Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Equation Solution and Solution Sets
Transféré par
Sandra Enn BahintingDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Equation Solution and Solution Sets
Transféré par
Sandra Enn BahintingDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
10/2/2015
Equations,
Solutions,
Solution Sets
Prepared by:
Engr. Sandra Enn Bahinting
Equation
An
equation is a statement denoting the equality
of two algebraic expressions.
10/2/2015
Linear equations
A
linear equation in one variable x is an equation
that can be written in the form
ax + b = 0,
where a and b are real numbers and a 0
Example : 2x+3 = 0
x+8 = 0
3x=7
2x+5 =9-5x
3+5(x-1) =-7 + x
Solving a Linear Equation in General
Example 2: Solve for the variable.
x - 5 = 2.
x-5=2
x-5+5=2+5
x=7
Solve for the variable.
y + 4 = -7.
y + 4 = -7
y + 4 - 4 = -7 - 4
y = -11
10/2/2015
Example 4: Solve for the variable.
x/2 = 5.
Example 5: Solve for the variable.
5x = 7.
Strategy for Solving a Linear Equation
Step 1: Simplify each side, if needed.
This would involve things like removing ( ), removing fractions, adding like terms, etc.
To remove ( ): Just use the distributive property found in Tutorial 5: Properties of Real Numbers.
To remove fractions: Since fractions are another way to write division, and the inverse of divide is to
multiply, you remove fractions by multiplying both sides by the LCD of all of your fractions.
Step 2: Use Add./Sub. Properties to move the variable term to one side and
all other terms to the other side.
Step 3: Use Mult./Div. Properties to remove any values that are in front of the
variable.
Step 4: Check your answer.
10/2/2015
10/2/2015
10/2/2015
Solve the following variables:
2(x + 5) - 7 = 3(x - 2)
Literal Equations
Equations with multiple variables where you are asked
to solve for just one of the variables.
Solve the following:
10/2/2015
SeatWork
Quadratic Equations
Definition
A quadratic equation in x is any equation that may be written in
the form
+ bx + c = 0,
where a, b, and c are coefficients and a 0.
Examples
2 + 2x = 4
(2 + x)(3 x) = 0
2 - 3 = 0
3 2 + 4 = 0 not a quadratic
10/2/2015
Solving Quadratic Equations Method 1 - Factoring
Here are the steps to solve a quadratic by factoring:
1. Write your equation in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0 by applying
the Distributive Property, Combine Like Terms, and apply the
Addition Property of Equality to move terms to one side of =.
2. Factor your equation by using the Distributive Property and
the appropriate factoring technique. Note: Any type of
factoring relies on the Distributive Property.
3. Let each factor = 0 and solve. This is possible because of the
Zero Product Law.
Solve the following by factoring
10/2/2015
Solving Quadratic Equations Method 2
Extracting Square Roots
Extracting Square Roots allows you
rewrite 2 = k as x = k, where k is
to
some real number
Simply
10/2/2015
Solve by square root method
10
10/2/2015
Solving Quadratic Equations Method 3
Completing the Square
Solve the following:
11
10/2/2015
Solving Quadratic Equations Method 4
Using The Quadratic Formula
Solving a quadratic equation that is in the form
+ bx + c = 0 only involves plugging a, b,
and c into the formula
the expression ( 2 4ac), denoted by D, is called Discriminant,
because it determines the number of solutions or nature of roots of
a quadratic equation.
