Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Operation Research 1
Transféré par
RK SinghCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Operation Research 1
Transféré par
RK SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
OPERATION RESEARCH
ASSIGNMENT SET – 1
1. Describe in details the different scopes of application of Operations Research.
Ans : - The application of Operations research methods helps in making decisions in such
complicated situations. Evidently the main objective of Operations research is to provide a scientific
basis to the decision-makers for solving the problems involving the interaction of various
components of organization, by employing a team of scientists from different disciplines, all
working together for finding a solution which is the best in the interest of the organization as a
whole. The solution thus obtained is known as optimal decision.
The different scopes of application of Operations Research are:
i) In Defence Operations: In modern warfare the defence operations are carried out by a
number of independent components namely Air Force, Army and Navy. The activities in each of
these components can be further divided in four sub-components viz.: administration, intelligence,
operations and training, and supply. The application of modern warfare techniques in each of the
components of military organizations requires expertise knowledge in respective fields.
Furthermore, each component works to drive maximum gains from its operations and there is
always a possibility that strategy beneficial to one component may have an adverse effect on the
other. Thus in defence operations there is a necessity to co-ordinate the activities of various
components which gives maximum benefit to the organization as a whole, having maximum use of
the individual components. The final strategy is formulated by a team of scientists drawn from
various disciplines who study the strategies of different components and after appropriate analysis
of the various courses of actions, the best course of action, known as optimum strategy, is chosen.
ii) In Industry: The system of modern industries is so complex that the optimum point of
operation in its various components cannot be intuitively judged by an individual. The business
environment is always changing and any decision useful at one time may not be so good some time
later. There is always a need to check the validity of decisions continually, against the situations.
The industrial revolution with increased division of labour and introduction of management
responsibilities has made each component an independent unit having their own goals. For
example: Production department minimize cost of production but maximizes output. Marketing
department maximizes output but minimizes cost of unit sales. Finance department tries to
optimize capital investment and personnel department appoints good people at minimum cost.
Thus each department plan their own objectives and all these objectives of various department or
components come to conflict with each other and may not conform to the overall objectives of the
organization. The application of OR techniques helps in overcoming this difficulty by integrating the
diversified activities of various components so as to serve the interest of the organization as a
whole efficiently.
OR methods in industry can be applied in the fields of production, inventory controls and
marketing, purchasing, transportation and competitive strategies etc.
iii) Planning: In modern times it has become necessary for every government to have careful
planning, for economic development of the country. OR techniques can be fruitfully applied to
maximize the per capita income, with minimum sacrifice and time. A government can thus use OR
for framing future economic and social policies.
iv) Agriculture: With increase in population there is a need to increase agriculture output. But
this cannot be done arbitrarily. There are a number of restrictions under which agricultural
production is to be studied. Therefore there is a need to determine a course of action, which serves
the best under the given restrictions. The problem can be solved by the application of OR
techniques.
v) In Hospitals: The OR methods can be used to solve waiting problems in out-patient
department of big hospitals. The administrative problems of hospital organization can also be
solved by OR techniques.
vi) In Transport: Different OR methods can be applied to regulate the arrival of trains and
processing times, minimize the passengers waiting time and reduce congestion, formulate suitable
transportation policy, reducing the costs and time of trans-shipment.
vii) Research and Development: Control of R and D projects, product introduction planning etc.
and many more applications.
2. What do you understand by Linear Programming Problem? What are the
requirements of L.P.P.? What are the basic assumptions of L.P.P.?
Ans : - One of the most important problems in management decision is to allocate limited and
scarce resource among competing agencies in the best possible manner. Resources may represent
man, money, machine, time, technology on space. The task of the management is to derive the best
possible output (or set of outputs) under given restraints on resources. The output may be
measured in the form of profits, costs, social welfare, effectiveness, etc. In many situations the
output (or the set of outputs) can be expressed as a linear relationship among a number of
variables. The amount of available resources can also be expressed as a linear relationship among
some system variables. The management problem may be to optimize (maximize or minimize) the
out-put or the objective function subject to the set of constraints An optimization problem in which
both the objective function and the constraints are represented by linear forms is a problem in
linear programming.
Requirements of L.P.P.
a. Decisions variables and their relationship
b. Well defined objective function
c. Existence of alternative courses of action
d. Non-negative conditions on decision variables.
