Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stroke
Transféré par
Meidy ShadanaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stroke
Transféré par
Meidy ShadanaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.1.
Definitions
Stroke is a collection of symptoms characterized by the development of
clinical manifestations of cerebral function disorders either focal or global (for
the patient in a coma), which happens quickly and more than 24 hours or
ended up with death without being discovered causes other than vascular
disorders. This definition includes stroke due to cerebral infarction (ischemic
stroke), nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage, intraventricular hemorrhage
and some cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage
1.2.
Epidemiology
The increasing age of life expectancy will tend to increase the risk of vascular
disease (coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral artery disease). Data
in Indonesia showed the tendency of an increase in stroke cases both in
terms of mortality, incidence, and disability. The mortality rate based on age is:
15.9% (age 45-55 years) and 26.8% (age 55-64 years) and 23.5% (age 65
years). The incidence of stroke (incidence) amounted to 51.6 / 100,000
population. Sufferers are men more than women and age profile under 45
years of 11.8%, 54.2% aged 45-64 years, and age over 65 years amounted to
33.5%. Stroke attacking reproductive age and the elderly that could potentially
give rise to new problems in health development nationally at a later date
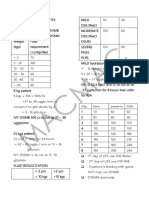
5. Basic management:
- Bed rest and positioned head and body 20-300 to maintain adequate
circulation to the brain.
- Infusion RL 20 drops / minute to maintain the state of euvolumic and needs
glucose.
- Infusion of Mannitol 125 cc / 6 hours to reduce cerebral edema.
- Injection 3x 2500 mg of tranexamic acid to control hemorrhage.
Giving citicolin aiming as a neuroprotective.
.5 Management
Stroke patients should be handled by a multidisciplinary team in conducting
the treatment of.
Management stroke be done by improving the general state of the patient,
treat disease risk factors, and prevent complications
1.6 Complications
Systemic complications often occurs on the first day of stroke. this condition
five time as much causing death than due to lessions. Some circumstances
that should always be monitored for systemic complications :
1. The blood pressure
Rise in blood pressure is usually the compensation the body as a result of a
stroke. This happens because the body's efforts to overcome the existing
shortage of blood supply in the lesion. However, this condition will improve in
2-3 days. Rise in blood pressure does not need to be reduced, but reach very
high values that is systolic> 220mmHg / Diastolic> 130mmHg.
2.
Blood Sugar
Rise in blood sugar in patients with a stroke or a compensation body of stress
mechanism. High blood sugar will aggravate brain damage, so that the rise
blood sugar in the first days of stroke should be lowered.
3.The state of cardiorespiratory
Cardiac disorders often occurs and worsen the stroke. Besides cardiac
disorders, respiratory disorders can also occur, either caused by infection or
the presence of an emphasis on the respiratory center.
4. ulcer stress
ulcer stress is one of the complications that can occurs in stroke patients and
need attention. This situation may lead to haematemesis and melena, and
can be effect on patient survival.
5. Other complications
Other complications that may arise on the state of stroke include: infection
and sepsis, kidney disorders, liver disorders, and pulmonary embolism and /
or deep vein thrombosis. So that the necessary monitoring from the start of
stroke occurs.
1.7 Prognosis
Stroke can cause a variety of morbidity, mortality, and recurrence in the future.
Deaths due to stroke was 41.4% from 100,000 population. A third of patients
who have had a stroke, 5-14% will suffer recurrent stroke within a span of five
years.
Statistical stroke data by the Stroke Association UK shows that 42% disability
caused by stroke is permanent. In 2010, stroke accounted for 7% of all
causes of mortality in men and 10% of all causes of death among women.
Recurrence of stroke increases with the time. The possibility of recurrent
stroke within five years was 26.4% and in ten years was 39.2%.
4. Basic investigations: bhasa inggris pemeriksaan penunjang?
( dasar usul atau asal usul?)
- Routine blood tests: to determine the risk factors for stroke include increased
hematocrit.
- Examination of blood chemistry: to determine stroke risk factors such as
diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia and useful also for management.
- ECG: determine cardiac abnormalities such as LVH (left ventricel hypertrofi),
atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction.
- Chest X-ray: know the existence of cardiac abnormalities such as
cardiomegaly.
- Head CT scans: pathologic abnormality diagnosis of stroke (hemorrhagic or
infarction), location and lesion area.
3.4. Basic Differential diagnosis
Gold standard diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke / non hemorrhagic is with a CT
scan. Considered non-hemorrhagic stroke because of the complaints appear
obtained when patients move lightly in the morning. Also according to the
family, patients had experienced with the mouth oblique, left side 2 years ago
but a few hours later disappears, neurologic deficit that lasted <24 hours
suspicion of a TIA which is a sign of stroke infarction.
3.5. Basic secondary diagnosis
From anamnesis it is known that the patient has a history of hypertension
since 1 year ago and based on a physical examination also obtained the
patient's blood pressure 170/90 mmHg. This is in accordance with the criteria
JNC 8 that in patients aged 60 years said to hypertension if the systolic
blood pressure 150 mmHg or diastolic 90mmHg.
3.6. The basis of the final diagnosis
The final diagnosis of these patients is hemorrhagic stroke + hypertension.
The diagnosis is established based on anamnesis, physical examination, and
are supported by the results of further examination.
