Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Edta
Transféré par
slchemDescription originale:
Copyright
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Edta
Transféré par
slchemDroits d'auteur :
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
EDTA-It is ethylene diammine tetra acetic acid.
Most widely used method to determine hardness of water.
It is a weak acid that can lose four H+ ions on complete
neutralization.
As it is not very water soluble hence its sodium salt is usedNa2H2C10H12N2O4.
Molecular weight-372.24
Reacts with only group-2 metal ions.
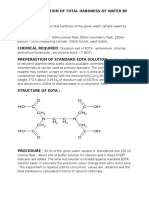
Structure of EDTA-
PRINCIPLE
Metal ion solution is titrated with standardized EDTA
solution.
Indicator used is Eriochrome black-T(EBT).
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
(EBT is alcoholic solution of blue eye. With Ca2+ and Mg2+
it forms wine red complex of pH-10
Buffer of NH4OH and NH4Cl is added to maintain pH at
10.
1.
INITIAL REACTION -
M2++EBT
[M-EBT]
(BLUE)
(WINE RED)
M=Ca2+ or Mg2+
2.
TITRATION REACTION
[M-EBT]complex+ EDTA
M2+ + EBT
[M-EBT] complex
( metal ions still present)
3.
(wine- red)
END POINT REACTION
[M-EBT] complex+ EDTA
[M-EDTA]complex +EBT
[M-EDTA]complex+ EBT
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
PROCEDURE
I. PREPARATION OF REAGENTS
a) Preparation of standard hard water-Take
1.0 gm of CaCO3 and dissolve in min. amount of HCl.
Evaporate the solution to dryness on a water bath. Make 1L
solution by dissolving residue in
Distilled water. Each ml of this solution will correspond to
1mg of CaCO3 hardness.
b) Preparation
of EDTA solution- Dissolve 3.72
gm of pure EDTA crystals +0.1g MgCl2 in 1L distilled
water.(MgCl2 binds to EDTA quicker forming M-EDTA
complex which is less stable than Ca- EDTA complex)
c) Preparation
of indicator- Dissolve 0.5g of EBT in
100ml of alcohol.
d) Preparation
of buffer solution- Add 67.5g of
NH4Cl to 570ml of conc. ammonia solution and then dilute
with distilled water to 1L
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
II. PROCEDURE
a) Standardization of EDTA solution- In conical
flask, pipette out 50ml of SHW and add 10-15ml of buffer
solution and 4-5 drops indicator. Titrate with EDTA till wine
color changes to clear blue. Let volume used be V1 ml.
b) Titration
of unknown hard water- Titrate water
sample similar to earlier step. Let volume used be V2 ml.
c) Titration
of permanent hardness-
In a large
beaker take 250 ml of water sample and boil it till 50ml
volume is reached (carbonates decomposed to insoluble
CaCO3+Mg(OH)2).Filter and wash precipitate with distilled
water and all filtrate and washings being collected in 250ml
flask. Then titrate as in previous step. Let volume used be
V3 ml.
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
III. CALCULATIONS
a) Total hardness
50ml of SHW =V1 ml EDTA
Hence 50 *1mg of CaCO3 =V1 ml of EDTA
1ml of EDTA=50/V1 mg of CaCO3
Now 50ml of hard water=V2 ml of EDTA
= V2*50/V1 mg of CaCO3 eq
1ml of given hard water = V2/ V1 mg of CaCO3 eq
1000ml of given hard water=1000* V2/ V1 mg of CaCO3 eq/L
Total hardness=1000* V2/ V1 ppm
b)
Permanent Hardness
Now, 50ml of boiled water=V3 ml of EDTA
V3*50/V1 mg of CaCO3 eq
1000ml of boiled water=1000* V3/V1 mg of CaCO3 eq/L
Hence permanent hardness=1000* V3/V1 mg of CaCO3 ppm
c)
Temporary Hardness
=TOTAL
HARDNESS- PERMANENT HARDNESS
=1000*(V2-V3)/V1 ppm.