Basic assumptions of L.P.P
a. Linearity: Both objective function and constraints must be expressed as linear inequalities.
b. Deterministic: All coefficient of decision variables in the objective and constraints expressions
c. should be known and finite.
d. Additivity: The value of objective function for the given values of decision variables and the
e. total sum of resources used, must be equal to sum of the contributions earned from each
f. decision variable and the sum of resources used by decision variables respectively.
g. Divisibility: The solution of decision variables and resources can be any non-negative values
including fractions.
3. Describe the different steps needed to solve a problem by simplex method.
Ans:- The different steps needed to solve a problem by simplex method are:
a. Introduce stack variables (Si’s) for” £” type of constraint.
b. Introduce surplus variables (Si’s) and Artificial Variables (Ai) for” ³” type of constraint.
c. Introduce only Artificial variable for “=” type of constraint.
d. Cost (Cj) of slack and surplus variables will be zero and that of Artificial variable will be “M”
e. Find Zj – Cj for each variable.
f. Slack and Artificial variables will form Basic variable for the first simplex table. Surplus variable
will never become Basic Variable for the first simplex table.
g. Zj = sum of [cost of variable x its coefficients in the constraints – Profit or cost coefficient of the
variable].
h. Select the most negative value of Zj – Cj. That column is called key column. The variable
corresponding to the column will become Basic variable for the next table.
i. Divide the quantities by the corresponding values of the key column to get ratios select the
minimum ratio. This becomes the key row. The Basic variable corresponding to this row will be
replaced by the variable found in step 6.
j. The element that lies both on key column and key row is called Pivotal element.
k. Ratios with negative and “a” value are not considered for determining key row.
l. Once an artificial variable is removed as basic variable, its column will be deleted from next
iteration.
m. For maximization problems decision variables coefficient will be same as in the objective
function. For minimization problems decision variables coefficients will have opposite signs as
compared to objective function.
n. Values of artificial variables will always is – M for both maximization and minimization
problems.
o. The process is continued till all Zj – Cj >0.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Mein Kampf - My Struggle - Unexpurgated Ed - Adolf HitlerDocument1 501 pagesMein Kampf - My Struggle - Unexpurgated Ed - Adolf Hitlerkabplop88% (8)
- Mein Kampf - My Struggle - Unexpurgated Ed - Adolf HitlerDocument1 501 pagesMein Kampf - My Struggle - Unexpurgated Ed - Adolf Hitlerkabplop88% (8)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- (EMERSON) Loop CheckingDocument29 pages(EMERSON) Loop CheckingDavid Chagas80% (5)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Modulus of Subgrade Reaction KsDocument1 pageModulus of Subgrade Reaction KsmohamedabdelalPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Engineering Modern ApproachesDocument775 pagesSoftware Engineering Modern ApproachesErico Antonio TeixeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 BPI V FernandezDocument1 page16 BPI V FernandezAngelica Joyce BelenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hindustan Coca ColaDocument63 pagesHindustan Coca ColaAksMastPas encore d'évaluation
- 5030si PDFDocument2 pages5030si PDFSuperhypoPas encore d'évaluation
- SAMSUNG Mba Summer ProjectDocument58 pagesSAMSUNG Mba Summer Projectpanpatil swapnil89% (37)
- A Study of Samsung Consumer DurablesDocument92 pagesA Study of Samsung Consumer DurablesRK Singh100% (3)
- MK0009 - International Marketing Assignment Set-1Document9 pagesMK0009 - International Marketing Assignment Set-1RK Singh100% (1)
- HR Project On Study of RecruitmentDocument63 pagesHR Project On Study of RecruitmentRK Singh100% (1)
- MK0007 - Advertising Management & Sales Promotion Assignment Set-1Document10 pagesMK0007 - Advertising Management & Sales Promotion Assignment Set-1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Project - Mba Hr-Raibahadur Singh PariharDocument79 pagesProject - Mba Hr-Raibahadur Singh Parihardalveer_eck100% (1)
- MB0037 - International Business Management Assignment Set-1Document28 pagesMB0037 - International Business Management Assignment Set-1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- MK0008 - E-Marketing Assignment Set-1Document10 pagesMK0008 - E-Marketing Assignment Set-1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- MK0006 - Services Marketing and Customer Relationship Management Assignment Set-1Document10 pagesMK0006 - Services Marketing and Customer Relationship Management Assignment Set-1RK Singh0% (1)
- MB0036 - Strategic Management & Business Policy Assignment Set-1Document23 pagesMB0036 - Strategic Management & Business Policy Assignment Set-1RK Singh100% (1)
- Marketing Project On SBI Channel DevelopmentDocument103 pagesMarketing Project On SBI Channel DevelopmentRK Singh100% (1)
