(34.7 J/m (0.65 ftlbf/in.)) under notch
se
Class
Identification:
Poly(vinyl chloride) homopolymer
8. Sampling
8.1 A batch or lot shall be considered as a unit of manufacture and may consist of a blend of two or more production runs
of material.
8.2 Sample using a statistically acceptable procedure.
Tensile strength
(48.3 MPa (7000 psi))
.p
Modulus of elasticity in tension
(2758 MPa (400 000 psi))
w
w
Deflection temperature under load
(70C (158F))
Provided by : www.spic.ir
NOTE 6The cell-type format provides the means for identification and
close characterization and specification of material properties, alone or in
combination, for a broad range of materials. This type format, however, is
subject to possible misapplication since unobtainable property combinations can be selected if the user is not familiar with commercially available
materials. The manufacturer should be consulted.
10. Specimen Preparation
10.1 Compliance with the designated requirements chosen
from Table 1 shall be determined with compression-molded,
extruded, or injection-molded test specimens for Izod impact
resistance, tensile strength, tensile modulus of elasticity, deflection temperature under load, and flammability. Specimens
cut from laminates of compression-molded or extruded sections (see Practice D4703) shall not be used unless it can be
shown by test that complete fusion is obtained. It is understood
that a material shall not be tested without also specifying the
method of specimen preparation. When comparative tests of
materials are desired, the greatest care shall be taken to ensure
4.3 Product application chemical resistance when specified
shall be classified in accordance with the classification section
of Classification D5260.
5. Ordering Information
5.1 The purchase order, or inquiry, for these materials shall
state the specification number and identify the class selected,
for example, D1784, Class 12454.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Nov 1 03:05:06 EDT 2011
Downloaded/printed by
(+98 - 21) 88 20 20 60
www.parsethylene-kish.com
Pars Ethylene Kish Co.
D1784 11
TABLE 1 Class Requirements for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Compounds
NOTE 1The minimum property value will determine the cell number although the maximum expected value may fall within a higher cell.
Cell Limits
Property and Unit
0
Impact resistance
(Izod), min:
J/m of notch
under notch
ftlb/in. of notch
under notch
Tensile strength,
min:
MPa
psi
Modulus of
elasticity in
tension, min:
MPa
psi
Deflection
temperature
under load, min,
1.82 MPa
(264 psi):
C
F
Flammability
10
11
unspecified
poly(vinyl
chloride)
homopolymer
chlorinated
poly
(vinyl
chloride)
vinyl copolymer
unspecified
<34.7
34.7
80.1
266.9
533.8
800.7
<0.65
0.65
1.5
5.0
10.0
15.0
unspecified
<34.5
<5 000
34.5
5 000
41.4
6 000
48.3
7 000
55.2
8 000
unspecified
<1930
<280 000
1930
280 000
2206
320 000
2482
360 000
2758
400 000
unspecified
<55
<131
55
131
60
140
70
158
80
176
90
194
100
212
110
230
120
251
130
266
140
284
sh
.c
om
3034
440 000
ki
Base resin
e-
en
Designation
Order
No.
th
yl
All compounds covered by this specification, when tested in accordance with Test Method D635, shall yield the following results: average extent of burning of <25 mm;
average time of burning of <10 s.
mens may be compression-molded, extruded, or injectionmolded with the provision that compression-molded or extruded specimens built up as laminates in which complete
fusion is obtained shall be acceptable. Complete fusion means
there shall be no evidence of fraying or delamination at the
break.
11.5 Deflection TemperatureTest Method D648Method
A- using 127 mm (5 in.) long, 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) wide, and 3.2
mm (0.125 in.) thick specimens under 1.82 MPa (264 psi) fiber
stress. Materials that require high-temperature annealing prior
to testing shall be annealed at 50C (122F) for 24 h or at the
manufacturers recommendation. Specimens shall be cooled in
accordance with Procedure B of Practice D618. The test report
for annealed specimens shall include the time and temperature
of annealing used.
