Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Relay Coordination Analysis Engineering Essay 5
Transféré par
Gary GohCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Relay Coordination Analysis Engineering Essay 5
Transféré par
Gary GohDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2.3.
3 Thermal relays
The thermal relay has a heat sensitive element that connected in series with the motor load circuit and an overload heater. So,
using this relay the higher the overload current, the quicker the heat sensitive element to be heated up and the faster the relay
operates [5]. In the protective thermal relay for high current fault, an additional heater and a direct current are applied to the
bimetal element. Sometimes, a current transformer also is used to supply the heat to the element. This action will break the
circuit through the operating coil of the main contactor as the heat sensitive clement to open the overload relay contact and
disconnects the power supply from the motor. Since, the bimetal element takes time to heat up, the inherent time delay is used
by the thermal overload relay to draw current at start without tripping the motor [21].
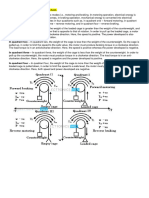
Induction relays
Basic induction motor principle is applied to the relay to operate base on induction principle. The moving conductor is placed
between two magnetic fields to produce the torque displaced both in phase and time [20]. The torque is produced when there is
an interaction of one alternating flux with another alternating flux that induced eddy current in the rotor. These two fluxes have
same frequency but are displaced in time and space. So, this type of relay only uses a.c. quantities.
The types of the induction relays are:
Shaded pole type
Watt hour meter type
Induction cup type
The torque produced is proportional to the product of upper and lower fluxes and the sine of the angle between these two
fluxes [19].
- Torque equation for induction type relay [19]
A maximum torque is produced when the angle between the fluxes is, proportional to and. The disc will continue to accelerate
when the torque is applied without control and only limited by friction. The disc can be controlled using two methods [12]:
Using a permanent magnet that will produce a braking force proportional to the disc speed which is its field passes through the
disc. So, this controls the time characteristic of the relay.
Using a control spring which produces a torque proportional to disc angular displacement. This will determine the relay setting
and control disc speed at low values of torque [12].
Typical application of the induction relays:
Shaded pole type
Wattmetric type
Overcurrent relay
Over/under voltage relay
Static relays
In this type of relay, all the function measurement and comparison are performed by static circuit and there is no moving part
like electromagnet relay [22]. The static circuit uses components such as transistor, diodes, resistor, and capacitor and so on
[23]. So, the change from the electromechanical relays to static relays is very slow because of the relative costs.
There are three terms for the static relays [22]:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 3 Rotational Speed MeasurementDocument7 pages3 Rotational Speed MeasurementLinda MeltonPas encore d'évaluation
- AlternatorsDocument42 pagesAlternatorsArsalan Ahmed Usmani100% (3)
- Overview of Single Phase Induction Type Energy Meter: Driving SystemDocument3 pagesOverview of Single Phase Induction Type Energy Meter: Driving Systemamrit323100% (1)
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 4 PDFMuhamad AmmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction MotorDocument6 pagesInduction MotorHamdani RizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - III Measuring InstrumentsDocument62 pagesUnit - III Measuring InstrumentsjyothirPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Type Energy MeterDocument19 pagesInduction Type Energy MeterArijit KaranPas encore d'évaluation
- PROJCTDocument32 pagesPROJCTSwati Agarwal100% (1)
