Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
IS and Econ 13 - First Midterm Examination Answers (Correct Answer Starred " ") Version A Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING YOUR Version (A)
Transféré par
FUSION Academics0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
47 vues4 pagesMidterm 1 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Titre original
ECON 13 W15: Midterm 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMidterm 1 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
47 vues4 pagesIS and Econ 13 - First Midterm Examination Answers (Correct Answer Starred " ") Version A Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING YOUR Version (A)
Transféré par
FUSION AcademicsMidterm 1 Solutions for ECON 13
S. Skaperdas
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
IS and Econ 13 - First Midterm Examination
Answers (correct answer starred *)
S. Skaperdas January 28, 2015
Version A
Fill in your scantron, INCLUDING YOUR
VERSION (A).
There are 35 questions in the exam. Questions
1-25 are worth 1 point each. Questions 26-35
are worth 2 points each.
1. Suppose that, at a particular price, quantity
demanded is 300 and quantity supplied is 500.
Then, we should expect the price in this market
to
a. Go up because there is excess demand.
b. Go down because there is excess
supply.*
c. Go up because there is excess supply.
d. Stay the same.
e. Go up or down, depending on whether
there is excess supply or excess
demand.
2. Which of the following factors cause a
movement along the demand curve?
a. change in the price of related goods.
b. change in the population.
c. change in income.
d. change in the price of the good.*
e. a and d.
3. In 2013, which one of the following
countries had the highest GNI per capita (at
PPP)?
a. Bangladesh.
b. Nigeria.
c. Indonesia.
d. India.
e. Qatar.*
4. In 19th century U.S. the largest industry was
a. Automobiles
b. Electricity generation
c. Railroads*
d. Computer electronics
e. The internet.
5. Which one of the following is NOT a
characteristic of the SECOND industrial
revolution:
a.
The spread of serfdom.*
b.
Growth of joint-stock companies or
corporations.
c.
High level of division of labor.
d.
Vertical integration of economic
activity.
e.
Growth of bureaucracies.
6. A point outside a production possibilities
frontier
a. indicates that some resources are
unemployed.
b. is worse than points on the production
possibilities frontier.
c. implies that too much capital and not
enough labor are used.
d. is unattainable for production
purposes.*
e. None of the above.
7. A decrease in incomes
a. shifts the demand curve to the right.
b. shifts the demand curve to the left.*
c. causes a movement along the demand
curve.
d. implies no change in the demand curve.
e.causes a movement along the Supply
curve.
8. Positive economics refers to
a. analyses that try to understand how the
economy actually works.*
b. the positive reinforcement that the media
can employ to pump up the economy.
c. the positive feelings that firms can
induce for the good of the economy.
d. a and b.
e. b and c.
9. Modern economic growth is correlated
a. with the gradual reduction of the public
sector as a share of GDP.
b. with an increase in the size of the public
sector.*
c. with a reduction in regulation and other
government interference in business.
d. a and c.
e. All of the above.
10. According to Jared Diamond in Guns,
Germs, and Steel, the most dominant
civilizations emerged in Eurasia because
a. the people were on average smarter
there.
b. there were fewer animals and plants that
were available for domestication there.
c. the propagation of agriculture along an
East-West axis was easier.*
d. Eurasians were better hunters and
gatherers.
e. c and d.
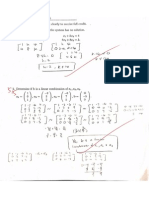
Consider two countries, Gaia and Virtualia, and
suppose that each can produce just two goods,
corn and virtual reality machines (VRMs). Their
production possibilities are described below:
Gaia
Virtualia
Corn
VRMs
Corn
VRMs
300
0
150
0
200
50
100
100
100
100
50
200
0
150
0
300
Use this information to answer questions 11-17.
.
11. The opportunity cost of one unit of corn in
Gaia is
a. 100 VRMs.
b. 200 VRMs
c. 2 VRMs.
d. 1 VRM.
e. VRM.*
12. The opportunity cost of one unit of corn in
Virtualia is
a. 2 VRMs.*
b. VRMs
c. 100 VRMs.
d. 200 VRMs.
e. 600 VRMs.
