Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
How a light switch illuminates Boolean algebra and the logic of computers
Transféré par
OrezMaiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
How a light switch illuminates Boolean algebra and the logic of computers
Transféré par
OrezMaiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A bright idea | plus.maths.
org
28/01/15 15:01
Search Plus
Search
A bright idea
by Yutaka Nishiyama (/content/list-by-author/Yutaka Nishiyama)
Submitted by Anonymous on September 28, 2005
A light switch is a simple object: it's either on or off. But this simple binary system is enough to
illustrate Boolean algebra, on which all modern computers are based. Yutaka Nishiyama
illuminates the connection between light bulbs, logic and binary arithmetic.
Maths in everyday life
Maths is hidden within the simplest things in life, and sometimes you don't even notice it. When
you come home at night, for example, and it is dark, you switch on the light in the hall. Later
on, when you go upstairs to bed, you switch it off again by another switch on the upstairs
landing. But how does the upstairs switch know that the light is on and its job is to switch it off?
Does it communicate with the switch downstairs somehow? Is it remote-controlled? The
answers to questions like these serve as a good example for the binary system that underlies
Boolean logic and the workings of modern computers.
Let's start with the simplest example of a light bulb connected to an
electric circuit (figure 1). The switch operates a gate, or relay, in the
circuit. If this gate is closed then so is the circuit and the light is on.
If it is open, the light is off. Flicking the switch acts as an "inverter",
changing the light from its current state (on or off) to the only other
state it can be in. Things get a little more interesting if we use a
circuit with two gates, as in figure 2. In the first circuit the light is on
only if both gates are pointing upward, and in the other it is on if at
least one of the two is pointing upward. Let's write "1" for "the gate
is pointing upward" and "0" for "the gate is pointing downward".
Figure 1: a simple circuit.
There are four possibilities, gate 1 up and gate 2 up, gate 1 up and
gate 2 down, gate 1 down and gate 2 up, and both down. If we write
"1" for "the light is on" and "0" for "the light is off", then the tables below show the four
possibilities and the corresponding state of the light for each circuit.
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
Page 1 of 6
A bright idea | plus.maths.org
28/01/15 15:01
Figure 2: the two circuits.
Circuit 1
Circuit 2
Gate 1 1 1 0 0
Gate 1 1 1 0 0
Gate 2 1 0 1 0
Gate 2 1 0 1 0
Light
Light
1 0 0 0
1 1 1 0
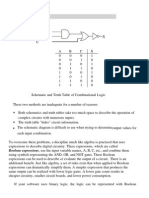
Mathematical logic and truth tables
These two tables are nothing more than the "truth tables" for the "logical operators" AND and
ORfrom mathematical logic. Let's replace the statement "gate 1 is pointing upward" by any
other statement P, for example "it is raining", and the statement "gate 2 is pointing upward" by
any other statement Q, for example "I am wet". Now the statement P AND Q - "it is raining
ANDI am wet" - is true precisely when both P and Q are true. If we write "1" for "the statement
is true" and "0" for "the statement is false", then the table below tells us exactly when the
statement P AND Q is true for the four different combinations of truth values for P and Q. This
table is exactly the same as that for the first circuit, which makes sense, as saying "the light is
on" is the same as saying "gate A AND gate B are pointing upward".
AND
P
1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
P AND Q 1 0 0 0
The second table corresponds to the OR operator. In mathematical logic, the statement P OR Q
is true when one of P or Q is true or when both are true, and false when both are false. This
reflects what happens in our second circuit: the light is on if gate 1 is pointing upward or gate 2
is pointing upward or if both are pointing upward. The truth table of the OR operator is exactly
the same as the table for the second circuit.
OR
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
Page 2 of 6
A bright idea | plus.maths.org
28/01/15 15:01
P OR Q 1 1 1 0
The simple on/off switch in figure 1 also has its logical meaning: it corresponds to the negating
operator NOT. If statement P - "it is raining" - is true then the statement NOT P - "it is not
raining" - is false, and vice versa.