- Electrical Principles 2 (CCEET 2)Document25 pagesElectrical Principles 2 (CCEET 2)Bernard MunyithyaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC MotorDocument8 pagesDC Motorven_avv3382Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Instruments: What Is Meant by ?Document42 pagesTypes of Instruments: What Is Meant by ?Anushya RavikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-Ii Operating Principles And Relay Construction: ωt cos I I K 2 1 I k FDocument26 pagesUnit-Ii Operating Principles And Relay Construction: ωt cos I I K 2 1 I k FpdselvamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter TwoDocument69 pagesChapter Twohaileasrat4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Relay CDGDocument1 pageRelay CDGYou TubePas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current Drives-Holland IndustrialDocument3 pagesEddy Current Drives-Holland IndustrialAirton FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- EDM - Wattmeter - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''EDM WattmeterDocument10 pagesEDM - Wattmeter - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''EDM WattmeterULFAT HUSSAINPas encore d'évaluation
- Speed Control of D C MOTOR Using Chopper-1308Document7 pagesSpeed Control of D C MOTOR Using Chopper-1308Moon3pellPas encore d'évaluation
- Ja Assignment3Document6 pagesJa Assignment3BookMaggotPas encore d'évaluation
- U1 EdDocument2 pagesU1 EdOMKAR PATILPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE 2321 Lecture 3 & 4 and 5Document75 pagesSPE 2321 Lecture 3 & 4 and 5Martinez MutaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument25 pagesSingle Phase Induction MotorKh Muhammad Mashood0% (1)
- Agenda ROBO 247 - Robotic Applications Week #12: DC Motor Control Cont'dDocument30 pagesAgenda ROBO 247 - Robotic Applications Week #12: DC Motor Control Cont'dŘājinderRajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Star Delta StaretrDocument22 pagesAutomatic Star Delta StaretrRiya Priyadarshni80% (5)
- Introduction To Measuring Instruments: Unit-IDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Measuring Instruments: Unit-IGangula Praneeth ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- ECNG-4010 Lecture 05Document37 pagesECNG-4010 Lecture 05Abel BatuPas encore d'évaluation
- BVCDocument4 pagesBVCD SPas encore d'évaluation
- LopDocument4 pagesLopD SPas encore d'évaluation
- Line Frequency But Also in The Lower Audio Frequency RangeDocument14 pagesLine Frequency But Also in The Lower Audio Frequency RangeNmg KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration MeasurementDocument26 pagesUnit 5 Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Measurementbhuyanuttam7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3 19BME069Document14 pagesTutorial 3 19BME06920BME005 INAM SABRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Machines VocabularyDocument2 pagesClass Machines VocabularyAli AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Power Generation and Excitation SystemDocument20 pagesElectric Power Generation and Excitation SystemMansen NsubugaPas encore d'évaluation
- Charging Systems For AutomobilesDocument56 pagesCharging Systems For AutomobilesIshu PattanayakPas encore d'évaluation
- D3.2 ActuatorsDocument9 pagesD3.2 ActuatorsTanya AayogPas encore d'évaluation
- (I) AC and DC Tachometer Generators (Ii) Drag Cup Rotor AC (Iii) Photo-Electric Tachometer (Iv) Stroboscopic MethodsDocument7 pages(I) AC and DC Tachometer Generators (Ii) Drag Cup Rotor AC (Iii) Photo-Electric Tachometer (Iv) Stroboscopic Methodsamritsaikias4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - IIDocument35 pagesUnit - IIthota nagajyothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamometer and Power Measurement: Work DoneDocument20 pagesDynamometer and Power Measurement: Work Donejung bi100% (3)
- 7 - Control of Electrical DriveDocument23 pages7 - Control of Electrical DriveRamadhani100% (1)
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument40 pagesMeasuring InstrumentsDndjsjwjsjPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motor: Motors Motor Motors Motors Motors MotorDocument6 pagesDC Motor: Motors Motor Motors Motors Motors MotorAvd KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iv: Energy Audit Instruments and Energy Efficient MotorsDocument16 pagesUnit - Iv: Energy Audit Instruments and Energy Efficient MotorsNmg KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Alat Ukur AnalogDocument12 pagesAlat Ukur Analogmuhammad zidan abdillahPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction MotorDocument43 pagesInduction MotorJanine Jade SetiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Protective RelaysDocument60 pagesProtective RelaysAnkit JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Important TermsDocument45 pagesImportant TermsrameshsmePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 - AC MotorsDocument33 pagesChapter 13 - AC MotorsjalilemadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Instruments: 3 Sem Department of Electrical Engineering Atmiya Institute of Tech. & Science, RajkotDocument30 pagesMeasuring Instruments: 3 Sem Department of Electrical Engineering Atmiya Institute of Tech. & Science, RajkotRaison D EtrePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Presentation: Electrical Drive Systems Presenter: Azmat Ali Matriculation Num: 441430 Topics: AC Motor & Full Wave RectifierDocument22 pagesLab Presentation: Electrical Drive Systems Presenter: Azmat Ali Matriculation Num: 441430 Topics: AC Motor & Full Wave RectifierAhmed IshaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument33 pagesSynchronous Motorvnyshreyas100% (2)
