Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ES Terms Ausat Reviewer
Transféré par
Dar AnicetoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ES Terms Ausat Reviewer
Transféré par
Dar AnicetoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
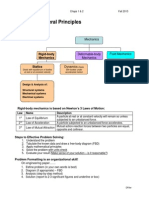
Engineering mechanics
The science that considers the
effects of forces on rigid bodies
Force
What exchanges or tends to change
the state of motion of a body
External effects
1.shear
2.moment
3.torque
Internal effects
Type of effect; Refers to stress
Resultant force
a single force that represents the net
effect of a force system
Moment of a force
Measure of the: tendency to rotate at a point
force, moment arm rotation, and moment
center
Free body diagram
A drawing of the structure/part of
the structure under consideration
Types of supports
1.cable
2.roller support
3.pin or hinge support
Equilibrium
state or condition in a body
wherein resultant is zero
Conditions of equilibrium
1.resultant is zero
2.the sum of moments about any point in
system is zero
Moment arm
distance between the axis of rotation and the
perpendicular of the line of action of a force
Components of a force
Fx-F x cos and Fy- Fx sin refers to
the ______________
Statics
The part of mechanics that considers the
effects of and the distribution of forces on
rigid bodies which are and remain at rest
Rigid body
A definite amount of matter whose parts are
fixed in position relative to one another
Concurrent force system
A type of force system wherein the lines of
action of forces meet at a common point
Method of joints
Finding the reactions at each
support
Method of sections
Utilizes the principle of moments and the
resolution of a force into its components
Axial force
This component measures the pulling
or pushing action over the section
Shear force
These are components of the total resistance
to sliding the portion to one side of the
exploration section
Torque
This component measures the
resistance to twisting the members
Bending moments
These components measure the resistance
to bending the member about the Y or Z
axes
Stress
Unit strength of a material
Concentrated load
Load acting on a particular point
Uniformly distributed load
(Rectangular loading) uniform
magnitude
Uniformly varying load
(Triangular loading) distributed load
which uniformly varies with the distance
Simple beam or simply supported
beam
Supported by a roller and a hinge
at both ends
Overhanging beam
Supported by a roller and a hinge with
one or both extending beyond supports
Cantilever beam
(beam) Supported by a fixed
support at one end only
Fixed or restrained beam
Type of beam having fixed support
at both ends
Propped beam
...
Continuous beam
type of beam With three or more
supports
Mechanics
Science of mechanics treats on forces,
motion and the effects of forces on the
bodies which they act
Applied mechanics
Concerns mainly on the applications of the
principles of mechanics to the solution of
problems commonly encountered
Structural system
A system of structural components that makes up a
structure. It is interconnected as to provide rigidity and
resist the effect of forces whether directly or indirectly
Structural system components
These are structural elements such as
beams, girders, columns, trusses, etc
Statics
Deals with forces and effect on
rigid bodies at rest
Dynamics
Deals with motion and with the effects
forces acting on rigid bodies in motion
Kinematics
Study of motion without consideration of
forces causing the motion
Kinetics
Study of forces acting on rigid bodies in
motion and their effect in changing such
motion
Force
Influence on a body producing a
change in shape or movement
Compressive force
An applied force which produces
compression in an elastic material
Tensile force
An applied force which produce
tension in an elastic material
Vector
A quantity possessing both magnitude and direction
represented by an arrow whose length is proportional to
the magnitude. Force, velocity, acceleration, moment
Scalar
Quantity having magnitude only.
