Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Plan F2 2013
Transféré par
Michael AustinTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Yearly Plan F2 2013
Transféré par
Michael AustinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Created by CDC SZA 10
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN
FORM 2
SCIENCE
SCIENCE PANEL OF SMKIS 2013
Created by CDC SZA 10
TABLE OF CONTENTS
THEMES & LEARNING AREAS
Page
THEME 1 :
MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
Learning Area:
1. World through our senses
Learning Area:
2. Nutrition
2-4
4-6
THEME 2 :
MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS
Learning Area:
1. Biodiversity
Learning Area:
2. Interdependence among living organisms and the environment
6
7-10
THEME 3 :
MATTER IN NATURE
Learning Area:
1. Water and Solution
Learning Area:
2. Air Pressure
10-15
16-17
THEME 4 : FORCE AND MOTION
Learning Area:
1. Dynamics
Learning Area:
2. Support and Movement
15-16
17
THEME 5 : TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
Learning Area:
1. Stability
Learning Area:
2. Simple Machine
18
19
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME:
MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE
LEARNING AREA: 1. THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES
Week &
date
1st Sem.
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
2
7
11/1/13
2
7
11/1/13
2
7
11/1/13
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR
SENSES
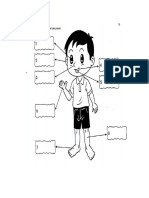
LO1 Sensory organs
The five senses, the sensory organs and
the stimuli.
The pathway from stimulus to response
Stimulus Sensory organs
Nerves Brain Nerves Response
Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses
that involved)
LO2 Sense of touch
The structure of the human skin involved
in stimuli detection,
The sensitivity of the skin at different
parts of the body towards stimuli.
Discuss the sensitivity of the skin in daily
life
Using models, charts, computer software and other
teaching aids.
LO3 Sense of smell
Identify the structure of the nose,
Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is
detected.
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Notes
Being objective.
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Visualising
Generalise
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Carry out activity to compare the sensitivity of different
parts of the body towards touch
Analyse
Discussion of connection to the following situations such as
receiving an injection, using Braille
Using models, charts, computer software and other
teaching aids.
Identify the position of the sensory cells
in the detection of smell.
LO4 Sense of taste.
The different areas of the tongue that
respond to different taste,
Relate the sense of taste with the sense
of smell.
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Being thankful to
God.
1
2-4/1/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
Interpreting data
Conclude
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Visualising
Carry out activities to detect the different areas of the
tongue that respond to different tastes.
Compare &
differentiate
Carry out activities to find how taste is related to smell.
Correlate
Classify
Inferring
Interpreting data
Conclude
Realising that
science is a
means to
understand
nature.
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Being thankful to
God
The structures of the
receptors are not
required.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
1st Sem.
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
3
14
18/1/13
3
14
18/1/13
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR
SENSES
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Notes
Being thankful to
God.
1
2-4/1/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
LO1 Sensory organs
The five senses, the sensory organs and
the stimuli.
The pathway from stimulus to response
Stimulus Sensory organs
Nerves Brain Nerves Response
Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses
that involved)
LO5 Sense of hearing
The structure of the human ear,
The function of the different parts of the
ear,
Mechanism of hearing.
Computer simulation to illustrate the hearing mechanism.
Characterise
Discussion of the hearing mechanism.
Visualising
LO6 Sense of sight.
Identify the structure of the human eye,
Explain the functions of different parts of
the eye,
Describe how we see.
Examine the cows eye or model of a human eye.
Characterise
Collect information on structure and function of each part of
the eye.
Visualising
Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is
detected.
Being objective.
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Visualising
Generalise
Observing
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Observing
Being objective.
Being thankful to
God.
Discuss of sight mechanism
4
21/1
25/1/13
LO7 Light and sight.
Describe the properties of light i.e.
Reflection, refraction.
State the various defects of vision,
Carry out activities to study:
a) reflection of light &
b) refraction of light between two mediums of different
density.
Visualising
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Collect information about the types of defects of vision and
the contribution/use of technology to rectify them.
Analyse
Measuring and
using numbers
Carry out activities to show what short sightedness and
long sightedness are and how to correct them.
Correlate
Inferring
Ways to correct vision defects,
The limitations of sight,
Defining
operationally
Relate the properties
of light to natural
Being honest and phenomena and daily
accurate in
usage.
recording and
Angles of incidence,
validating data.
reflection, refraction
and normal are not
Appreciating the
required.
contribution of
Astigmatism, optical
science and
illusions, blind-spot,
technology.
monocular and
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
1st Sem.
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
LO1 Sensory organs
The five senses, the sensory organs and
the stimuli.
The pathway from stimulus to response
Stimulus Sensory organs
Nerves Brain Nerves Response
Stereoscopic and monocular visions with
the survival of animals,
The appropriate device to overcome the
limitations of sight.
Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses
that involved)
Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is
detected.
28/1
1/2/13
Describe the properties of sound,
The reflection and absorption of sound,
Explain the defects of hearing,
Ways of rectifying the defects in hearing,
The limitations of hearing,
The device used to overcome the
limitations of hearing,
Explain stereophonic hearing.
LO9 The stimuli and responses in plants.
The stimuli that cause response in plants,
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Notes
Being objective.
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Visualising
Generalise
Discuss what astigmatism is and the way to correct it.
Carry out activities to investigate
a) optical illusion,
b) blind-spot.
Making analogy
by stating and
give examples
Defining
operationally
Thinking
rationally.
Communicating
Gather information about the device to overcome the
limitation of sight.
LO8 Sound and hearing.
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Being thankful to
God.
Discuss the connection between stereoscopic vision and
monocular vision with the survival of animals.
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR
SENSES
1
2-4/1/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
Discuss the limitations of hearing and ways of improving it.
Carry out activities to investigate the need for stereophonic
hearing in determining the direction of sound.
Compare &
contrast by
connecting
Generate ideas
by identifying
Correlate
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Relating
Predicting
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology.
stereoscopic visions
should be introduced.
