Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
114 16 Formulating and Choosing Strategies Using Swot Analysis and QSPM Matrix A Case Study of Hamadan Glass Company
Transféré par
GuillermoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
114 16 Formulating and Choosing Strategies Using Swot Analysis and QSPM Matrix A Case Study of Hamadan Glass Company
Transféré par
GuillermoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
FORMULATING AND CHOOSING STRATEGIES USING SWOT ANALYSIS AND
QSPM MATRIX: A CASE STUDY OF HAMADAN GLASS COMPANY
Nima Fakhim Hashemi, Mohammad Mahdavi Mazdeh, Amirali Razeghi, Ashkan Rahimian
Head of Industrial Engineering Dept. and R&D Manager, Industrial Engineering and R&D Dept.,
Hamadan Glass Company, +9809123175605, research@hamadanglass.com
Assistant Professor, Department of Industrial Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology,
+98(21)73225002, mazdeh@iust.ac.ir
Chief Information Officer, IT Branch, Industrial Engineering and R&D Dept., Hamadan Glass
Company,+989127197947, it@hamadanglass.com
Consultant, Hamadan Glass Company, +989122225333, rahimian@acm.org
Abstract
Glass industry is one of the largest and most important industries of the country. This industry is divided
to several different groups which differ from each other in terms of production process and raw-material
combinations. One of these groups is bottles and jars industry and Hamadan Glass Company is placed in
this group. This research is a case study of this company and investigates its position in Irans glass
industry. In this paper, the process of formulating strategic planning is presented for this company and
the way the proposed strategies are provided and organized is explained by applying strategic planning
paradigms and evaluating internal and external environments. In this regard, SWOT (Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis and QSPM (Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix)
were used for producing strategies and their evaluation. At last, the proposed strategies were presented
in the order of priority.
Keywords
Strategic planning, SWOT analysis, TOWS matrix, QSPM, Glass container (Bottles & Jars)
Introduction
Strategic management can be defined as the art and science of formulating, executing and evaluating
function decisions which enable organizations to reach their long-term objectives [1].
In fact, strategic management is a process through which organizations can recognize themselves and
their surrounding environments and plan, implement and monitor their strategies. Strategic planning is
considered as one of the most important duties of organization managers and, at present, because of the
extent and speed of social and economic development and the increase in competitiveness, its importance
is increasingly growing and all the organizations are compelled to consider it for their survival sooner or
later. In this paper, first, Hamadan Glass Company is briefly introduced. Then, research methodology and
the strategic planning process for the company are presented; the way the proposed strategies could be
achieved for the company using strategic planning paradigms is explained and internal and external
environments are evaluated.
An Overview of the Company
Hamadan Glass Company (PLC) was established in 1975 by a donor from Hamadan and in cooperation
with the former Industrial Credit Bank (currently, Bank of Industry and Mines) and was inaugurated in
1982. The intention was to create employment in the deprived Hamadan Province and to satisfy the
packaging requirements of food and beverage industries. The plant was constructed on a land of 40 acres
and on the 12th km of Hamadan-Tehran road. The company products include different types of bottles for
packaging soda, juice, lime juice and vinegar and different types of jars for packaging pickles, sauce,
olives and so on. The company products hold a share of about 33% of Irans market. Moreover, a part of
products are exported to Iraq, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan. Unit I of this plant includes a melting
furnace with the capacity of 170 Tons and four production lines equipped with I.S. (Individual Section)
366
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
machines. The annual production of this unit is 40000 Tons. This unit was reconstructed and renewed in
2004 and has modern machinery and is able to produce light and half-light glasses. Unit II of the plant
was established in 1999 as the development plan with the capacity of 130 Tons and three production lines
equipped with I.S. machines; the annual production of this unit is 30000 Tons. All the required raw
materials are available in Iran and there is no dependence on imports from foreign countries. Also, since
the companys products are voluminous, their import from other countries is not cost-effective, which can
be an advantage against foreign competitors if Iran joins the World Trade.