- Project: Customer Relationship ManagementDocument65 pagesProject: Customer Relationship ManagementAbhishek GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- MBADocument100 pagesMBArahulppppp0% (1)
- Customer Satisfaction Tata MotorsDocument92 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Tata MotorsRK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management 2Document5 pagesProject Management 2RK Singh0% (1)
- Marketing Project On ICICI PrudentialDocument69 pagesMarketing Project On ICICI PrudentialRK Singh100% (1)
- Project Management 1Document5 pagesProject Management 1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Production and Operation Management 2Document4 pagesProduction and Operation Management 2RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mis 1Document12 pagesMis 1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Production and Opeartion Management 1Document8 pagesProduction and Opeartion Management 1RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Management 1Document5 pagesMarketing Management 1RK Singh100% (1)
- Operation Research 2Document7 pagesOperation Research 2RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Management 2Document5 pagesMarketing Management 2RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Roll No.: Learning Centre: Subject: Assignment No.: Date of SubmissionDocument5 pagesName: Roll No.: Learning Centre: Subject: Assignment No.: Date of SubmissionRK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Mis 2Document7 pagesMis 2RK SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Management 1Document5 pagesFinancial Management 1RK Singh50% (2)
- Puzzles To Puzzle YouDocument136 pagesPuzzles To Puzzle Youshahisk100% (1)
- Borneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Document6 pagesBorneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Cheng LeongPas encore d'évaluation
- PDS-1st PageDocument1 pagePDS-1st PageElmer LucreciaPas encore d'évaluation
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceAnurag SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Knowledge and SkillDocument2 pagesDifference Between Knowledge and SkilljmPas encore d'évaluation
- Road Safety GOs & CircularsDocument39 pagesRoad Safety GOs & CircularsVizag Roads100% (1)
- Nucleic Acid Isolation System: MolecularDocument6 pagesNucleic Acid Isolation System: MolecularWarung Sehat Sukahati100% (1)
- The Power of Flexibility: - B&P Pusher CentrifugesDocument9 pagesThe Power of Flexibility: - B&P Pusher CentrifugesberkayPas encore d'évaluation
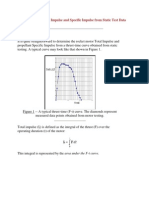
- Determining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test DataDocument4 pagesDetermining Total Impulse and Specific Impulse From Static Test Datajai_selvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wheat as an alternative to reduce corn feed costsDocument4 pagesWheat as an alternative to reduce corn feed costsYuariza Winanda IstyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Keynes Presentation - FINALDocument62 pagesKeynes Presentation - FINALFaith LuberasPas encore d'évaluation
- Leapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then SellDocument3 pagesLeapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then Sellayesha noorPas encore d'évaluation
- Serras Tilted Arc Art and Non Art Senie in Art Journal 1989Document6 pagesSerras Tilted Arc Art and Non Art Senie in Art Journal 1989api-275667500Pas encore d'évaluation
- Building A Computer AssignmentDocument3 pagesBuilding A Computer AssignmentRajaughn GunterPas encore d'évaluation
- Forms of Business Organization: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Corporation, CooperativesDocument17 pagesForms of Business Organization: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Corporation, CooperativesSanti BuliachPas encore d'évaluation
- I-Parcel User GuideDocument57 pagesI-Parcel User GuideBrian GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- RF Power Measurements Basic PrinciplesDocument27 pagesRF Power Measurements Basic PrinciplesHector Velasco100% (1)
- Exercise Manual For Course 973: Programming C# Extended Features: Hands-OnDocument122 pagesExercise Manual For Course 973: Programming C# Extended Features: Hands-OnAdrian GorganPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrepreneurship and EconomicDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurship and EconomicSukruti BajajPas encore d'évaluation
- "Corbel" - Concrete Corbel Analysis: Program DescriptionDocument4 pages"Corbel" - Concrete Corbel Analysis: Program DescriptioniuliandurdureanuPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformerDocument50 pagesTransformerبنیاد پرست100% (8)
- JWCh06 PDFDocument23 pagesJWCh06 PDF007featherPas encore d'évaluation
- BILL OF SALE Pre ApproveDocument1 pageBILL OF SALE Pre ApprovedidinurieliaPas encore d'évaluation
- OPIM101 4 UpdatedDocument61 pagesOPIM101 4 UpdatedJia YiPas encore d'évaluation
- WSM 0000410 01Document64 pagesWSM 0000410 01Viktor Sebastian Morales CabreraPas encore d'évaluation