Ft, kg, newton
Characteristics of a force
Magnitude
Line of action
Point of application
Direction
Applied or contacting forces
Forces that refers to the push or
pull produced by mechanical effort
Acting force
Force acting directly on a body
Reacting force
Generated by the action of one
body to another
Non-applied or non contacting
force
Gravitational pull, magnetic force
or inertia force
Coplanar
Condition where all forces lie on
one plane
Parallel force system
Non-concurrent forces having
parallel lines of action
Concurrent
Where the lines of action of all the
forces intersect at a common point
Non-coplanar
Forces do not lie on one plane
Non-concurrent
Lines do not intersect at a
common point
Collinear
All forces in a parallel system act
along a single line of action
Triangle method
Graphic technique for finding the vector sum of 2 concurrent
forces by displacing one force vector parallel to itself
completing the triangle with a vector that represents the
resultant force
Parallelogram law
System of determining the resultant force of 2
concurrent forces obtained from the diagonal at a
parallelogram having adjacent sides which represent the
2 force vectors being added
Polygon method
Graphic technique for finding the vector sum of a coplanar force
system of several concurrent forces by drawing to scale each force
vector in succession with the tall of each of the head of one preceding
it and completing the polygon with a vector that represents the
resultant force
Strength of materials
Extends the study of forces that was begun in
mechanics. Deals with relations between externally
applied loads and their internal effects on bodies
Theory of structures
Deals with the principles and methods by which the direct
stress, shear and bonding moment and the deflection art any
section of each constituent member in the structure may be
calculated
Moment
Tendency of a force to produce rotation of a body about
a point or line, equal in magnitude to the product of the
force and the moment arm acting in a
clockwise/counter direction
Moment center
Point at which the axis of a moment
intersects the plane of the forces causing the
moment
Moment arm
Perpendicular distance from the line of
action of a force to the point or line about
which a moment occurs
Couple
Force system of 2 equal, parallel forces
acting in opposite directions and tending to
produce rotation
Moment of a force
Tendency to produce a rotation of the
body on which it acts about an axis
Static equilibrium
Condition in which forces in a state of rest
are acting in opposite direction of the same
magnitude
Force law of equilibrium
Implies a balance of opposing
forces within a system
Stress
Resistance to external forces
Strain
Subjected to an external force
Tensile stress
it is a type of stress that refers to
"Pull"
Compressive stress
Push
Normal stress
Perpendicular to stressed surface
Shearing stress
Parallel
Axial stress
External stress acting on a member parallel
to its major axis and member is of constant
cross section
Bearing stress
Compressive stress exerted on an
external surface of a body
Ultimate stress
Greatest unit stress a material can
withstand
Allowable stress
Portion of the ultimate strength
which may safely be used in design
Live load
Moving load on a structure, acts
downward
Dead load
Static load, downward
Dynamic load
Often with rapid change in
magnitude and location
Moving load
Kinetic load of a short duration due to moving vehicles
Occupancy load
Live on structure resulting from
the weight of people, etc
Wind load
Exerted by the kinetic energy of a
moving mass of air
Transverse load
Load applied perpendicular to the
longitudinal axis
Axial load
Tensile acting along the
longitudinal axis
Roller type support
Offers resistance in a direction normal to the
surface beneath the roller, does not resist
movement parallel to the supporting surface
Hinge type support
Prevents movement along the horizontal
and vertical directions but does not resist
rotation about the hinge
Link type support
Offers resistance in the direction
along the link and through 2 pins
Fixed-end type support
Type of support that resists rotation about
the support and to movements along the
horizontal and vertical directions
Section properties centroid
Center of one or two dimensional figure
about which the sum of the displacements of
all points is zero
Center of gravity
Point at which the entire weight is
considered concentrated
Center of mass
(Section property) Point at which
the entire mass is concentrated
Moment of inertia
Sum of the products obtained by multiplying
an element of mass by the square of its
distance from the axis
Radius of gyration
Distance from its moment of inertia axis at which the
entire area is considered concentrated without changing
the numerical value of its moment of inertia
Modulus of elasticity
The ratio of the shearing stress to the shearing strain
Modulus of rigidity
Coefficient of elasticity expressing the ratio
between shearing stress and strain produced
by stress
Truss
Structural frame based on the geometric rigidity
of the triangle and composed of linear members
subject to axial tension and compression
Creep
Property which causes some materials under
constant stress to deform slowly over a
period of time
Machinability
Readiness with which a material
yields to shaping with cutting tools
Strength
Resist stress without failure
Elasticity
Returns to original size
Stiffness
Resist deformation
Ductility
Drawn permanently through great
change
Brittleness
Opposite of ductility. Fail without
warning
Malleability