Methodology
The following stages are followed for strategic planning. At first, the organizations vision and mission
statement are determined. Internal and external environments of the organization are analyzed and the
obtained information specifies opportunities and threats (external factors) and strengths and weaknesses
(internal factors). Then, using SWOT (TOWS matrix), the organizations strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities and threats are evaluated. In fact, this is used as an instrument for the systematic analysis of
internal and external environments of an organization; Terrados et al. (2007) considered it as an effective
instrument for identifying the problems and drawing lines of future actions [2]. Finally, QSPM matrix is
used, which was considered in David et al. (2009) as an excellent and useful instrument for formulating
the strategies based on internal and external evaluations and SWOT analysis. Among strategic
alternatives, the relative importance of different facts, roles, tendencies and data may be determined in
order to provide the advantages of an important competition for the company. QSPM provides a
transparent framework for this prioritization process [3].
In this regard, after initial conversations were made and company managers asked the strategic advisory
team to plan for the company, team members, chosen by consultation with the company director, started
their activities. It is worth mentioning that no strategic planning has been conducted in this company so
far. At first, it was essential to obtain the required information and an awareness of the industry which
were accomplished by receiving different related resources from the company and doing research by team
members. Then, the team developed the required questionnaires according to the obtained information.
These questionnaires were mainly organized considering the companys conditions and following the
strategic pattern model designed by Fred R. David. After that, the companys vision and mission
statement were formulated by conducting supplementary interviews, distributing and gathering the
organized questionnaires and holding different sessions with the members of board of directors, company
director and experts. Mission statement has been considered the main factor of business success [4].
Strategy selection and evaluation were conducted in three session of: 1) input stage, 2) coordination and
comparison stage and 3) decision-making stage and using different types of matrix including external
factor evaluation matrix (EFE), internal factor evaluation matrix (IFE), competitive profile matrix (CPM),
SWOT matrix, strategic position and action evaluation matrix (SPACE) and quantitative strategic
planning matrix (QSPM) [1].
Mission & Vision statements
At first, the companys vision and mission statements were determined, which is available at
www.hamadanglass.com. Then, external and internal factors were identified and investigated.
External Factors Evaluation
The objective of analyzing industries and examining environmental factors is to exploit opportunities and
avoid threats. The forces which should be considered in this regard include: 1- economic forces, 2environmental, ecological, cultural and social forces, 3- legal, governmental and political forces, 4technological forces, and 5- competitive forces. It should be considered that external factors can influence
various organizations activity process in different ways; that is, some factors which may be considered
opportunities for an organization may be regarded as a threat for another organization and vice versa [1].
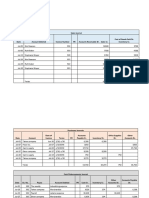
Table (1) shows the list of competing companies for Hamadan Glass Company and the comparative status
367
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
of this company. To observe ethics (observe the companies legal rights), the names of these companies
are demonstrated by alphabetic letters (A, B, C, D, E & F).
Table 1
List of competitors and the companys comparative status
From 1992 To 1997
From 1998 To 2003
Average
Average
Company
production
Market
production
Market
name
capacity
share
capacity
share
(ton)
(ton)
HGC*
34500
24%
37402
24.8%
Company A
55200
38%
49205
32.7%
Company B
11400
8%
14067
9.4%
Company C
9000
6%
11959
8%
Company D
24500
17%
21325
14.1%
Company E
10800
7%
16478
11%
Company F
Total
145400
100%
150436
100%
(*HGC: Hamadan Glass Company)
From 2004 To 2008
Average
production
Market
capacity
share
(ton)
75000
33%
60000
26.4%
10000
4.4%
6000
2.7%
25000
11%
15000
6.6%
36000
15.9%
227000
100%
Also, Table (2) shows the list of the companys opportunities and threats which were collected after
summarizing the questionnaires and then weighted during the discussions in the meetings. As can be seen,
the companys important opportunities include the possibility of providing all the raw material from
inside the country, changing trend of food consumption culture within the country, high shipping costs
from overseas (which is a competitive advantage for the internal companies) and, at last, population
growth. Also, the most important threats include replacing PET containers with glass containers in food
and beverage industries, ongoing developments in competing companies and entry of new competitors,
excessive annual increase of shipping fare inside the company for transporting raw materials and products
and, finally, lack of access to refractory bricks and accessories, components and equipment, in case of
sanctions by European countries (influenced by the political situation).
