Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 Charles Notes
Transféré par
Anh Thu TranDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 9 Charles Notes
Transféré par
Anh Thu TranDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Friday, November 20, y
Chapter 9 (Pg. 148-154)
9.1
Cell cycle: stages that take place when a eukaryotic cell divides and the time the
daughter cells also divide
Cell gets larger and DNA and # of organelles double when cell abt to divide
Two Part of cell cycle: interphase and mitotic stage
Interphase
- Most of cell cycle in Interphase
- Cell performs normal function
- Duration varies by cell
- very busy and prep for mitosis occurring
-
Three Stages: G1, S, G2
-
G1
- Before DNA replication
- cell recover from previous division
- cell grow, increase # of organelles, store materials needed for DNA replication
- Nerve and Muscle cell do not go through cell cycle
- go into G0 > perform everyday process, no prep for cell division
- completion of cell cycle tightly controlled
1
Friday, November 20, y
- S
- Dna replication happens
- 1 chromosome= 1 double helix -(S)-> chromosome=2 identical double helix
- each double helix: chromatid
- two identical chromatid: sister chromatids
- sister chromatids attached @ centromere before pulled apart
-
G2
- create protein that helps with cell division
Mitotic State
- include mitosis (nucleic division) and cytokinesis (cell division)
- mitotic spindle separate chromosome into 2 separate daughter cells
- divison of cytoplasm done= 2 new daughter cells
Control of the Cell Cycle
- signal: control activities of cell
- Growth Factors
- receive @ plasma membrane
2
Friday, November 20, y
- tell cell to finish cell cycle
- cell cycle check point:
- 3 cell cycle check points indicate whether parts of cycle stop or continue
- cyclins: internal signal proteins that must be present for the cell to go from 1
stage to the next
- G1 checkpoint
- p53 (protein & weight of protein 53 kilodaltons) stop cell cycle if DNA damaged
- attempt to repair DNA
- High levels of p53> cell apoptosis: cell suicide
- RB (retinablastoma) interpret growth signals and nutrient availability
- G2 checkpoint:
- if DNA not finish replicating
- prevent M stage starting before S stage finish
- another chance to fix damage DNA
- M checkpoint:
- stop if chromosome not attached to mitotic spindle correctly > may prevent
accurate separation of chromatids
- Apoptosis
- programmed cell death
1. cell rounds up> lose contact with neighbors
Friday, November 20, y
2. nucleus fragments
3. cell membrane blisters
4. cell fragments engulf by white blood cells or nearby cells
- caspases: enzyme catalyze cell death
- always present in cell
- kept in check by inhibitors
- Apoptosis and Cell division
- Cell division increase # , apoptosis decrease # of somatic cells (normal body
cells)
- prevent tumor and limit spread of virus
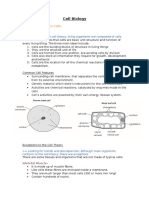
9.2 The Eukaryotic Chromosome
chromosome made of DNA and mostly protein (histone)
5 main types of Histone molecules: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, & H4
H3 and H4 amino acid sequence doesn't vary much
1. DNA wrapped around core of 8 histones (2 of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) >
nucleosome: DNA and histone
2. string fold into zigzag structure: histone H1 help coiling
Friday, November 20, y
3. loop back and forth into radial loops> euchromatin: active chromatin w/ gene
that are being transcribed
4. heterochromatin: part of DNA that highly compact
5. protein scaffold condense chromosome further
9.3 Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Chromosome Number
not in cell division: DNA > chromatin
chromatin condense into chromosome
Diploid (2n): total # chromosome found in all cell of individual, 2 chromosome
Haploid (n): found in gametes, only one chromosome of each kind
Chromosome Duplication
2n divide to make identical daughter and parent cells
occur during S phase
each chromosome have 2 identical molecules
each double helix: chromatid (2 identical chromatid= sister chromatid)
sister chromatid attach at the centromere
kinetochores: protein complex on either side of centromere
Cell division: sister chromatid separate at centromere
Friday, November 20, y
Division of centromere
centrosome: microtubule organizing center of cell
divide before mitosis
contain centrioles
organize mitotic spindle
begin to break apart when spindle fibers form
Phases of Mitosis
2. Prophase
chromatin condense and chromosome visible
nucleolus disappear
nuclear envelop break down
spindle starts to form
microtubule radiate to cell membrane from centromere > aster
2. Prometaphase
kinetochores appear
extend from pole to chromosome
chromosome not in alignment
Friday, November 20, y
3. Metaphase
centromere/ chromosome are lined up in center of cell
metaphase plate: indicate where next cell division start
4. Anaphase
2 sister chromatid separate > 2 daughter chromosome
daughter chromosome pulled apart as the kinetochore spindle fibers disconnect
5. Telophase
spindle disappear
new nuclear envelope form
chromosome become chromatin
nucleolus reappear
2 daughter nucleus with identical chromatin
6. Cytokinesis
Different in plant and animal cells
Plant Cells
build new cell walls btw daughter cells
flattened disk appear btw 2 daughter cells
golgi apparatus make vesicle that fuse at the region of the disk forming cell plate:
new plasma membrane
cell plate expand until fuse with old membrane
7
Friday, November 20, y