12
10/2/2015
13
10/2/2015
Summary
14
10/2/2015
Solve the following:
15
10/2/2015
ASSIGNMENT (1 whole)
factoring
Square
root property
Completing
the square
Quadratic equation
16
10/2/2015
17
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- New Secondary Mathematics Teacher Resource Book 1 APSACDocument124 pagesNew Secondary Mathematics Teacher Resource Book 1 APSACKhuzama Aman100% (4)
- QT Study Pack 2006 WipDocument446 pagesQT Study Pack 2006 WipJasiz Philipe Ombugu100% (1)
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocument29 pagesLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Solids (V 1) 3bh) ConeDocument13 pagesSolids (V 1) 3bh) ConeSandra Enn Bahinting0% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument16 pagesLab ReportSandra Enn Bahinting100% (1)
- c01 Se m01 t01 l04Document12 pagesc01 Se m01 t01 l04api-261894355Pas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Math Core Ext SODocument32 pagesIGCSE Math Core Ext SOhang yinPas encore d'évaluation
- H2 Mathematics Textbook (Choo Yan Min)Document2 228 pagesH2 Mathematics Textbook (Choo Yan Min)Lys NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Pascal's Treatise On The Arithmetical Triangle: Mathematical Induction, Combinations, The Binomial Theorem and Fermat's TheoremDocument14 pagesPascal's Treatise On The Arithmetical Triangle: Mathematical Induction, Combinations, The Binomial Theorem and Fermat's TheoremYEAG92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations in One Variable: A Quadratic Equation in X Is Any Equation That May Be Written in The Form 0Document4 pagesQuadratic Equations in One Variable: A Quadratic Equation in X Is Any Equation That May Be Written in The Form 0Nirmal ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Equalities and InequalitiesDocument14 pagesApplications of Equalities and Inequalities鄭仲抗Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2d - Linear and Quadratic EquationsDocument11 pages2d - Linear and Quadratic EquationsNihad MehmedovićPas encore d'évaluation
- L2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassDocument35 pagesL2-Equation & Inequalities Oct 21-After ClassVINAYAGADHARSINI RAJENDRANPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations: FSC Chapter 4Document6 pagesQuadratic Equations: FSC Chapter 4Shan MajeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Reviewer 9Document8 pagesMath Reviewer 9Kurt Dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Programming FinalDocument9 pagesLinear Programming FinalJester LabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationDocument15 pagesMath 9 Lesson 1 Quadratic EquationJosielyn ValladolidPas encore d'évaluation
- In Teg by Partial Frac 2Document5 pagesIn Teg by Partial Frac 2DDeevv SShhaahhPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Inequalities and Diophantine EquationsDocument12 pagesBasic Inequalities and Diophantine EquationsKhor Shi-Jie78% (9)
- 8 Equations and Inequalities With Absolute ValueDocument6 pages8 Equations and Inequalities With Absolute ValueAli AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- MC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1Document9 pagesMC Ty Quadeqns 2009 1PrayasAgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equations Inequalities and ApplicationsDocument37 pagesLinear Equations Inequalities and ApplicationsCelina CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben McgaheeDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equations Workbook By: Ben Mcgaheemaihuongmaihuong1905Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument10 pagesMathematics Reviewerian naPas encore d'évaluation
- A Semester Course in TrigonometryDocument264 pagesA Semester Course in TrigonometryMestreLouPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigbook PDFDocument264 pagesTrigbook PDFsouvikbesu89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trig BookDocument264 pagesTrig BookAshenafi100% (1)
- Math Las G9 Q1 WK1 PDFDocument29 pagesMath Las G9 Q1 WK1 PDFJezreel TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Math Q1 M1Document12 pagesGrade 9 Math Q1 M1Renny Romero Luzada100% (2)
- CHAPTER 7 EquationsDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 7 EquationsSathish Sarma SathianarayananPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Quadratic Equation by FactoringDocument5 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation by FactoringAlexander BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hdfi 302Document13 pagesHdfi 302Lazarus AmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Quadratic EquationDocument41 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationMarites BalmasPas encore d'évaluation
- Completing SquareDocument8 pagesCompleting SquareliverpoolengineerPas encore d'évaluation