- Industrial Motor Control: Control Devices Control Diagram Starting MethodDocument51 pagesIndustrial Motor Control: Control Devices Control Diagram Starting MethodMuhd Izwan Ikhmal Rosli100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Prime MoversDocument90 pagesChapter 2 Prime Moversaimi wahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit II-NOTES For IA1Document30 pagesUnit II-NOTES For IA1anks202Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Instruments: By: Sajid Hussain QaziDocument30 pagesMeasuring Instruments: By: Sajid Hussain Qaziurvish_soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Starting Methods of Syncronous Motor Criollo - RoggerDocument7 pagesStarting Methods of Syncronous Motor Criollo - RoggerRogger FabricioPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsDocument19 pagesPower Supply Description:: The Power Supply Circuit Comprises of Four Basic PartsEr. Piush Jindal100% (1)
- An Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterDocument5 pagesAn Application of Matlab/Simulink For Speed Control of DC Series Motor Using Buck ConverterArghya MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 06 - Protective Relay PDFDocument25 pagesLecture 06 - Protective Relay PDFEmdadul Hoq Rakib100% (1)
- Spa 2Document4 pagesSpa 2millionPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Gary Eye 1 CN1123631ADocument4 pagesGary Eye 1 CN1123631AGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Case A in kVARDocument1 pageTest Case A in kVARGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Gary Eye 2 CN103784573ADocument6 pagesGary Eye 2 CN103784573AGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Case A in KWDocument1 pageTest Case A in KWGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Star Sequence-of-Operation) : 0 KV 0 25.036 Ka - 84. 29 0 KV 0 25.036 Ka - 84. 29Document1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Star Sequence-of-Operation) : 0 KV 0 25.036 Ka - 84. 29 0 KV 0 25.036 Ka - 84. 29Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarDocument1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Case A With Panel - !Document1 pageTest Case A With Panel - !Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Ggivadan Shot CircuitDocument1 pageGgivadan Shot CircuitGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVDocument1 pageOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Givdan Load FlowDocument1 pageGivdan Load FlowGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Drag DropDocument1 pageDrag DropGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Spore Solar StatisticsDocument1 pageSpore Solar StatisticsGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen SpecDocument1 pageGen SpecGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental ElectricDocument1 pageFundamental ElectricGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Phase TransformerDocument1 page3 Phase TransformerGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel ScheduleDocument2 pagesPanel ScheduleGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDocument1 pagePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Acting LimiterDocument1 pageFast Acting LimiterGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Speed Math RotateDocument1 pageSpeed Math RotateGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDocument1 pagePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Switchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryDocument1 pageSwitchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- GG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitDocument1 pageGG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Phase Transformer PDFDocument115 pages3 Phase Transformer PDFGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- TX Impedance Reader9382Document1 pageTX Impedance Reader9382Gary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Isolator GGDocument1 pageIsolator GGGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Generator RoomDocument1 page3D Generator RoomGary GohPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Alectro.ca: Freezer / Fridge Door Alarm With Adjustable Delay Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesWWW - Alectro.ca: Freezer / Fridge Door Alarm With Adjustable Delay Installation InstructionsAnna AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 633 Volt Ohm Milliammeter Weston F3742 R4 3 1976Document36 pagesModel 633 Volt Ohm Milliammeter Weston F3742 R4 3 1976jimPas encore d'évaluation