ADVANTAGES OF EDTA METHOD:
Great accuracy
Convenience
More rapid procedure
WATER
EDTA PROCESS
THEORY
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hardness of WaterDocument11 pagesHardness of WaterVikrant Singh0% (1)
- Determining The Hardness of Water Via EDTA-TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermining The Hardness of Water Via EDTA-Titrationstudent_4_eva0% (1)
- CMT552 4 Electrolyte ConductanceDocument57 pagesCMT552 4 Electrolyte ConductanceAira Ariana100% (1)
- Lab Report Hardness of WaterDocument13 pagesLab Report Hardness of WaterFelix YeboahPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Transference Number by Hittorf's MethodDocument5 pagesDetermination of Transference Number by Hittorf's MethodRichmond NyamadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Alloy Analysis Class 12Document18 pagesAlloy Analysis Class 12TusharSharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1Document4 pagesExperiment 1gajenraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Practical FileDocument26 pagesChemistry Practical FileAyushPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardness of WaterDocument12 pagesHardness of WaterMohd AfnaanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12th PracsDocument4 pages12th Pracssuryav123100% (1)
- Surface Chemisrty ExperimentDocument3 pagesSurface Chemisrty ExperimentOnkar RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation of Copper in Brass AlloyDocument3 pagesEstimation of Copper in Brass AlloyMg H100% (1)
- TitrationDocument31 pagesTitrationAtul BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pagesChemistry ProjectUday SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Available Chlorine in Bleaching PowderDocument2 pagesDetermination of Available Chlorine in Bleaching Powderkuthappady50% (4)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 1Document16 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 1Shubhankar Oad100% (1)
- Oxalic Acid Vs NaOH Lab ReportDocument2 pagesOxalic Acid Vs NaOH Lab ReportAkhil Menon100% (1)
- Practical XI Class 11 ChemistryDocument18 pagesPractical XI Class 11 ChemistryTechno GuruPas encore d'évaluation
- To Prepare Ferric Hydroxide Sol - Chemistry Practical Class 12 - Learn CBSEDocument1 pageTo Prepare Ferric Hydroxide Sol - Chemistry Practical Class 12 - Learn CBSESujal JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 CHEMISTRY Project SHAURYADocument14 pagesClass 12 CHEMISTRY Project SHAURYAShaurya Tripathi100% (1)
- Class - Xii Subject: Chemistry (Practical) Term-2 Experiments (2021 - 22)Document34 pagesClass - Xii Subject: Chemistry (Practical) Term-2 Experiments (2021 - 22)CarbonPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 12 Chemistry Observation (Ex 13-25)Document25 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry Observation (Ex 13-25)thirumalaivasan GPas encore d'évaluation
- Danelia Gordon - Standardization of Sulphuric Acid With Sodium Carbonate (Lab #1)Document2 pagesDanelia Gordon - Standardization of Sulphuric Acid With Sodium Carbonate (Lab #1)Danelia Gordon0% (1)
- Conductometric TitrationDocument2 pagesConductometric TitrationDelin Shaji JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissolved OxygenDocument2 pagesDissolved OxygenkuthappadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Salt AnalysisDocument8 pagesSalt AnalysisB.K.Sivaraj raj0% (1)
- Chem ProjectDocument15 pagesChem ProjectBharath P JayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem PracticalsDocument28 pagesChem PracticalsSnigdha GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Conductometric Titration of Mixture of AcidsDocument3 pagesConductometric Titration of Mixture of AcidsHet100% (2)
- Volumetric Analysis Mohr SaltDocument3 pagesVolumetric Analysis Mohr SaltAbhishek PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Lab Manual Class-Xii Practical File Term-I (2021-22)Document16 pagesChemistry Lab Manual Class-Xii Practical File Term-I (2021-22)Tapan BadheiPas encore d'évaluation
- Titration Lab ReportDocument5 pagesTitration Lab ReportvaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Vitamin C in Fruit JuiceDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Vitamin C in Fruit JuiceManav RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Crystalline, Amorphous & Polymorphism PDFDocument33 pagesSolid Crystalline, Amorphous & Polymorphism PDFPrabhas Meher100% (1)
- Term - 2 Chem Project DetailsDocument3 pagesTerm - 2 Chem Project DetailsMouli CsPas encore d'évaluation
- Qualitative Analysis: Identification of The AnionDocument40 pagesQualitative Analysis: Identification of The AniontwinkledreampoppiesPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch08 The Dblock F-Block ElementsSwaroop SurendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Expt 6-Conductometric TitrationDocument4 pagesExpt 6-Conductometric TitrationAsriandy Ramadhan100% (1)
