Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 Demand and Supply Analysis
Transféré par
Mir Fida NadeemCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 3 Demand and Supply Analysis
Transféré par
Mir Fida NadeemDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
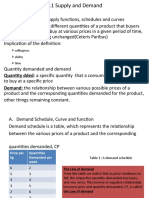
Chapter 3
The market system 1
demand and supply
analysis
w w w . s t ud y i n t e r a c t i v e . o r g
33
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
CHAPTER CONTENTS
LEARNING OUTCOMES -------------------------------------------------- 35
THE DEFINITION OF A MARKET ---------------------------------------- 36
THE DEMAND CURVE ---------------------------------------------------- 37
THE SUPPLY CURVE ----------------------------------------------------- 41
FORMATION OF EQUILIBRIUM PRICE --------------------------------- 44
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS -------------------------------------- 45
34
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
LEARNING OUTCOMES
(a) Identify the equilibrium price in a product or factor markets likely to result
from specified changes in conditions of demand or supply.
35
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
THE DEFINITION OF A MARKET
and does not necessarily refer to a
physical location, but instead a place whereby potential buyers and sellers meet for
the purposes of exchanging goods / services.
Examples include:
Type of market
Goods / services exchanged
Product market
Commodity market
Financial market
Factor market
Note: This chapter focuses upon product markets, the term goods is used to
denote the provision of tangible goods and intangible services.
36
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
THE DEMAND CURVE
Demand for a good is the quantity of that good that potential purchasers would be
willing and able to buy, at a given price.
The law of demand states that as the price of a good falls, ceteris paribus, the
quantity demanded will increase.
Graphical representation
Price $
Quantity (Units)
Market demand
The total quantity of a product that all purchasers would want to buy at each price.
37
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Determinants of demand (excluding price)
1.
Household income
Income type
Variable factor
Gross income
Disposable income
Discretionary income
As household income increases
increase. Examples include
As household income increases
decrease. Examples include
2.
Expectations for the future
3.
Availability of substitutes
4.
Complementary Goods
38
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Discussion 1
Substitute goods
Complementary goods
Try to come up with your own examples for substitute and complementary
goods.
5.
Tastes and fashions
6.
Population
39
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Changes in demand
Examination questions will typically require students to interpret the impact on
demand following changes to price and the conditions of demand. Changes may
affect the demand curve in one of two ways:
(i)
Movement along the demand curve (extensions/contractions)
(ii)
Shift of the demand curve.
A movement along the demand curve occurs when a change in the price of a
product leads to a change in the quantity demanded, as shown below:
A shift to the right in the demand curve arises when at every price consumers are
willing and able to buy more than they did before, as shown below:
Conversely a shift to the left would arise if consumers are able and willing to buy
less than they did before at each available price.
Shifts in the demand curve arise when the conditions of demand, as previously
discussed, change.
40
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
THE SUPPLY CURVE
Supply refers to the quantity of a good that existing suppliers, or would be
suppliers, are willing and able to produce for the market at a given price.
The law of supply states that as prices rise, ceteris paribus, the quantity supplied
of the good will increase.
Graphical representation
Price $
Quantity (Units)
Market supply
The total quantity of a product that all producers, existing and potential, would
want to supply at each price.
41
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Determinants of supply (excluding price)
1.
Cost to produce
2.
Price of substitute goods
3.
Price of complements
4.
Technology
5.
Other factors
42
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Changes in supply
Understanding the effect of changing prices / conditions of supply on the supply
curve are key learning points for the exam.
A movement along the supply curve occurs following a change in the price of a
product which leads to a change in the quantity supplied, as shown below:
Extension
Contraction
Shifts in the supply curve arise when the conditions of supply change (other than
the price of the good itself!)
A reduction in the cost of supply will cause the supply curve to shift right, an
increase in the cost of supply will cause the supply curve to shift to the left.
Exercise 1
Move Along
Shift Left
Shift Right
Drought (no rain)
Fall in labour cost
Increase
wheat
price
of
Enhanced harvest
technology
Complete the above table to denote the impact on the supply curve for
wheat production as a result of the various events described?
43
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
FORMATION OF EQUILIBRIUM PRICE
Market price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply.
equilibrium price being where demand equals supply.
The
Functions of the price mechanism
There are three functions of the price mechanism, as follows:
1.Signalling
2.Rationing
3.Rewarding
Discussion 2
Discuss the likely implications of price falling below P1 in the context of the three
functions of the price mechanism.
