Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ME451: Control Systems Course Roadmap
Transféré par
Serdar BilgeDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ME451: Control Systems Course Roadmap
Transféré par
Serdar BilgeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Course roadmap
ME451: Control Systems
Modeling
Analysis
Laplace transform
Lecture 10
Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion
Transfer function
Models for systems
electrical
mechanical
electromechanical
Dr. Jongeun Choi
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Michigan State University
Linearization
Time response
Transient
Steady state
Frequency response
Bode plot
Stability
RouthRouth-Hurwitz
Nyquist
Design
Design specs
Root locus
Frequency domain
PID & LeadLead-lag
Design examples
(Matlab simulations &) laboratories
1
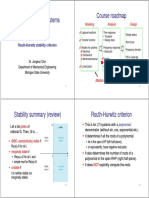
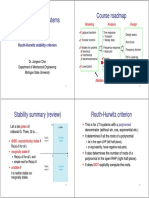
Stability summary (review)
Routh-Hurwitz criterion
This is for LTI systems with a polynomial
denominator (without sin, cos, exponential etc.)
It determines if all the roots of a polynomial
Let si be poles of
rational G. Then, G is
(BIBO, asymptotically) stable if
Re(si)<0 for all i.
marginally stable if
Re(si)<=0 for all i, and
simple root for Re(si)=0
unstable if
lie in the open LHP (left halfhalf-plane),
or equivalently, have negative real parts.
It also determines the number of roots of a
polynomial in the open RHP (right half-plane).
It does NOT explicitly compute the roots.
it is neither stable nor
marginally stable.
3
Polynomial and an assumption
Routh array
Consider a polynomial
From the given
polynomial
Assume
If this assumption does not hold, Q can be factored as
where
The following method applies to the polynomial
Routh array
(How to compute the third row)
Routh array
(How to compute the fourth row)
Routh-Hurwitz criterion
Example 1
Routh array
The number of roots
in the open right halfhalf-plane
is equal to
the number of sign changes
in the first column of Routh array.
Two sign changes
in the first column
Two roots in RHP
10
Example 2
Example 3
Routh array
Routh array
If 0 appears in the first column of a
nonzero row in Routh array, replace it
with a small positive number. In this
case, Q has some roots in RHP.
Two sign changes
in the first column
If zero row appears in Routh array, Q
has roots either on the imaginary axis
or in RHP.
No sign changes
in the first column
Two roots
in RHP
Take derivative of an auxiliary polynomial
(which is a factor of Q(s))
Q(s))
11
No roots
in RHP
But some
roots are on
imag.
imag. axis.
12
Example 4
Simple & important criteria for stability
1st order polynomial
Find the range of K s.t.
s.t. Q(s)
Q(s) has all roots in the left
half plane. (Here, K is a design parameter.)
Routh array
2nd order polynomial
No sign changes
in the first column
Higher order polynomial
13
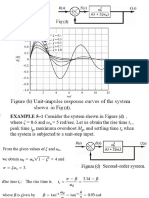
Examples
14
Summary and Exercises
All roots in open LHP?
Routh-Hurwitz stability criterion
Routh array
RouthRouth-Hurwitz criterion is applicable to only
Yes / No
polynomials (so, it is not possible to deal with
exponential, sin, cos etc.).
Yes / No
Next,
RouthRouth-Hurwitz criterion in control examples
Yes / No
Exercises
Yes / No
Read RouthRouth-Hurwitz criterion in the textbook.
Do Examples.