Microscope,
magnifying glass,
telescope, binoculars,
ultrasound scanning
device, X-ray,
periscope should be
included.
.
Included devices such
as hearing aids and
stethoscope.
Thinking
rationally.
Carry out experiments to investigate:
a)
stimuli detected by plants,
Analyse
Synthesizing
Experimenting
Being accurate in
recording data.
Responses in plants
should include
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
1st Sem.
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
28/1
1/2/13
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR
SENSES
LO1 Sensory organs
The five senses, the sensory organs and
the stimuli.
The pathway from stimulus to response
Stimulus Sensory organs
Nerves Brain Nerves Response
The parts of plants sensitive to specific
stimulus,
Relate the response in plants to their
survival.
LEARNING AREA:
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses
that involved)
Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is
detected.
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Being objective.
Being responsible
about the safety
of oneself, others,
and environment
Visualising
Generalise
b)
identify the parts of the plants sensitive to
specific stimulus.
Discuss in what ways the response of plants towards
stimuli are important for their survival.
Differentiate
Conclude
Sequencing
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Being systematic.
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
LO1 The classes of food.
4 -8/2/13
phototropism,
geotropism,
hydrotropism, nastic
movement,
thigmotropism.
2. NUTRITION
CHAPTER 2 :NUTRITION
Notes
Being thankful to
God.
1
2-4/1/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
Explain through the classes of food,
State the function of each class of food,
Test for starch, glucose, protein and
fats.
Discuss the classes of food i.e. carbohydrate, protein, fats,
vitamins, minerals, fibre and water and state their functions.
Carry out activities to test for starch (iodine solution), glucose
(Benedicts solution), protein (Millons reagent) and fats
(alcohol-emulsion test).
Characterise
Observing
Compare &
contrast
Classifying
Correlate
Visualising
Making analogy
Defining
operationally
Realising that
science is
tools to
understand
nature
Being kindhearted
Only the major vitamins [ A,
B, C, D, E and K ] &
minerals [calcium, sodium,
iron, iodine, phosphorus
and potassium ] are
required .
Vitamin B need not be
classified into B1, B2 and
so on.
Introduce alcohol-emulsion
test for fat.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
6
4 -8/2/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
LO2 The importance of a balanced diet.
Meaning of a balanced diet is,
The factors that must be considered when
planning a balanced diet,
Explain how the factors affect a balanced
diet,
The quantity of energy in each gram of
carbohydrate, protein and fats,
Estimate the calories of food taken in a
meal,
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Being cooperative.
Discuss:
a) what a balanced diet is,
b) the factors that determine a persons
balanced diet: age, size, sex, job, climate,
state of health.
Compare & contrast
Correlate
Measuring and
using numbers
Analyse
Generalise
Communicating
Collect food wrappers that show calorific value of
food and make a list to show the calorific value
for each type of food.
Correlate
Compare & contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Discuss that digestion is the breakdown of large
food molecules into smaller soluble molecules
that can be readily absorbed by the body.
Characterise
Compare & contrast
by identifying
Observing
Identify parts of the digestive system and the
flow of food particles in the alimentary canal
using model/chart/CD ROM.
Analyse
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Correlate
Compare & contrast
Inferring
Sequencing
Prioritising
Generalise
Communicating
Carry out activities to show the action of the
enzyme in the saliva on starch.
Discuss the process of absorption of the
products of digestion in the small intestine.
Correlate
Compare & contrast
Inferring
Carry out an experiment to show the absorption
of glucose through a Visking tube.
Analyse
Making analogy
Defining
operationally
Appreciating and
practising clean
and healthy living.
Notes
The unit of energy in
food can be measured
either in joules or
calories.
Discuss to estimate the calories of food taken in
a meal.
Plan a balanced diet.
Plan a balanced diet for a day (breakfast, lunch
and dinner).
8
18
22/2/13
8
18
22/2/13
LO3 The digestive system in man.
Explain what digestion is,
The parts of the digestive system,
The flow of food particles in the alimentary
canal,
The functions of the organs in the
digestive system,
The process of digestion in the alimentary
canal,
End products of digestion of
carbohydrate, protein and fats.
LO4 The process of absorption of digested food.
The process of absorption of the products
of digestion,
The absorption of glucose through a
Visking tube.
Practising healthy
living.
Enzymes should only
include amylase,
protease and lipase.
Being objective.
Discuss the functions of the various organs in
the digestive system and the enzymes found.
Being cooperative.
Thinking rationally.
Being cooperative.
The structure of vilus
is not required. Need
only mention vilus
increases the surface
area for absorption.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
9
25/2
1/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
LO5 The re-absorption of water and defecation.
Water reabsorption in the large intestine,
Defecation,
The problem of defecation with eating
habits.
LO6 The habits of healthy eating.
9
25/2
1/3/13
The importance of eating nutritious food,
Practice good eating habits,
The generous distribution of food to the
underprivileged / needy,
The dining culture of different people
conforming to sensitivities and religious
beliefs.
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Thinking rationally.
Discuss the reabsorption of water by the large
intestine and the process of defecation.
Correlate
Compare & contrast
Inferring
Discuss the importance of good eating habits to
avoid constipation.
Analyse
Making analogy
Defining
operationally
Correlate
Compare & contrast
Inferring
Relating
Visualising
Predicting
Being cooperative
Plan and carry out a healthy eating habit.
Discuss the following topics :
a) practicing good eating habits i.e. eating
nutritious food and eating in moderation,
b) the generous distribution of food to the
underprivileged / needy,
c) cultural practices in dining conforming to
sensitivities and religious beliefs.
THEME:
MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS
LEARNING AREA: 1. BIODIVERSITY
Appreciating and
practicing clean
and healthy living.
Being kind-hearted
and caring.
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
11
11
15/3/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
Having critical
and analytical
thinking
Basic concept of prey
predator and competition has
been taught in primary school.
Realising that
science is a
means to
understand
nature..
Refer all to local issues like
the crow problem in Klang.
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
CHAPTER 4: THE INTER-DEPENDENCE
AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS.
