Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rd2 White Paper
Transféré par
yildyusufCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rd2 White Paper
Transféré par
yildyusufDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Planetary VS Cycloid
A planetary gearbox is comprised of
three members: a sun gear, multiple
satellite or planet gears (hence the
gearboxs name), and an internal ring
gear.
A cycloidal gearbox (or cycloidal
reducer) is comprised of four
components: the input shaft, a
cycloidal cam (single or
compound), cam followers, and
an output shaft.
page 1
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Planetary gearboxes
A planetary gearbox is comprised of three members: a SUN gear, multiple satellite or PLANET gears, and an
internal ring gear. The input shaft attaches to the sun gear, which transmits rotational motion to the planet gears,
which in turn rotate the internal RING gear, which is part of the gearbox housing. Planet gears rotate on rigid
shafts attached to a plate called a planet carrier; this rotation of the planet carrier is what causes the output shaft
to rotate. As with all mechanical speed reduction, this gives the output shaft a lower rotational speed and higher
torque than the input shaft. Planetary gearboxes may also be single- or double-reduction, with reduction ratios
ranging from 3:1 to over 100:1. Additional stages can be added for even higher reduction, or to change output
shaft orientation (i.e. via bevel gearing, miter gearing, etc.).
page 2
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Cycloidal gearboxes
A cycloidal gearbox (or cycloidal reducer) is
comprised of four components: the input shaft, a
cycloidal cam (single or compound), cam followers,
and an output shaft. The input shaft attaches to a
drive member that induces an eccentric rotation of
the cycloidal cam; in compound reducers, the first
cycloidal cam engages a second cycloidal cam
(double reduction), which may then engage a third
cycloidal cam (triple reduction). The cam followers
act as gear teeth, and will exceed the number of
cam lobes. Cycloidal gearboxes offer ratios from as
low as 10:1 to over 300:1 without stacking stages in
the manner of a planetary gearbox, and thus
cycloidal gearboxes may have a more compact
footprint. A typical cycloidal gear is seen here:
page 3
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
The drive or servomotor is
connected to the spur gear stage
of the gearbox via a pinion.
The first reduction gears are connected to crankshafts which
drive the cams using needle bearings. These cams rotate
inside the case which is lined with pins.
page 4
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Planetary VS Cycloid
Planetary Gears may run at higher
speeds.
Cycloidal Gears are very good for extremely heavy
loads.
Planetary Gears will work with very low
Ratios.
Cycloidal Gears work at higher ratios allowing them to be driven with less
power.
Planetary Gears are good if positioning accuracy and lost motion are not a
concern.
Cycloidal Gears are best in applications for high positioning accuracy and a
minimum lost motion is required.
Planetary Gears are ok if regular monthly maintenance is acceptable for the
application.
Cycloidal Gears are best if little maintenance and long gear life are
required.
page 5
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Things to consider when choosing a Gearbox.
After many years developing Cycloidal Gears our engineers have created some basic
questions to help you in the beginning steps of selecting a gearbox for your
application.
What environmental conditions will gear box need to endure? (Operating
temperature, dust, moisture exposure, ect.)
What physical size envelope does your gear box need? (any shape or space
requirements)
Maintenance and lubrication access? (After the application is assembled how will
you maintain the gear box?)
page 6
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
How much torque do you require to do the work required by the application?
(Weight it needs to move.)
What if any, speed requirement does the application require? (How
fast you need the gear box to go.)
Angle of the gearbox mounting? (Horizontally ,vertically or angled.)
Moment rigidity? (Weight deflection of the gear box shaft due to the fixture
and work load.)
Torsional rigidity? (Shaft deflection, stopping and starting the application
load.)
page 7
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Momentary Maximum allowable torque? (Worst case
E-stop condition with a load.)
What kind of duty cycle will the Gear box have? (Hours
of operation and number of days per week.)
page 8
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
Description
Ferris Wheel
Positioner
Major
Minor
Center of Gravity
12 off center max
Center of Gravity
12 off center max
60
5000 lb
5000 lb
page 9
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
page 10
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
page 11
White Papers
MOTION CONTROL, INC.