Table 2
EFE matrix for Hamadan Glass Co.
External Factors
Opportunities:
Changing the culture of food consumption from traditional to industrial
products
Population growth
Export to neighboring countries
Possibility of supplying all the raw materials from inside the country
Cost-ineffectiveness of glass import because of high shipping cost due to
the products bulkiness
Threats:
Replacing PET containers with glass containers in food and beverage
industries
The ongoing developments of competing companies and entry of new
competitors
Excessive annual increase of shipping fare for transporting raw materials
and products
Lack of access to refractory bricks and accessories, components and
368
Weight
Rating
Score
0.1
0.1
0.05
0.15
3
3
3
4
0.3
0.3
0.15
0.6
0.1
0.3
0.15
0.3
0.1
0.2
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.15
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
equipment in case of sanctions
Being affected (being influenced) by economic conditions of food
industries in terms of packaging glass industry as an intermediate good
Total
0.05
0.05
2.45
Internal Factor Evaluation
The objective of recognizing the industrys inside environment is to recognize an organizations internal
strengths and weaknesses. The factors which should be considered in this regard include: 1- management
and its structure, 2- sales and marketing, 3- finance and accounting, 4- research and development, 5competitive forces, and 6- manpower. Table (3) demonstrates the companys strengths and weaknesses
for evaluation. They were obtained after summarizing the questionnaires and then weighted during
discussion sessions. As can be seen, the companys appropriate research and development unit and its
modern and advanced machinery in Unit 1 are considered the most important strengths and, on the other
hand, poor liquidity and lack of production experts who are at the level of European experts are the main
weaknesses.
Table 3
IFE matrix for Hamadan Glass Co.
Internal Factors
Strengths:
Research and development unit
Experienced managers
Modern, up-to-date and advanced machinery in the plants Unit 1
The plants large area of land (40 acres)
Enjoyment from the silica mine in the city of Abhar
Weaknesses:
Problem of liquidity (lack of sufficient working capital)
Lack of production experts who are at the level of experts in the European
and advanced countries
Old and surplus manpower
Old support equipment and facilities
Impossibility for the full settlement of maturity debt of the received
facilities from the banking system
Total
Weight
Rating
Score
0.2
0.05
0.15
0.05
0.05
4
4
4
2
3
0.8
0.2
0.6
0.1
0.15
0.15
0.45
0.15
0.3
0.1
0.05
2
1
0.2
0.05
0.05
0.1
2.95
SWOT analysis
In this matrix, as its name reveals, first, the weaknesses and strengths and the factors identified as
opportunities and threats are placed in a three-by-three matrix in a special order. Then, by combining
weaknesses, strengths, opportunities and threats, new strategies are invented and placed in the blanks
corresponding with these combinations [1], [5]. In the following table (Table 4), SWOT matrix is shown
for Hamadan Glass Company using the investigations of internal and external factors (Tables 2 and 3).
Below, all the strategies which are implementable for the company can be observed.
Table 4
The TOWS matrix for Hamadan Glass Co.