- Lab Redox TitrationDocument5 pagesLab Redox TitrationLuIs I. GuTi0% (1)
- Estimation of Water Hardness by EDTA Method and Its Removal by Ion-Exchange ResinDocument5 pagesEstimation of Water Hardness by EDTA Method and Its Removal by Ion-Exchange ResinAnurag karkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterlization of WaterDocument21 pagesSterlization of WaterAnonymous eQLybzbh50% (2)
- Determination of Caffeine in Tea SamplesDocument17 pagesDetermination of Caffeine in Tea SamplesAkshat Lomas100% (1)
- 5.0 Experiment On Determination of Total Hardness: Sl. NoDocument13 pages5.0 Experiment On Determination of Total Hardness: Sl. NoJomana JomanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesChem Investigatory ProjectLolaa M HPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Dying of FibresDocument9 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project Dying of FibresYogesh BharambePas encore d'évaluation
- Titration of Mohr SaltDocument2 pagesTitration of Mohr SaltPriyanshee Songara100% (1)
- Prepare 250 ML of M/10 Solution of Oxalic Acid From Crystalline Oxalic AcidDocument3 pagesPrepare 250 ML of M/10 Solution of Oxalic Acid From Crystalline Oxalic AcidVeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation of Cu (II) Using Sodium Thiosulphate Solution (Iodometrically)Document11 pagesEstimation of Cu (II) Using Sodium Thiosulphate Solution (Iodometrically)Gayatri Govind NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Tooth Paste Analysis CBSE Class 12Document23 pagesTooth Paste Analysis CBSE Class 12Radhey Patel100% (1)
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 2: SolutionDocument14 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 2: SolutionLuisgarciaBerlangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Constituents of AlloyDocument5 pagesStudy of Constituents of Alloyaryan kushwaha100% (2)
- Experiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTADocument2 pagesExperiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTAizz isalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Apparatus:: Estimation of Total Hardness of Water by Edta AimDocument3 pagesApparatus:: Estimation of Total Hardness of Water by Edta AimRADHESHYAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 2: Complexometric Titration 1.0 ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 2: Complexometric Titration 1.0 ObjectivesSangetha ChelladoraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On EDTADocument4 pagesProblems On EDTAAniket Kundu100% (1)
- Chemistry Experiment ManualsDocument34 pagesChemistry Experiment Manualsmnasir328115Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposeDocument4 pagesChemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposekuochsochinPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Technology Unit - IDocument40 pagesWater Technology Unit - ISathis KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ChemDocument24 pagesProject Chemsiddharth jugalePas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Opearations and Properties of SetsDocument4 pagesSolved Opearations and Properties of SetsslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthetic RubberDocument3 pagesSynthetic RubberslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of Set TheoryDocument4 pagesLaws of Set TheoryslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Sets and Operations On SetsDocument4 pagesSets and Operations On SetsslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Partition of SetsDocument6 pagesPartition of Setsslchem0% (1)
- Calorific ValuesDocument3 pagesCalorific ValuesslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Compounding of PlasticsDocument3 pagesCompounding of PlasticsslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Polymers Theory: Polymer - Poly (Many) + Miros (Parts)Document3 pagesPolymers Theory: Polymer - Poly (Many) + Miros (Parts)slchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Zeolite or Permutit Process - Zeolite: Na ZeDocument3 pagesZeolite or Permutit Process - Zeolite: Na ZeslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Component Water SystemDocument6 pagesTwo Component Water SystemslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- SolvedDocument3 pagesSolvedslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Rubber and VulcanisationDocument3 pagesNatural Rubber and Vulcanisationslchem100% (1)
- Classification of LubricantsDocument12 pagesClassification of Lubricantsslchem100% (5)