The three little words AND, OR and NOT are immensely powerful. They are the basis of
mathematical logic, which in turn gives rise to Boolean algebra. Mathematical logic provides a
rigorous way to decide whether complicated statements, which often occur in mathematics, are
true or false. It is based on the following idea: we have a number of statements, such as "it is
raining", which can be either true or false. The operator NOT is used to negate a statement.
Using AND and OR we can connect two statements. In this fashion, we can build up long
"sentences", for example P AND ((Q AND S) OR NOT (T OR W)), where P,Q,S,T and W are
statements. We can figure out whether such a sentence is true by looking at the truth values of
the individual statements and consulting the truth tables of AND and OR.
You might think that you can't say much using only AND, OR
and NOT. But it turns out that many logical relationships
between statements can be expressed just using these three.
One example is the statement "if P is true then Q is true" - "if it
rains then I get wet". This is often called "P IMPLIESQ". The
truth table for this operator is given below.
To see why this truth table makes sense, let us first assume
that the statement P IMPLIES Q - "if it rains then I get wet" - is
true, the situation indicated by a "1" in the last line of the truth
table. This could happen, for example, if standing in the middle
of a field without any umbrella or other protection. Now if it is indeed raining, then you know
immediately that I am wet. Both the statements "it is raining" and "I am wet" are true, and we
get the entry "1" for both P and Q in the truth table. If it is not raining, you don't know if I'm
wet or not - I might have fallen into a pond and got soaked, or I might be dry. The statement "I
am wet" can be either true or false, and this accounts for the last two columns in the truth
table. The only remaining possibility is that it is raining but I am not wet. In this case the
statement "if it rains then I get wet" is clearly false - I must have brought an umbrella after all.
This is the second column of the truth table.
IMPLIES
P
1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
P IMPLIES Q 1 0 1 1
But this truth table is exactly the same as that for the expression NOT P OR Q "it is not raining
or I am wet". This makes sense: if P IMPLIES Q is true, then I can replace the statement "it is
raining" by "I am wet", as one follows directly from the other. The true statement "it is not
raining or it is raining", then becomes "it is not raining or I am wet" - NOT P OR Q is true. If P
IMPLIES Q is false, then I may well be dry even though it is raining - the statement "it is not
raining or I am wet" is false. We see that P IMPLIES Q is true or false precisely when NOT P OR
Q is true or false. The two are equivalent, and we can express the relationship P IMPLIES Q
using only the operators NOT and OR.
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
Page 3 of 6
A bright idea | plus.maths.org
28/01/15 15:01
Boolean Algebra
In the mid-nineteenth century, the English mathematician George
Boole invented what is known today as "Boolean algebra". His
ingenious idea was to treat the individual statements, like P and Q
above, as variables and to define the logical operators as
mathematical operations, similar to addition and multiplication. If,
for example, we write PQ for P ANDQ and P+Q for P ORQ, then
our two circuits above can be expressed by the two equations
Light = AB
Light = A+B.
Dealing with logical statements, simplifying them and finding their
truth value, then just turns into manipulation of algebraic
expressions, like simplifying or solving an equation. These algebraic manipulations are of course
governed by strict rules, and performing them becomes a "mindless" activity - you just follow a
set of rules, a machine can do it. Indeed, today, all computers are based on Boolean algebra,
another example that mathematics is often a hundred years ahead of its time.
Incidentally, it was Boole's work that inspired the English mathematician John Venn to establish
his comprehensive theory of Venn diagrams. Venn diagrams deal with sets, their union and
intersection.
Saying that an element x lies in the intersection of two
sets A and B is the same as saying x lies in A ANDx lies
in B. Similarly, the union of two sets corresponds to the
logical operator OR- x lies in A ORx lies in B - while the
complement of a set corresponds to the operator NOT.