Strengths:
Weaknessess:
- Research and development unit
- Experienced managers
369
- Problem of liquidity (lack of sufficient
working capital)
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
- Modern, up-to-date and advanced
machinery in the plants Unit 1
- The plants large area of land (40
acres)
- Enjoyment from the silica mine in the
city of Abhar
- Lack of production experts who are at
the level of experts in the European and
advanced countries
- Old and surplus manpower
- Old support equipment and facilities
- Impossibility for the full settlement of
maturity debt of the received facilities
from the banking system
Opportunities:
SO Strategy:
WO Strategies:
- Changing the culture of food
consumption from traditional to
industrial products
- Population growth
- Export to neighboring countries
- Possibility of supplying all the raw
materials from inside the country
- Cost-ineffectiveness of glass import
because of high shipping cost due to the
products bulkiness
-Establishing Unit 3 for producing
colored bottles (S1, S4, S5, O1, O2,
O3, O4, O5)
- Creating a unit of crushing and
arranging silica (W3, O4)
- Renewing support equipment and
facilities (W4, O3)
Threats:
ST Strategies:
- Replacing PET containers with glass
containers in food and beverage
industries
- The ongoing developments of
competing companies and entry of new
competitors
- Excessive annual increase of shipping
fare for transporting raw materials and
products
- Lack of access to refractory bricks and
accessories, components and equipment
in case of sanctions
- Impossibility for the full settlement of
maturity debt of the received facilities
from the banking system
- Cooperating with a transportation
company (S2, T3)
- Creating the culture of using glass
bottles instead of PET for packaging
through Consumers Awareness and
Environmental Protection
Organization (S1, S5, T1)
WT Strategies:
- Increasing the capital through the
shareholders cash and paid interests
for the shares (W1, W5, T2, T3)
- Using legal benefits and early
retirement regulations of the staff
(W3, T5)
Evaluating and Prioritizing the Strategies
In this stage, it is required to select the best possible strategies from among the strategies that are
implementable in the company, which are obtained using TOWS matrix analysis. This evaluation can be
done using QSPM matrix [3]. The results of this examination about Hamadan Glass Company are given
in Table (5).
Table 5
QSPM for Hamadan Glass Co.
Factors
Op.1
Op.2
Op.3
Op.4
Op.5
Th.1
Th.2
Th.3
Th.4
Th.5
Weight
0.1
0.1
0.05
0.15
0.1
0.15
0.1
0.05
0.15
0.05
WO-1
AS FAS
1
0.1
1
0.1
1
0.05
4
0.6
1
0.1
2
0.2
2
0.1
-
WO-2
AS FAS
1
0.1
1
0.1
2
0.1
3
0.45
-
SO-1
AS FAS
4
0.4
4
0.4
3
0.15
3
0.45
3
0.3
3
0.45
4
0.4
4
0.6
-
370
WT-1
AS FAS
2
0.2
1
0.05
2
0.3
2
0.1
WT-2
AS FAS
2
0.2
-
ST-1
AS FAS
2
0.1
3
0.3
4
0.2
1
0.5
ST-2
AS FAS
1
0.1
4
0.6
3
0.3
0.05
-
Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers & Industrial Engineering
St.1
St.2
St.3
St.4
St.5
We.1
We.2
We.3
We.4
We.5
Total
0.2
0.05
0.15
0.05
0.05
0.15
0.15
0.1
0.05
0.05
1
1
4
2
1
3
2
0.2
0.05
0.2
0.3
0.15
0.3
0.1
2.55
1
1
2
4
4
0.2
0.05
0.3
0.2
0.2
1.7
3
2
2
3
4
2
4
2
4
0.6
0.1
0.3
0.15
0.2
0.3
0.6
0.2
0.2
5.8
4
4
3
4
0.2
0.6
0.15
0.2
1.8
2
2
3
1
4
2
0.1
0.3
0.45
0.15
0.4
0.1
1.7
2
1
2
-
0.1
0.05
0.3
1.1
2
1
1
4
2
1
3
0.4
0.15
0.05
0.2
0.3
0.05
0.15
2.35
(AS: Attractiveness Score; FAS: Final Attractiveness Score)
Considering the results of QSPM matrix , the priority of strategies are as follows:
1: Establishing Unit 3 for producing colored bottles,
2: Establishing a unit for crushing and arranging silica,
3: Creating the culture of using glass bottles instead of disposable plastic PET (Poly Ethylene
Terephthalate) containers,
4: Increasing the capital through the shareholders cash and paid interests,
5.1: Reconstructing and developing equipment and facilities,
5.2: Using benefits of the early retirement regulations for the old staff and employing new and
experienced forces, and
6: Cooperating with a transportation company.