LO1 The inter-dependence among living
organisms
Species, population and community are,
Carry out a field work to study species, habitat,
population, community in an ecosystem.
Habitat and ecosystem
Characterise
Observing
Form mental
image
Analyse
Classify
Various habitats in one ecosystem,
The interdependence among living
organisms and the environment to
create a balanced ecosystem,
Carry out a discussion on interdependence among
living organisms and the environment to create a
balanced ecosystem.
Correlate by
explaining
through
examples
Appreciating
the balance of
nature.
Basic concept of habitat has
been introduced in primary
school.
During the field work the
concept of ecology will be
constructed through
contextual learning.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
11
11
15/3/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
LO2 The interaction between living organisms.
The types of interactions between
living organisms,
The interactions between living
organisms,
The importance of interaction
between living organisms and the
environment,
The advantages and disadvantages
of biological control in regulating the
number of pest in certain areas.
Collect and interpret data on the types of
interactions as follows:
a) prey-predator,
b) symbiosis: commensalism, mutualism and
parasitism e.g. remora and shark, algae and
fungi, tape worm and man,
c) competition.
Characterise
Observing
Conclude by
explaining with
examples
Compile &
differentiate
Interpreting data
Conduct an activity to show the importance of the
interaction between organisms and the environment.
Analyse by
justifying &
explaining
through
examples
Inferring
Defining
operationally
Discuss the advantages of biological control in
regulating the numbers of pests in certain areas.
Classifying
Communicating
Realising that
science is a
means to
understand
nature.
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
11
11
15/3/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
LO3 The food web.
Meanings of producers, consumers
and decomposers
Combination of a few food chains to
construct a food web,.
The producer, consumer and
decomposer in a food web,
Pyramid number from a food chain,
Relate the food web and the pyramid
number to energy flow.
Predict the consequences if a certain
component of living organisms in the
ecosystem is missing
Collect and interpret data on the producer,
consumer, decomposer and pyramid number.
Construct a food web from a few food chains and
identify the producer, consumer and decomposer.
Discuss the energy flow in the food web
constructed.
Conduct a game to show the effects of an increase
or decrease in the number of organisms in a
pyramid number. Discuss the consequences if a
component of living organisms in an ecosystem is
missing
10
Characterise
Observing
Conclude by
identifying &
constructing
Interpreting data
Visualising
Correlate
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Forecasting
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Food chain has been taught in
primary science
Predicting
Being
cooperative
Refer to the crown of thorn
problem in the coral reef in the
marine park
Communicating
Being honest
.
Predicting
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
12
18/3
22/3/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
LO4 Photosynthesis.
Meaning of photosynthesis
The factors required for
photosynthesis,
Carry out discussion on what photosynthesis is.
Carry out experiments to determine the factors
needed for photosynthesis i.e. carbon dioxide,
water, light and chlorophyll.
Characterise
Hypothesising
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Experimenting
Synthesising
Hypothesising
Correlate
Inferring
State the products of photosynthesis,
The variables that are required for
photosynthesis,
Discuss the importance of photosynthesis in
maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
The role of photosynthesis in
maintaining a balanced ecosystem
Discuss the carbon and oxygen cycles.
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL PERTAMA
23 MAC 2013 31 MAC 2013
11
Being honest
and accurate in
recording and
validating data.
Being
responsible of
the
environment.
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
The carbon and oxygen cycle
should be included.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
13
1
5/4/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
LO5 The importance of conservation and
preservation of living organisms.
Explain what conservation and
preservation are,
Explain the steps taken to preserve
and conserve living organisms,
Justify the importance of conservation
and preservation of living organisms,
Support activities organised by various
parties to preserve and conserve the
living organisms.
Collect and interpret data on the conservation and
preservation of living organisms.
Carry out a field work in a natural forest reserve
(wetlands, highland forest or tropical rain forest) or
an animal sanctuary to study the conservation and
preservation of living organisms.
Discussion on how the improvement in science and
technology helps in the conservation and
preservation of living organisms.
Run a campaign to stress on the importance of
conservation and preservation / Carry out a role play
involving the parties concerned in solving problems
related to the conservation and preservation of living
organisms.
12
Conclude
Interpreting data
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Being
cooperative.
The role of man in
conservation and preservation
has been highlighted in
primary school.
Appreciating
the balance of
nature.
Forest is also home to some
indigenous people should be
included.
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
10
25/2
1/3/13
10
4
8/3/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY
LO1 The variety of living organisms and their
classification.
Explain the diversity of living organisms
in a habitat,
Classify various animals based on
common characteristics,
Classify various plants based on
common characteristics,
Explain the importance of biodiversity to
the environment.
Suggested Learning Activities
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of
living organisms.
Collect and classify various plants and animals into
a system based on common characteristics.
a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish,
bird, amphibian, reptile.
b) Plant: Flowering plant, non-flowering plant,
monocotyledon, dicotyledon.
c) Build a concept map on living organisms based
on the classification above.
Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological
diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
LEARNING AREA:
14
8
12/4/13
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes &
Noble Values
Correlate
Compare &
contrast
Inferring
Characterise
Observing
Having an
interest and
curiosity
towards the
environment.
Compare &
differentiate
Classifying
Being
systematic.
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Having critical
and analytical
thinking.
Notes
.
Basic concept on variety of
living organisms has been
introduced in primary science.
Emphasize only on the
classification in the suggested
learning activities.
Malaysia is one of the twelve
mega-biodiversity countries in
the world should be
highlighted
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
LO6 The role of man in maintaining the
balance in nature.
The effects of human activities on the
balance in nature,
How man solve problems related to
environment,
Carry out a brainstorming session to discuss the
environmental issues affecting the balance in nature
and how to solve it.
Carry out a discussion to justify that man needs
stable and productive ecosystem to ascertain a
harmonious life.
Human need a stable, productive and
balanced ecosystem.
Correlate
Analyse
Generate ideas
(justify)
Inferring
Communicating
Being
respectful and
well-mannered.
Being flexible
and openminded.
Daring to try.