Yes / No
15
16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExDocument25 pagesECE317 L10 - RouthHurwitzExumarsaboPas encore d'évaluation
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapZafer GökPas encore d'évaluation
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapAiO VietnamPas encore d'évaluation
- Routh-Hurwtz Criterion & Root-Locus Criteria: Stability of Feedback Control SystemsDocument19 pagesRouth-Hurwtz Criterion & Root-Locus Criteria: Stability of Feedback Control Systemsember_memoriesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Document33 pages1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Tahmid ShihabPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisDocument59 pagesCs 8343 Stability Concept AnalysisCrescent MnyamaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesDocument37 pagesME3245 Spring 2023 Chapter 6 NotesK LugujePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6hari17101991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 - StabilityDocument42 pagesChapter 7 - Stabilityvenosyah devanPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshiDocument22 pagesRegulation and Control: by Tewedage SileshihermelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 14 StabilityDocument26 pagesLecture 14 StabilityHamza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture17 PDFDocument19 pagesLecture17 PDFAriesFranandaPanjaitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruth Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument22 pagesRuth Herwitz Stability CriterionMD MUSFIQUR RAHMANPas encore d'évaluation
- EE331 - L09 - Signals & SystemsDocument51 pagesEE331 - L09 - Signals & Systemsahmetyasinbulut99Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionDocument30 pages6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionJyotirmayee Panda100% (1)
- Lab Experiment 11Document10 pagesLab Experiment 11Sohail Afridi100% (1)
- Lab No. 4-System Stabilty Using Routh Table, Root LocusDocument4 pagesLab No. 4-System Stabilty Using Routh Table, Root LocusAshno KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document40 pagesChapter 6Umer Mushtaq GujjarPas encore d'évaluation
- FeedCon (Unit 5)Document18 pagesFeedCon (Unit 5)Christelle Cha LotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability of Linear Control System: Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) StabilityDocument9 pagesStability of Linear Control System: Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) Stabilitymeseret sisayPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 14, 15 StabilityDocument45 pagesLecture 14, 15 StabilityHamza KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- RH CriterionDocument2 pagesRH CriterionmailmadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 08 PDFDocument10 pagesLab 08 PDFAbdul Rehman AfzalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control 05Document27 pagesControl 05أحمد تركي كحيوشPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec#19-24 - Laplace DomainDocument42 pagesLec#19-24 - Laplace DomainDaniya AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7B - Online Classes - S2020Document21 pagesWeek 7B - Online Classes - S2020Muhammad Tayyab YousafzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 18-Stability Analysis - Routh Array and Root Locus Method-07!03!2024Document16 pages18-Stability Analysis - Routh Array and Root Locus Method-07!03!2024yadavpravin5151Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7Document19 pagesLecture 7Derrick Maatla MoadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsDocument19 pagesChapter 6 - : The Stability of Linear Feedback SystemsNikhil V NainoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Document68 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transient Response Stability STB 35103Muhammad Irvan FPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 System StabilityDocument32 pagesChapter 6 System StabilityIzzat AiresPas encore d'évaluation
- Lcs 9Document5 pagesLcs 9MianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecturer 19 Signals & SystemsDocument27 pagesLecturer 19 Signals & SystemsPrashanna YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruth Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument24 pagesRuth Herwitz Stability Criterionpratik KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Feedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture19-20 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument24 pagesFeedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture19-20 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionRajPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University Biomedical EngineeringMandy745Pas encore d'évaluation
- System StabilityDocument16 pagesSystem Stabilityeugeni madaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - System StabilityDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - System StabilityANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTPas encore d'évaluation
