Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26
Transféré par
JUSASB0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentToronto Notes Nephrology 2015
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
49 vues1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26
Transféré par
JUSASBToronto Notes Nephrology 2015
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
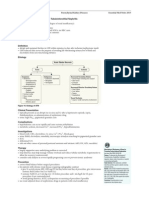
NP26 Nephrology
Parenchymal Kidney Diseases
Signs and Symptoms
AKI
if hypersensitivity reaction: may see fever, skin rash, arthralgia, serum sickness-like syndrome
(particularly rifampin)
if pyelonephritis: flank pain and costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness
other signs and symptoms based on underlying etiology
HTN and edema are uncommon
Investigations
mild, non-nephrotic range proteinuria and microscopic hematuria
urine
sterile pyuria, WBC casts, mild proteinuria, hematuria
eosinophils if AIN
blood work
increased Cr and urea
eosinophilia if drug reaction
normal AG metabolic acidosis (RTA)
hypophosphatemia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia
gallium scan often shows intense signal due to inflammatory infiltrate
renal biopsy definitive
Treatment
treat underlying cause (e.g. stop offending medications, antibiotics if pyelonephritis)
corticosteroids (may be indicated in allergic or immune disease)
Prognosis
recovery within 2 wk if underlying insult can be eliminated
the longer the patient is in renal failure, the less likely full renal recovery becomes
2. CHRONIC TUBULOINTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS
Definition
characterized by slowly progressive renal failure, moderate proteinuria, and signs of abnormal
tubule function
Etiology
persistence or progression of acute TIN
urinary tract obstruction: most important cause of chronic TIN (tumors, stones, bladder outlet
obstruction, vesicoureteral reflux)
chronic pyelonephritis due to vesicoureteral reflux or UTI with obstruction
nephrotoxins
exogenous
analgesics: NSAIDs (common), acetaminophen
cisplatin, lithium, cyclosporine, tacrolimus
heavy metals (lead, cadmium, copper, lithium, mercury, arsenic)
radiation
Chinese herbs
endogenous
hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, oxalate, uric acid nephropathy
vascular disease: ischemic nephrosclerosis, atheroembolic disease
malignancies: multiple myeloma, lymphoma
granulomatous: TB, sarcoidosis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis
immune: SLE, Sjgrens, cryoglobulinemia, Goodpastures, amyloidosis, renal graft rejection,
vasculitis
hereditary: cystic diseases of the kidney, sickle cell disease
others: radiation, Balkan (endemic) nephropathy
Pathophysiology
fibrosis of interstitium with atrophy of tubules, mononuclear cell inflammation
Signs and Symptoms
tubular dysfunction (e.g. acidosis, electrolyte disturbances)
progressive renal failure with azotemia and uremia
dependent on underlying etiology
Treatment
stop offending agent or treat underlying disease
supportive measures: correct metabolic disorders (Ca2+, PO43-) and anemia
Essential Med Notes 2015
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Genetic Diseases of the KidneyD'EverandGenetic Diseases of the KidneyRichard P. LiftonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandDocument54 pagesNephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandManmeet SPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubulointerstitial nephritis: an overview of kidney diseases involving the tubules and interstitiumDocument34 pagesTubulointerstitial nephritis: an overview of kidney diseases involving the tubules and interstitiumIaros OlgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 pageReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- AKI in SepsisDocument45 pagesAKI in SepsisIkeBundaAdellulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument40 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasePaul SinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- DR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiDocument39 pagesDR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiBasri BaslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascites Hrs B WPDocument101 pagesAscites Hrs B WPGhias Un Nabi TayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDocument22 pagesAn Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDz PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaDocument48 pagesTubulointerstitial Diseases: Dr. Raid JastaniaThomas McconnellPas encore d'évaluation
- Lange Nephrology EssentialsDocument9 pagesLange Nephrology EssentialsAlejandro GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuDocument65 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuFloreaAndreiPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulonephritis Dwi Fin PDFDocument108 pagesGlomerulonephritis Dwi Fin PDFOvyanda Eka MItraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management GuideDocument5 pagesKidney Disease Diagnosis and Management GuideJerin XavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis - P. Devarajan PDFDocument48 pagesRapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis - P. Devarajan PDFHerman HermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Presentation Slide EditedDocument22 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Presentation Slide EditedTerence Chin0% (1)
- Outcomes of SGLT2i in diabetic kidney disease: is it all diabetesDocument29 pagesOutcomes of SGLT2i in diabetic kidney disease: is it all diabetesVaibhav DafalePas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Platelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedDocument31 pagesPlatelet, FFP and Cryoprecipitate Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Riaz AhamedAETCM Emergency medicinePas encore d'évaluation
- CKD Guidelines Focus on Early Detection, Evaluation and ManagementDocument11 pagesCKD Guidelines Focus on Early Detection, Evaluation and Managementnaty77777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart GuideDocument9 pagesAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison Chart Guideconcoz100% (1)
- Anemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Document31 pagesAnemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Richard 151289Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Pharma DiureticsDocument38 pages2010 Pharma DiureticsSri Nurliana BasryPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacotherapy of PneumoniaDocument56 pagesPharmacotherapy of Pneumoniahoneylemon.co100% (1)
- GlomerulonephritisDocument59 pagesGlomerulonephritistressPas encore d'évaluation