13
Example of environmental
Issues: Global climate change,
habitat destruction, species
extinction, air, soil and water
pollution, loss of wetlands,
solid waste management,
deforestation, land overuse,
over fishing, toxin in the
environment.
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME:
MATTER IN NATURE
LEARNING AREA: 1.
WATER AND SOLUTION
Week &
date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking
skills)
SPS
(Science
Process
Skills)
CHAPTER 5 : WATER & SOLUTION
15
LO1 The physical characteristics of water.
16
19/4/13
State the meaning of the freezing point of
water,
The meaning of the boiling point of water,
The physical characteristics of water,
Explain through example the effects of
impurities on the physical characteristics of
water.
16
22
26/4/13
Carry out activities to determine the following:
a) the freezing point of water,
b) the boiling point of water.
Carry out an electrolysis to determine the ratio of
hydrogen to oxygen in a molecule of water.
Test the presence of hydrogen and oxygen.
14
Observing
Correlate
Defining
operationally
Conclude
Interpreting
data
Characterise
Observing
Analyse
Inferring
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Carry out an activity to observe the effects of
impurities on the physical characteristics of water.
LO2 The composition of water.
Determine the composition of water,
Characterise
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Notes
Being honest and
accurate in
recording and
validating data
The kinetic Theory
should be introduced.
Having critical and
analytical thinking
The ionic theory on
electrolysis is not
needed.
Understand ng that
hydrogen is discharge
at the cathode and
oxygen at the anode is
adequate. The ratio of
gases is required.
Relate the freezing and
boiling point of water to
the kinetic Theory.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
17
29/4
3/5/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
LO3 The process of evaporation of water.
Meaning of evaporation
Examples the factors that affect the rate of
evaporation of water with reference to the
kinetic theory,
Compare and contrast between evaporation
and boiling,
The application of the evaporation of water in
daily life.
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking
skills)
SPS
(Science
Process
Skills)
Carry out experiments to study the factors affecting
the rate of evaporation of water i.e. humidity, the
temperature of the surrounding, surface area and the
movement of air.
Characterise
Observing
Compare &
contrast
Measuring and
using numbers
Discuss the factors affecting the rate of evaporation
in relation to the kinetic theory.
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Experimenting
Interpreting
data
Defining
operationally
Spacing-time
relationship
Discuss the similarities and differences between
evaporation and boiling.
Gather information on evaporation process and its
application in daily life i.e. drying of clothes,
preservation of agricultural products and processing
of food.
Correlate
Compile &
differentiate
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Notes
Being honest and
accurate in
recording and
validating data
Appreciating the
balance of nature
Inferring
Classifying
18
6
10/5/13
19
13/5
17/5/13
LO4 Solution and solubility.
Discuss the differences between solute, solvent and
solution.
Characterise
Observing
Compare,
Compile ,
differentiate &
contrast
Classifying
Having critical and
analytical thinking
Meanings of solute, solvent and solution
Contrast and compare between dilute
solution, concentrated and saturated
solution,
Carry out activities to prepare a dilute solution, a
concentrated solution and a saturated solution.
Explain what suspension is,
Discuss the similarities and differences between
dilute solution, concentrated solution and saturated
solution.
Explain what solubility is,
Carry out activities to illustrate the differences
between a solution and a suspension.
15
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Correlate
Inferring
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology
Daring to try
Being honest and
accurate in
recording and
Introduce insoluble
sediments are known as
residue.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
20
20/524/5
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Explain the factors affecting the solubility of
solutes in water,
Explain the importance of water as a
universal solvent in life,
Give examples on the uses of organic
solvents in our everyday life.
Suggested Learning Activities
Carry out experiments to determine the factors
affecting the solubility of a solute.
a) Nature of solvent,
b) Nature of solute,
c) Temperature.
Carry out experiment to determine the factors
affecting the rate of dissolving:
a) temperature,
b) rate of stirring,
c) size of solute particle.
Discuss the importance of water as a universal
solvent in life.
Gather information on the application of organic
solvents in daily life.
CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
25 MEI 2013 9 JUN 2013
16
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking
skills)
SPS
(Science
Process
Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
validating data.
Compare &
contrast
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Generalise
Conclude
Forecasting
Communicating
Experimenting
Spacing-time
relationship
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
LO5 Acid and alkali.
21
10
14/6/13
Identify the properties of acid, identify the
properties of alkali,
State that acid and alkali only show their
properties in the presence of water,
Explain through examples the definition of
acid and alkali,
Identify the substances which are acidic or
alkaline in everyday life,
17
21/6/13
Carry out activities to study:
a) the properties of acid in terms of pH value,
taste, corrosive nature, effect on litmus paper,
reaction with metals such as magnesium and
zinc,
b) the characteristics of alkali in terms of pH value,
taste, corrosive nature, effect on litmus paper,
c) carry out a discussion to define acid and alkali
operationally.
Carry out activities to determine the acidic and
alkaline substances in daily life.
State the uses of acid and alkali in daily life,
Gather information on the usage of acid and alkali in
everyday life such as in agriculture and industry.
Explain the meaning of neutralisation,
Discuss on the meaning of neutralisation.
Write an equation in words to describe the
neutralisation process,
Carry out an activity to show neutralisation using the
hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide of the same
concentration.
Explain through examples the uses of
neutralization in daily life.
22
Suggested Learning Activities
LO6 The methods of water purification.
List the natural sources of water,
State the reasons for water purification,
Describe the various types of water
purification,
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking
skills)
SPS
(Science
Process
Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Observing
Characterise
Classifying
Compile &
differentiate
Correlate
Making
analogy
Interpreting
data
Defining
operationally
Compare &
contrast
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Generalise
Conclude
Forecasting
Communicating
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Communicating
Notes
Caution:
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology
Having critical and
analytical thinking
Appreciating the
balance of nature
Chemicals in the
laboratory should not
be tasted.
Use only dilute acid and
dilute alkali.
Do not use active metal
such as potassium and
sodium in the reaction
with acid.
Discuss the application of neutralization in daily life
e.g. using shampoo and conditioner and, insect bite.
