Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PIP BA Role Interview Prep
Transféré par
IshanSaneDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PIP BA Role Interview Prep
Transféré par
IshanSaneDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Services not chargeable to client (spread over all clients as
overhead)
General management & administration
Marketing & promotion
Staff training
Recruitment
Chargeable time is calculated as:
Total available time (less leave, sickness, publicH) Less
(training, marketing, research, meetings) = chargeable time
Annual utilization rate: Chargeable time/Total time (70-80%)
2nd Differential Ratio: Chargeable time/Days available (8090%) can be used for differential rates for consultants (Lower
as we move to senior consultants to principals)
Costing
Every fee earning day has to earn a portion of the total
budgeted income
Total income (budgeted forecast)/Fee-earning days = ~80%
(average daily fee rate)
Cannot charge same daily rate for all clients as clients could
opt for senior & principals for all their projects
Less experience consultants doing projects would turn costly
too
Differential fee rates applied according to available time ratio
(chargeable days)
Multiple ratio (fee salary factor): Total fees earnt/wages =
factor (2.5-4); goes up with overhead
Types of Fees
Per unit of time
Flat lump-sum
Fee plus royalty (where new IP is created)
Fees contingent on results (contingency fees): risk involved
Equity participation
Percentage fee (type of contingency fee): transaction related
Retainer
Table 1: Lehman Formula; Can be applied in bands
$1--$1M
$1M--$2M
$2M--$3M
$3M--$4M
$4N--UP
5%
4%
3%
2%
1%
Assignment Management
Top-down (Available weeks & activity allocation)
Bottom-up (Activity based time requirement)
Financial & Operational Control
Operating workplan & operating budget (prepared annually,
represented monthly & quarterly)
Volumes of consulting services sold, work portfolio,
recruitment & training, volume of marketing activities....
Projected income, expenses, reveals fixed vs. variable costs...
Improving Profitability = Appropriate use of staff as per
competence, Higher utilization rates, Efficient execution of
assignments, Save on overhead items, Prompt fee collection,
Cross-sell, Sell more profitable work, Cut unprofitable services
Expenses billed to clients are not part of income
Profit: Fees earnt less expenses paid (gross income) = for use
as profit share to owners, security reserves, working capital,
capital expenses.
Controls
Forward workload (backlog) 1.5-3 months
Client visits to assignments negotiated (strike rate for
marketing)
Actual vs budgeted utilization of total time
Actual vs planned fee earning days
Actual vs budgeted fee rates
Fees earnt vs budgeted fees (monthly & YTD)
Fees earnt vs expenses (monthly & YTD)
Expenses incurred vs budgeted (by lines & total)
Monthly billing vs fees earnt
No. of months of outstanding fees
Performance Indicators (Firm performance)
growth rate
profit vs total income
profit per consultant
volume sold per consultant involved in marketing
staff turnover
utilisation rates & time allocation to various services
expense & cost structure
marketing & bd costs
fee rates
performance per team/department/practice area
Fee structures (flat fee, hourly, contingency, pro-bono)
Collection realisation rates (60-99%)
A/R: Accounts Receivable as per days due; how much written
off
Behavioural Q&A
What do you think takes to be successful in this role:
Collaborate & an open-mind prepared to work collaborative as
part of one team; in addition to left & right brain analytical
insight, drive to exceed KPI targets
How do you determine or evaluate success: Having key
milestones on a timeline with progressive quantitative
indicators that visualise the realisation of goals
Success in previous role/Why hire you/Trackrecord/Proud achievement: Successfully fulfilling multiples
roles while working in the capacity of an analyst in a microconsultancy environment
Root cause analysis is an approach for identifying the underlying
causes of why an incident occurred so that the most effective
solutions can be identified and implemented. It's typically used
when something goes badly, but can also be used when something
goes well. Within an organization, problem solving, incident
investigation and root cause analysis are all fundamentally
connected by three basic questions: What's the problem? Why did it
happen? and What will be done to prevent it?