page 12
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- User Manual - SOLAS - Rescue - Boat - Type - IRB - EN - 20190813 PDFDocument167 pagesUser Manual - SOLAS - Rescue - Boat - Type - IRB - EN - 20190813 PDFyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Assessment Exam 03 1Document7 pagesAssessment Exam 03 1Andrea Magtuto100% (1)
- Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 8Document8 pagesHybridization of Atomic Orbitals 8Vikas SinghPas encore d'évaluation
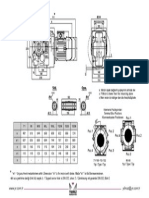
- DR272.0E DR273.0E: Klemens PozisyonlarıDocument1 pageDR272.0E DR273.0E: Klemens PozisyonlarıyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Manual Timing BeltsDocument124 pagesTech Manual Timing BeltsyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- MR272 MR273: Opsiyonel Flanş Ölçüleri / Optional Flange Dimensions / Auswählbare FlanschabmessungenDocument1 pageMR272 MR273: Opsiyonel Flanş Ölçüleri / Optional Flange Dimensions / Auswählbare FlanschabmessungenyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
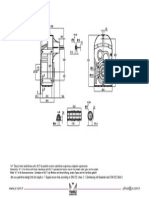
- Std. Ops.: X:wen Motor Ist Nidriger Den Die AnschlußplatteDocument1 pageStd. Ops.: X:wen Motor Ist Nidriger Den Die AnschlußplatteyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Abmessungsseiten: Ölçü SayfalarıDocument1 pageAbmessungsseiten: Ölçü SayfalarıyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Inhaltsverzeichnis: IndexDocument312 pagesInhaltsverzeichnis: IndexyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- DT772 00Document1 pageDT772 00yildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- General Information: EinführungDocument1 pageGeneral Information: EinführungyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- KaynaklarDocument2 pagesKaynaklaryildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Oiyce0103 0909 PDFDocument35 pagesOiyce0103 0909 PDFyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- PlumbingDocument62 pagesPlumbingyildyusuf100% (2)
- Stress Analysis INVENTORDocument266 pagesStress Analysis INVENTOROvidiu67% (6)
- KettenHandbuch E Iwis ChainDocument86 pagesKettenHandbuch E Iwis ChainKiran Kumar K TPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Planetary Gears PDFDocument7 pagesOptimizing Planetary Gears PDFyildyusuf100% (1)
- Scuffing PDFDocument32 pagesScuffing PDFyildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Planetary Gears PDFDocument7 pagesOptimizing Planetary Gears PDFyildyusuf100% (1)
- MDK1Document1 pageMDK1yildyusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Relativity: Einstein Messes With Space and TimeDocument18 pagesSpecial Relativity: Einstein Messes With Space and TimeKýñg ButlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Try This!: Subtyp Es Subtyp EsDocument3 pagesScience Try This!: Subtyp Es Subtyp Esrr100% (1)
- Pressure Drop CalculationDocument13 pagesPressure Drop CalculationknsaravanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5348 Chapter7 10Document46 pages5348 Chapter7 10Nihir PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Control, Basic Course FRTF05: ReglerteknikDocument6 pagesAutomatic Control, Basic Course FRTF05: ReglerteknikAl-ShukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tensile Splice ACI 350-06Document4 pagesTensile Splice ACI 350-06YioYinPas encore d'évaluation
- Bethe Lattice PaperDocument13 pagesBethe Lattice PaperArdani MunaqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Exploration Technique and ProcessingDocument211 pagesSeismic Exploration Technique and ProcessingDimas PradanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundSenica Caydil Jay D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moment Redistribution in BeamsDocument12 pagesMoment Redistribution in BeamsChukwuka WayemeruPas encore d'évaluation
- General Specification For Mass Flow MeterDocument138 pagesGeneral Specification For Mass Flow MeterRenalyn TorioPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 MB Moment Area TheoremDocument10 pages11 MB Moment Area Theoremkenny liePas encore d'évaluation
- The Polar DiagramDocument7 pagesThe Polar DiagramJason RossPas encore d'évaluation
- Karpagam University, Coimbatore - 641 021 Department of Physics I MSC Physics (15Php103) Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsDocument35 pagesKarpagam University, Coimbatore - 641 021 Department of Physics I MSC Physics (15Php103) Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsporseenaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEC 60793-1-30-2001 Fibre Proof TestDocument12 pagesIEC 60793-1-30-2001 Fibre Proof TestAlfian Firdaus DarmawanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - 1 Introduction To Heat TransferDocument15 pages4 - 1 Introduction To Heat TransferHassam khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: The Second Law of Thermodynamics: in A Cyclic ProcessDocument42 pagesChapter 5: The Second Law of Thermodynamics: in A Cyclic Processأحمد صلاح الدينPas encore d'évaluation
- Forced Response of Swirl Stabilized Flames in Hydrogen Enriched Gas TurbinesDocument129 pagesForced Response of Swirl Stabilized Flames in Hydrogen Enriched Gas TurbinesLi-An DingPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) in PharmaceuticalsDocument21 pagesOperation and Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) in PharmaceuticalsMd Tayfuzzaman100% (1)
- Motion Along A Straight Line (Past-Year Questions) : 1. SPM 2003 P2 Q12Document2 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line (Past-Year Questions) : 1. SPM 2003 P2 Q12Muhammad Redzuan SaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- GodaDocument22 pagesGodaLazaros NtoanidisPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Procedure For Two Phase SeparatorsDocument6 pagesDesign Procedure For Two Phase Separatorsmadx222222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Finite Element Method in Structural EngineeringDocument8 pagesApplications of Finite Element Method in Structural Engineeringdennis khisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jss 2 Basic Technology JSS 2 Third Term Examination - Marvel LearnDocument1 pageJss 2 Basic Technology JSS 2 Third Term Examination - Marvel LearnTriple Jay COC100% (1)
- 02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214Document20 pages02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214kltowerPas encore d'évaluation
- Aashto M332-14Document8 pagesAashto M332-14tony juarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Coefficient of ViscosityDocument16 pagesCoefficient of ViscosityDaksh ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation and Control Systems 2 Mid Online BitsDocument8 pagesInstrumentation and Control Systems 2 Mid Online BitstslnarayanaPas encore d'évaluation