Make a visit to a water purification site.
Brainstorming on the following:
natural resources of water,
the reasons for water purification.
Discuss the various types of water purification such
as filtration, boiling, chlorination and distillation.
17
Defining
operationally
Generalise
Conclude
Classifying
Appreciating and
practicing clean
and healthy living
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology
The latest development
in water purifications
e.g. ultraviolet treatment
can be discussed.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical &
creative
thinking
skills)
SPS
(Science
Process
Skills)
Carry out activities to study the various types of water
purification such as filtration, boiling and distillation.
Compare the strengths and weaknesses of
the various types of water purification.
22
17
21/6/13
LO7 The water supply system.
Describe how the water supply system
works,
Explain ways to save water.
22
17/6
21/6/13
LO8 The preservation of water quality.
Give examples of water pollutants,
Explain the effect of water pollution on living
things,
Explain ways to control water pollution,
Explain ways to preserve water and its
quality.
Pupils present their findings to discuss the strengths
and weaknesses of the various types of water
purification.
Being thankful to
God.
Compile &
differentiate
Make a visit to a water processing plant to study the
water supply system and stages involved in water
purification.
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Communicating
Discuss the ways to save water. Do a project on how
much water the average household uses.
Generalise
Conclude
Interpreting
data
Collect and interpret data on types of water pollutants
which include:
a) industrial waste such as chemical and
radioactive residues,
b) domestic waste such as garbage and sewage,
c) chemicals from the agricultural activities such as
fertilisers and pesticides,
d) siltation caused by constructions and
deforestation,
e) accidental spillage from tankers.
Compile &
differentiate
Classifying
Characterise
Observing
Conclude
Interpreting
data
Conduct discussion on the effect of water pollution on
living things.
Generalise
Conclude
Relating
Visualising
Generate ideas on ways to control water pollution.
Discuss ways to conserve and preserve water and its
quality. Run a campaign on Love Our Rivers.
18
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Generate
ideas
Analyse
Communicating
Inferring
Predicting
Having an interest
and curiosity
towards the
environment.
Being objective
Having an interest
and curiosity
towards the
environment.
Appreciating and
practicing clean
and healthy living.
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE
LEARNING AREA:
2. AIR PRESSURE
Week &
date
23
24
28/6/13
23
24
28/6/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CHAPTER 6 : AIR PREESURE
LO1 Air pressure.
LO2
Carry out an activity to discuss the kinetic theory
of gases.
Explain the existence of air pressure
with reference to the Kinetic Theory,
Carry out an activity to show that air exerts
pressure.
Explain the factors affecting air pressure.
Carry out activities to show the factors affecting
air pressure, i.e. volume and temperature.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Characterise
Observing
Analyse
Inferring
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Generate ideas
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Characterise
Observing
Conclude
Interpreting data
Generate ideas
Analyse
Communicating
The principle of air pressure in daily life.
Explain with examples things that use
the principle of air pressure,
Collect and interpret data on appliances that use
the principle of air pressure.
Generate ideas to solve problems using
the principle of air pressure,
Gather information and discuss the application of
air pressure in syringe, siphon, spraying pump
and drinking straw.
Relate the safety measures taken when
using gas under high pressure.
Discuss ways of using the principle of air
pressure to solve daily problems such as
blockage in sinks and pouring condensed milk
from a can.
*Teachers can design some activities.
Gather information on how a gas tank
containing gas under high pressure works.
Discuss the safety precautions taken when using
gas under high pressure.
19
Generalise
Conclude
Correlate
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Realising that
science is a mean
to understand
nature.
Having critical and
analytical thinking
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
Technology.
Having critical and
analytical thinking.
Inferring
Notes
Being cooperative.
Caution:
Do not place tank
containing gas under
high pressure near
heat.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
Characterise
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Observing
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Sequencing
Using time spacerelationship
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Notes
PENTAKSIRAN PUSAT
24 - 27
THEME: FORCE AND MOTION
LEARNING AREA:
1. DYNAMICS
Week &
date
28
29/7
2/8/13
28
29/7
2/8/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
5
6/8/13
Notes
CHAPTER 7 : DYNAMICS
LO1 Force.
State that a force is a push or a pull,
Explain the effects of forces,
Explain the various types of forces.
Carry out activities to show pushing and pulling
are forces.
Carry out activities to show the effects of force
(changes in shape, position, speed and
direction).
Carry out activities to show different types of
forces (frictional, gravitational, electrostatic and
magnetic force).
29
Scientific Attitudes
& Noble Values
LO2 The measurement of force.
State the unit of force.
Discuss the unit of force and the principle of a
spring balance.
Compile &
differentiate
Generate ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Generalise
Classifying
Communicating
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Measuring and
using numbers
Conclude
Interpreting data
Rational and
objective in
thinking.
Being cooperative
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology.
Being honest and
accurate in
recording and
validating data.
Principle of a spring balance works.
The magnitude of force.
30
19
Carry out activity to measure the magnitude of
force.
LO3 Application of frictional force.
Explain with example the existence of
Discuss with examples to show the existence of
frictional force.
20
Being systematic.
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Measuring and
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
Ignore static
frictional force
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
23/8/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
frictional force,
State the direction and the magnitude of
frictional force,
Carry out an experiment to show how
different types of surfaces affects
frictional force,
Explain the advantages and
disadvantages of friction,
Explain ways to increase friction.
Explain ways to reduce friction,
Explain with examples the application of
friction in daily life.
Suggested Learning Activities
Carry out activities to identify the direction of
frictional force and measure the magnitude of
the force.
Carry out an experiment to show how different
types of surfaces affect the magnitude of
frictional force.
Gather information and discuss the advantages
and disadvantages of friction.
Carry out activities on ways to
a) increase friction,
b) reduce friction.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
using numbers
Scientific Attitudes
& Noble Values
technology.
Conclude
Interpreting data
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Compile &
differentiate
Generate ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Conclude
Generalise
Having critical and
analytical thinking.
Experimenting
Being cooperative.