11.6 FlammabilityTest Method D635. All compounds
covered by this specification, when tested in accordance with
Test Method D635, shall yield the following results: average
extent of burning of <25 mm; average time of burning of <10
s.
se
that all specimens are prepared in exactly the same way used to
certify the cell class of the compound. Procedures used in
preparing the test specimens shall be as recommended by the
supplier for each specific compound.
ar
NOTE 7It is possible that a specimen taken from a finished product
will not produce the same results as a specimen prepared by the method
used for purposes of cell class testing and certification.
Provided by : www.spic.ir
w
w
.p
11. Test Methods
11.1 ConditioningThe test specimen for deflection temperature (Test Method D648) shall be conditioned in accordance with Procedure B of Practice D618, except that the
minimum conditioning time in the circulating air oven shall be
24 h. All other molded test specimens shall be conditioned in
accordance with Procedure A of Practice D618. The minimum
conditioning time shall be 24 h.
11.2 Test ConditionsUnless otherwise specified in the test
methods or in this specification, tests shall be conducted in the
standard laboratory atmosphere of 23 6 2C (73.4 6 3.6F)
and 50 6 5 % relative humidity. In cases of disagreement, the
tolerances shall be 61C (61.8F) and 62 % relative humidity.
11.3 Tensile Strength and Modulus of ElasticityTest
Method D638, using Type I specimens of 3.2 6 0.4 mm (0.13
6 0.02 in.) thickness and testing speed of 5.1 mm (0.20
in.)/min 6 25 %. Report tensile strength at the yield point if the
material yields, otherwise at break.
11.4 Impact Resistance (Izod)Method A of Test Method
D256, using 3.2-mm (0.125-in.) thick specimens. The speciCopyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Nov 1 03:05:06 EDT 2011
Downloaded/printed by
12. Inspection
12.1 Inspection of the material shall be made as agreed upon
between the purchaser and the seller as part of the purchase
contract.
13. Packaging and Package Marking
13.1 PackagingThe material shall be packaged in standard commercial containers, so constructed as to ensure
3
(+98 - 21) 88 20 20 60
www.parsethylene-kish.com
Pars Ethylene Kish Co.
D1784 11
acceptance by common or other carriers for safe transportation
at the lowest rate to the point of delivery, unless otherwise
specified in the contract or order.
13.2 MarkingUnless otherwise agreed upon between the
purchaser and the seller, shipping containers shall be marked
with the name of the material and the name of the manufacturer; class, batch, or lot number; quantity contained therein, as
defined by the contract or order under which shipment is made;
the name of the seller; and the number of the contract or order.
13.3 All packing, packaging, and marking provisions of
Practice D3892 shall apply to this specification.
14. Keywords
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
sh
.c
om
14.1 chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride) (CPVC); CPVC compounds; poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC); PVC compounds; recycle
plastics; rigid PVC
Committee D20 has identified the location of selected changes to this standard since the last issue (D1784 - 08)
that may impact the use of this standard. (Approved May 1, 2011.)
(4) Deleted old 1.3, which contained the D3915 and D4396
references.
(5) Deleted the D3915 and D4396 references from 2.1.
(6) Deleted the reference to special heat resistance because
D1784 lacks any reference to a heat resistance test method.
(7) Deleted old 1.4, which contained the reference to D1216.
en
e-
ki
(1) Deleted the chemical resistance reference from 1.1. Standard D 5260 governs chemical resistance classification for
PVC and CPVC compounds.
(2) Created a new 1.2, directing those users with special
chemical resistance requirements to Classification D5260.
(3) Replaced the word shall with should in Note 1 in
keeping with the directive that notes must not contain requirements.
yl
ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned
in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk
of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
se
th
This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every five years and
if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards
and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should
make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below.
Provided by : www.spic.ir
w
w
.p
ar
This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,
United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above
address or at 610-832-9585 (phone), 610-832-9555 (fax), or service@astm.org (e-mail); or through the ASTM website
(www.astm.org). Permission rights to photocopy the standard may also be secured from the ASTM website (www.astm.org/
COPYRIGHT/).