1.
Signalling;
2.
Rationing;
3.
Rewarding.
44
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALSYSIS
In the exam you may be asked to consider the resulting impact on demand and
supply for substitute or complementary goods! Show the impact below on
Exercise 2
Fish and Chips
fish supplies fall as a result of overfishing.
Fish
Chips
S0
S0
D0
Coca-Cola and Pepsi
Coca-Cola through innovation reduce their production costs.
Coca-Cola
Pepsi
S0
D0
45
D0
S0
D0
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
CHAPTER 3
46
DEMAND AND SUPPLY ANALYSIS
ww w. stu dyi n t e ra cti v e .or g
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Demand Supply MarketDocument53 pagesDemand Supply MarketwasisiPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply and DemandDocument13 pagesSupply and DemandChieka ChietoPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Demand Study GuideDocument6 pagesSupply Demand Study GuideJoep MinderhoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Revision QuestionsDocument3 pagesWeek 6 Revision QuestionsDavid Tayla McCarthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1533834004EC101, Practice Questions, August 2018Document2 pages1533834004EC101, Practice Questions, August 2018Luke MadzikotoPas encore d'évaluation
- LaytonIM Ch03Document8 pagesLaytonIM Ch03astin brownPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand, Supply, and PriceDocument20 pagesDemand, Supply, and PriceoreoPas encore d'évaluation
- BUS017 Economics For Business: Dr. Lucia CornoDocument18 pagesBUS017 Economics For Business: Dr. Lucia CornoSaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics PDFDocument34 pagesEconomics PDFSam ShoukatPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles ProblemSet4Document2 pagesPrinciples ProblemSet4antialonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics - Supply and DemandDocument34 pagesEconomics - Supply and DemandAnusha Ivaturi0% (1)
- Week 2Document34 pagesWeek 2chooisinPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Theory and AnalysisDocument46 pagesSupply Theory and AnalysisFuad HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Markets, Organizations, and The Role of KnowledgeDocument16 pagesChapter 3: Markets, Organizations, and The Role of KnowledgeJosé Luis VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Elements of DemandDocument33 pagesChapter 3 - Elements of DemandMiguel SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity EconomicsDocument28 pagesElectricity EconomicsAnderson Arenas MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 03Document16 pagesChap 03Syed Hamdan100% (1)
- Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument42 pagesDemand and Supply AnalysisamberfakePas encore d'évaluation
- Test Forms of Market & Price DeterminationDocument2 pagesTest Forms of Market & Price DeterminationGatik BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics For Managers - NotesDocument17 pagesEconomics For Managers - NotesPhillip Gordon MulesPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand and Supply New HandoutDocument12 pagesDemand and Supply New Handoutjodes_jmPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading 12a CFAL1 EconDocument54 pagesReading 12a CFAL1 EconSteve Sambu JrPas encore d'évaluation
- 51706301Document34 pages51706301Abdulrahman AlotaibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Ag - EconDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Ag - EconJay Kenneth Bajar CernalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document36 pagesChapter 2Qamar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- LN03 Keat020827 07 Me LN03Document43 pagesLN03 Keat020827 07 Me LN03DRIP HARDLYPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7Document11 pagesLecture 7Rabie HarounPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Elements of Supply and Demand: I. Chapter OverviewDocument18 pagesBasic Elements of Supply and Demand: I. Chapter OverviewGeorge WagihPas encore d'évaluation
- Microeconomic Theory and Practice: San Beda University AY 21-22Document63 pagesMicroeconomic Theory and Practice: San Beda University AY 21-22Sergio ConjugalPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Test - 5.6.22 - Rodrigo MartinezDocument7 pagesEconomics Test - 5.6.22 - Rodrigo MartinezRodrigo MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2cristianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Micro Economics Question Bank Ist SemDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Micro Economics Question Bank Ist Semyjayasanka588Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture03 D&S BDocument34 pagesLecture03 D&S BMirza Wajahat BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics Chapter 3Document17 pagesEconomics Chapter 3Monica SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Samuelson PPPTDocument68 pagesSamuelson PPPTBhagirath Baria100% (2)