Binary arithmetic
So how do we get logic into a computer? How can we
use the ideas set out above to get a computer to perform
sets A and B.
high-speed, high-precision calculations? A computer
operates on six basic electronic circuits: the AND, ORand
NOTcircuits described above, the negations of ANDand OR, known as NANDand NOR, and a
circuit called XOR, or exclusive OR. XORcorresponds to the logical expression (P ANDNOTQ)
OR(NOTP ANDQ), its truth table is given below.
A Venn diagram showing two intersecting
XOR
P
1 1 0 0
1 0 1 0
P XOR Q 0 1 1 0
When performing binary addition, just like for addition in base ten, we need to reserve two
spaces for our result. In one space, the right hand one, we write down the result of adding up
the units. The other left-hand space is an overflow area: here we enter a 1 if our result exceeds
two. The table below gives the rules for binary addition.
0 0 1 1
+0 +1 +0 +1
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
Page 4 of 6
A bright idea | plus.maths.org
28/01/15 15:01
0 1 1 10
If we ignore the overflow area, then what we get is exactly the truth table for XOR. Ignoring the
area for the units gives the truth table for AND. Superimposing the two logical operations we
can define binary addition. And once we have that, the other three arithmetical operations come
for free: subtraction is just addition "backwards", multiplication is repeated addition and division
is repeated subtraction. The arithmetic operations can be replaced by logical operations, which
are performed using Boolean algebra.
And this brings us neatly back to our light switch theme: the XOR circuit - or, to be precise, its
negation - is exactly what you need to wire up a light to two switches. For this we have to
abandon our simple gates for so-called "three-way switches", which connect to part of the
circuit in either position (see figures 3 and 4).
Each of the two gates can
be in an upward-pointing or
in a downward-pointing
position. We write "1" for
"the gate is pointing
upward", "0" for "the gate is
Figure 3: a three-way
pointing downward" and "1"
switch.
for the light is on. The
various positions are
indicated in the table below - which is exactly the
truth table for NOT XOR.
Switch 1 1 1 0 0
Figure 4: wiring two switches to one bulb.
Switch 2 1 0 1 0
Light
1 0 0 1
An infinite story house
And what if you live in a three story house and want to have three switches for the light in the
hall? For this you need two three-way switches and one four-way switch, which is shown in
figure 5. You arrange the three switches in a row, with the four-way switch in the middle, as in
figure 6. As before, we write "0" for "the three-way switch is pointing downward" and "1" for
"the three-way switch is pointing upward". There are now eight different possibilities for the
arrangement of the switches.
Figure 5: the left-hand position of the switch is 0 and
the right-hand position is 1.
As you can see in figure 6, the light is on when
two or none of the three switches are in position
1. To put it in the language of logic, the
statement "the light is on" is true exactly when
the statement "the switch is in position 1" is true
for two of the switches, or for none of the
switches. It is true precisely when the values for
the three switches add up to an even number. If
we write "A" for the statement "switch 1 is in
position 1", "B" for "switch 2 is in position 1" and
"C" for "switch 3 is in position 1", then the light is
on precisely when the statement
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
Page 5 of 6
A bright idea | plus.maths.org
28/01/15 15:01
(A AND B AND NOT C) OR (A AND NOT B AND C) OR
(NOT A AND B AND C) OR (NOT A AND NOT B AND NOT
C)
is true.
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 3
Light
1
Figure 6: wiring three switches to a bulb.
Switches 1 and 2 are in position 1 and switch
And the good thing about all this is that it will work for
3 is in position 0. The switches' values add
any number of switches. No matter how tall your house
up to an even number and the light is on.
is, the same principles will apply: the light will come on
whenever the values of the different switches add up to
an even number, and you can wire up the switches using a circuit with three-way switches at
each end and four-way switches in the middle. The process works all the way up to infinity.
About the author
Yutaka Nishiyama is a professor at Osaka University of Economics, Japan.