Undergoes great change in shape without
rupture
Hardness
Resist indentation or abrasion
Resilience
Material Property: Absorbs
Toughness
Absorb energy at high stress
Chord
Either of the 2 principal members
extending end to end
Web member
Connects upper and lower chord
Panel
Space between any 2 panel points
on a chord and joint
Panel point
Joint between 2 or more members
of a truss
Panel length
Space on the chord of a truss between 2
adjacent joints made of principal web
members
Span
Distance between supports
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanics of Materials GlossaryDocument0 pageMechanics of Materials GlossaryDr. Madhukar Vable100% (1)
- DuasoDocument56 pagesDuasoCj RAMOSPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics Concurrent Forces: Force SystemDocument3 pagesEngineering Mechanics Concurrent Forces: Force SystemFranklin EsguerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Duaso QuizDocument20 pagesDuaso QuizCharchar HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg Mech and Strength of MaterialsDocument73 pagesEngg Mech and Strength of MaterialsClaire NecesitoPas encore d'évaluation
- MechaDocument5 pagesMechaGlen GulayPas encore d'évaluation
- Def of TermsDocument4 pagesDef of TermsujudalynPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech - 3502 - DefsDocument5 pagesMech - 3502 - Defsbrody lubkeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Period 24 BridgeDocument4 pagesPeriod 24 Bridgeapi-328107638Pas encore d'évaluation
- StaticsDocument5 pagesStaticsAmiel DionisioPas encore d'évaluation
- 12101dep-Notice 04242021Document104 pages12101dep-Notice 04242021ahmed titoPas encore d'évaluation
- Components of A Force in XY PlaneDocument22 pagesComponents of A Force in XY PlaneRomalyn GalinganPas encore d'évaluation
- BS SF FundamentalsDocument77 pagesBS SF FundamentalsAlvin Bariuan GuiyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1Document5 pagesTask 1elking.ahmed1562002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engg. MechanicsDocument125 pagesCivil Engg. MechanicsSunish GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuum Mechanics - WikipediaDocument2 pagesContinuum Mechanics - Wikipediadarnit2703Pas encore d'évaluation
- CEA Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesCEA Definition of Termsartchitect.angelcoPas encore d'évaluation
- BM Lecture 1Document43 pagesBM Lecture 1Aggrey MukondePas encore d'évaluation
- Statics - Force SystemDocument4 pagesStatics - Force SystemReynald RenzPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering MechanicsDocument169 pagesEngineering MechanicsRADHA KRISHNAN T93% (15)
- Mechanics PortionDocument6 pagesMechanics PortionRupak MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cestat30 Midterms ReviewerDocument17 pagesCestat30 Midterms ReviewerIan Arnold FamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery: Uniti - Force AnalysisDocument30 pagesDynamics of Machinery: Uniti - Force Analysismkumar_823341Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2: Statics of Structures and ReactionsDocument32 pagesUnit 2: Statics of Structures and ReactionsBhuwan JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Compendium of SomDocument13 pagesCompendium of SomVivek BajpaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of StructureDocument15 pagesTheory of StructureAngel LudovicePas encore d'évaluation
- EM - PPT - FinalpptxDocument28 pagesEM - PPT - FinalpptxShawn HunterPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document73 pagesLecture 3HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics PowerpointDocument12 pagesMechanics PowerpointRoy MarkPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 400 Questions and AnswerDocument1 page1 400 Questions and AnswerJenemarPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Unit-1A (EME-151,152)Document17 pagesFinal Unit-1A (EME-151,152)guptakrish330Pas encore d'évaluation
- Architectural Structures Terminologies ReviewersDocument5 pagesArchitectural Structures Terminologies Reviewersbalictar.jyllpatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Mechanicsapi-248483124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Som ReassessDocument76 pagesSom Reassessdineshsharma4ayushPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap. 1 General Principles: What Is Mechanics? What Is Statics? MechanicsDocument4 pagesChap. 1 General Principles: What Is Mechanics? What Is Statics? Mechanicsrj2263Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Vibration IntroductionDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Vibration IntroductionSaya SantornoPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural AnalysisDocument11 pagesStructural AnalysisErRajivAmiePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 01Document18 pagesLec 01Arslan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesHazelNoreenSabileManalo100% (1)