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Nov 1 03:05:06 EDT 2011
Downloaded/printed by
(+98 - 21) 88 20 20 60
www.parsethylene-kish.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Astm D1785-15Document11 pagesAstm D1785-15david franco0% (1)
- Astm F441-02 PDFDocument7 pagesAstm F441-02 PDFedelvallemp93100% (2)
- ASTMD1998Document8 pagesASTMD1998sgttomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm f441 NewDocument7 pagesAstm f441 NewhendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2239Document7 pagesAstm D2239Hernando Andrés Ramírez GilPas encore d'évaluation
- Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Gaskets For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary, and Storm Plumbing SystemsDocument3 pagesPoly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Gaskets For Drain, Waste, and Vent (DWV), Sewer, Sanitary, and Storm Plumbing SystemsveintavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D1784-03Document4 pagesAstm D1784-03adanserranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D1785-2012Document11 pagesAstm D1785-2012mavericklf1100% (1)
- Astm D3034 00 PDFDocument10 pagesAstm D3034 00 PDFngronau124545Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F477Document4 pagesAstm F477Hernando Andrés Ramírez Gil100% (1)
- D2665 PDFDocument6 pagesD2665 PDFDavid SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F714Document10 pagesAstm F714CarlosChaconPas encore d'évaluation
- D3350Document7 pagesD3350Luis Fernando Morales100% (1)
- Astm D3311Document27 pagesAstm D3311Hernando Andrés Ramírez GilPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2467-2013Document8 pagesAstm D2467-2013Renato CorrêaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM F412-12 TerminologyDocument18 pagesASTM F412-12 TerminologyMarlon TurnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2683 (1998)Document5 pagesAstm D2683 (1998)SANKARAN.K100% (1)
- Thickness and Density of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material (SFRM) Applied To Structural MembersDocument5 pagesThickness and Density of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material (SFRM) Applied To Structural MembersBeymerBustamanteMejía100% (2)
- Astm D2855Document7 pagesAstm D2855Hernando Andrés Ramírez Gil100% (1)
- Astm D 4437 D 4437MDocument2 pagesAstm D 4437 D 4437Mdarthluiss100% (5)
- Centrifugally Cast "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) PipeDocument5 pagesCentrifugally Cast "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) PipeShaker Qaidi100% (1)
- Astm D1599 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm D1599 PDFChemical Engineer100% (3)
- Astm D3212.380331 1Document3 pagesAstm D3212.380331 1anish_am2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- C969 02 (2009)Document3 pagesC969 02 (2009)YOVANI100% (1)
- Norma Astm 2412Document7 pagesNorma Astm 2412Jluis IpnPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM F412 12 Terminology PDFDocument18 pagesASTM F412 12 Terminology PDFBinodh DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F2769Document10 pagesAstm F2769Hernando Andrés Ramírez GilPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesDetermining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings: Standard Test Method ForhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- D2444-99 (2010) Standard Test Method For DeterminatDocument9 pagesD2444-99 (2010) Standard Test Method For Determinatjavier perezPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D1599-18Document4 pagesAstm D1599-18Parewa Scorp100% (1)
- Astm D3035 - 06Document7 pagesAstm D3035 - 06Raul Humberto Mora VillamizarPas encore d'évaluation
- F439Document7 pagesF439cenkunal100% (1)
- Astm d4101Document17 pagesAstm d4101asdrecvPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D3261 (1997)Document6 pagesAstm D3261 (1997)anish_am2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D6392 2012 Rev 2018 PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D6392 2012 Rev 2018 PDFWard BentPas encore d'évaluation
- F2164Document5 pagesF2164Hernando Andrés Ramírez Gil100% (1)
- D2412-11 Standard Test Method For Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate LoadingDocument7 pagesD2412-11 Standard Test Method For Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loadingjavier perezPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM E84-15a Standard Test Method For Surface Burning Characteristics of Building MaterialsDocument22 pagesASTM E84-15a Standard Test Method For Surface Burning Characteristics of Building MaterialsDiego Egoávil Méndez100% (2)
- Ductile-Iron Compact Fittings For Water Service: AWWA StandardDocument48 pagesDuctile-Iron Compact Fittings For Water Service: AWWA StandardGerman FavelaPas encore d'évaluation
- D3299 Standard Specification For Filament-Wound Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermoset Resin Corrosion-Resistant TanksDocument17 pagesD3299 Standard Specification For Filament-Wound Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermoset Resin Corrosion-Resistant TanksCalidad Equisplast100% (2)
- ASTM-D543 (2014) - Evaluating The Resistance of Plastics To Chemical ReagentsDocument7 pagesASTM-D543 (2014) - Evaluating The Resistance of Plastics To Chemical ReagentsAndre Castelo100% (1)