3 Stages:
1. Define issue & its impact to overall goals
2. Analyse causes in a visual map
3. Prevent or mitigate negative impacts to goals
Root cause analysis is an approach for identifying the underlying
causes of why an incident occurred so that the most effective
solutions can be identified and implemented. It's typically used
when something goes badly, but can also be used when something
goes well. Within an organization, problem solving, incident
investigation and root cause analysis are all fundamentally
connected by three basic questions: What's the problem? Why did it
happen? and What will be done to prevent it?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cost Reduction Strategies for the Manufacturing Sector With Application of Microsoft ExcelD'EverandCost Reduction Strategies for the Manufacturing Sector With Application of Microsoft ExcelPas encore d'évaluation
- Budgeting and ForecastingDocument11 pagesBudgeting and ForecastingGrace XYZPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelim Reviewer ManagerialDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer ManagerialMargaux Julienne CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Performance Indicators HousekeepingDocument11 pagesKey Performance Indicators Housekeepingseduct3ur100% (2)
- Cost and Benefits of TrainingsDocument28 pagesCost and Benefits of TrainingsNikita Sangal100% (1)
- As The Head of HR Department You Have Been Asked To Assess The Cost Benefit Analysis of Training Conducted For Basic Skills in ExcelDocument4 pagesAs The Head of HR Department You Have Been Asked To Assess The Cost Benefit Analysis of Training Conducted For Basic Skills in ExcelHanisha RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Mangment Acc UnitDocument16 pagesMangment Acc Unitpriyanshu shrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- KPIs For Different Roles and Ways To Measure Them QuantitativelyDocument7 pagesKPIs For Different Roles and Ways To Measure Them QuantitativelyDebalina DasguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- KPI AssignmentDocument7 pagesKPI AssignmentErfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Keep Performance Indicator Presentation by TV Bba (Ib)Document26 pagesKeep Performance Indicator Presentation by TV Bba (Ib)Ameya PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1Ayub ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Way To Utilize Productivity MatricsDocument5 pagesBest Way To Utilize Productivity MatricsMansi TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- HR's Role As An Information AnalystDocument39 pagesHR's Role As An Information Analystsupriya127Pas encore d'évaluation
- 204 Final ShortDocument22 pages204 Final ShortLovePas encore d'évaluation
- Management Control Systems: Session 1Document20 pagesManagement Control Systems: Session 1varuntyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Financial Performance IndicatorsDocument4 pagesNon Financial Performance Indicatorsgrey100% (1)
- MIS (Bhavika 19010)Document6 pagesMIS (Bhavika 19010)Bhavika GholapPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Advantages of BudgetingDocument8 pagesWhat Are The Advantages of Budgetingram1312100% (1)
- Quality Management SummaryDocument12 pagesQuality Management Summarymarc_receveurPas encore d'évaluation
- Operations and Suppy Chain StratergiesDocument8 pagesOperations and Suppy Chain StratergiesAral RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - INTRODUCTIONDocument54 pagesLecture 1 - INTRODUCTIONTgrh TgrhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lo 2Document38 pagesLo 2yuulooPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Accounting Costing and BudgetingDocument20 pagesManagement Accounting Costing and BudgetingDigontaArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Jariatu MGMT AssignDocument10 pagesJariatu MGMT AssignHenry Bobson SesayPas encore d'évaluation
- Training and Development of SupervisorsDocument7 pagesTraining and Development of SupervisorsNidhiSinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ManagementDocument18 pagesProject ManagementShehryar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 and 5: Responsibility CentersDocument30 pagesChapter 4 and 5: Responsibility CentersRajat SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Process (PODC)Document57 pagesManagement Process (PODC)Brian Javier100% (3)
- Summary Chapter 1Document13 pagesSummary Chapter 1Danny FranklinPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Chapter 10Document21 pages10 Chapter 10Ruben SucionoPas encore d'évaluation
- Supporting Business Functions in The Company Purchasing FunctionDocument5 pagesSupporting Business Functions in The Company Purchasing FunctionDesiree Vera GrauelPas encore d'évaluation
