Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Multi View Projection
Transféré par
py ongDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Multi View Projection
Transféré par
py ongDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Multiview Projection Drawing
Sr Dr Md Azree Othuman Mydin
azree@usm.my
Sub-topics
Multiview Projection
6 Principle Views
Rules of Orthographic Projection
Principle Views
Glass Box
Line Types
Example Orthographic Projection
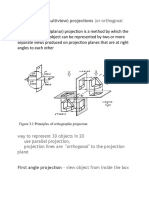
Orthographic Projection
Orthographic Projections are a collection of
2-D drawings that work together to give an
accurate overall representation of an object.
Six Principle Views
The 6 views of
projection include:
FRONT
RIGHT SIDE
TOP
BOTTOM
LEFT SIDE
REAR
Rules of Orthographic Drawing
Pick a Front View that is most descriptive
of object, normally the longest dimension
is chosen as the width (or depth)
Most common combination of views is to
use are Front, Top, and Side View
Principle Views
Front, Right Side
and Top are
views that simply
represented by
rotating the
object
Glass Box
Most powerful technique to
understand orthographic projections
Suspend the object with transparent
strings inside a glass box
Freeze the view from each direction
(each of the six sides of the box) and
unfold the box
Glass Box
Glass Box
Glass Box
Glass Box
Glass Box
Glass Box
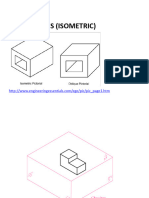
Front, Side and Top Views
Width
Top View
Front
View
Depth
Right
Side
View
Heigh
t
Line Types
Visible Lines used to represent features that are seen in
the current view
Hidden Lines used to represent features that cannot be
seen in the current view
Centerlines used to represent symmetry and to mark the
center of circles and the axes of cylinders, and the axes of
symmetrical parts, such as cylinders and bolts
Example
1. Visible
2. Hidden
3. Center
Drawing the Views
To complete an orthographic
projection drawing follow
these steps.
Step 2:
Space the top view 25-40 mm above
the front view. Lightly construct the
top view directly over the front view.
Extend the lower side of the top view
to intersect a vertical line drawn to
the right of the front view.
25-40 mm
Step 1:
Lightly construct the front view.
Drawing the Views
Step 3:
Project the features of the front view to the right
of the vertical line. Draw a line at 45o from the
point of intersection as shown.
The use of a 45o mitre
line helps to project
features from the top
view to the side view.
Drawing the Views
Step 4:
Where the horizontal projection lines of the top view
intersect with the mitre line, draw vertical projection
lines to the side view.
Drawing the Views
Step 5:
Erase all unnecessary lines. Complete the finished
linework to complete the required orthographic
views. Add the necessary information into the
title block.
Spacing Orthographic Views
To determine the starting point of your drawing use the following criteria:
to find X:
Measure the horizontal distance between borders
Subtract the total length of the views to be drawn
Divide the result by 2
(HSA)
(HSN)
HSA HSN = ? 2
to find Y:
Measure the vertical distance between borders
Subtract the total height of the views to be drawn
Divide the result by 2
VSA VSN = ? 2
(VSA)
(VSN)
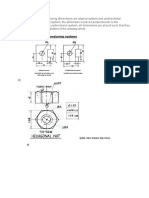
Spacing Orthographic Views
Distance between borders HSA 260
Length
120
Space
40
Width
38
56
120
38
31
(HSA) (HSN) = ? 2 =
260
120
+ 40
+ 38
198
= 62
2 = 31
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Teacher's Resource Book 1Document248 pagesTeacher's Resource Book 1Fazi Imi62% (13)
- Draw Better: Learn To Draw With ConfidenceDocument26 pagesDraw Better: Learn To Draw With ConfidencebackitPas encore d'évaluation
- ME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFDocument64 pagesME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFRamesh Jangala100% (1)
- Isometric: Topics Covered in This Lesson: Orthographic Drawing Techniques in Autocad What Is Orthographic Projection?Document24 pagesIsometric: Topics Covered in This Lesson: Orthographic Drawing Techniques in Autocad What Is Orthographic Projection?Genelyn caritosPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Unit 3 Notes and Practice PDFDocument57 pagesGeometry Unit 3 Notes and Practice PDFSHAWANDA MCCULLOUGHPas encore d'évaluation
- GENG 111 - Lecture 05 - Orthographic ProjectionDocument38 pagesGENG 111 - Lecture 05 - Orthographic ProjectionNaeem NasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson2 Orthographicdrawing Tdj3m0 120227180553 Phpapp01Document22 pagesLesson2 Orthographicdrawing Tdj3m0 120227180553 Phpapp01Yatin NgadiyonoPas encore d'évaluation