- Astm D2122.23100Document6 pagesAstm D2122.23100Mariano Emir Garcia OdriozolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2466Document6 pagesAstm D2466Hernando Andrés Ramírez Gil0% (1)
- ASTM - D 5685 - Standard Specification For Fiberglass Pressure Pipe FittingsDocument5 pagesASTM - D 5685 - Standard Specification For Fiberglass Pressure Pipe FittingsmonitorsamsungPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F438Document7 pagesAstm F438Hernando Andrés Ramírez GilPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2321Document12 pagesAstm D2321Emre AkınayPas encore d'évaluation
- AWWA C151-02 Ductile-Iron Pipe, Centrifugally Cast, For WaterDocument50 pagesAWWA C151-02 Ductile-Iron Pipe, Centrifugally Cast, For Waterneno2405Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astm - D4097-01 PDFDocument17 pagesAstm - D4097-01 PDFJEAN PIEREPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm F 477 - 02 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm F 477 - 02 PDFRaul Humberto Mora Villamizar100% (8)
- Astm D4218 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm D4218 PDFthlpapPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D 746 PDFDocument9 pagesAstm D 746 PDFmanoj madurangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2837 (2001)Document14 pagesAstm D2837 (2001)Muzammil Khalil100% (3)
- Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe (DR-PR) Based On Outside DiameterDocument12 pagesPolyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe (DR-PR) Based On Outside DiameterBayron Parra100% (2)
- Astm D 543-06Document7 pagesAstm D 543-06varniktpPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D5685Document5 pagesAstm D5685biondimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm A53Document23 pagesAstm A53hermes willian santiago floresPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Specification For RIGID PVCDocument5 pagesStandard Specification For RIGID PVCvongoctu2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astm d1784 03 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm d1784 03 PDFCarlos ArosPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D1784 - Jtvo9242Document4 pagesASTM D1784 - Jtvo9242Nayth Andres GalazPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D1784Document4 pagesAstm D1784kashif ehsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2412-2008Document6 pagesAstm D2412-2008hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D2122-2004 - 2Document5 pagesAstm D2122-2004 - 2hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesDetermining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings: Standard Test Method ForhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe Under Constant Internal PressureDocument4 pagesTime-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe Under Constant Internal PressurehashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 4437 - Cor1 (1999)Document1 pageIso 4437 - Cor1 (1999)hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarawat A 200 (: Glycine Max L.)Document8 pagesTarawat A 200 (: Glycine Max L.)hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Absorbent 5Document9 pagesSuper Absorbent 5hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Absorbent 2Document8 pagesSuper Absorbent 2hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- ژل هاوا2Document8 pagesژل هاوا2hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Absorbent 6Document8 pagesSuper Absorbent 6hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument8 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
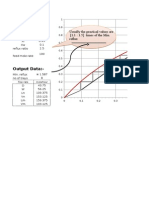
- Input Data:-: Usually The Practical Values Are (1.1: 1.5) Times of The Min. RefluxDocument6 pagesInput Data:-: Usually The Practical Values Are (1.1: 1.5) Times of The Min. RefluxhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument12 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument8 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument7 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument5 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument8 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument6 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Archive of SIDDocument8 pagesArchive of SIDhashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Prafulla Chandra Roy Was Born On 2nd AugustDocument1 pagePrafulla Chandra Roy Was Born On 2nd AugustAnjan SarbadhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Vessel Plates, Carbon Steel, For Moderate-And Lower-Temperature ServiceDocument4 pagesPressure Vessel Plates, Carbon Steel, For Moderate-And Lower-Temperature ServiceGerman FavelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BrucePas encore d'évaluation
- Mannich BaseDocument7 pagesMannich BaseDamar Nurwahyu BimaPas encore d'évaluation
- DefaultDocument19 pagesDefaultNitrosieniPas encore d'évaluation
- Monday 20 May 2019: ChemistryDocument24 pagesMonday 20 May 2019: Chemistryahumad aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Nomenclature Bank 1Document18 pagesOrganic Nomenclature Bank 1talaaty599Pas encore d'évaluation