Conclusion
Considering that strategic planning has not been done in the Hamadan Glass Company so far, such kind
of plan was essential for the company. The results show that this industry is in an optimum condition and
the company is in a good competitive situation; however, its financial situation is not desirable.
The strategies and their priorities were identified as follows:
The companys strategic advisory team identified establishing a third unit for producing colored bottles
as the first and most important priority among other strategies.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank the respected authorities, experts and managers of Hamadan Glass Company for their
sincere cooperation.
References
[1] David, Fred R., Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases (7th Edition), Prentice Hall, January 1999.
[2] Terrados, J., Almonacid, G., Hontoria, L., (August 2007), Regional energy planning through SWOT
analysis and strategic planning tools.: Impact on renewables development, Renewable & Sustainable
Energy Reviews, Vol. 11, Issue 6, (2007). pp. 1275-1287.
[3] David, M. E., David, R.F., David, F.R., (Spring 2009), The quantitative strategic planning matrix
(QSPM) applied to retail computer store, The Coastal Business Journal, Vol. 8, Number 1, (2009), pp. 4252.
[4] Bartkus, B., Glassman, M., McAfee, B., (February 2006), Mission statement quality and financial
performance, European Management Journal, Vol. 24, Issue 1, (2006), pp. 86-94.
[5] Dyson, R. G., (February 2004), Strategic development and SWOT analysis at the university of
Warwick, European Journal of Operational Research, Vol. 152, Issue 3, (2004), pp. 631-640.
371
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Exploring The Base of The Pan-Mayan MovementDocument24 pagesExploring The Base of The Pan-Mayan MovementGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- List of Countries, Territories and AreasDocument40 pagesList of Countries, Territories and AreasTugas HeinzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Archaeology Org PDFDocument3 pagesArchaeology Org PDFGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Live Your Truth (Kamal Ravikant)Document89 pagesLive Your Truth (Kamal Ravikant)Guillermo100% (2)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Mosaic Mystery ArchaeologyDocument5 pagesMosaic Mystery ArchaeologyGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Title: Calvario-Tehuacan: Page of 1 2Document2 pagesTitle: Calvario-Tehuacan: Page of 1 2GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Archaeology Org PDFDocument3 pagesArchaeology Org PDFGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Defending A Jungle KingdomDocument3 pagesDefending A Jungle KingdomGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Cultural Resources: Guatemala: I, Rigoberta MenchúDocument2 pagesCultural Resources: Guatemala: I, Rigoberta MenchúGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Bitter Fruit PresentationDocument48 pagesBitter Fruit PresentationGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Temple in Tikal Lesson Student PrintableDocument1 pageTemple in Tikal Lesson Student PrintableGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Story Behind Eh!Document4 pagesThe Story Behind Eh!GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Case For Faith-Based Competitive Advantage: Thought LeadersDocument9 pagesThe Case For Faith-Based Competitive Advantage: Thought LeadersGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Tourism Business Toolkit VOL2 Chapter3Document6 pagesTourism Business Toolkit VOL2 Chapter3GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Well Blogs Nytimes ComDocument3 pagesWell Blogs Nytimes ComGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Invest in Entrepreneurs in Emerging EconomiesDocument5 pagesInvest in Entrepreneurs in Emerging EconomiesGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- How Does A Company Communicate Through Storytelling?Document80 pagesHow Does A Company Communicate Through Storytelling?GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Bitter Fruit PresentationDocument48 pagesBitter Fruit PresentationGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloomberg Businessweek 2011 10 17Document136 pagesBloomberg Businessweek 2011 10 17calvfooPas encore d'évaluation