13. The opportunity cost of one VRM in Gaia is
a. 100 units of corn.
b. 2 units of corn.*
c. 1 unit of corn.
d. units of corn.
e. 200 units of corn.
14. The following statement is true:
a. Virtualia has an absolute advantage
(AA) in the production of VRMs.
b. Virtualia has and AA in corn
production.
c. Gaia has an AA in VRM production.
d. b and c.
e. Absolute advantage cannot be
determined from the information
provided.*
15. The following statement is true:
a. Gaia has a comparative advantage
(CA) in VRM production.
b. Gaia has CA in corn production.*
c. Virtualia has CA in both VRM and
corn.
d. Virtualia has a CA in corn production.
e. Comparative advantage cannot be
determined from the information
provided.
Now suppose that VRMs can be used for
electronic warfare and for each country to defend
itself against the other (either under autarky or
under trade), it needs to produce 50 VRMs and
solely dedicate them to defense. Questions 16
and 17 apply to this new situation but with the
same production possibilities in the previous
table.
16. The maximum amount of corn that Gaia can
produce for consumption or trade is
a. 200*
b. 150
c. 100
d. 50
e.
0
17. The maximum amount of VRMs that
Virtualia can produce for consumption or trade
is
a. 300
b. 250*
c. 200
d. 150
e. 100
18. An increase in the cost of producing a good
a. shifts the demand curve to the right.
b. shifts the demand curve to the left.
c. causes a movement along the demand
curve.
d. implies no change in the demand
curve.*
e. causes a movement along the supply
curve.
19. During the Great Recession sales of new
cars went down by almost 40% while their prices
slightly decreased. This fact can best be
explained by
a. a reduction in the demand for new cars.*
b. an increase in the demand for new cars.
c. a reduction in the supply of new cars.
d. an increase in the supply of new cars.
e. b and c.
20. Suppose the demand for Ipads is downward
sloping and supply is upward sloping. If Ipads
become cheaper to produce
a. the demand for Ipads shifts to the left.
b. the demand and supply of Ipads both shift
c. the demand for Ipads shifts to the right.
d. the supply of Ipads shifts.*
e. none of the above
Suppose that each of Xena and Robinson
face the choice between, on the one hand,
Not Arming and Specializing in Production
(with the intention to Trade) and, on the
other hand, Arming with the intention of
remaining autarkic. Denote the first
strategy by N and the second by A. The
matrix of possible outcomes is then as
follows:
Xena
N
A
Robinson N (No
Robinson
Robinson
arming)
obtains:
obtains:
(5coconuts, (0coconuts,
10 fish);
0 fish);
Xena
Xena
obtains (10 obtains (15
coconuts, 5 coconuts,
fish)
20 fish)
A
Robinson
Robinson
(Arming) obtains:
obtains: (2
(20
coconuts, 6
coconuts,
fish); Xena
10 fish);
obtains (7
Xena
coconuts, 4
obtains (0
fish)
coconuts, 0
fish)
21. If Robinson were to pursue his self-interest,
he would choose:
a. N
b. A*
c. Sometimes N and sometimes A.
d. Can never be determined from the
information provided.
22. If Xena were to pursue her self-interest, she
would choose:
a. N
b. A*
c. Sometimes N and sometimes A.
d. Can never be determined from the
information provided.
23. If Robinson and Xena were each to pursue
their own self-interest, the outcome that will
occur is
a. N for Robinson and N for Xena
b. N for Robinson and A for Xena
c. A for Robinson and N for Xena
d. A for Robinson and A for Xena*
e. Can never be determined from the
information provided.
24. The collectively rational outcome is for
a. N for Robinson and N for Xena*
b. N for Robinson and A for Xena
c. A for Robinson and N for Xena
d. A for Robinson and A for Xena
e. Can never be determined from the
information provided.
25. The Industrial Revolution began in
a. The United States.
b. France.
c. Japan.
d. Scandinavia
e. Great Britain.*
(Note that questions 26-35 are worth 2 points
each.)