membrane release molecule that form primary cell wall
filled with middle lamella
Animal Cell
cleavage furrow: indentation on plasma membrane btw two daughter cells
band of actin filament (contractile ring) tighten and constrict area between 2
daughter cells
2 daughter cells pinched away from each other
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Leg Day PDFDocument1 pageLeg Day PDFAnh Thu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Leg Day PDFDocument1 pageLeg Day PDFAnh Thu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Basic ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Basic ExercisesAnh Thu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- CHapter 2.odtDocument1 pageCHapter 2.odtAnh Thu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Chronic Diseases On The Rise: Bmi Height In. Bmi Weight (KG) Height MDocument3 pagesChronic Diseases On The Rise: Bmi Height In. Bmi Weight (KG) Height MAnh Thu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Chad SheetDocument2 pagesChad SheetMatthew TongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureDocument39 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureYonathan Christyanto100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Mitosis Dan Meiosis: DR I G K Nyoman Arijana, M.Si - MedDocument16 pagesMitosis Dan Meiosis: DR I G K Nyoman Arijana, M.Si - MedRisma SintyaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Class - 11 Science Subject - BiologyDocument6 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: Class - 11 Science Subject - BiologyAshok KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Baghdad College of Medical Science (Human Biology)Document9 pagesBaghdad College of Medical Science (Human Biology)علي صلاح مهديPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Lab REport Number Who Knows What (Mitosis)Document12 pagesLab REport Number Who Knows What (Mitosis)Michelle SeywaldPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelMena YasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology An Australian Focus 5Th Edition Knox Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument51 pagesBiology An Australian Focus 5Th Edition Knox Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJacquelineLopezodkt100% (10)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- 211 Mitosis LabDocument5 pages211 Mitosis LabadekPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Cell Biology NotesDocument18 pagesCell Biology NotesZara100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Cell CycleDocument19 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Cell Cycleakiza100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- 2019 Genetics Lab ManualDocument27 pages2019 Genetics Lab ManualViệt TiếnPas encore d'évaluation
- HistologyDocument63 pagesHistologyMichelle TheresePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper2 Form 4Document12 pagesBiology Paper2 Form 4hqbehPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Document27 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Bio Lab-131 Session-Fall 2021 Section-001Satya NadellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Guides 2011Document142 pagesReading Guides 2011henrym1095Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Introduction To Genetics MODULEDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Genetics MODULEWilma TorinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan in Biology IiDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Biology IiPablo Ragay Jr100% (27)
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Module 2Document23 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Module 2eljentabzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Cell Cycles: Mitosis, Cytokinesis and MeiosisDocument22 pagesCell Cycles: Mitosis, Cytokinesis and MeiosisRestiyana VitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive Systems A. B. C. DDocument6 pagesReproductive Systems A. B. C. DJamie BagundolPas encore d'évaluation
- AP BiologyDocument5 pagesAP BiologyAnil ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 9 - To Study Mitosis Through Onion Root TipDocument3 pagesExperiment 9 - To Study Mitosis Through Onion Root Tipshr sem75% (4)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Mitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatDocument28 pagesMitosis: Aarifa Hoosein-RiyasatAkiela JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Freytag Mitosis Lesson PlanDocument71 pagesFreytag Mitosis Lesson Planapi-247664759Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vikash Residential School: Laboratory Manual Biology Cbse Class-Xii TERM-1Document24 pagesVikash Residential School: Laboratory Manual Biology Cbse Class-Xii TERM-1bhakta_babiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJ.L.Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIO152 Lab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis VocabularyDocument6 pagesBIO152 Lab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis VocabularySasusaku3625Pas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE CELL CYCLEDocument31 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE CELL CYCLEJeanPaule Joumaa100% (2)
- The Puzzle of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesThe Puzzle of Mitosis and MeiosisDaniel LopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 11 Biology Exam ReviewDocument16 pagesGrade 11 Biology Exam ReviewPavni ChandaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)