Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-Base Titrations
Transféré par
Crockington0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
90 vues2 pagesExperiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-base Titrations
Titre original
04112015 Experiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-base Titrations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentExperiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-base Titrations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
90 vues2 pagesExperiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-Base Titrations
Transféré par
CrockingtonExperiment 2 - Investigation of Acid-base Titrations
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Daniel Crockett Group 2, Cupboard 28
04/11/2015 EXPERIMENT 2 - INVESTIGATION OF ACID-BASE TITRATIONS
OBJECT Compare the curve of pH against titre volume for strong and weak electrolytes. Also assess
which indicator should be used for a weak electrolyte titration by experimentation.
THEORY A potentiometer calculates, by electrical conductivity, the hydrogen ion concentration. We
use this to track the pH of the solution against the volume of acidic titrant added to the alkaline titrand.
PROCEDURE
Add 25ccm of alkaline titrand to beaker, on top of magnetic stirrer platform. Position potentiometer
under the surface of the liquid. Place coated ferrous stirrer in the beaker. Ensure the arc of the
spinning stirrer does not breach the delicate potentiometer. Activate magnetic stirrer and turn on
potentiometer. Titrate the titrand slowly with the titrant. Record data (pH versus volume of titrant
added) at appropriate intervals so that a nice curve can be achieved when the data is plotted on an
XY graph. Carry out these steps for both the titration of 0.1M NaOH with 0.1M HCl, and the titration of
0.1M NaOH with 0.1M ethanoic acid.
Then fill beaker with 25ccm of 0.1M of NaOH. Do not use the Potentiometer this time, instead
add a drop of indicator solution. Titrate with 25ccm of 0.1M ethanoic acid. Comment on colour change
and assess suitability of the candidate indicators for this titration. Carry out this experiment using both
Methyl Red and Phenolphthalein indicators.
RESULT
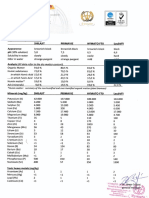
HCl titrating NaOH, and Ethanoic acid titrating NaOH see graph on separate sheet. Curves plotted
on the same axes. pH against volume titrant added to 25ccm titrand (all in 0.1mol/litre concentration).
The indicator Methyl Red did not change colour. The equivalence point of Ethanoic acid and
NaOH is greater than seven because the acid is weak and the base is strong, this is why the colour
change did not occur. The Phenolphthalein changed to red when ~24.5ccm of Ethanoic acid was
added.
>FULL TABLE OF RESULTS DOES NOT FIT ON THIS PAGE, SEE OTHER SIDE
>CURVES FOR POTENTIOMETER-TRACKED TITRATIONS IS ON A THIRD PAGE
CALCULATIONS None
CONCLUSION
The pH displayed on the potentiometer was similar for both acids titrating NaOH because they are
both monoprotic, and as such the same number of moles achieves the same effect. It is only the
dissociation constant that differs. The pH where Phenolphthalein colour changes coincides with the
equivalence point. It is the best candidate for equivalence point indication.