- Felodipine: FelodipinumDocument2 pagesFelodipine: FelodipinumIoana-Alexandra Lungu-NastasePas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum-Ultraviolet (VUV) Photo-Polymerization of Amine-Rich Thin Films From Ammonia-Hydrocarbon Gas MixturesDocument12 pagesVacuum-Ultraviolet (VUV) Photo-Polymerization of Amine-Rich Thin Films From Ammonia-Hydrocarbon Gas MixturessabzinehPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3Document14 pagesLec 3anuda09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water PurificationDocument316 pagesWater Purificationshapelesswind100% (2)
- SGP Fusion enDocument4 pagesSGP Fusion enTimmyJuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document259 pagesChapter 7Hafizszul Feyzul100% (1)
- 6CH05 01 Que 20170621 PDFDocument28 pages6CH05 01 Que 20170621 PDFAhmad MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Salt Analysis - Viva QuestionsDocument7 pagesSalt Analysis - Viva Questionsnoora100% (1)
- Subsea: Fluids Pte LTDDocument7 pagesSubsea: Fluids Pte LTDcacalot93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cbse QP - XI - CHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesCbse QP - XI - CHEMISTRYRamana PadalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Chemistry Unit 5 KeyDocument10 pagesAp Chemistry Unit 5 Keycookiesadries629Pas encore d'évaluation
- Misconceptions On SN1 SN2 ReactionsDocument3 pagesMisconceptions On SN1 SN2 ReactionsEdcademiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Not CR or CR (II) .: A2-Level Chemistry Unit 5.3 (Transition Metal Chemistry) Mark Scheme For Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesNot CR or CR (II) .: A2-Level Chemistry Unit 5.3 (Transition Metal Chemistry) Mark Scheme For Sample QuestionsJake RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Analytical Testing of Cannabis and Hemp: Anthony MacheroneDocument27 pagesComprehensive Analytical Testing of Cannabis and Hemp: Anthony MacheroneyixovPas encore d'évaluation
- CY1101Document3 pagesCY1101Anurag BaralPas encore d'évaluation
- Ino & Org Chemistry PrelimsDocument16 pagesIno & Org Chemistry PrelimsG8 ODL Mary Angeline M. GalmanPas encore d'évaluation
- #26 ImmunochemistryDocument44 pages#26 ImmunochemistryasclswisconsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Notes IGCSE Grade 7Document57 pagesScience Notes IGCSE Grade 7callista.d.fPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 22Document10 pagesUnit 22Ankit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactivity of Oximes For Diverse Methodologies and Synthetic ApplicationsDocument13 pagesReactivity of Oximes For Diverse Methodologies and Synthetic ApplicationsAnahí TessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid State ChemistryDocument6 pagesSolid State ChemistryAravindan B BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Amorphous SolidDocument17 pagesAmorphous SolidFeni FebriyantiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009-02-20 Bartoli Indole Synthesis, AlexDocument6 pages2009-02-20 Bartoli Indole Synthesis, AlexBen de LangePas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyD'EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (21)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsD'EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityD'EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Lees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlD'EverandLees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignD'EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Troubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersD'EverandTroubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3D'EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsD'EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (10)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersD'EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersPas encore d'évaluation
- High Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesD'EverandHigh Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationD'EverandDistillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationD'EverandThe Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsD'EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesD'EverandA New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandFun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsD'EverandHandbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsH. W. HibbottÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Fun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandFun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Coulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesD'EverandCoulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesAjay Kumar RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesD'EverandPulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Bioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringD'EverandBioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringGuang YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Biochemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to ExcellenceD'EverandMastering Biochemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to ExcellencePas encore d'évaluation
- Transport Phenomena in Heat and Mass TransferD'EverandTransport Phenomena in Heat and Mass TransferJ.A. ReizesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringD'EverandThe Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringS. S. GillÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersD'EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersPas encore d'évaluation