26. Economic growth can be represented by
a. a movement along the Production
Possibilities Frontier (PPF).
b. an inward (down and left) shift of the
PPF.
c. a downward shift in the demand curve.
d. an outward expansion of the PPF.*
e. c and d.
27. The province of Shanghai in China has
about the same life expectancy and per capita
income as
a. Bangladesh.
b. India.
c. Ghana.
d. the rest of China.
e. Italy.*
28. Suppose that to produce 10 pounds of rice in
Japan requires 2 hours of labor, whereas in the
U.S. it requires 1 hour of labor. As a result, we
can conclude that
a. Japan has a comparative advantage
(CA) in producing rice.
b. The U.S. has the absolute advantage in
producing rice.*
c. Japan has the absolute advantage in
producing rice.
d. The U.S. has a CA in producing rice.
e. None of the above
29. David Ricardo, a British political economist
of the 19th century, used the production of
wine and cloth in Britain and Portugal to
illustrate the idea of comparative advantage. In
his classic example, the unit labor costs of
production (i.e., how much labor it takes to
production one unit of output) of these two
goods in these two countries are
Cloth Wine
Britain
100
110
Portugal
90
80
According to these numbers, which of the
following statements is correct?
a. Britain has comparative advantage in
producing wine.
b. Britain has absolute advantage in
producing wine.
c. Portugal has absolute advantage in
producing wine.*
d. Portugal has comparative advantage in
producing cloth.
e. Neither comparative advantage nor
absolute advantage can be determined by the
information provided.
30. Corporations
a. were the main form of firm organization
since the beginning of the industrial revolution.
b. became the dominant form of firm
organization in the US in the late 19th century.*
c. have always been the most efficient form
of firm organization.
d. arose in the late Middle ages and have
been dominant since then.
e. a and c.
31. There are more people on earth
a. living on less than $1 a day than those living
on less than $2 a day.
b. living on less $2 a day than those living in
high-income countries (as defined by the World
Bank).*
c. living in high-income than those living in
middle-income.
d. living in high-income countries than those
living on less than $2 a day.
e. living in high-income countries than those
living in middle and low-income countries.
32. Consider the market for the Samsung
Galaxy Note II. Samsung has started an effective
advertising campaign for its product and more
segments of the population consider it a cool
product. At the same time, improvements in
production techniques imply that the Note II is
not becoming more expensive to produce. Which
of the following MUST be true?
a. The equilibrium quantity will rise.*
b. The equilibrium quantity will fall.
c. The equilibrium price will fall.
d. The equilibrium price will rise.
e. Neither the equilibrium price nor
quantity will be affected.
33. Adam Smith
a. argued in favor of corporations as the
most efficient form of firm organization.
b. considered the corporate form of firm
organization critical for the success of the
industrial revolution.
c. considered the corporate form of firm
organization too immature for the
nineteenth century economy.
d. argued against corporations because of
the intractable problems inherent in the
separation of ownership from
management.*
e. a and b.
34. When the price of oil decreases, the price of
jet fuel decreases and we can expect
a. a shift to the left in the supply curve of
air travel and higher airfares.
b. a shift to the right in the demand curve
for air travel and lower airfares.
c. a shift to the left in the demand curve for
air travel and higher airfares.
d. a shift to the right in the demand curve
for air travel and higher airfares.
e. a shift to the right in the supply curve of
air travel and lower airfares.*
35. The military superiority of European states
over the rest of the world since the 15th century
could ultimately be attributed to
a. the philosophers of ancient Greece and
Rome.
b. their economies being more advanced
than China in the 15th century.
c. solely to the industrial revolution.