- 497 500, Tesma503, IJEASTDocument4 pages497 500, Tesma503, IJEASTLarry Nelson BorbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cordex 48-1.2kW Rectifier Shelf System: Technical Guide: 010-619-J0 Effective: 10/2018Document88 pagesCordex 48-1.2kW Rectifier Shelf System: Technical Guide: 010-619-J0 Effective: 10/2018jcolmosmora5212Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hytera MT680 Plus F1&F3&F4&F5 Service Manual V01 - EngDocument772 pagesHytera MT680 Plus F1&F3&F4&F5 Service Manual V01 - EngHytera MNC580Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Acid Batteries Installation GuideDocument2 pagesLead Acid Batteries Installation GuideBernardo Mikjhael Mamani IñiguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Enhanced Physical Interface With Selectable Slew-RateDocument22 pagesLocal Interconnect Network (LIN) Enhanced Physical Interface With Selectable Slew-RateDanny Alexander Bodegas pinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Diagnosis Technique - BRDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Diagnosis Technique - BRSadrina MahamudPas encore d'évaluation
- Ical Theory: Electric Charge: Path To GroundDocument4 pagesIcal Theory: Electric Charge: Path To GroundMD TANVIR HOSSAINPas encore d'évaluation
- FJ SM Aryg30-36lmle Aoyg30-36letlDocument24 pagesFJ SM Aryg30-36lmle Aoyg30-36letlMiguel SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2sop EpflDocument2 pages2sop EpflAli Sanadi100% (1)
- Absolute Rotary EncoderDocument4 pagesAbsolute Rotary EncoderRezaadityamuhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deye On Grid 10KW Data Sheet BIS ApprovedDocument2 pagesDeye On Grid 10KW Data Sheet BIS Approvedkathiravan muruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Timer ML-095052-CTDocument7 pagesTimer ML-095052-CTAbdul BasitPas encore d'évaluation
- Canon Reset ManualDocument11 pagesCanon Reset ManualJames GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 1: Short Line InvestigationDocument19 pagesExperiment No. 1: Short Line InvestigationJoseph VitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.ManimegalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three: Operation of Auto Recloser and Sectionalizer 3.1.Document14 pagesChapter Three: Operation of Auto Recloser and Sectionalizer 3.1.Umar Wijaksono100% (1)
- Achieva 1.5T Pulsar SEDocument3 pagesAchieva 1.5T Pulsar SEISRAEL MATEOS GARCIA-SALAMANCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Lab Experiments On Fault Diagnosis of Combintional Circuits 2021Document4 pagesRevised Lab Experiments On Fault Diagnosis of Combintional Circuits 2021Melsougly BrycePas encore d'évaluation
- 34 Samss 625 PDFDocument23 pages34 Samss 625 PDFFlorin Daniel AnghelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Evolution of Traditional To New Media: Module in Media and Information LiteracyDocument13 pagesThe Evolution of Traditional To New Media: Module in Media and Information LiteracyJoiemmy Sumedca Bawengan GayudanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem-1 FOOD CHEMISTRY AND NUTRITIONDocument24 pagesSem-1 FOOD CHEMISTRY AND NUTRITIONSubhankar MaityPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Example 5 With MATLABDocument4 pagesSolution To Microwave Engineering Pozar Chapter 14 Example 5 With MATLABJohn Bofarull GuixPas encore d'évaluation
- URIT 5160 Service ManualDocument50 pagesURIT 5160 Service ManualIngenieria IngeLabPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesClass 12 Physics Investigatory Projectdjjeena619Pas encore d'évaluation
- Panasonic tx-28ld2c (ET)Document8 pagesPanasonic tx-28ld2c (ET)Ricardo DolcePas encore d'évaluation
- New Final Major Project Exam ReportDocument21 pagesNew Final Major Project Exam ReportAruna ParekhPas encore d'évaluation
- Specification: Generator Circuit Breaker SystemsDocument11 pagesSpecification: Generator Circuit Breaker SystemsThangarajan NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reduced Modified T-Type Topology For Cascaded Multilevel InvertersDocument8 pagesReduced Modified T-Type Topology For Cascaded Multilevel Inverterssilky jainPas encore d'évaluation