- Assignment StaticDocument24 pagesAssignment StaticSuhayl AzminPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of StructureDocument15 pagesTheory of StructureClaire BarriosPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-1 Force Analysis FullDocument101 pagesUnit-1 Force Analysis FullshanmechanicPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1Document34 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1rout79858Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4-Topic 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument21 pagesLesson 4-Topic 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesNicholas Bonn SingPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machines Two MarksDocument13 pagesDynamics of Machines Two MarksJegan ParamasivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics I CHAP 4Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics I CHAP 4nvnrevPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 VibrDocument11 pagesModule 1 VibrShockBlade ZedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Equivalent Solution Is A Mathematical Technique Used in Vibration Engineering To Simplify The Analysis of Complex Vibrating SystemsDocument4 pagesThe Equivalent Solution Is A Mathematical Technique Used in Vibration Engineering To Simplify The Analysis of Complex Vibrating SystemsReinhart Levin Russ NicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT4Document47 pagesUNIT4Vijay KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- MaterialDocument23 pagesMaterialbiruk gesesePas encore d'évaluation
- Re Write Chapter 1Document25 pagesRe Write Chapter 1biruk gesesePas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Mechanics PDFDocument18 pagesApplied Mechanics PDFSrinivas KandukuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-1 IntroductionDocument29 pagesChapter 1-1 Introductionالخليل إبراهيمPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress (Mechanics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaqDocument34 pagesStress (Mechanics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaqAshish MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsD'EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?D'EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas HKSA Deskriptor (Fitriani Choerunnisa (11171013) 3FA1)Document4 pagesTugas HKSA Deskriptor (Fitriani Choerunnisa (11171013) 3FA1)fitriani choerunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Educational Aspiration and Socio-Economic Status of Secondary School StudentsDocument11 pagesStudy of Educational Aspiration and Socio-Economic Status of Secondary School StudentsvivekPas encore d'évaluation
- DCS800 Firmware Manual EnglishDocument298 pagesDCS800 Firmware Manual EnglishMadson FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP QM Calibration MethodDocument3 pagesSAP QM Calibration MethodvrkattulaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECA 2markDocument4 pagesECA 2markthangarajelectresPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital - 123328-R010818-Analisa Balik-BibliografiDocument5 pagesDigital - 123328-R010818-Analisa Balik-BibliografiEncep Septian CaturPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 Lesson 3 Activity Guide - Unreasonable TimeDocument2 pagesUnit 10 Lesson 3 Activity Guide - Unreasonable Timetrivediom427Pas encore d'évaluation
- ISG Services OverviewDocument12 pagesISG Services OverviewsdonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-III - EEFA - CostsDocument70 pagesUnit-III - EEFA - CostsRamalingam ChandrasekharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Dimmer BukeDocument10 pagesManual Dimmer BukeJavi KatzPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding of Thermoplastics Heated Tool Butt Welding Directive DVS 2207-25Document7 pagesWelding of Thermoplastics Heated Tool Butt Welding Directive DVS 2207-25Yuriy Nechaevskiy100% (1)
- Pov Nori Apr2007Document31 pagesPov Nori Apr2007DMRPas encore d'évaluation
- LC08 L1TP 120065 20180318 20180403 01 T1 MTLDocument4 pagesLC08 L1TP 120065 20180318 20180403 01 T1 MTLrendy aswinPas encore d'évaluation
- 04931V - 396 ToolingDocument52 pages04931V - 396 Toolingpiston brokePas encore d'évaluation
- 23-Article Text-89-3-10-20200704Document16 pages23-Article Text-89-3-10-20200704cholifah agumPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1Document120 pagesPart 1Raju Halder0% (1)
- Back To Basics in Optical Communications TechnologyDocument178 pagesBack To Basics in Optical Communications TechnologyAyanPas encore d'évaluation
- JAVA NotesDocument12 pagesJAVA NotesVarun BawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab Reportivan glenn baldomerostPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Iv Ce 6405Document13 pagesUnit Iv Ce 6405HanafiahHamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Lincdoc?Document2 pagesWhat Is Lincdoc?Daniel O'Leary0% (1)
- NDT VTL-3-3Document2 pagesNDT VTL-3-3Priyesh MauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- P103154 - 7.00 - Doc - Manual - 8000 WindlassDocument43 pagesP103154 - 7.00 - Doc - Manual - 8000 WindlassDanPas encore d'évaluation
- Devlopment and Analysis of Natural Banana Fiber CompositeDocument3 pagesDevlopment and Analysis of Natural Banana Fiber CompositeEditor IJRITCCPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea Stereonet-HelpDocument32 pagesTarea Stereonet-HelpJosueHuillcaPortilloPas encore d'évaluation
- SOPRANO TIM SMTP Interface Developers GuideDocument43 pagesSOPRANO TIM SMTP Interface Developers GuidenettellectPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Chemistry - Lab Report 5Document7 pagesInorganic Chemistry - Lab Report 5AlpPas encore d'évaluation
- 5510 0004 04 - 18 1021 Basic Principles of Ship Propulsion - MAN PDFDocument68 pages5510 0004 04 - 18 1021 Basic Principles of Ship Propulsion - MAN PDFAlex FatecPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity Measurements On Oligoesters From Terephthalic Acid and GlycoDocument7 pagesViscosity Measurements On Oligoesters From Terephthalic Acid and GlycoMaria RincondePas encore d'évaluation
- Python Fundamentals SheetDocument29 pagesPython Fundamentals Sheetwp1barabaPas encore d'évaluation