Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Assigment A 1
Transféré par
aasthamathurTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Assigment A 1
Transféré par
aasthamathurDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.
Classify computer systems according to capacity. How they are
different from computers according to the classification of technology.
Provide comparative study also.
Answer.
Capacity of a computer refers to the volume of data that a
computer system can process. Formerly a computers size was a sign of its
capacity. With the current state of smallness, dimension of capacity is based
on throughput of the computer. Throughput is the quantity of processing
that can be performed in a given amount of time. Based on throughput
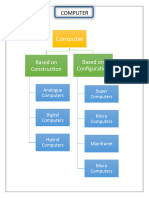
computer systems can be divided into four major categories:
Microcomputers
Minicomputers
Mainframe computes
Supercomputers
Microcomputers:
Microcomputers are generally known as personal computers-PCs and
are microprocessor based small notebook or laptop or desktop systems with
changeable capacity. Personal digital assistants (PDAs) are very small
portable computers. PDAs are also recognized as the palmtop computers.
The brain of a microcomputer is the microprocessor; it is a silicon chip
containing essential circuits to execute logic or arithmetic operations and to
manage the input/output operations. A microprocessor is an integrated
circuit which usually contains millions of transistors squeezed onto a small
silicon chip. A microcomputer system is formed by adding input and output
facility along with memory to the microprocessor.
Microcomputers
At the initial time the microcomputers had very limited processing
power and limited choice of input/output devices. But at modern days they
have wider processing capabilities and maintain a wide range of
input/output devices. Today microcomputers are available with a collection
of input/output devices varying from a tape recorder to a voice synthesizer.
In addition to general-purpose computations, microcomputers are also used
for exceptional purpose applications in automobiles, airplanes, toys, clocks,
appliances etc.
Workstations: The High-end microcomputers are also recognized as
workstations. They symbolize the bridge between the microcomputers and
minicomputers. It is a microcomputer with many of the facilities and
abilities of bigger minicomputers but price much less. At first it was
designed for use by designers and engineers who need extremely powerful
processing and output capabilities.
Servers: Servers are not designed to be used directly. They make programs
and data available for users having access to a computer network. A
computer network is a collection of computers connected together.
Clients: To use servers, users run desktop programs called clients, which
know how to contact the server and obtain information from the server. Use
of desktop clients and centralized servers is called client/server computing.
Terminals: Although terminals look like the personal computers, they have
some limitations when compared with personal computers. Terminals have
only a screen and a keyboard and the electronics that allow them to
communicate with the computer to which they are connected. Because they
lack the ability to process data on their own, they are called dumb
terminals. There is a variety of dumb terminals that can perform limited
processing. These are called smart terminals. A personal computer is an
example of a smart terminal.
Minicomputers:
A minicomputer system performs the basic arithmetic and logic
functions and supports some of the programming language used with large
computer systems. They are physically smaller, less expensive, and have
small storage capacity compared to mainframes. Minicomputers are ideally
suited for processing tasks that do not require access to huge volumes of
stored data. As a result of low cost, ease of operation, and versatility,
minicomputers have gained repaid acceptance since their introduction in the
mid-sixties. Some of the larger and expensive minicomputers are capable of
supporting a number of terminals in a time-shared mode. Uses of
minicomputers are gradually being diminished with the rapid development
of microcomputers.
Mainframe Computers:
A larger computer normally consists of modules accumulated on a
chassis and is terms as a mainframe computer. They differ in size, from
those a little larger than a minicomputer to supercomputers. These
computer systems present extensive benefits over minicomputers or
microcomputers. Some of these are: greater storage facility, greater
processing speed, a larger assortment of input/output devices, and support
for a number of high-speed storage devices, multiprogramming, and time
sharing.
Owing to wonderful expense, a mainframe computer system must be
operated powerfully. Operating mainframes at the necessary level of
effectiveness requires a very large and highly trained staff. These are
normally used by government agencies, large business, military and the
universities. These systems are often coupled with other computer systems
in a large network to give massive computing power. This is referred to as a
distributed data processing system.
Supercomputer:
A very powerful and large mainframe computer is known as a
supercomputer. The astronomical cost of super-computers has limited their
development to only a few hundred worldwide. The example of a
supercomputer is the Cray X-MP. Such supercomputers are applied to the
solution of very difficult and complicated scientific and technical problems.