- Module No. 1: Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesDocument6 pagesModule No. 1: Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesJustine DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Equations and InequalitiesDocument51 pagesEquations and Inequalitieschristian aldwin canlapanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Linear Equations: PrerequisitesDocument21 pagesSolving Linear Equations: PrerequisitesSandy VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 - Dicrete MathDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 - Dicrete MathNguyên VũPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebric Expression and ManipulationDocument21 pagesAlgebric Expression and Manipulationneriv65946Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-140032165Pas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Manipulating and Solving Equations I & IIDocument15 pages06 Manipulating and Solving Equations I & IIharshilPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in MATH 7 3 Periodical Test Content UpdateDocument4 pagesReviewer in MATH 7 3 Periodical Test Content UpdateGayzelPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1 Completing The Square-WeeblyDocument19 pages10 1 Completing The Square-Weeblyapi-233527181100% (1)
- Algebra Review PacketDocument34 pagesAlgebra Review PacketLara HulbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7Document32 pagesUnit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7 Unit 7AjiteshPaddaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic EquationDocument35 pagesQuadratic EquationTimothy De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cayanan-Mbbc 514-8865Document107 pagesCayanan-Mbbc 514-8865Veronica CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 FinalDocument16 pagesWeek 1 FinalRizza Mae RepontePas encore d'évaluation
- MEI Structured Mathematics Module Summary Sheets: C1, Introduction To Advanced MathematicsDocument11 pagesMEI Structured Mathematics Module Summary Sheets: C1, Introduction To Advanced MathematicsMohammad KhanPas encore d'évaluation
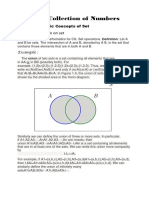
- Unit I-Collection of Numbers: Lesson 3-Operation On SetDocument9 pagesUnit I-Collection of Numbers: Lesson 3-Operation On SetAnonymous 2Jl89uPas encore d'évaluation
- Ax BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleDocument2 pagesAx BX +C 0 Ax BX +C 0: Grade 9 Summarized ModuleIsrael MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- RSM QuadraticsDocument11 pagesRSM QuadraticsCatherine RozePas encore d'évaluation
- Commutative Property of AdditionDocument7 pagesCommutative Property of AdditionAxl TorrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- A Level Core Pure Maths by Michael Cook PDFDocument188 pagesA Level Core Pure Maths by Michael Cook PDFhpant100% (1)
- Section 1 Linear Equations and InequalitiesDocument20 pagesSection 1 Linear Equations and Inequalitiesjeff00128Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Let Advanced Algebra - pdf6Document10 pages3 Let Advanced Algebra - pdf6novey_casioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Let - Advanced Algebra - pdf6 PDFDocument10 pages3 Let - Advanced Algebra - pdf6 PDFboninay operioPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equation: By, Prenisha Sanjel Class-12 C2 Exam Symbol No-77s Ps 7558Document17 pagesQuadratic Equation: By, Prenisha Sanjel Class-12 C2 Exam Symbol No-77s Ps 7558aabhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equation: By, Prenisha Sanjel Class-12 C2 Exam Symbol No-77s Ps 7558Document17 pagesQuadratic Equation: By, Prenisha Sanjel Class-12 C2 Exam Symbol No-77s Ps 7558aabhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equation CalculatorDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Calculatorapi-150547803Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathDocument3 pagesThe Quadratic Formula Explained - PurplemathHappy SunshinePas encore d'évaluation
- Module2 EquationsDocument17 pagesModule2 EquationsBrent Reyes PalayonPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 1 Number Unit Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Unit SubjectDocument16 pagesFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 1 Number Unit Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help YouDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equations: Use This Sheet To Help Youtrevbuiter6961100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Sec7Document21 pagesChapter 2 Sec7Batyr AbdikassovPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyDocument16 pages5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyAndyMavia100% (1)
- Lectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Document48 pagesLectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Sandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Convective Mass TransferDocument46 pagesConvective Mass TransferSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing A Thesis ProposalDocument4 pagesWriting A Thesis ProposalSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Centrifugal Separation Processess: Prepared by Engr. Sandra Enn BahintingDocument31 pagesCentrifugal Separation Processess: Prepared by Engr. Sandra Enn BahintingSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Solids HandlingDocument13 pagesSolids HandlingSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Hazard: Industrial Process SafetyDocument11 pagesChemical Hazard: Industrial Process SafetySandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Shell Momentum BalanceDocument13 pagesShell Momentum BalanceSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 1Document5 pagesHomework 1Sandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Set of Real Numbers and Its PropertiesDocument29 pagesThe Set of Real Numbers and Its PropertiesSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Vsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometryDocument16 pagesVsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometrySandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- SET IdentitiesDocument21 pagesSET IdentitiesSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Process IndustriesDocument29 pagesChemical Process IndustriesSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Factoring PolynomialsDocument2 pagesFactoring PolynomialsSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Mindanao State University-Iligan Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesMindanao State University-Iligan Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering College of EngineeringSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient Response of Simple Control SystemsDocument8 pagesTransient Response of Simple Control SystemsSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM Trial 2009 Matht Q&A (PCGHS, Penang)Document14 pagesSTPM Trial 2009 Matht Q&A (PCGHS, Penang)SimPorPas encore d'évaluation
- Polynomials: 1 Roots of UnityDocument4 pagesPolynomials: 1 Roots of UnityFadil Habibi DanufanePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesDocument7 pages11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesManas Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Philoid-In)Document19 pagesChapter 1 (Philoid-In)govindPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths emDocument396 pagesMaths emSri D0% (1)
- 1900265276class X-Maths Resource Material 2015Document197 pages1900265276class X-Maths Resource Material 2015preeti.2405Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document13 pagesChapter 4Hannah Jane LopresPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Number System ZDocument22 pagesReview of Number System ZDev KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mats College of Technology Modified Course Syllabus Math 107 - Teaching Math in The Primary GradesDocument2 pagesMats College of Technology Modified Course Syllabus Math 107 - Teaching Math in The Primary GradesDiosdado II MarimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pure Maths Guide From Love of MathsDocument1 028 pagesPure Maths Guide From Love of MathsLove of MathsPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits of Algebraic Functions: Basic CalculusDocument40 pagesLimits of Algebraic Functions: Basic CalculusLucky Canda Gojetia100% (1)
- Lesson 3 SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATION BY FACTORINGDocument17 pagesLesson 3 SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATION BY FACTORINGLianne Jhanne VictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Logarithms and Polynomials: What You Will LearnDocument67 pagesLogarithms and Polynomials: What You Will Learnvimitha.balakrishnanschoolPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics MODULE 3 Part 1 OPERATIONS OF FUNCTIONSDocument16 pagesGeneral Mathematics MODULE 3 Part 1 OPERATIONS OF FUNCTIONSJohn Jericho U RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Notice: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/4029 GCE O Level 2007Document20 pagesImportant Notice: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/4029 GCE O Level 2007mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aqa 6360 W SP 12Document119 pagesAqa 6360 W SP 12Neelam Rathod MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet: Grade 9 MathematicsDocument14 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Grade 9 MathematicsJames Dharell Trinidad100% (1)
- Year 8 MCQ Test FactorisationDocument12 pagesYear 8 MCQ Test FactorisationSweety SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Book Mathematics Class IXDocument294 pagesNCERT Book Mathematics Class IXDeepesh Gulati100% (1)
- Bridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesBridge 2 Linear and Quadratic EquationsDearly Niña OsinsaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12 May/June 2021Document22 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12 May/June 2021JuanaPas encore d'évaluation
- As Pure Maths Revision NotesDocument14 pagesAs Pure Maths Revision NotesSundarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Theory - English Fundamental of Mathematics - 01Document18 pages1 - Theory - English Fundamental of Mathematics - 01Shubham KumarPas encore d'évaluation