Volume of HCl titrant
added/ccm
Volume of Ethanoic
acid titrant
added/ccm
pH
pH
12.98
12.56
12.97
12.55
12.91
12.54
12.88
12.52
12.82
12.5
10
12.74
12.48
12
12.66
12.45
14
12.56
12.42
15
12.51
12.38
16
12.44
12.34
17
12.36
10
12.29
18
12.28
11
12.24
19
12.19
12
12.19
20
12.11
13
12.13
21
11.98
14
12.07
22
11.8
15
11.97
22.5
11.7
16
11.89
23
11.53
17
11.78
23.2
11.44
18
11.63
23.4
11.35
19
11.38
23.6
11.23
20
10.83
23.8
11.05
20.5
10.44
24
10.86
21
10
24.2
10.65
21.5
9.62
24.4
10.41
22
8.44
24.6
10.15
22.5
6.84
24.8
9.92
23
6.39
25
9.46
23.5
6.07
25.2
8.95
24
5.97
25.4
7.18
25
5.71
25.5
7.03
26
5.57
25.6
6.85
27
5.43
25.8
6.52
28
5.32
26.5
6.2
29
5.22
27
6.08
30
5.15
27.5
32
5.03
34
4.94
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- S151929 - 20210127.indd KAO SURFACTANTESDocument12 pagesS151929 - 20210127.indd KAO SURFACTANTESAlfredo Méndez100% (1)
- Dishwashing Liquid FormulaDocument7 pagesDishwashing Liquid FormulaChendikato Pinas100% (4)
- Cement: Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesCement: Sample ProblemsFlorencePas encore d'évaluation
- So What Do You NeedDocument2 pagesSo What Do You NeedFoaad FoaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 24: CarbohydratesDocument46 pagesChapter 24: CarbohydratesYocca AsmaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Am in ADocument7 pagesAm in ARega LinzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 962 / 3 - Marking Scheme Section A (15 Marks)Document6 pagesChemistry 962 / 3 - Marking Scheme Section A (15 Marks)Khang Ni 康妮 FooPas encore d'évaluation
- NaphtaDocument2 pagesNaphtaVictor fajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- BALURAN Molecular CompoundsDocument15 pagesBALURAN Molecular CompoundsTito V. Bautista Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biomolecules PartDocument22 pagesBiomolecules PartYashPas encore d'évaluation
- Material FDIDocument10 pagesMaterial FDIAmy Lin ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic AcidsDocument28 pagesBiological Molecules: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic AcidsVinith PillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 5 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 5 - Acids, Bases and SaltsADARSH RAJ SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- Pat056021-Ep-Etd02 B1Document84 pagesPat056021-Ep-Etd02 B1Elitsa IvanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Shilajit-Primavie-HymatoF70-LaubVFI PDFDocument1 pageComparison Shilajit-Primavie-HymatoF70-LaubVFI PDFYousef WardatPas encore d'évaluation
- Percent API Content Per TabletDocument3 pagesPercent API Content Per TabletRey BrondaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Acid Base EquilibriaDocument3 pages2 Acid Base EquilibriaHayley Meek100% (1)
- Bromine Numbers of Petroleum Distillates and Commercial Aliphatic Olefins by Electrometric TitrationDocument9 pagesBromine Numbers of Petroleum Distillates and Commercial Aliphatic Olefins by Electrometric TitrationMr GhostPas encore d'évaluation
- A Genetic Model For Na-Carbonate Mineral Precipitation in The MioceneDocument13 pagesA Genetic Model For Na-Carbonate Mineral Precipitation in The MioceneYiğitcan AkyüzPas encore d'évaluation
- Synolac 1529 Ba 80Document2 pagesSynolac 1529 Ba 80I Love MusicPas encore d'évaluation
- JTBaker Solid Phase ExtractionDocument16 pagesJTBaker Solid Phase Extractionerminb1525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crate & Cage Cleaner: Non-Toxic Cleaner and Pet Odor Neutralizer in OneDocument1 pageCrate & Cage Cleaner: Non-Toxic Cleaner and Pet Odor Neutralizer in OneElsha Amalia PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Fr9-Link1, PL1, FR10-PL5Document4 pagesFr9-Link1, PL1, FR10-PL5Chan ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12.1 Gases in The Atmosphere (1C) QPDocument12 pages12.1 Gases in The Atmosphere (1C) QPSrijita RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Produksi Garam Dan Bittern Di Tambak Garam: Jurnal Kelautan Tropis July 2016Document6 pagesProduksi Garam Dan Bittern Di Tambak Garam: Jurnal Kelautan Tropis July 2016MitraArthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kimia-Analitik Analisa-Kation 16651 0Document13 pagesKimia-Analitik Analisa-Kation 16651 0Nur AidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Company Profile PT Tribhakti InspektamaDocument18 pagesCompany Profile PT Tribhakti InspektamaMaekel Abdul HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Checkpoint Revision Worksheet # 1Document2 pagesCheckpoint Revision Worksheet # 1Sana ShakeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Document9 pagesWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehPas encore d'évaluation
- HessPumice FactSheetDocument1 pageHessPumice FactSheetjhscribdaccPas encore d'évaluation