After studying mathematics at the University of Kyoto he went on to work for
IBM Japan for 14 years. He is interested in the mathematics that occurs in
daily life, and has written seven books about the subject. The most recent
one, called "The mystery of five in nature", investigates, amongst other
things, why many flowers have five petals. Professor Nishiyama is currently
visiting the University of Cambridge.
http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue36/features/nishiyama/index
Page 6 of 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1 + 1 = 1 An Introduction to Boolean Algebra and Switching CircuitsD'Everand1 + 1 = 1 An Introduction to Boolean Algebra and Switching CircuitsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- EE2255 - Digital Logic CircuitsDocument147 pagesEE2255 - Digital Logic CircuitsSatyajit MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- CountersDocument130 pagesCountersNitin SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Algebra ThesisDocument4 pagesBoolean Algebra Thesistammibuschnorman100% (4)
- 3.1 Why Boolean Algebra?Document18 pages3.1 Why Boolean Algebra?Giri PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic Signals Gates FunctionsDocument39 pagesDigital Logic Signals Gates Functionsnitinkumar1964Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic - Gates, Boolean AlgebraDocument27 pagesDigital Logic - Gates, Boolean AlgebraJoey LeePas encore d'évaluation
- LP2 ES7 Unit2-1Document28 pagesLP2 ES7 Unit2-1Razel Mae LaysonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Boolean AlgebraDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Boolean AlgebraashrafPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-1 - Boolean AlgebraDocument35 pagesUNIT-1 - Boolean AlgebraPARTEEK RANAPas encore d'évaluation
- MathDocument9 pagesMathGenaline FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- +ve &-Ve LogicDocument5 pages+ve &-Ve LogicAnushiMaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Algebra and Basic OperationsDocument7 pagesBoolean Algebra and Basic OperationsPrafull BPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Algebra RulesDocument7 pagesBoolean Algebra Rulesapi-126876773Pas encore d'évaluation
- CS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) - Fall 2011: Antonina KolokolovaDocument3 pagesCS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) - Fall 2011: Antonina KolokolovaZhichaoWangPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean AlgebraDocument3 pagesBoolean Algebrashar_grvPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Making DecisionsDocument22 pages3 Making Decisionsanurag_kapila3901Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics ProjectPRAVEENPas encore d'évaluation
- AI Assignment: Plagiarism StatementDocument3 pagesAI Assignment: Plagiarism StatementGarvitPas encore d'évaluation
- CS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : Antonina KolokolovaDocument2 pagesCS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : Antonina KolokolovaZhichaoWangPas encore d'évaluation
- Truth Table of Five Common Logical Operators or ConnectivesDocument16 pagesTruth Table of Five Common Logical Operators or Connectivesmeer aquibPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 - Logic FundamentalsDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Logic Fundamentalsfmwansa806Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2Document11 pagesLec 2Shubham SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- CS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : 4 Boolean Functions and CircuitsDocument5 pagesCS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : 4 Boolean Functions and Circuitsgrdprashant974Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math RDPDocument7 pagesMath RDPJhace CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Hassan Assignment 1 DLDDocument7 pagesHassan Assignment 1 DLDsanee rajpootPas encore d'évaluation
- How to build logic circuits and derive their truth tablesDocument2 pagesHow to build logic circuits and derive their truth tablesJhon David TabunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Expressions and Truth TablesDocument11 pagesBoolean Expressions and Truth TablesfaizalpaptPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG1021 Electronic Principles: Kirchoff's Laws ExplainedDocument134 pagesENG1021 Electronic Principles: Kirchoff's Laws ExplainedRobert MaxwellPas encore d'évaluation
- ErcdsDocument13 pagesErcdsKadir SezerPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Electronics BasicsDocument30 pagesDigital Electronics BasicsAravinda A KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic Circuits Experiment 4Document14 pagesLogic Circuits Experiment 4Eman Albino100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1shadPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean and GateDocument69 pagesBoolean and GatevsbistPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Level MinimizationDocument50 pagesGate Level MinimizationsssbulbulPas encore d'évaluation