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDocument29 pagesIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Document23 pagesHyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Emily EresumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteDocument2 pagesDrugs For Heart Failure: Drugs Catego Ry Drug Function Adverse Effect NoteyukariPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Cardiorenal SyndromeDocument71 pages1 Cardiorenal SyndromeHermann HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAcute Renal Failurearif kurnia timurPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrology Best RDocument6 pagesNephrology Best Rfrabzi100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding PDFDocument10 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding PDFKetut Suwadiaya P AdnyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- PD Prescription Present 4-8-52Document74 pagesPD Prescription Present 4-8-52Kong Kong KongPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of HIV/AIDS by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaDocument13 pagesManagement of HIV/AIDS by DR Gireesh Kumar K P, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaSreekrishnan TrikkurPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatic Encephalopathy Is by DR Gireesh Kumar K PDocument16 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy Is by DR Gireesh Kumar K PAETCM Emergency medicinePas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Management in HD PatientsDocument75 pagesAnemia Management in HD PatientsAn TonPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryology and Development of KidneyDocument75 pagesEmbryology and Development of Kidneyranjitha sraatePas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Renal PhysiologyDocument56 pages2 Renal PhysiologyNoraine Princess TabangcoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Antihyperglycemic Agents Comparison ChartDocument9 pagesAntihyperglycemic Agents Comparison ChartBonniePas encore d'évaluation
- Organo Phosphate Poisoning by DR Gireesh Kumar K PDocument16 pagesOrgano Phosphate Poisoning by DR Gireesh Kumar K PAETCM Emergency medicinePas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- COMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesDocument5 pagesCOMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesJUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Antipsychotics - FactsheetDocument12 pagesAntipsychotics - FactsheetColonPas encore d'évaluation
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDocument2 pagesFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Antipsychotics Factsheet pg2Document1 pageAntipsychotics Factsheet pg2JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 pageReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35JUSASB50% (2)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15JUSASBPas encore d'évaluation
- (IJCST-V9I3P10:Akshat Rustagi, Rudrangshu Tarafder, J. Rene BeulahDocument7 pages(IJCST-V9I3P10:Akshat Rustagi, Rudrangshu Tarafder, J. Rene BeulahEighthSenseGroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Embarazo y Ae PDFDocument13 pagesEmbarazo y Ae PDFraquel lopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Pre Ovarian CystDocument56 pagesCase Pre Ovarian Cystthesa1201Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Progressive Aphasia: Neurological ProgressDocument8 pagesPrimary Progressive Aphasia: Neurological ProgressDranmar AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 125409orig1s113 PDFDocument268 pages125409orig1s113 PDFKarl SaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Otc DrugsDocument71 pagesOtc DrugsEthan Morgan100% (2)
- Chronic HK NewInsightDocument107 pagesChronic HK NewInsightKHALID NAAMPas encore d'évaluation
- NetworkHospital NEW UPDATEDDocument488 pagesNetworkHospital NEW UPDATEDalina0% (1)
- Ayurvedic Perspectives on Fetal Nutrition and GrowthDocument50 pagesAyurvedic Perspectives on Fetal Nutrition and GrowthKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology of Eating DisorderDocument5 pagesEtiology of Eating DisorderCecillia Primawaty100% (1)
- 4.paramyxoviridae Henipa (K)Document10 pages4.paramyxoviridae Henipa (K)NatAsyaPas encore d'évaluation
- QUIZDocument14 pagesQUIZhahaha0% (1)
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge Plankim arrojado100% (1)
- University of Hargeisa Faculty of Nutrition and Food ScienceDocument9 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa Faculty of Nutrition and Food Scienceumalkhayr A/rahmaanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Alteration ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Alteration Comforttinea nigraPas encore d'évaluation
- Peppermint: (Mentha Piperita)Document12 pagesPeppermint: (Mentha Piperita)MarjoryStewartBaxter100% (2)
- Blood Collection and Blood Smear PreparationDocument6 pagesBlood Collection and Blood Smear PreparationSol Kizziah MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Cost Portable Ventilator DesignDocument8 pagesLow Cost Portable Ventilator DesignRashmi SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- College Nursing Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesCollege Nursing Exam ReviewKenneth NovenoPas encore d'évaluation
- DX Report - Steven SimucaseDocument6 pagesDX Report - Steven Simucaseapi-494012486100% (3)
- Effectiveness of Homoeopathic Therapeutics in The Management of Childhood Autism DisorderDocument13 pagesEffectiveness of Homoeopathic Therapeutics in The Management of Childhood Autism DisorderShubhanshi BhasinPas encore d'évaluation
- Title: Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Ran Sacker Escaping Under The Nose AbstractDocument6 pagesTitle: Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Ran Sacker Escaping Under The Nose AbstractKavita KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Starting an IV: Preparation, Equipment, Venipuncture StepsDocument10 pagesStarting an IV: Preparation, Equipment, Venipuncture StepsNurse NotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case ManagementDocument4 pagesCase ManagementPraveena.R100% (1)
- Chest PainDocument13 pagesChest Paing3murtulu100% (1)
- Tugas B.inggris 28 Agt 2K20 Eli Irna eDocument3 pagesTugas B.inggris 28 Agt 2K20 Eli Irna eAhmad AsrullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Paediatric Clinical Examination (24 PGS)Document24 pagesGuide To Paediatric Clinical Examination (24 PGS)Shre RanjithamPas encore d'évaluation
- Merged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Document15 pagesMerged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Ericsson CarabbacanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhavnagar DrsDocument39 pagesBhavnagar DrsCHETAN MOJIDRA75% (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionD'EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (13)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (168)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsPas encore d'évaluation
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementD'EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (40)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisD'EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (130)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesD'EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (327)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassD'EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (21)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingD'EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (31)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsD'EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeD'EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (253)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)