- 7SWorksheet PDFDocument1 page7SWorksheet PDFGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Business Meeting MinutesDocument4 pagesBusiness Meeting MinutestengkunorPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- SWOT Analysis TemplateDocument1 pageSWOT Analysis TemplateGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- LINUX Terminal CommandsDocument3 pagesLINUX Terminal CommandsGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basil Pork ChopsDocument1 pageBasil Pork ChopsGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basil Pork ChopsDocument1 pageBasil Pork ChopsGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cuban Mango MousseDocument1 pageCuban Mango MousseGuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lapid V CADocument11 pagesLapid V CAChami YashaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- 34-Samss-718 (12-02-2015)Document14 pages34-Samss-718 (12-02-2015)Mubin100% (1)
- Tower BridgeDocument6 pagesTower BridgeCalvin PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- New Micra BrochureDocument14 pagesNew Micra BrochureGlobalGroupOfDealersPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesun 2009-07-09 Page05 Ex-Pka Director Sues Nine For rm11mDocument1 pageThesun 2009-07-09 Page05 Ex-Pka Director Sues Nine For rm11mImpulsive collectorPas encore d'évaluation
- AAU Karate Handbook: "Sports For All, Forever"Document58 pagesAAU Karate Handbook: "Sports For All, Forever"jeffrey_trzaskusPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04Document35 pages03 CTAL TM Sample ISTQB Questions - v2.04CorniciucOanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complaint - Burhans & Rivera v. State of New York PDFDocument34 pagesComplaint - Burhans & Rivera v. State of New York PDFpospislawPas encore d'évaluation
- Yesenia Acc SjournalsDocument7 pagesYesenia Acc SjournalsFileon ChiacPas encore d'évaluation
- CHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryDocument30 pagesCHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryLeo Archival ImperialPas encore d'évaluation
- k90mcc6 PDFDocument381 pagesk90mcc6 PDFTammy JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Document3 pagesDLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Lovely Shiena Cain AragoncilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 8 - Surface Mining - Wire - RopeDocument11 pages8 - Surface Mining - Wire - RopeSuelen Barbosa Sdrill do BrasilPas encore d'évaluation
- Fly The Maddog X User Manual MSFS 2020Document15 pagesFly The Maddog X User Manual MSFS 2020KING OF NOOBSPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFDocument18 pagesCreating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFLiza ZakhPas encore d'évaluation
- HD785-7 Fault Codes SEN05900-01-3Document16 pagesHD785-7 Fault Codes SEN05900-01-3ISRAEL GONZALESPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 0000362296Document1 page17 0000362296Ekansh BarsiwalPas encore d'évaluation
- JKBMS Tutorial SetupDocument7 pagesJKBMS Tutorial SetupFabricio Varovsky Muñiz ArteagaPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF 20699Document102 pagesPDF 20699Jose Mello0% (1)
- Shortcrete PDFDocument4 pagesShortcrete PDFhelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Casio Aq140w UputstvoDocument1 pageCasio Aq140w UputstvoalazovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic History of The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesEconomic History of The PhilippinesBench AndayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Evidence Rule CasesDocument5 pagesBest Evidence Rule CasesRemy Rose AlegrePas encore d'évaluation
- Level 5 Diploma in Business Management: Assignment BriefsDocument22 pagesLevel 5 Diploma in Business Management: Assignment BriefsyehashaPas encore d'évaluation
- United States v. Hollis, 4th Cir. (2001)Document3 pagesUnited States v. Hollis, 4th Cir. (2001)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- MT7605B DSDocument7 pagesMT7605B DSVishal dtuPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: PointDocument1 pageCase Study: PointprasadzinjurdePas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing The Office.: Transforming Business ProcessesDocument10 pagesOptimizing The Office.: Transforming Business ProcessesNOSHEEN MEHFOOZPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterprise Management System: Reference W.S.JawadekarDocument34 pagesEnterprise Management System: Reference W.S.JawadekarPolice stationPas encore d'évaluation
- Debugging With The PL/SQL Debugger: PhilippDocument51 pagesDebugging With The PL/SQL Debugger: PhilippBenjytox BenjytoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksD'EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensD'EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensPas encore d'évaluation