d. advances in military technology induced
by the considerable internal political
fragmentation of Europe.*
e. b and c.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 1Document4 pagesECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 1FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECON 13 W15: FinalDocument8 pagesECON 13 W15: FinalFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesAP Macroeconomics Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice QuestionsKayPas encore d'évaluation
- Professor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument8 pagesProfessor Elliott Parker Spring 2006 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of Microeconomicshyung_jipmPas encore d'évaluation
- Specific Factors Model Chapter QuestionsDocument13 pagesSpecific Factors Model Chapter QuestionsBill BennttPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ exam+1+VADocument13 pagesEcon exam+1+VABlackBunny103Pas encore d'évaluation
- Econ202 Tt1 2012f HellmanDocument12 pagesEcon202 Tt1 2012f HellmanexamkillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply and Demand Problem Sets EconomicsDocument5 pagesSupply and Demand Problem Sets Economicsjesse jamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro Chapter 3 Study Guide Questions 14eDocument6 pagesMicro Chapter 3 Study Guide Questions 14eBeauponte Pouky MezonlinPas encore d'évaluation
- đã gộp456Document14 pagesđã gộp456Hoàng Sơn Phạm VũPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 3Document7 pagesSession 3omaritani2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brandeis Tjniversity Department of EconomicsDocument5 pagesBrandeis Tjniversity Department of EconomicsPeesashizPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Review 1 1Document20 pagesTutorial Review 1 1Trần Triệu VyPas encore d'évaluation
- File - 20210823 - 100510 - Chapter 04Document6 pagesFile - 20210823 - 100510 - Chapter 04Trãi NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice 2 - ECON1010Document6 pagesPractice 2 - ECON1010veres.tankerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambedkar UNI Versi TY MA Economi CS Questi ON Paper 2013Document19 pagesAmbedkar UNI Versi TY MA Economi CS Questi ON Paper 2013Siddhant MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Questions PDFDocument8 pagesEconomic Questions PDFAurovind LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics exam questionsDocument14 pagesEconomics exam questionsbopgalebelayPas encore d'évaluation
- MP1VDocument8 pagesMP1Vturuu224Pas encore d'évaluation
- EKO201E Sample 1Document13 pagesEKO201E Sample 1Kadir Y. DemirPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ 351 Midterm 1 Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesEcon 351 Midterm 1 Questions and Answerstony4dongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ôn tập 1Document18 pagesÔn tập 1Gia HânPas encore d'évaluation
- Test B and D Key ExplainedDocument8 pagesTest B and D Key ExplainedGamze ŞenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 35 Practice QuestionsDocument24 pagesChapter 35 Practice QuestionsHannah Ma Ya LiPas encore d'évaluation
- Professor Elliott Parker Spring 2005 Midterm Exam 1 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of MicroeconomicsDocument9 pagesProfessor Elliott Parker Spring 2005 Midterm Exam 1 Name: ECON 102 - Principles of Microeconomicshyung_jipmPas encore d'évaluation
- Microeconomics ECON1001 Homework 1 Supply DemandDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics ECON1001 Homework 1 Supply Demandsl1zePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1ramizulPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ204A2 F07 LeeG Fall05 Midterm1Document7 pagesEcon204A2 F07 LeeG Fall05 Midterm1bevinjPas encore d'évaluation
- Microeconomics Sample QuestionsDocument10 pagesMicroeconomics Sample QuestionsFarzana Alamgir0% (1)
- Sample Paper MCQ Micro EconomicsDocument8 pagesSample Paper MCQ Micro EconomicsbineshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 Chapter 7Document8 pagesTutorial 1 Chapter 7Aqila Syakirah IVPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Forces and Demand & Supply AnalysisDocument13 pagesMarket Forces and Demand & Supply AnalysisDiem Suong100% (1)
- Topic 4 The Market Forces of Supply and Demand QuestionDocument9 pagesTopic 4 The Market Forces of Supply and Demand QuestionMIN ENPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009fall Test1Document12 pages2009fall Test1Rosablanca Moniquie HayesPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesEconomics Exam Questionsmastersaphr1898Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHPT 2 EconDocument8 pagesCHPT 2 EconJindessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 37 Practice MC QuestionsDocument12 pagesCh. 37 Practice MC QuestionsMianda InstitutePas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Macro Economy Today 14th Edition Schiller Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Macro Economy Today 14th Edition Schiller Test Bank PDF Full Chapterparcelmelligonh0g100% (15)