Communicating
Discuss the application of increasing and
decreasing friction in our daily life.
31
26
30/8/13
LO4 Application of work.
Explain with examples how work is done,
State the unit for work,
Calculate the work done.
31
26
30/8/13
LO5 Application of power.
State the meaning of power,
Discuss with examples to show work done when
an object is moved by a force.
Carry out activities to determine the work done
by using:
Work (J) = Force (N) X
Distance (m)
Carry out activities to determine power by using:
Power (W) = Work (J)
Time (s)
State the unit for power,
Compile &
differentiate
Correlate
Generate ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Conclude
Generalise
Communicating
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Correlate
Measuring and
using numbers
Being cooperative.
Measuring and
using numbers
Having critical and
analytical thinking.
Interpreting data
Being honest and
accurate in
recording and
validating data.
Being systematic.
21
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
Calculate power on the work done.
32
LO6 The importance of force in life.
Describe life if force does not exist.
2
6/9/13
Create an activity to show how life would be
without force, e.g. in a poster, a sketch or skit.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
Conclude
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Interpreting data
Characterise
Generate ideas
Analyse
Synthesising
Generalise
Observing
Scientific Attitudes
& Noble Values
Communicating
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology.
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Characterise
Observing
Interest and
inquisitive.
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Notes
THEME:
FORCE AND MOTION
LEARNING AREA: 2. SUPPPORT AND MOVEMENT
Week &
date
33
9
13/9/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CHAPTER 8 : SUPPORT & MOVEMNT
LO1 The support system in animals.
Explain the various support systems in
vertebrates and invertebrates,
Compare and contrast the support
system between land and aquatic
vertebrates,
Gather information and discuss the various
support systems in
a) land and aquatic vertebrates,
b) land and aquatic invertebrates.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
.
Compile &
differentiate
Compare and contrast the support
system between land and aquatic
invertebrates.
22
Classifying
Realising that
science is a
means to
understand nature.
Notes
For invertebrates
introduce exoskeleton
endoskeleton,
hydrostatic skeleton
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
33
913/9/13
34
17
20/9/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
LO2 The support system in plants.
Explain the various support systems in
plants, in woody and non-woody plants
Classify plants based on their support
systems.
LO3 Appreciating the support system in living
things.
Justify the important of the support
system to living things
Carry out activities to study the various support
systems in plants.
Carry out activities to classify plants based on
their support systems.
Discuss issues i.e.:
a) inability of whales to move back to the sea
after being washed to shore,
b) a crippled person using crutches for
support.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Characterise
Observing
Interest and
inquisitive.
Visualising
Defining
operationally
Compile &
differentiate
Classifying
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Visualising
Having an interest
and curiosity
towards the
environment.
Notes
Features that help
non-woody plants
include tendrils,
thorns, air sacs in
aquatic plants.
Being thankful to
God.
Defining
operationally
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
LEARNING AREA: 1. STABILITY
Week &
date
35
23
27/9/13
36
30/9
4/10/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 9 : STABILITY
LO1 Factors affecting the stability
Determine the point of equilibrium in
regular and irregular shapes,
Relate the point of equilibrium as the
centre of gravity of objects,
Suggested Learning Activities
Carry out activities to find the point of
equilibrium in regular and irregular shapes.
Carry out an experiment to find out how the
centre of gravity affects the stability of an object
by manipulating the
a) height,
b) base area.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Characterise
Observing
Being cooperative.
Correlate
Inferring
Having critical and
analytical thinking.
Compile &
differentiate
Classifying
Visualising
Relate the centre of gravity to the stability
of objects.
Discuss the relationship between the centre of
gravity to stability.
23
Defining
operationally
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
37
7
11/10/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
LO2 Appreciating the importance of stability.
Ways to improve the stability of objects
around them,
Explain with examples the application of
stability in life.
Carry out a brain storming session on ways to
improve stability.
Carry out activities like projects or games to
build models by applying the concept of stability.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
Characterise
Correlate by
suggesting
Observing
Inferring
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Communicating
Visualising
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
LEARNING AREA:
2. SIMPLE MACHINE
24
SPS
(Science
Process Skills)
Defining
operationally
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology.
Notes
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week &
date
38
14
18/10/13
39
21
25/10/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
CHAPTER 10 : SIMPLE MACHINE
LO1 Levers.
List things around them that use
the principle of the lever,
Classify levers,
Explain what is meant by the
moment of a force,
Solve problems related to levers.
28/10
8/11/13
Make an observation to identify the load, force and
fulcrum then classify them into first, second and third
class levers.
Carry out an activity to show the relationship between
moment and the product of force and distance.
CCTS
(Critical & creative
thinking skills)
SPS
(Science Process
Skills)
Scientific
Attitudes & Noble
Values
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Inferring
Ability to think
critically and
analytically.
Making analogy
Defining
operationally
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Compile &
differentiate
Communicating
Correlate
Measuring and
using numbers.
Characterise
Observing
Correlate
Generate ideas
Analyse
Generalise
Conclude
Measuring and
using numbers
Solving problems related to levers using the following
formulae:
Load (N) X distance of the load from fulcrum (m) =
Force (N) X distance of the force from the fulcrum (m)
LO2 Appreciating the innovative efforts in
the design of machine to simplify
work.
Design or improvise a device
using the principle of a lever.
42
Discuss that the lever enables us to:
a) change a small force into a big force,
b) change a small movement into a large movement,
c) state that the moment of force = force X
perpendicular distance from pivot to force.
State what a lever can do,
Identify load, force and fulcrum in
the lever,
40-41
Suggested Learning Activities
Carry out a project to build a device using the principles
of a lever.
Kemaskini fail peribadi pelajar sains tingkatan 2 2013.
25
When we open the
door or use a
wrench to loosen a
nut, we are applying
a force that causes a
turning effect to
accomplish the
desired task. The
turning effect is
called the moment of
a force.