Supercomputers are also used for the various national security purposes of
some advanced nations.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS:According to Technology used Computer can be classified on the basis
of different factors such as circuits and the task performance capabilities
under this classification, computer have been classified into three
categories.
Analog computers
Digital computer
Hybrid computer.
Analog computers.
An analog computer works with current rather
them by the process of counting. Analog computer works on supply of
continuous signal and display continuous speed. Thus an analog computer
is special purpose computer that recognize data as a continuous
measurement of a physical property (voltage, pressure, speed and
temperature).
Example: Automobile speedo meter but cannot give accuracy more
than.
Digital computers.
As its name suggest it works with digits 0s and 1s
in other words digital computers is a counting device. These are high speed
programmable electronic devices that perform mathematical calculations,
compare values and store results. They recognize data by counting discrete
signal representing either a high or low voltage state of electricity.
Hybrid computer.
It is a combination of Analog computers used in
continuous system also non-linear discrete features of a digital computer
such as storing values logical operations and switching.
These computers are mostly used with process control equipment in
continuous production plants like all refineries etc. and used at places
where signals as well as data are to be entered into computer. Areas of
applicationnuclear power plants mine etc.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Classification of Computers According To Technology and SizeDocument12 pagesClassification of Computers According To Technology and SizeNadun Mihiranga Herath90% (20)
- Classifying Computers by Operating Principle, Purpose, CapacityDocument4 pagesClassifying Computers by Operating Principle, Purpose, CapacityLata SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ClasClassification of Computers According To Size and Purposesification of Computers According To Size and PurposeDocument5 pagesClasClassification of Computers According To Size and Purposesification of Computers According To Size and PurposeNicole SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifications of ComputersDocument3 pagesClassifications of Computersjaimededios80% (5)
- BBA SEM II Classification of Computer by DR. RAKESH RANJANDocument6 pagesBBA SEM II Classification of Computer by DR. RAKESH RANJANJogeshwar BaghelPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT in Science Education: An Overview of Information and Communication Technology Tools and ResourcesDocument18 pagesICT in Science Education: An Overview of Information and Communication Technology Tools and ResourcesYusha'u SaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Applications for BusinessDocument12 pagesComputer Applications for BusinessSameel RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 LESSON 3 Classifications of ComputersDocument8 pagesModule 3 LESSON 3 Classifications of ComputersType FaorePas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 1.1 - Types of ComputerDocument4 pagesActivity Sheet 1.1 - Types of ComputerLyssa BasPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Computers-1Document4 pagesClassification of Computers-1DENIS OKUMUPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Computers Basic Computer TypesDocument4 pagesTypes of Computers Basic Computer TypesAgrippa MungaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding ComputerDocument18 pagesUnderstanding ComputerJerson E. RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputersDocument8 pagesChapter One Introduction To Computer: of ComputershailePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Notes RevisedDocument19 pagesComputer Notes RevisedAgrippa MungaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Communication Technology: Understanding Computers Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesInformation Communication Technology: Understanding Computers Classification of ComputersLawrencePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultDocument7 pagesUnit-I: Data Operations or Calculations ResultSiva SankariPas encore d'évaluation
- ISMT Assignment on Computer ClassificationDocument9 pagesISMT Assignment on Computer ClassificationAlex KharelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction-1Document25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction-1bonsa tashomePas encore d'évaluation
- Catholic University ICT LessonDocument45 pagesCatholic University ICT LessonJoaquim CHICOPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer ClassificationDocument6 pagesComputer ClassificationTrevor SelwynPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Computer?Document25 pagesWhat Is Computer?Ali KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Classification of ComputersDocument9 pages2 Classification of ComputersMaira HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- De Nition 1Document14 pagesDe Nition 1brian mburuPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifications of Computers: 1. According To PurposeDocument2 pagesClassifications of Computers: 1. According To PurposeRosen LPPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter OneDocument21 pagesChapter OnetashalePas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Computer (ICRI)Document43 pagesBasics of Computer (ICRI)Harshada VasanePas encore d'évaluation