- Microeconomic Principles Midterm Exam With AnswersDocument15 pagesMicroeconomic Principles Midterm Exam With AnswersBerrin AkbalıkPas encore d'évaluation
- EKO201E Sample 2Document9 pagesEKO201E Sample 2Kadir Y. DemirPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand PaperDocument13 pagesDemand Paperhiranya939509Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Set 2 2022Document5 pagesPractice Set 2 2022Romit BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1Document7 pagesTest 1rqwfsrxkfqPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe Final Mocktest - Fow9Document12 pagesPe Final Mocktest - Fow9wwwpa2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Use The Following To Answer Questions 5-7:: Figure: Strawberries and SubmarinesDocument16 pagesUse The Following To Answer Questions 5-7:: Figure: Strawberries and SubmarinesMahmoud FariedPas encore d'évaluation
- Model A: Damietta University Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics 2 Semester Final Exam 2020/ 2021Document6 pagesModel A: Damietta University Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics 2 Semester Final Exam 2020/ 2021Testo PartPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageDocument7 pagesPractice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageGabby CustodioPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Grade 10 TestDocument7 pagesEconomics Grade 10 TestThomassiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Review 1Document19 pagesTutorial Review 1chang vicPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Review Questions - Supply and DemandDocument9 pagesChapter 3 Review Questions - Supply and DemandDiamante GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tài liệuDocument18 pagesTài liệuTrần Quốc HuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 Practice 111Document18 pagesWeek 3 Practice 111David LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Review-1Document21 pagesTutorial Review-1Nguyên HoàngPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ 202 Pre-Test 1 Chapters (4, 22-24)Document8 pagesEcon 202 Pre-Test 1 Chapters (4, 22-24)Amogh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Old FinalDocument13 pages101 Old Finalntc7035Pas encore d'évaluation
- EconomicsDocument25 pagesEconomicsAlexa FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionD'EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- International Relations: A Simple IntroductionD'EverandInternational Relations: A Simple IntroductionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- Summary Of "The American Crisis And The Persian Gulf War" By Pablo Pozzi: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESD'EverandSummary Of "The American Crisis And The Persian Gulf War" By Pablo Pozzi: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESPas encore d'évaluation
- PSYCH 9A F14: Final PreparationDocument18 pagesPSYCH 9A F14: Final PreparationFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- PSYCH 9A F14: Midterm PrepDocument20 pagesPSYCH 9A F14: Midterm PrepFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS 4 W15: Sample MidtermDocument6 pagesICS 4 W15: Sample MidtermFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 7Document1 pageMath 3A W15: Quiz 7FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 3Document1 pageICS 6D W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Midterm 1Document2 pagesMath 3A W15: Midterm 1FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 6Document1 pageMath 3A W15: Quiz 6FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 3A W15: Quiz 5Document1 pageMATH 3A W15: Quiz 5FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 2Document1 pageMath 3A W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 3Document1 pageMath 3A W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 3A W15: Quiz 4Document1 pageMATH 3A W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 3A W15: Quiz 1Document1 pageMath 3A W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 4Document1 pageICS 6D W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 1Document1 pageICS 6D W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 2Document1 pageMATH 13 W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS 6D W15: Quiz 2Document1 pageICS 6D W15: Quiz 2FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pridtiwo: Roblen1 1 Ulti Ple Choice (20 Points) Rite Your Answer Or1 The First PageDocument4 pagesPridtiwo: Roblen1 1 Ulti Ple Choice (20 Points) Rite Your Answer Or1 The First PageFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Final Study GuideDocument3 pagesMATH 13 W15: Final Study GuideFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECON 13 W15: Final ReviewDocument8 pagesECON 13 W15: Final ReviewFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 2Document4 pagesECON 13 W15: Sample Midterm 2FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECON 13 W15: Practice FinalDocument6 pagesECON 13 W15: Practice FinalFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 1Document1 pageMATH 13 W15: Quiz 1FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECON 13 W15: Midterm ReviewDocument1 pageECON 13 W15: Midterm ReviewFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 4Document1 pageMATH 13 W15: Quiz 4FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Please Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING Your Version/Test Form (A)Document4 pagesPlease Fill in Your Scantron, INCLUDING Your Version/Test Form (A)FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Sample FinalDocument9 pagesMATH 13 W15: Sample FinalFUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 13 W15: Quiz 3Document1 pageMATH 13 W15: Quiz 3FUSION AcademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyzing Investment Projects in Grey LtdDocument20 pagesAnalyzing Investment Projects in Grey LtdNam NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- British Imperialism Revisited The Costs and Benefits of 'Anglobalization'Document29 pagesBritish Imperialism Revisited The Costs and Benefits of 'Anglobalization'thunderdomePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Islamic EconomicDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Islamic EconomicShiela AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ghana Banking Survey 2009Document54 pagesGhana Banking Survey 2009Maxwell Annor-williamsPas encore d'évaluation
- To What Extent Can Decentralised Forms of Government Enhance The Development of Pro-Poor Policies and Improve Poverty-Alleviation Outcomes?Document61 pagesTo What Extent Can Decentralised Forms of Government Enhance The Development of Pro-Poor Policies and Improve Poverty-Alleviation Outcomes?Michel Monkam MbouePas encore d'évaluation
- Rural Livelihood StrategiesDocument3 pagesRural Livelihood StrategiesDeoPudakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Administration EbookDocument24 pagesPublic Administration Ebookapi-371002988% (17)
- Decoupling: Natural Resource Use and Environmental Impacts From Economic GrowthDocument174 pagesDecoupling: Natural Resource Use and Environmental Impacts From Economic GrowthUnited Nations Environment ProgrammePas encore d'évaluation
- Research SampleDocument8 pagesResearch SampleAngela Jesca Medina JabidoPas encore d'évaluation
- June 2012 Economics Unit 3 MarkschemeDocument21 pagesJune 2012 Economics Unit 3 MarkschemeEzioAudi77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch 5: Risk Return Portfolio Theory Assets PricingDocument4 pagesCh 5: Risk Return Portfolio Theory Assets PricingMukul KadyanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Foreign Direct Investment On Ethiopian Economic GrowthDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Foreign Direct Investment On Ethiopian Economic GrowthWORKNEH GIRMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch13 - Parkin - Econ - Lecture PresentationDocument62 pagesCh13 - Parkin - Econ - Lecture PresentationSu Sint Sint HtwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Canada NewsletterDocument6 pagesCanada Newslettercjrumbines100% (1)
- PESTLE Analysis Ed Tech IndustryDocument3 pagesPESTLE Analysis Ed Tech Industryshashikant prasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Order Flow Analytics Revealing The MarketDocument5 pagesOrder Flow Analytics Revealing The MarketChoris Figaro57% (7)
- 101 Business EnvironmentDocument142 pages101 Business Environmentbijal mehta100% (1)
- 13 Developing Pricing Strategies and ProgramsDocument34 pages13 Developing Pricing Strategies and ProgramsBahar RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- How bribery undermines ethics, law and economyDocument4 pagesHow bribery undermines ethics, law and economyAnis ShafiePas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Asset Pricing Model For Johnson and JohnsonDocument6 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model For Johnson and Johnsonviettuan91Pas encore d'évaluation
- QUICK GUIDE TO TNPSC GROUP 2/2A ONLINE TEST SERIES AND STUDY PLANDocument19 pagesQUICK GUIDE TO TNPSC GROUP 2/2A ONLINE TEST SERIES AND STUDY PLANNaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Competition ActDocument25 pagesCompetition ActAnjali Mishra100% (1)
- Cost Analysis GraphDocument3 pagesCost Analysis GraphItss Louie'sPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 Ratio AnalysisDocument59 pagesLecture 3 Ratio AnalysisJiun Herng LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Expedia Industries Inventory Valuation MethodsDocument1 pageExpedia Industries Inventory Valuation MethodsJunzen Ralph YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahasa Inggris Niaga Tugas 2Document2 pagesBahasa Inggris Niaga Tugas 2Sherly OktaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vair ValueDocument15 pagesVair ValueyrperdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring National IncomeDocument7 pagesMeasuring National Incomeanora7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tiffany's Exchange Rate Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesTiffany's Exchange Rate Risk ManagementJames BurdenPas encore d'évaluation
- UTI-LEF Fund detailsDocument68 pagesUTI-LEF Fund detailsSurbhi JoshiPas encore d'évaluation