- Propositional Logic and Hardware2023-1Document11 pagesPropositional Logic and Hardware2023-1Assassin GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- CS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : Antonina Kolokolova September 28, 2009Document4 pagesCS 2742 (Logic in Computer Science) : Antonina Kolokolova September 28, 2009ZhichaoWangPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolen ExpressionDocument8 pagesBoolen ExpressionDivyanshi BajpaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Algebra: An Investigation of The Laws of ThoughtDocument28 pagesBoolean Algebra: An Investigation of The Laws of ThoughtMehar ShreePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project CBSE CLASS XII LOGIC GATES 2017Document16 pagesPhysics Project CBSE CLASS XII LOGIC GATES 2017Jasmine James83% (12)
- PLC 4Document40 pagesPLC 4Hector IbarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean algebra theorems and logic gate circuitsDocument6 pagesBoolean algebra theorems and logic gate circuitsCristal Ann MilarpisPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean AlgebraDocument2 pagesBoolean Algebraarghya_bi108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical LogicDocument15 pagesMathematical LogicEfean KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Introductory Calculus, Semester 1 Errata Course Version 3.0.1Document1 pageIntroductory Calculus, Semester 1 Errata Course Version 3.0.1Michael MaddoxPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) When Implemented, A Minterm Boolean Expression Produces What Pattern of Logic Gate ?Document9 pages1) When Implemented, A Minterm Boolean Expression Produces What Pattern of Logic Gate ?sxesplly4uPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic GateDocument14 pagesLogic GateADARSH SHUKLA 2337 PCBPas encore d'évaluation
- C F L P: Hapter OUR Adder RogrammingDocument40 pagesC F L P: Hapter OUR Adder RogrammingMohamed OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical LogicDocument10 pagesMathematical LogicSravaan Reddy100% (1)
- Logic Gates: Boolean Variables & Truth TablesDocument9 pagesLogic Gates: Boolean Variables & Truth TablesIbz AjagbePas encore d'évaluation
- De MorgansDocument166 pagesDe MorganssaconnectsPas encore d'évaluation
- And Industral University: Discrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsDocument37 pagesAnd Industral University: Discrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsFidan IbadullayevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Logic Fundamentals ExplainedDocument3 pagesBoolean Logic Fundamentals ExplainedIulia RusuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) When Implemented, A Minterm Boolean Expression Produces What Pattern of Logic Gate ?Document9 pages1) When Implemented, A Minterm Boolean Expression Produces What Pattern of Logic Gate ?sxesplly4uPas encore d'évaluation
- 402 Lab 10Document5 pages402 Lab 10api-284738200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Logic GatesDocument15 pagesLogic GatesShubham Tiwari67% (3)
- From Logic To Fuzzy LogicDocument22 pagesFrom Logic To Fuzzy LogicArjob MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Boolean Algebra FundamentalsDocument77 pagesBoolean Algebra FundamentalsjimmyboyjrPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For 64-Bit Global Identifier (EUI-64) : GeneralDocument3 pagesGuidelines For 64-Bit Global Identifier (EUI-64) : GeneralOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Annexure IDocument3 pagesAnnexure IOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of SAP R/3 Architecture: Submitted By: Manjinder Singh Sohi Mss046000@utdallas - EduDocument17 pagesStudy of SAP R/3 Architecture: Submitted By: Manjinder Singh Sohi Mss046000@utdallas - EduOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch3new PDFDocument73 pagesCh3new PDFవేలుసామి లింగాసామిPas encore d'évaluation
- Pratap PDFDocument2 pagesPratap PDFOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Network Security TimetableDocument1 pageCommunication Network Security TimetableOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ops \defbeamerte\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{title in head/foot}\insertshortdate% \end{beamercolorbox}}% \vskip0pt% }\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/foDocument19 pagesOps \defbeamerte\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{title in head/foot}\insertshortdate% \end{beamercolorbox}}% \vskip0pt% }\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/foOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- TESTDocument114 pagesTESTOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- https://dt60.energycdn.com/torrenthttps://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4https://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4https://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5Document14 pageshttps://dt60.energycdn.com/torrenthttps://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4https://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4https://dt60.energycdn.com/torrentdl/30TvjF5OuCXPH4z3B7ySJw/1465697103/3530336/0b41a71dbf3632a12d43a8a6d56e31830563468b/Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5BShareKing%5D%3D-.mp4?f=Yamadonga%20%282007%29%20Telugu%201080P%20x264%203CD%20WeBRiP%20%5BxRG%5D%20-%3D%5OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Taylor Expansion of 1 + XDocument2 pagesTaylor Expansion of 1 + XOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap06\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}Document17 pagesChap06\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.FFT & InputDocument2 pages3.FFT & InputOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}Document4 pages\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}Document21 pages\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- NokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54NokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54NokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54Document1 pageNokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54NokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54NokiaPhotoTransfer - 2016 01 18 - 11 08 54OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Suvadugal - Nagaramvjsh, Dvhsdvmahjvl AvjklbfdalkDocument15 pagesSuvadugal - Nagaramvjsh, Dvhsdvmahjvl AvjklbfdalkOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Plagiarism Checking Result For Your DocumentDocument9 pagesPlagiarism Checking Result For Your DocumentOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Network Security TimetableDocument1 pageCommunication Network Security TimetableOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ofdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 3 of 3: SofdmaDocument2 pagesOfdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 3 of 3: SofdmaOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- OFDM, OFDMA, and SOFDMA in WiMAX - PageDocument1 pageOFDM, OFDMA, and SOFDMA in WiMAX - PageOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fir Filter: //rectangular WindowDocument17 pagesFir Filter: //rectangular WindowOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coimbatore Institute of Technology: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution) COIMBATORE-641014Document1 pageCoimbatore Institute of Technology: (Government Aided Autonomous Institution) COIMBATORE-641014OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Screen Shot 2015-12-19 at 12.15.11Document1 pageScreen Shot 2015-12-19 at 12.15.11OrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ofdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 2 of 3: OfdmaDocument1 pageOfdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 2 of 3: OfdmaOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nyquist Sampling TheoremDocument2 pagesNyquist Sampling TheoremOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ofdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 3 of 3: SofdmaDocument2 pagesOfdm, Ofdma, and Sofdma in Wimax - Page 3 of 3: SofdmaOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 National JournalsDocument1 page2014 National JournalsOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- FB1 SDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJDocument1 pageFB1 SDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJSDJKDSVHJOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 14MVD15 &22 Eryws HFSDSFGHF GDFGDF GDGNDFGFDocument4 pages14MVD15 &22 Eryws HFSDSFGHF GDFGDF GDGNDFGFOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- DB1 - Data ViewDocument1 pageDB1 - Data ViewOrezMaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ben Wilkins PRISON MADNESS and LOVE LETTERS: THE LOST ARTDocument5 pagesBen Wilkins PRISON MADNESS and LOVE LETTERS: THE LOST ARTBarbara BergmannPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeDocument2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise 2 Mole-Mole Mass-Mass: Sorsogon State CollegeJhon dave SurbanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutics | Water Solubility and Dissolution RateDocument11 pagesPharmaceutics | Water Solubility and Dissolution RateAnnisa AgustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toaz - Info Chemtech Reviewer PRDocument1 pageToaz - Info Chemtech Reviewer PRchristy janioPas encore d'évaluation
- Xoro Hrs 8540 HD Sat ReceiverDocument33 pagesXoro Hrs 8540 HD Sat ReceiverPinoPas encore d'évaluation