- Md. Al Mamun IT Officer CRP-MirpurDocument37 pagesMd. Al Mamun IT Officer CRP-Mirpurmamun183Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computers: An Overview of Types, Generations, and ApplicationsDocument37 pagesComputers: An Overview of Types, Generations, and ApplicationsAVINASH ANANDPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of ComputersDocument41 pagesTypes of Computerssubramani muthusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of ComputerDocument20 pagesClassification of ComputerJagannath GujiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Understanding Computer (Autosaved)Document27 pagesLesson 5 Understanding Computer (Autosaved)alma agnasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To ComputersDocument16 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To ComputersMiranda MahunzePas encore d'évaluation
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2too robaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Computers ExplainedDocument4 pagesTypes of Computers ExplainedMarya BalochPas encore d'évaluation
- Mainframes Are A Type of ComputersDocument14 pagesMainframes Are A Type of Computersimtiazahmedfahim87Pas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT Ichapter1 (Introduction To Computer)Document12 pagesUNIT Ichapter1 (Introduction To Computer)Vinutha SanthoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ComDocument134 pagesBasic ComRosli MohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computing PrelimDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Computing PrelimApril Jane AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- KMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDocument15 pagesKMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDeepankar singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of ComputersDocument7 pagesClassification of ComputersscsdfvdgPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Skills: Lecture No:1Document17 pagesComputer Skills: Lecture No:1rabia sattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Jayaraj JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifying computers by size, function and data handlingDocument2 pagesClassifying computers by size, function and data handlingMamta Mohit DhandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comuter: 1. What Is Computer ?Document4 pagesComuter: 1. What Is Computer ?PenjPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE 1 COMPUTER APPLICATIONDocument26 pagesLECTURE 1 COMPUTER APPLICATIONAisha LawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of ComputersDocument16 pagesClassification of ComputersTEEPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Understanding ComputerDocument2 pages2 Understanding ComputerAngel Marie TisadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Module 3 Lesson 1Document2 pagesComputer Module 3 Lesson 1yuuna yuunaPas encore d'évaluation
- I C T - NotesDocument166 pagesI C T - NotesKangogo PettPas encore d'évaluation
- ComputersDocument4 pagesComputersZujajah Gull100% (1)
- Classification of ComputerDocument29 pagesClassification of ComputerArpoxonPas encore d'évaluation
- MPU & MCU 8 X Lessons NotesDocument233 pagesMPU & MCU 8 X Lessons NotesserjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPUTERDocument16 pagesCOMPUTERLiam Zhaeden TavuPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Computers: Arisha Fatima DPT 01, MihsDocument12 pagesClassification of Computers: Arisha Fatima DPT 01, MihsAbdullah NaeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of ComputerDocument30 pagesClassification of ComputerTes 536472Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Types of ComputerDocument8 pagesClassification of Types of Computershawai8009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1: Introduction To ComputingDocument123 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To ComputingKartel Gunter100% (1)
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesD'EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingD'EverandFundamentals of Modern Computer Architecture: From Logic Gates to Parallel ProcessingPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer 1Document5 pagesAnswer 1abhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- Date Scrip Lot Size Trade Signal Date Entry Price Exit Price Exit DateDocument5 pagesDate Scrip Lot Size Trade Signal Date Entry Price Exit Price Exit Dateabhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Wonders of Life PDFDocument8 pages7 Wonders of Life PDFabhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- Village Culture PDFDocument53 pagesVillage Culture PDFabhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Wonders of LifeDocument11 pages7 Wonders of Lifeabhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- PARK ReleaseNotesDocument5 pagesPARK ReleaseNotesmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Weekends-2017-Plan Ur Holidays PDFDocument8 pagesLong Weekends-2017-Plan Ur Holidays PDFabhishekh328Pas encore d'évaluation
- Release Notes UpdateNowDocument5 pagesRelease Notes UpdateNowSagen MandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Advt For Recruitment of CWE RRBs V Proforma-B 160317Document50 pagesDetailed Advt For Recruitment of CWE RRBs V Proforma-B 160317prembiharisaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Advt Clerical 05-04-2016-17Document5 pagesFinal Advt Clerical 05-04-2016-17UploadingfilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivative Market Dealer Module Practice Book SampleDocument35 pagesDerivative Market Dealer Module Practice Book SampleMeenakshi0% (1)