- LE 8 Drafting (3rd Quarter)Document26 pagesLE 8 Drafting (3rd Quarter)Edrian Angelo KoPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthographic ProjectionDocument44 pagesOrthographic ProjectionAzizi YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multi View OrthographicDocument26 pagesMulti View Orthographicamitha AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing Meng 2203: Teshome Bogale May 2021Document41 pagesEngineering Drawing Meng 2203: Teshome Bogale May 2021Abdi ZerihunPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - Orthographic ProjectionDocument56 pagesLecture 5 - Orthographic ProjectionLaiba KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Architectural Drawing SystemsDocument13 pagesArchitectural Drawing SystemsHerbert Allan GarelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Draw Better SampleDocument26 pagesDraw Better SampleSimona DumitruPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing IsometricDocument16 pagesEngineering Drawing Isometricpanashezhou321Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2D EssentialsDocument70 pages2D EssentialsTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluepring ReadingDocument54 pagesBluepring ReadingElcam ScreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Best DRG Practices Presentation - 1Document44 pagesBest DRG Practices Presentation - 1Sri NavinPas encore d'évaluation
- 008-Orthographic Projection (Detailed)Document27 pages008-Orthographic Projection (Detailed)Stevie NicksPas encore d'évaluation
- Pp-Chapter 5 Technical Sketching and Shape DescriptionDocument39 pagesPp-Chapter 5 Technical Sketching and Shape Descriptionapi-241720955Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drafting: Orthographic and Isometric DrawingsDocument7 pagesDrafting: Orthographic and Isometric DrawingsrosesforliliesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-Multiview DrawingsDocument58 pagesChapter 3-Multiview DrawingsamdevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthographic Projections - ModifiedDocument58 pagesOrthographic Projections - ModifiedSalah Ud DinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4: Isometric and ObliqueDocument28 pagesChapter 4: Isometric and Obliquehisham_eyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ortographic DrawingDocument71 pagesOrtographic DrawingCiro FerrariPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories and Principles of Orthographic ProjectionDocument19 pagesTheories and Principles of Orthographic ProjectionZab50% (2)
- Chapter 6 - ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONDocument35 pagesChapter 6 - ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONHumberto AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Design and RealizationDocument25 pagesProduct Design and RealizationScribdman ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFEngr Muhammad Asif JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- TDDocument10 pagesTDNathan ElliotPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsDocument47 pagesOrthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsLeo Dev WinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Design and Graphics: Engineer 1C03Document44 pagesEngineering Design and Graphics: Engineer 1C03lebronPas encore d'évaluation
- CAD Lab ManualDocument45 pagesCAD Lab ManualAmul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 002 Principles of Orthographic Projection MN112 PDFDocument55 pages002 Principles of Orthographic Projection MN112 PDFMbarouk Shaame MbaroukPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Orthographic Multi Vew 1Document59 pages3 Orthographic Multi Vew 1ArDaveAnandPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st & 3rd Angle ProjectionsDocument23 pages1st & 3rd Angle ProjectionsSaadii RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Drawing - BasicsDocument38 pagesTechnical Drawing - Basicsbasarica100% (2)
- Draw Better Learn To Draw With Confidence Dominique AudetteDocument26 pagesDraw Better Learn To Draw With Confidence Dominique Audettesaioa plastikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Isometric DrawingDocument38 pagesIsometric DrawingSanthan SalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson02 Sketching Ortho IsoDocument32 pagesLesson02 Sketching Ortho IsoRanjith AddagallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Isometric DrawingDocument89 pagesIsometric DrawingAina MiswanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing - Chapter FiveDocument35 pagesEngineering Drawing - Chapter FiveEmmanuel EduafulPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGR1025U - Winter 2023 Lecture 3Document51 pagesENGR1025U - Winter 2023 Lecture 3ronald.onyiorahPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide Set 2 - Orthographic Projection - Third Angle ProjectionDocument36 pagesSlide Set 2 - Orthographic Projection - Third Angle ProjectionRahul Gupta0% (1)
- Orthographic ProjectionDocument51 pagesOrthographic ProjectionAjit ParwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- WK 4 6Document8 pagesWK 4 6padayaojonsamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-5 ReviewDocument196 pagesChapter 1-5 Reviewnurulsakinah97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Engineering Design Study GuideDocument14 pagesIntro To Engineering Design Study GuideMadeline Rice57% (7)
- Overview of 1st Angle and 3rd AngleDocument14 pagesOverview of 1st Angle and 3rd AngleM SureshPas encore d'évaluation
- W Engineeringdrawing 74 160Document87 pagesW Engineeringdrawing 74 160nkuepdisignerPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiview Orthographic DrawingDocument23 pagesMultiview Orthographic DrawingJessica LucenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review For Exam 2.1Document6 pagesReview For Exam 2.1Quân Bảo100% (1)