From anamnesis it is known that patients experience decrease in
consciousness while on the move. Previously patients vomited 2 times and
spraying. Headache was also felt in all parts of the head. Besides the patient
has a history of hypertension since 1 year ago. a physical examination
obtained from the patient's blood pressure 170/90 mmHg, GCS E1M4Vtube,
pathological reflex positive Babinsky. Examination of head CT scan is the gold
standard for determining the cause of a stroke is happening. Head CT scan
results indicate the presence of intraventricular hemorrhage.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MNGBJKDocument1 pageMNGBJKMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- BNMDocument2 pagesBNMMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- HjhijijDocument1 pageHjhijijMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- WJDNFKJDFDocument4 pagesWJDNFKJDFMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ucm 452860Document2 pagesUcm 452860Meidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- BNMDocument2 pagesBNMMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuropathic Pain: Vanja Basic-Kes/ Iris Zavoreo/ Marijana Bosnar Mira Ivankovic", Milan Bitunjac'Document7 pagesNeuropathic Pain: Vanja Basic-Kes/ Iris Zavoreo/ Marijana Bosnar Mira Ivankovic", Milan Bitunjac'Meidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- EAU Guidelines LUTS 2014 (Pocket Guide)Document14 pagesEAU Guidelines LUTS 2014 (Pocket Guide)Bruno D'AlmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nipple and Areolar Eczema in The Breastfeeding Woman - JCMS, April '04Document5 pagesNipple and Areolar Eczema in The Breastfeeding Woman - JCMS, April '04Meidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum and Gestational Transient Hyperthyroidism: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum and Gestational Transient Hyperthyroidism: A Case ReportInne Fia MarietyPas encore d'évaluation
- 0025 81051212521P PDFDocument6 pages0025 81051212521P PDFtr14niPas encore d'évaluation
- DasdsdaDocument1 pageDasdsdaMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- S 00016 P 160Document2 pagesS 00016 P 160Meidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- KmasfmkdDocument10 pagesKmasfmkdMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- STROKEDocument5 pagesSTROKEMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fournier GangreneDocument4 pagesFournier GangreneMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rumus Transfusi PRCDocument2 pagesRumus Transfusi PRCMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wpr25610 - AnaestheticDocument2 pagesWpr25610 - AnaestheticMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neo-Natal Seizure ManagementDocument18 pagesNeo-Natal Seizure ManagementGregorio CrosserPas encore d'évaluation
- RCOG - Management of Tubal PregnancyDocument10 pagesRCOG - Management of Tubal PregnancyMeidy ShadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- DOWN SYNDROME - A Case Report: October 2008Document14 pagesDOWN SYNDROME - A Case Report: October 2008Diana DiancikPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE #79: DISCLAIMER: The Information in This Document Does Not Replace Professional Medical AdviceDocument2 pagesCASE #79: DISCLAIMER: The Information in This Document Does Not Replace Professional Medical AdviceIvyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionCamilogs80% (10)
- BronchopneumoniaDocument13 pagesBronchopneumoniaSabella Gustika VernandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Hematologic Disorders - : Blood Blood CoagulationDocument6 pagesPediatric Hematologic Disorders - : Blood Blood Coagulationcayla mae carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument7 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseRosalinda PerigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) : DR Wan Muhammad Farhan Bin Wan Fauzi Ukkp HKTDocument16 pagesLatent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) : DR Wan Muhammad Farhan Bin Wan Fauzi Ukkp HKTfarhan fauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Smoking Cessation: Prepared by Dr. Ahmed El MasryDocument77 pagesSmoking Cessation: Prepared by Dr. Ahmed El Masryاحمد المصرىPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC of Reading Chest XrayDocument1 pageABC of Reading Chest Xraykrisnochura100% (3)
- Altitude PDFDocument47 pagesAltitude PDFMohd AsadPas encore d'évaluation
- DVTDocument13 pagesDVTapi-253732526Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute ischemic stroke managementDocument40 pagesAcute ischemic stroke managementMohamed AbdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)Document37 pagesHepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)Jeriz Marie GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Care What If Child Becomes Sick FlowchartDocument1 pageChild Care What If Child Becomes Sick FlowcharthmareidPas encore d'évaluation
- HNF 8 SRO Blanchard2018Document11 pagesHNF 8 SRO Blanchard2018Abhinav InglePas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Talipes Equino-VarusDocument48 pagesCongenital Talipes Equino-VarusKojo DuncanPas encore d'évaluation
- Athero 2 Dr. Raquid 2021Document93 pagesAthero 2 Dr. Raquid 2021oreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleed From Anal Means - Google SearchDocument1 pageBleed From Anal Means - Google SearchKaran deep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Epidemiology TerminologyDocument33 pages2 Epidemiology Terminologynithin shenoiPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs VTEDocument7 pagesMCQs VTEMUHAMMADPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal BPH Fathan Ula SalinanDocument15 pagesJurnal BPH Fathan Ula Salinanelsy oktaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomarkers Improve NMIBC ManagementDocument62 pagesBiomarkers Improve NMIBC ManagementHugo PrazeresPas encore d'évaluation
- Ent ModuleDocument14 pagesEnt ModuleVishnu KrshPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study SampleDocument4 pagesCase Study SamplemandyPas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Metabolic &genetic Bone DiseasesDocument12 pages11-Metabolic &genetic Bone Diseasesفراس الموسويPas encore d'évaluation
- Ok Ok Notes PediaDocument14 pagesOk Ok Notes PediaChristian PasicolanPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Drug Resistance in Bacteria Using AntibioticsDocument47 pagesStudy Drug Resistance in Bacteria Using Antibioticskioilui;lphio961% (18)
- The 14 Disability CategoriesDocument1 pageThe 14 Disability CategoriesFrance Bejosa100% (1)
- Understanding Nutritional Needs for Ulcerative ColitisDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Nutritional Needs for Ulcerative ColitisJessica GlitterPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Abuse and NeglectDocument23 pagesChild Abuse and NeglectStephen StrangePas encore d'évaluation