Classifying
Communicating
Notes
Appreciating the
contribution of
science and
technology.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PBSDocument26 pagesPBSAhmad Bin ZainalPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 2 Yearly Plan 2007: Theme Learning Area and Learning Objectives Vol/Page WeekDocument19 pagesScience Form 2 Yearly Plan 2007: Theme Learning Area and Learning Objectives Vol/Page Week206542Pas encore d'évaluation
- Plan Sains t2Document39 pagesPlan Sains t2Arif ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 Syllabus SY 2019-2020Document16 pagesScience 9 Syllabus SY 2019-2020Lindon Jay EnclunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Ting2Document9 pagesRancangan Tahunan Sains Ting2Suei Suhaniez SuriyatPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work: ScienceDocument37 pagesScheme of Work: ScienceMasitah ArPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary ScienceDocument103 pagesElementary ScienceAnushikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigatory ProcessDocument23 pagesInvestigatory ProcessJo Che RencePas encore d'évaluation
- Research IV: Objectives and Preparation for Science FairsDocument5 pagesResearch IV: Objectives and Preparation for Science FairsMary Joy Calimlim SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Science Lesson Plan for Form 2 StudentsDocument26 pagesSensory Science Lesson Plan for Form 2 StudentsAldrich Malaga Gregory MPas encore d'évaluation
- RPH SC Form 2Document50 pagesRPH SC Form 2lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- GRD 11 TextbookDocument375 pagesGRD 11 TextbookKrishna Mae GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching of Science, Theories, Approaches, Guiding Principles and Methods of Teaching ScienceDocument13 pagesTeaching of Science, Theories, Approaches, Guiding Principles and Methods of Teaching ScienceBurgos MJPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Science f2Document26 pagesYearly Plan Science f2lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6: Divine Word College of LegazpiDocument33 pagesGrade 6: Divine Word College of LegazpiJanelle Grecia NepomucenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2cristine panerPas encore d'évaluation
- BASICSCIENCEDocument185 pagesBASICSCIENCENeha Sharma100% (1)
- RPH Sains T2Document11 pagesRPH Sains T2anon_438795505Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sciences: Grade 12 TextbookDocument373 pagesSciences: Grade 12 TextbookTamiePas encore d'évaluation
- Gr3 Science SyllabusDocument12 pagesGr3 Science SyllabusRose Ann LamontePas encore d'évaluation
- Year 8 BASIC SCIENCE - Finau A. Nanovo RepairedDocument185 pagesYear 8 BASIC SCIENCE - Finau A. Nanovo RepairedDrSuesh Kumar Pandey69% (13)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 2Document16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 2Nicobella10090% (1)
- Environmental Education - Class II Scheme of Work 2021 - 2022 Our PhilosophyDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Education - Class II Scheme of Work 2021 - 2022 Our PhilosophyAnmol Shoukat - 83197/TCHRPas encore d'évaluation
- Roxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Document10 pagesRoxas City For Revision Research 7 Q1 MELC 23 Week2Rachele DolletePas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Science Term 2 Learning Sequence 2013Document5 pagesBiological Science Term 2 Learning Sequence 2013api-226538617Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Endeavour (2023)Document89 pagesScientific Endeavour (2023)Geovy SimPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Wise BreakupDocument10 pagesTerm Wise BreakupSaima UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching Science DomainsDocument14 pagesTeaching Science DomainsRoselle Groyon EcleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan 7es Fourth QuarterDocument33 pagesLesson Plan 7es Fourth QuarterChenee HornalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Seeing Science Final PDFDocument8 pagesSeeing Science Final PDFClaudiu FlorinPas encore d'évaluation
- General Science Grade-7 PDFDocument249 pagesGeneral Science Grade-7 PDFmohammed jimjam100% (6)
- Class 6 Science Scheme of WorkDocument9 pagesClass 6 Science Scheme of WorkSaima Usman/TCHR/MGBPas encore d'évaluation
- GST211-LECTURE NOTE 2022-2Document21 pagesGST211-LECTURE NOTE 2022-2ahmadmuhammadbuhari313Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sci101 Prefinal M3L1Document22 pagesSci101 Prefinal M3L1Ej PunlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Science Unit Plan Skillman CPA 2020Document32 pagesIntegrated Science Unit Plan Skillman CPA 2020sjPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f2 2011Document17 pagesYearly Lesson Plan SC f2 2011FedyaFithriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2Document25 pages2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2qq235100% (1)
- The Eye: Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesThe Eye: Structure and FunctionNicketa AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- College Department Course Code Course TitleDocument15 pagesCollege Department Course Code Course TitleRoselle Groyon EcleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiroz GEE102 Activity #1Document3 pagesQuiroz GEE102 Activity #1Reycel MisolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 1Document10 pagesYearly Plan Science Yr 1Alif NasriPas encore d'évaluation
- Envi Sci Module FINAL .DjbramirezDocument33 pagesEnvi Sci Module FINAL .Djbramirezdaniel ramirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Let'S Check Activity No. 1. Now That You Have Know The Most Essential Terms in The Study ofDocument5 pagesLet'S Check Activity No. 1. Now That You Have Know The Most Essential Terms in The Study ofopxPas encore d'évaluation
- SCI 321 Module MIDTERM1Document21 pagesSCI 321 Module MIDTERM1Cherry May ArrojadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 7 Science Long Range PlanDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Science Long Range Planapi-266874931Pas encore d'évaluation
- YEARLY PLAN FOR SCIENCE FORM 1Document27 pagesYEARLY PLAN FOR SCIENCE FORM 1Nor FaizahPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETYDocument6 pagesModule 1 SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETYKaiRae AsakuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Observation and Questioning: Summary: Students Will Explore The Nature and Process of ScienceDocument19 pagesObservation and Questioning: Summary: Students Will Explore The Nature and Process of ScienceKenneth AtokPas encore d'évaluation