- A Drawing Is Made Up of Different LinesDocument35 pagesA Drawing Is Made Up of Different LinesIP GPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7: MultiviewsDocument10 pagesChapter 7: Multiviewsapi-25981522Pas encore d'évaluation
- Isometrics - CcoryDocument27 pagesIsometrics - Ccorynaik4u2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- DWG - Lec 02Document40 pagesDWG - Lec 02Muhammad FARHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventor 3Document30 pagesInventor 3Mai Van DongPas encore d'évaluation
- MM101-w-2-Lecture 2Document29 pagesMM101-w-2-Lecture 2Rahul NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2-Theory of ProjectionDocument57 pagesChapter 2-Theory of ProjectionamdevaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1) The Two Systems of Placing Dimensions Are Aligned System and UnidirectionalDocument11 pages1) The Two Systems of Placing Dimensions Are Aligned System and Unidirectionalrahul m nairPas encore d'évaluation
- Sketching TechniquesDocument24 pagesSketching Techniquesapi-31812472Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Guide to Drawing: Perspective & CompositionD'EverandEssential Guide to Drawing: Perspective & CompositionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Template For Preparation of Manuscripts: IcwsaudDocument4 pagesTemplate For Preparation of Manuscripts: Icwsaudpy ongPas encore d'évaluation
- REG 562 Building Services TechnologyDocument15 pagesREG 562 Building Services Technologypy ongPas encore d'évaluation
- Banner For PrintingDocument1 pageBanner For Printingpy ongPas encore d'évaluation
- Banner For PrintingDocument1 pageBanner For Printingpy ongPas encore d'évaluation
- WORKSHEET-understanding Quadrilaterals - Class 8Document12 pagesWORKSHEET-understanding Quadrilaterals - Class 8Manoj Pandey50% (2)
- Grade 8 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGrade 8 ReviewerMario Recto50% (2)
- Free Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadDocument1 pageFree Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadLeonardo AguileraPas encore d'évaluation
- Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and TransversalDocument36 pagesAngles Formed by Parallel Lines and TransversalHanna Grace Honrade100% (1)
- Sangram Classes CIRCULAR MOTION IIT JEE NOTESDocument15 pagesSangram Classes CIRCULAR MOTION IIT JEE NOTESprem19999Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACT Test1Document12 pagesACT Test1Clay BowmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Balt92 05 PDFDocument159 pagesBalt92 05 PDFeisatoponPas encore d'évaluation
- Lines and Angle CL 9Document10 pagesLines and Angle CL 9Tanishq AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - CirclesDocument24 pagesModule 2 - CirclesjeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg. MechanicsDocument29 pagesEngg. MechanicsSunand Pongurlekar100% (1)
- Projectile Motion NotesDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Notesdou86Pas encore d'évaluation
- My PPT On ConstructionsDocument37 pagesMy PPT On ConstructionsPedup Dukpa100% (4)
- Chapter 2-Phy220Document55 pagesChapter 2-Phy220Jordan TuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Revolutions in Physics and The Second Quantum RevolutionDocument24 pagesFour Revolutions in Physics and The Second Quantum Revolution똑금물Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Analysis of Rhombic Dodecahedron (Catalan Solid) Applying HCR's Theory of PolygonDocument11 pagesMathematical Analysis of Rhombic Dodecahedron (Catalan Solid) Applying HCR's Theory of PolygonHarish Chandra Rajpoot100% (1)
- Combining Error Ellipses: John E. DavisDocument17 pagesCombining Error Ellipses: John E. DavisAzem GanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cox, L. (2015) - Scholarship and Activism A Social Movements Perspective. Studies in Social Justice, 9Document21 pagesCox, L. (2015) - Scholarship and Activism A Social Movements Perspective. Studies in Social Justice, 9irene MPas encore d'évaluation
- MasteringPhysics - Assignment 7 Motion in 2-DDocument5 pagesMasteringPhysics - Assignment 7 Motion in 2-DStrange Sht100% (1)
- Angry Birds Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesAngry Birds Projectile MotionReza TarmuziPas encore d'évaluation
- Classnote 50ca22ef04818Document24 pagesClassnote 50ca22ef04818Puneet GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Lecture Notes (Kinematics) - Part1Document35 pagesChapter 5 - Lecture Notes (Kinematics) - Part1akash kahsyapPas encore d'évaluation
- LP Mam TambongDocument9 pagesLP Mam TambongGladys Degones GuillerPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Let Trigonometry - pdf7Document7 pages8 Let Trigonometry - pdf7novey_casioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-Two Part 1Document26 pagesChapter-Two Part 1Wiz Nati XvPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1.4 Linear MotionDocument9 pages1.1.4 Linear MotionMohammad Jahangir AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Zemansky - 13va Edición (Solucionario) (1-400) PDFDocument10 pagesZemansky - 13va Edición (Solucionario) (1-400) PDFJar05Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4 Force System ResultantDocument50 pagesCH 4 Force System ResultantSyahrul Nizam AnuarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclic QuardilateralDocument5 pagesCyclic Quardilateralapi-3731257Pas encore d'évaluation