- Routh-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Document8 pagesRouth-Hurwitz Criterion: Name: Aamir Irshad Section:B SAB NO:70065601 REG NO:BSME-016-047 Assignment No:02Äâmïř ÌřşhądPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Document22 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Rajath UpadhyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyze Stability of Causal System: Application of Laplace TransformDocument13 pagesAnalyze Stability of Causal System: Application of Laplace TransformAbdullah WaqasPas encore d'évaluation
- Routh HurwitzDocument14 pagesRouth HurwitzVipul SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems Engineering: StabilityDocument30 pagesControl Systems Engineering: StabilityEren ÖzataPas encore d'évaluation
- Transient & Steady State Response AnalysisDocument32 pagesTransient & Steady State Response AnalysisMisbah Sajid ChaudhryPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Engineering MT-353: StabilityDocument47 pagesControl Engineering MT-353: StabilityTahaKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Elements of Realizability TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 4 Elements of Realizability TheoryEndeshaw KebedePas encore d'évaluation
- FeedCon (Unit 5) PDFDocument43 pagesFeedCon (Unit 5) PDFAbby MacallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFDocument45 pagesWeek 6 - Stability of Linear Control Systems - PDFgigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Feedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument19 pagesFeedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture-26 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionSARTHAK BAPATPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 StabilityDocument32 pages11 StabilityLufrenzPas encore d'évaluation
- Root-Locus Analysis of Delayed First and Second Order SystemsDocument8 pagesRoot-Locus Analysis of Delayed First and Second Order SystemsSanika TalathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Identication of Linear Parameter-Varying Systems Using Nonlinear ProgrammingDocument27 pagesIdentication of Linear Parameter-Varying Systems Using Nonlinear ProgrammingRACHEL BOSSPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemDocument52 pagesControl SystemvijayPas encore d'évaluation
- StabilityDocument66 pagesStabilityLiying ChewPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1Document31 pagesWeek 1salim ucarPas encore d'évaluation
- NMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionDocument37 pagesNMB 34203 Control Systems: System Stability: The Routh-Hurwitz CriterionfatinPas encore d'évaluation
- First-Order Partial Differential Equations, Vol. 1D'EverandFirst-Order Partial Differential Equations, Vol. 1Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- How To Add OpenMPI To CodeblocksDocument1 pageHow To Add OpenMPI To CodeblocksSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- StaticDocument3 pagesStaticSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Repeated EigenvaluesDocument16 pagesRepeated EigenvaluesSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Repeated Eigenvalues 3Document23 pagesRepeated Eigenvalues 3Serdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- OrthogonalityDocument1 pageOrthogonalitySerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Laplace Derivatives PDFDocument18 pagesLaplace Derivatives PDFSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Repeated Eigenvalues 2Document17 pagesRepeated Eigenvalues 2Serdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Orthogonality of Cosine, Sine and Complex ExponentialsDocument5 pages1 Orthogonality of Cosine, Sine and Complex ExponentialsSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- MT 1 SolDocument4 pagesMT 1 SolSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesTrig Cheat Sheetapi-284574585Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent 13.0 Workshop02-Airfoil PDFDocument67 pagesFluent 13.0 Workshop02-Airfoil PDFSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- CFD LearnDocument20 pagesCFD LearnAbed NaemPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12: Solutions For Equations With Constants Coefficients (Ii)Document5 pagesLecture 12: Solutions For Equations With Constants Coefficients (Ii)Serdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation of Wing Loading and Thrust Loading (Lectures 9 To 18)Document15 pagesEstimation of Wing Loading and Thrust Loading (Lectures 9 To 18)Serdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12: Solutions For Equations With Constants Coefficients (Ii)Document5 pagesLecture 12: Solutions For Equations With Constants Coefficients (Ii)Serdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- CAETraining (Fluid)Document129 pagesCAETraining (Fluid)andysarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Intro 14.5 L02 BasicsDocument42 pagesMechanical Intro 14.5 L02 BasicsChandreshPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent Tutorial 1 - Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in A Mixing ElbowDocument56 pagesFluent Tutorial 1 - Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in A Mixing Elbowklausosho100% (1)