- Design DocumentDocument9 pagesDesign Documentapi-208533376Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1Document44 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 7.v1Sue Adames de VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Science Syllabus JHS 1 - 3Document79 pagesIntegrated Science Syllabus JHS 1 - 3Mohammed Abu Shaibu85% (27)
- Saint Columban College Pagadian City Unit Plan For Science I Unit 1Document8 pagesSaint Columban College Pagadian City Unit Plan For Science I Unit 1John Ace Revelo-JubayPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptation Lesson PlanDocument32 pagesAdaptation Lesson PlanCrystal PennypackerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 Chapter 1 SCIENTIFIC SKILLSDocument25 pages1.0 Chapter 1 SCIENTIFIC SKILLSJaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan of Science Form 2 2012: Theme 1: Management and Continuity of LifeDocument22 pagesYearly Lesson Plan of Science Form 2 2012: Theme 1: Management and Continuity of LifeNurul AzniPas encore d'évaluation
- ECOLOGY OutlineDocument2 pagesECOLOGY OutlineRealyn Delos Santos TañecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ubd Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesUbd Lesson PlanLove BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Q1 MELCsunpacked Inventory 1Document6 pagesGrade 9 Q1 MELCsunpacked Inventory 1Merry Chris TabliganPas encore d'évaluation
- Ict 22Document5 pagesIct 22api-250192253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ DeriaDocument4 pagesOrgan DeriaMichael AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Sungai Ruan Physics Lesson Plan Form 4 2016Document1 pageSMK Sungai Ruan Physics Lesson Plan Form 4 2016Michael AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Borang Gred Induk FizikDocument2 pagesBorang Gred Induk FizikMichael AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument14 pagesElectricity Series and Parallel CircuitsMichael AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Seriesandparallelcircuits 090320152217 Phpapp01Document12 pagesSeriesandparallelcircuits 090320152217 Phpapp01Michael AustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument29 pagesArchimedes PrincipleMichael Austin50% (4)
- List of ADWEA Product GroupsDocument24 pagesList of ADWEA Product GroupsSalman FaisalPas encore d'évaluation
- IVT Network - API Pharmaceutical Water Systems Part I - Water System Design - 2014-06-13Document5 pagesIVT Network - API Pharmaceutical Water Systems Part I - Water System Design - 2014-06-13davincicode888Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSF Guidance Delivering Quality PotWater To Offshore Installations 18th July 2103Document27 pagesMSF Guidance Delivering Quality PotWater To Offshore Installations 18th July 2103heppyfaebanffPas encore d'évaluation
- Exhaust Carbon FilterDocument16 pagesExhaust Carbon FilterCj HealyPas encore d'évaluation
- What Microorganisms Are Deactivated by UltravioletDocument2 pagesWhat Microorganisms Are Deactivated by UltravioletBurak UçkaçPas encore d'évaluation
- Swimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideDocument24 pagesSwimming Pool Risk Management Plan GuideAbdulmalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Desalination & Wastewater Treatment For Vietnam 18.2Document5 pagesWater Desalination & Wastewater Treatment For Vietnam 18.2Luan NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic StructureDocument56 pagesHydraulic StructureMahesh RamtekePas encore d'évaluation
- Environment Management Guwahati UniversityDocument17 pagesEnvironment Management Guwahati UniversityRahul DekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrochemical Activation A Key To Ecologically Pure Technologies of WaterDocument15 pagesElectrochemical Activation A Key To Ecologically Pure Technologies of Watervahid0% (1)
- Minncare Cold Sterilant - Product TrainingDocument46 pagesMinncare Cold Sterilant - Product TrainingRidwan ArifandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lbymatc Lab Handouts Ay 2014-2015Document31 pagesLbymatc Lab Handouts Ay 2014-2015Stefanie EstillorePas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Chemistry - Water TreatmentDocument87 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry - Water TreatmentVikas KabburiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aqua Water Purification - Aqua Soft NaturalDocument5 pagesAqua Water Purification - Aqua Soft NaturalIsrael ExporterPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizational Study Report at Travancore Cochin ChemicalsDocument59 pagesOrganizational Study Report at Travancore Cochin ChemicalsSarath P Babu100% (4)
- Modul4 CRT SPT SystDocument22 pagesModul4 CRT SPT SystwandameritaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Tannins From Turkish Acorns (Valonia) in WaterDocument9 pagesThe Use of Tannins From Turkish Acorns (Valonia) in WaterRadwan AjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Coast Guard Public School, Daman: (Type Here)Document13 pagesCoast Guard Public School, Daman: (Type Here)Rajeev SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Coca Cola Factory Visit Report by FSNM StudentsDocument6 pagesCoca Cola Factory Visit Report by FSNM StudentsSweety SenguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12th Chemistry Project On Sterilization of Water by Using Bleaching PowderDocument14 pagesClass 12th Chemistry Project On Sterilization of Water by Using Bleaching Powdernishra keshav100% (3)
- Water Treatment Solutions For Municipalities and Drinking-Water PlantsDocument8 pagesWater Treatment Solutions For Municipalities and Drinking-Water PlantsbimbremboPas encore d'évaluation
- Jesco BrochureDocument16 pagesJesco BrochureOktiara Dwita PertiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Water Management PlanDocument41 pagesWaste Water Management PlanAsif100% (1)
- RM-Comparative Study of Mineral Water Sunrich Aqua Vs BisleriDocument40 pagesRM-Comparative Study of Mineral Water Sunrich Aqua Vs BisleriAatishKoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Colloidal Silver GuideDocument17 pagesColloidal Silver GuideKaren PolzinPas encore d'évaluation
- DO Sag Curve PDFDocument55 pagesDO Sag Curve PDFDrShrikant JahagirdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Water Treatment Plant To Pulivendula Municipal Corporation of Kadapa (DT), Andhra PradeshDocument3 pagesDesign of Water Treatment Plant To Pulivendula Municipal Corporation of Kadapa (DT), Andhra PradeshDeepakRavindraPrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Tower Safety MaintenanceDocument4 pagesCooling Tower Safety MaintenancePratham KamathPas encore d'évaluation
- EarthCruiser InnovationDocument8 pagesEarthCruiser Innovation@mac100% (1)
- Indian Ray OneDocument96 pagesIndian Ray Oneધ્રુવ પટેલPas encore d'évaluation