- Comparison and ClassificationDocument4 pagesComparison and ClassificationslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and LubricationDocument9 pagesIntroduction and LubricationslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Moulding of PlasticsDocument4 pagesMoulding of PlasticsslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Softening Method: - "The Process of Removing ofDocument5 pagesSoftening Method: - "The Process of Removing ofslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- One Compenent Water SystemDocument7 pagesOne Compenent Water Systemslchem80% (5)
- Hardness of WaterDocument3 pagesHardness of WaterslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Cement T5 TheoryDocument5 pagesCement T5 Theoryslchem100% (2)
- Ion ExchangeDocument4 pagesIon ExchangeslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Refractories T1 TheoryDocument12 pagesRefractories T1 TheoryslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Nanotubes T2 TheoryDocument6 pagesCarbon Nanotubes T2 TheoryslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Bod and CodDocument3 pagesBod and CodslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Cement T3 TheoryDocument6 pagesCement T3 TheoryslchemPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementLouie Jay Cañada AbarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Namma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163Document36 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163609001Pas encore d'évaluation
- TOS 1st QuarterDocument6 pagesTOS 1st QuarterQuerisa Ingrid MortelPas encore d'évaluation
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Document49 pagesCpa Review School of The Philippines: Related Psas: Psa 700, 710, 720, 560, 570, 600 and 620Jasmine LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinson Hoehn and Yahr ScaleDocument3 pagesParkinson Hoehn and Yahr ScaleCarol Artigas GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- LoRa TechnologyDocument10 pagesLoRa TechnologyAnonymous CGk2roPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5Document1 pageUnit 5-People Should Manage Nature-Ts-Planning Guide-Grade 5api-457240136Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Locomotive and Multi-Unit Fatigue Strength Considering The Results of Certifi Cation Tests in Ukraine and EU CountriesDocument8 pagesAssessment of Locomotive and Multi-Unit Fatigue Strength Considering The Results of Certifi Cation Tests in Ukraine and EU CountriesLeonardo Antônio Pereira100% (1)
- Samsung WF8500NMW8Document180 pagesSamsung WF8500NMW8Florin RusitoruPas encore d'évaluation
- Hortee OromooDocument48 pagesHortee OromooAsnaafii BantiiPas encore d'évaluation
- WRhine-Main-Danube CanalDocument6 pagesWRhine-Main-Danube CanalbillPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailJay MPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Assignment 17-M-518 MMM - Eicher MotorDocument33 pagesFM Assignment 17-M-518 MMM - Eicher MotorTrilokPas encore d'évaluation
- 1349122940100212diggerDocument24 pages1349122940100212diggerCoolerAdsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20Document46 pagesLazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20macPas encore d'évaluation
- Kajima's Three PolicyDocument2 pagesKajima's Three PolicyBe Seang SePas encore d'évaluation
- 43 Best Passive Income Streams & OpportunitiesDocument7 pages43 Best Passive Income Streams & OpportunitiesEri Nur Sofa50% (2)
- Genie Awp SpecsDocument4 pagesGenie Awp SpecsIngrid Janet GuardadoPas encore d'évaluation
- AS Film Production Lesson.Document13 pagesAS Film Production Lesson.MsCowanPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 6 - Performance AppraisalDocument50 pagesCH 6 - Performance AppraisalMark SullivanPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat TreatmentDocument14 pagesHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- New DOCX DocumentDocument2 pagesNew DOCX DocumentPunjabi FootballPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Enterprise LeadersDocument148 pagesCreating Enterprise LeadersValuAidPas encore d'évaluation
- Booklet The 8th JAKINUDocument20 pagesBooklet The 8th JAKINUsamuelionardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-4.Vector CalculusDocument32 pagesUnit-4.Vector Calculuskhatua.deb87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mucic Acid Test: PrincipleDocument3 pagesMucic Acid Test: PrincipleKrizzi Dizon GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Explicit Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesExplicit Lesson PlanBanjo De Los SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Canon JX 500 - 200 - Service ManualDocument154 pagesCanon JX 500 - 200 - Service ManualFritz BukowskyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fulltext PDFDocument454 pagesFulltext PDFVirmantas JuoceviciusPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect Mind MapDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Mind MappaulssPas encore d'évaluation