- Ode 11Document4 pagesOde 11Muhammad Saad ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent 13.0 Workshop02-Airfoil PDFDocument67 pagesFluent 13.0 Workshop02-Airfoil PDFSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- HW05 Aerospace StructureDocument2 pagesHW05 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Ae362 - 2006 - hw1 Aerospace StructureDocument1 pageAe362 - 2006 - hw1 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- hw2 PDFDocument2 pageshw2 PDFSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- HW04 Aerospace StructureDocument2 pagesHW04 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Hw4 - 2016 Flight MechanicsDocument2 pagesHw4 - 2016 Flight MechanicsSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- HW06 Aerospace StructureDocument1 pageHW06 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- HW02 Aerospace StructureDocument2 pagesHW02 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- HW03 Aerospace StructureDocument2 pagesHW03 Aerospace StructureSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Hw3 - 2016 Flight MechanicsDocument2 pagesHw3 - 2016 Flight MechanicsSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Hw2 - 2016 Flight MechanicsDocument2 pagesHw2 - 2016 Flight MechanicsSerdar BilgePas encore d'évaluation
- Poynting Vector and Its Time Average ExpressionDocument1 pagePoynting Vector and Its Time Average ExpressionJose Ricardo DescardeciPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition Maths HSSC I Waqas SulaimanDocument10 pagesDefinition Maths HSSC I Waqas SulaimanAwais BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Abstract Algebra - Chapter 1 (Dummit and Foote, 3e)Document25 pagesSolutions To Abstract Algebra - Chapter 1 (Dummit and Foote, 3e)Chandranan Dhar0% (1)
- SPM Practice Add Maths Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesSPM Practice Add Maths Quadratic EquationsSarah Farina50% (2)
- Functions and Their RepresentationsDocument7 pagesFunctions and Their RepresentationsLuis Ignacio Lomeli GalazPas encore d'évaluation
- MathDocument12 pagesMathjanelle blanqueraPas encore d'évaluation
- Con MCQDocument76 pagesCon MCQazeem sheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Remarks On The Formal Power Series RingDocument13 pagesSome Remarks On The Formal Power Series RingMohamed KhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument19 pagesIntroductionandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Math ExaminationDocument6 pagesGen Math ExaminationErica AmolarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Age ProblemDocument14 pagesThe Age ProblemGena Ishira ColePas encore d'évaluation
- SHCC 1819 S6 M2 Mock Exam PDFDocument24 pagesSHCC 1819 S6 M2 Mock Exam PDFHuson 0710Pas encore d'évaluation
- Black and White Illustrative Animal Habitat Worksheet PDFDocument15 pagesBlack and White Illustrative Animal Habitat Worksheet PDFAIVIE MELITADO ESTOQUEPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Equations Practice 3Document2 pagesTrigonometric Equations Practice 3Ben CohenPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Six Lesson One Notes Guided NotesDocument10 pagesModule Six Lesson One Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- A.B B.A: Boolean Algebra Commutative LawDocument7 pagesA.B B.A: Boolean Algebra Commutative LawDhanwanth JPPas encore d'évaluation
- Symmetry: The American Mathematical MonthlyDocument9 pagesSymmetry: The American Mathematical Monthlyrhab13Pas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 1 - Introduction To Differential EquationDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 - Introduction To Differential EquationJeff Lennon BequillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tensors in Special Relativity: 3.1 Metrics and FormsDocument13 pagesTensors in Special Relativity: 3.1 Metrics and FormsPrince N XabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics: Factoring PolynomialsDocument13 pagesMathematics: Factoring PolynomialsPrecious Elaine RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Solutions To 2D Reaction Diffusion Systems in Matlab: Finite Difference and Spectral MethodsDocument8 pagesNumerical Solutions To 2D Reaction Diffusion Systems in Matlab: Finite Difference and Spectral MethodsmileknzPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics 6 - 2nd Quarter 3rd SummativeDocument5 pagesMathematics 6 - 2nd Quarter 3rd SummativeShaine Dzyll Kuizon100% (2)
- The To Prepare For Only App You NeedDocument77 pagesThe To Prepare For Only App You Needsai mukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- FunctionDocument35 pagesFunctionDae DayPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths - Race#056Document1 pageMaths - Race#056PkrPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Systems of Equations Section 5.1 Gaussian Elimination Matrix Form of A System of EquationsDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Systems of Equations Section 5.1 Gaussian Elimination Matrix Form of A System of EquationsvictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Lectures Series B1Document6 pagesMathematics Lectures Series B1KoustavGhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Mathematica: Laura Otálora Ramírez Edward Rojas Mesa Cálculo IntegralDocument8 pagesTaller Mathematica: Laura Otálora Ramírez Edward Rojas Mesa Cálculo IntegralLaura OtáloraPas encore d'évaluation
- Vandermonde DeterminantsDocument8 pagesVandermonde DeterminantsAmada LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- PromoDocument7 pagesPromoGujarati GamersPas encore d'évaluation