- Descriptive AnalyticsDocument20 pagesDescriptive Analyticsmanveen kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- ENTREPQ2Document12 pagesENTREPQ2Florenz DacilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Performance Indicators - KPIsDocument6 pagesKey Performance Indicators - KPIsRamesh Kumar ManickamPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 112191051 - Atahar HussainDocument15 pagesAssignment - 112191051 - Atahar HussainAtahar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Based Costing (ABC)Document3 pagesActivity Based Costing (ABC)amirq4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bob Keller HR Metrics Presentation Indiana SHRM 8-29-06 - Final 8-21-06Document48 pagesBob Keller HR Metrics Presentation Indiana SHRM 8-29-06 - Final 8-21-06Alyanna MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Is It Wise To Challenge The Usefulness of Cost andDocument3 pagesIs It Wise To Challenge The Usefulness of Cost andMomoh PessimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Modeling By: CA Tapan Kumar DasDocument16 pagesFinancial Modeling By: CA Tapan Kumar DasLAMOUCHI RIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Orca Share Media1670374193894 7006057162954118241Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1670374193894 7006057162954118241JULLIE CARMELLE H. CHATTOPas encore d'évaluation
- Bi AssignmentDocument35 pagesBi Assignmentalish khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Recruitment Is A Challenge in Call CenterDocument4 pagesRecruitment Is A Challenge in Call CenterManvi KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 - Reading MaterialDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - Reading MaterialEmillie Kristine SalorPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Test02Document11 pagesBusiness Test02Tomás TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledV CPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment: Cost AccountantDocument6 pagesAssignment: Cost AccountantSabeedEjazPas encore d'évaluation
- Reducing Regulatory CapitalDocument18 pagesReducing Regulatory CapitalLee WerrellPas encore d'évaluation
- Productivity Improvement Guide For Supervisors and ManagersDocument4 pagesProductivity Improvement Guide For Supervisors and ManagersRalph Serrao100% (1)
- Opm 121Document7 pagesOpm 121Sabu VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- I. ProductivityDocument16 pagesI. ProductivityChan Jolan CarlaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Benchmarking PDFDocument17 pages8 Benchmarking PDFMohammad Owais ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project Report On Cost Analysis and ControlDocument88 pagesA Project Report On Cost Analysis and ControlNagireddy KalluriPas encore d'évaluation
- U13A1T1Document12 pagesU13A1T1Aishath NadhaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost and Financial AccountingDocument9 pagesCost and Financial AccountingSrikant RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Performance MeasureDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Performance MeasureShirwaan MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Measures - Quality CostDocument7 pagesPerformance Measures - Quality Costgemma rose magbanuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balance Scorecard ImplementationDocument6 pagesBalance Scorecard ImplementationShormistha SenPas encore d'évaluation
- My Passport: StudioDocument37 pagesMy Passport: StudioIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- KURADEBhagwant (Bhupesh)Document5 pagesKURADEBhagwant (Bhupesh)IshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Hedging For Grain ProcessorsDocument25 pagesStrategic Hedging For Grain ProcessorsIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Stewart McglashanDocument4 pagesStewart McglashanIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Constantine Kosma SDocument2 pagesConstantine Kosma SIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Akshay MehtaDocument9 pagesAkshay MehtaIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Nandu Madhekar: CEO at Innovative Chemical Technologies PVT LTDDocument3 pagesNandu Madhekar: CEO at Innovative Chemical Technologies PVT LTDIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Australia India Business Council 25sept12 - 0Document11 pagesAustralia India Business Council 25sept12 - 0IshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Pune 1. Blades of Glory Museum 2. PL Deshpande Japanese Garden/Mughal Garden/Okayama Friendship Garden 3. Pataleshwar Gardens 4Document1 pagePune 1. Blades of Glory Museum 2. PL Deshpande Japanese Garden/Mughal Garden/Okayama Friendship Garden 3. Pataleshwar Gardens 4IshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Mcs 2015 LithiDocument2 pagesMcs 2015 LithiIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Docs INSG Insight 23 Global Ebike MarketDocument6 pagesDocs INSG Insight 23 Global Ebike MarketIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Using Mfa For SDDocument13 pages2012 Using Mfa For SDIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes: Dropbox Folder Shared For Collaboration and WorkingDocument3 pagesNotes: Dropbox Folder Shared For Collaboration and WorkingIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Sector in IndiaDocument10 pagesEngineering Sector in IndiaIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Australia India Business Council: AIBC Submission On Australia India Comprehensive Economic Cooperation AgreementDocument14 pagesAustralia India Business Council: AIBC Submission On Australia India Comprehensive Economic Cooperation AgreementIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- CHNG3807 Products and Value Chains: Andrew HarrisDocument40 pagesCHNG3807 Products and Value Chains: Andrew HarrisIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
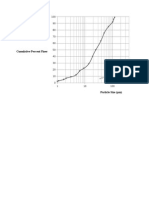
- Cumulative Percent FinerDocument2 pagesCumulative Percent FinerIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Coal Gasification IGCCDocument2 pages6 Coal Gasification IGCCIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetics and ModellingDocument12 pagesKinetics and ModellingIshanSanePas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Vs Competitive AdvantageDocument19 pagesComparative Vs Competitive AdvantageSuntari CakSoenPas encore d'évaluation
- Tender Doc-Supply & Installation of UPS For KTDA Data CentreDocument18 pagesTender Doc-Supply & Installation of UPS For KTDA Data Centre77matiahPas encore d'évaluation
- AbcdefghijkDocument13 pagesAbcdefghijkGaurav DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost - Estimation Chem PlantDocument39 pagesCost - Estimation Chem PlantriffPas encore d'évaluation
- Tally ERP 9: Shortcut Key For TallyDocument21 pagesTally ERP 9: Shortcut Key For TallyDhurba Bahadur BkPas encore d'évaluation
- Collective BargainingDocument20 pagesCollective BargainingsanthiyasandyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Political Implications of The Peer To Peer Revolution - BawensDocument10 pagesThe Political Implications of The Peer To Peer Revolution - BawenskosmasgPas encore d'évaluation
- Lean and Six Sigma - Not For AmateursDocument6 pagesLean and Six Sigma - Not For AmateursmsasgesPas encore d'évaluation
- ILO Declaration For Fair GlobalisationDocument7 pagesILO Declaration For Fair GlobalisationjaishreePas encore d'évaluation
- Ticks Hunter Bot GuideDocument7 pagesTicks Hunter Bot GuideKingtayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Leadership and Differentiation An Investigation of The Fundamental Trade-OffDocument38 pagesCost Leadership and Differentiation An Investigation of The Fundamental Trade-Offjulie100% (3)
- Appendix 2.1 First Screen Part 1: Strength of Business IdeaDocument4 pagesAppendix 2.1 First Screen Part 1: Strength of Business IdeaMohammad ArslaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Quality Management Session by MukherjeeDocument2 pagesTotal Quality Management Session by Mukherjeearnab.for.ever9439Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam SampleDocument11 pagesFinal Exam SampleFelixEternityStabilityPas encore d'évaluation
- BuisinessmanDocument57 pagesBuisinessmanLourencoPas encore d'évaluation
- REPLIDYNE INC 10-K (Annual Reports) 2009-02-24Document74 pagesREPLIDYNE INC 10-K (Annual Reports) 2009-02-24http://secwatch.comPas encore d'évaluation
- 20150815Document16 pages20150815alanchan10246868Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adani Mundra Port LTDDocument2 pagesAdani Mundra Port LTDGiriraj Asawa MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT AnalysisDocument9 pagesSWOT AnalysisAnjali SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Articles of Confederation EssayDocument2 pagesArticles of Confederation Essayapi-251089957Pas encore d'évaluation
- Avante Global Services Pvt. LTD.: L&T ECC DivisionDocument1 pageAvante Global Services Pvt. LTD.: L&T ECC DivisionPardeep KhosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parking Garage Case PaperDocument10 pagesParking Garage Case Papernisarg_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 18 Multinational Capital BudgetingDocument15 pagesChapter 18 Multinational Capital Budgetingyosua chrisma100% (1)
- 2316 (1) 2Document2 pages2316 (1) 2jeniffer pamplona100% (2)
- Consolidation at The Date of AcquisitionDocument54 pagesConsolidation at The Date of AcquisitioniptrcrmlPas encore d'évaluation
- Law Offices of Todd M. Friedman, P.C: Attorneys For PlaintiffsDocument24 pagesLaw Offices of Todd M. Friedman, P.C: Attorneys For PlaintiffsGawker.comPas encore d'évaluation
- CEO or Head of Sales & MarketingDocument3 pagesCEO or Head of Sales & Marketingapi-78902079Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Make An Advance Payment?Document6 pagesHow To Make An Advance Payment?Renzo SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Inward ManifestDocument102 pagesInward Manifestjohn yrePas encore d'évaluation
- WSMDocument4 pagesWSMWaseem MughalPas encore d'évaluation