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 6Document30 pagesJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 6Adib AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- Sdre14-5 Ral 1-2-Rev17Document3 pagesSdre14-5 Ral 1-2-Rev17lwin_oo2435Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariDocument2 pagesChinkon Kishin - Origens Shintoístas Do Okiyome e Do Espiritismo Na MahikariGauthier Alex Freitas de Abreu0% (1)
- GBDocument10 pagesGBQuoctytranPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Natural Bamboo Fibers-1: Experimental Approaches To Different Processes and AnalysesDocument13 pagesProduction of Natural Bamboo Fibers-1: Experimental Approaches To Different Processes and AnalysesrabiulfPas encore d'évaluation
- Etabloc Technical DataDocument108 pagesEtabloc Technical Dataedward ksbPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialyser Reprocessing Machine Specification (Nephrology)Document2 pagesDialyser Reprocessing Machine Specification (Nephrology)Iftekhar AhamedPas encore d'évaluation
- General Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsDocument108 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsharleyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsDocument64 pages2019 Torch and Consumables Catalog: For Mechanized Plasma SystemsRaj DomadiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blower Selection For Wastewater Aeration PDFDocument10 pagesBlower Selection For Wastewater Aeration PDFRobert MontoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- CV of Shaila (Me)Document4 pagesCV of Shaila (Me)Masud RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar 360 KWDocument6 pagesCaterpillar 360 KWAde WawanPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsDocument5 pagesHow To Use Dr. Foster's Essentials: Essential Oils and BlendsemanvitoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- P198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0Document10 pagesP198 Software and Atlases For Evaluating Thermal Bridges 0cm08909Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kultura I InteligencijaDocument15 pagesKultura I InteligencijaToni JandricPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryDocument12 pagesChapter 14 The Communist Manifesto As International Relations TheoryLaurindo Paulo Ribeiro TchinhamaPas encore d'évaluation
- CalderaDocument56 pagesCalderaEsteban TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Iot Finals Clap Switch Group 5Document15 pagesIot Finals Clap Switch Group 5RICHYBOY SALACPas encore d'évaluation
- Tyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023Document17 pagesTyco TY8281 TFP680 - 03 - 2023First LAstPas encore d'évaluation
- Vedic Astrology OverviewDocument1 pageVedic Astrology Overviewhuman999100% (8)
- Mastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesDocument48 pagesMastercam 8.1 Beta 4: New Verification Engine in Beta 4! Sub-Programs Post ChangesSaul Saldana LoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0Document144 pagesWater System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0moinu85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hart Transmitter Calibration: Application NoteDocument8 pagesHart Transmitter Calibration: Application NoteThulasi Raman KowsiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Return SectionDocument1 pageReturn SectionDaniel Pouso DiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Error Correction - Test 1Document4 pagesError Correction - Test 1phucnguyen0429Pas encore d'évaluation
































































![Ops \defbeamerte\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{title in head/foot}\insertshortdate% \end{beamercolorbox}}% \vskip0pt% }\defbeamertemplate*{footline}{shadow theme} {% \leavevmode% \hbox{\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm plus1fil,rightskip=.3cm]{author in head/foot}% \usebeamerfont{author in head/foot}\insertframenumber\,/\,\inserttotalframenumber\hfill\insertshortauthor \end{beamercolorbox}% \begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.5\paperwidth,ht=2.5ex,dp=1.125ex,leftskip=.3cm,rightskip=.3cm plus1fil]{title in head/fo](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/310346323/149x198/42591fecf6/1461576749?v=1)



![Chap06\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/309726952/149x198/42d3f82dda/1461085719?v=1)

![\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/309727006/149x198/50e3263caf/1461085736?v=1)
![\begin{beamercolorbox}[wd=.6\paperwidth]{example header} \centering \usebeamercolor{title in headline}{\color{fg}\textbf{\Huge{\inserttitle}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{author in headline}{\color{fg}{\huge{\insertauthor}\\[1ex]}} \usebeamercolor{institute in headline}{\color{fg}{\LARGE{\insertinstitute}\\[1ex]}} \end{beamercolorbox}](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/309726848/149x198/91200401b7/1469771464?v=1)