- Chapter Two Introduction To EconomicsDocument36 pagesChapter Two Introduction To Economicsnigusu deguPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Questions Assignment Question 1 This QuestionDocument2 pagesAssignment Questions Assignment Question 1 This QuestionhwcdkPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand & SupplyDocument13 pagesDemand & SupplyMeenakshi AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Inbound 8780824254492600428Document4 pagesInbound 8780824254492600428oussamabenyani78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Price Discrimination Notes: 1 PreliminariesDocument12 pagesPrice Discrimination Notes: 1 Preliminarieserdoo17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Abm Module 3 NewDocument21 pagesAbm Module 3 NewAiza BelandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Market Demand, Market Supply and Market EquilibriumDocument7 pagesApplied Economics: Market Demand, Market Supply and Market Equilibriumma. donna v. detablanPas encore d'évaluation
- EC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsDocument6 pagesEC 307 Summer Flexi Tutorial 1 - SolutionsR and R wwePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2. The Basics of Supply and DemandDocument9 pagesChapter 2. The Basics of Supply and DemandkasebPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantity Dded: A Specific Quantity That A Consumer Is Willing and Able Demand: The Relationship Between Various Possible Prices of ADocument84 pagesQuantity Dded: A Specific Quantity That A Consumer Is Willing and Able Demand: The Relationship Between Various Possible Prices of Aanduamlak wondimagegnPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 3 SlidesDocument49 pagesSection 3 SlidesLiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply and DemandDocument17 pagesSupply and DemandFiona UsherPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ 202: Chapter 3Document49 pagesEcon 202: Chapter 3Thomas WooPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document27 pagesChapter 3aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Producing Two Substitutable Products Under A Supply Chain Including Two Manufacturers and One Retailer A Game-Theoretic ApproachDocument21 pagesProducing Two Substitutable Products Under A Supply Chain Including Two Manufacturers and One Retailer A Game-Theoretic Approach翁慈君Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: SupplyDocument15 pagesChapter 5: SupplysweettejuPas encore d'évaluation
- Agricultural Marketing Trade & PricesDocument24 pagesAgricultural Marketing Trade & PricesAsutosh PanigrahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental of EconomicsDocument3 pagesFundamental of EconomicsYou TubePas encore d'évaluation
- The Market Forces of Demand and SupplyDocument47 pagesThe Market Forces of Demand and SupplyQammer ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand TheoryDocument30 pagesDemand TheoryPushpak RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ Micro QuestionsDocument2 pagesEcon Micro QuestionsRiddhima SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand and Supply ReportDocument12 pagesDemand and Supply Reportapi-23966514850% (2)
- Commodity Market Trading and Investment: A Practitioners Guide to the MarketsD'EverandCommodity Market Trading and Investment: A Practitioners Guide to the MarketsPas encore d'évaluation
- Today's Lecture Outline: - Loops - While LoopDocument16 pagesToday's Lecture Outline: - Loops - While LoopMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Write Output of Following Piece of Code: Roll No: - 15091519-012Document2 pagesWrite Output of Following Piece of Code: Roll No: - 15091519-012Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs 104: Programming Fundamentals: Lecture # 01Document25 pagesCs 104: Programming Fundamentals: Lecture # 01Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 19Document5 pagesLecture 19Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Characters and StringsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Characters and StringsMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 16Document16 pagesLecture 16Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Undergraduate ProgramDocument12 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Undergraduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramDocument14 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramDocument17 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Today's Lecture Outline: - Introduction To Array - Accessing Elements of Array - A Simple Array ProgramDocument9 pagesToday's Lecture Outline: - Introduction To Array - Accessing Elements of Array - A Simple Array ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramDocument23 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Graduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 15Document10 pagesLecture 15Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 17Document16 pagesLecture 17Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- For Loop: - The Most Popular Looping Instruction - The For Loop Allows Us To Specify Three Things in A Single LineDocument17 pagesFor Loop: - The Most Popular Looping Instruction - The For Loop Allows Us To Specify Three Things in A Single LineMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Undergraduate ProgramDocument18 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2015, Undergraduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- C/C++ Instructions: - Type Declaration InstructionDocument21 pagesC/C++ Instructions: - Type Declaration InstructionMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document9 pagesLecture 3Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2014, Undergraduate ProgramDocument21 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2014, Undergraduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Map The Mind, Tap The Brain: in Class, at HomeDocument3 pagesMap The Mind, Tap The Brain: in Class, at HomeMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6Document22 pagesLecture 6Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Cima c04 2013 Class Revision 1Document6 pagesCima c04 2013 Class Revision 1Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prepare For ExamsDocument5 pagesHow To Prepare For ExamsMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics For Business - Monetary PolicyDocument4 pagesEconomics For Business - Monetary PolicyMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundementals of Business Economics FM - Feb08 - p46-48Document3 pagesFundementals of Business Economics FM - Feb08 - p46-48Mir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2014, Undergraduate ProgramDocument10 pagesProgramming Fundamentals: 4.00 Credit Hours, Fall 2014, Undergraduate ProgramMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Back To Basics - Uncertainty and SensitivityDocument5 pagesBack To Basics - Uncertainty and SensitivityMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective Note TakingDocument32 pagesEffective Note TakingMir Fida NadeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Spotlight Case StudyDocument13 pagesProduct Spotlight Case StudyPuvvula Bhavya Sri chandPas encore d'évaluation
- Ist 3 ChaptersDocument19 pagesIst 3 Chaptersrkpreethi100% (1)
- Case Study 2Document9 pagesCase Study 2Isabella ChristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment ON Steel Authority of India (SAIL)Document32 pagesAssignment ON Steel Authority of India (SAIL)Bhupender MehtoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unilever, Leader in Social Responsibility: E-135: Corporate Sustainability StrategyDocument4 pagesUnilever, Leader in Social Responsibility: E-135: Corporate Sustainability StrategyVictor TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- NCSP Value and BehavioursDocument55 pagesNCSP Value and Behavioursberry MikePas encore d'évaluation
- Homberg Jensen 2007Document20 pagesHomberg Jensen 2007Anas SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Memorandum of AssociationDocument8 pagesMemorandum of AssociationSohail AnjumPas encore d'évaluation
- To Generate Facility Plans, The Following Questions Must Be AnsweredDocument30 pagesTo Generate Facility Plans, The Following Questions Must Be AnsweredPuneet GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Peace Corps Facilitator Retreat - Oct 2013 REQUEST FOR PROPOSALDocument2 pagesPeace Corps Facilitator Retreat - Oct 2013 REQUEST FOR PROPOSALAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Solution On Basic Variance AnalysisDocument3 pagesAccounting Solution On Basic Variance AnalysisAssignmentstore100% (2)
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisHinata UzumakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mission StatementsDocument14 pagesMission StatementsSatyam DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Valuation of Residential and Commercial Property - Case StudyDocument3 pagesStudy of Valuation of Residential and Commercial Property - Case Studyvaibhav kunghatkarPas encore d'évaluation
- (PDF) KK Refined List IIIDocument440 pages(PDF) KK Refined List IIIhappylifePas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation On Commercial BanksDocument4 pagesDissertation On Commercial BanksNeedHelpWithPaperSingapore100% (1)
- RFBT First Preboard B94 - QuestionnaireDocument17 pagesRFBT First Preboard B94 - QuestionnaireRevs AsjeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Payment of Bonus Act PDFDocument16 pagesPayment of Bonus Act PDFAnukrati BagherwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Easy JetDocument8 pagesCase Study: Easy JetAslam Hossain100% (3)
- CIDAM EntrepDocument4 pagesCIDAM EntrepCharles100% (3)
- Internship ReportDocument51 pagesInternship Reportshubhangi gargPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing SystemDocument20 pagesMarketing SystemAldrich BunyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Key TermsDocument10 pagesKey Termscuteserese rosePas encore d'évaluation
- Making Automobile and Housing DecisionsDocument12 pagesMaking Automobile and Housing DecisionsSteve SenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Literature On Inventory Management For MbaDocument7 pagesReview of Literature On Inventory Management For Mbac5hc4kgxPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate GovernanceDocument5 pagesCorporate GovernanceDani ShaPas encore d'évaluation
- Redstone Commodity Update Q1 2020Document13 pagesRedstone Commodity Update Q1 2020Frianata ZrPas encore d'évaluation
- Samsung Distribution Channel ProjectDocument28 pagesSamsung Distribution Channel ProjectShivendra Singh0% (2)
- Ass Intacc 3 - GonzagaDocument12 pagesAss Intacc 3 - GonzagaLalaine Keendra GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing - Chapter 17Document53 pagesMarketing - Chapter 17denixngPas encore d'évaluation