Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Hazard Analysis
Transféré par
Shawn JamesCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Activity Hazard Analysis
Transféré par
Shawn JamesDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
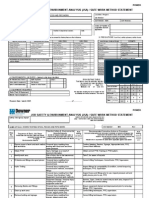
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
General Physical Hazards
Slip, trip, fall
Poor housekeeping
Manual lifting
Minor cuts and bruises
Chemical contact
Equipment to be Used:
Hard Hat
Safety glasses with side
shields
Steel-toe Boots
Work Gloves
Inspection Requirements
Daily during Daily Safety
Meeting
Control Measures
Site employees will be required to wear hard hat, type II safety vest and
steel toe boots.
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
Flag or cover inconspicuous holes to protect against falls.
Work areas will be kept clean and orderly.
Garbage and trash will be disposed of daily in approved refuse
containers.
Tools and accessories will be properly maintained and stored.
Work areas and floors will be kept free of dirt, grease, and slippery
materials.
Materials shall be stored to allow clear access to aisles, pathways, and
travel routes.
Field vehicles will be kept clean and orderly.
Size up the job, think it through.
Lift with your legs, not your back. Use mechanical equipment
whenever possible.
Get assistance when manually lifting awkwardly-sized items or those
items over 60 pounds.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
Tools not functioning properly shall be removed from service
immediately and tagged.
Workers shall wear cotton or leather work gloves when handling
equipment.
Have at least two persons on site trained in First Aid/CPR.
All crew personnel on site shall use the buddy system (working in pairs
or teams).
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) shall be obtained for chemicals
brought on site.
MSDSs shall be reviewed with project personnel before using the
chemical material.
Training Requirements
Project-specific training
Proper use and operation of hand tools
First Aid/CPR (American Red Cross)
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Materials Handling
Equipment to be Used:
Flammable storage
containers/cabinets
Drum dolly
Forklift
Potential Hazards
Back injury
Pinch points
Drum Spillage/Puncture
Slip, trip, or fall
Cuts, bruises
Splashes
Chemical burns
Inspection Requirements:
Daily
Control Measures
Size up the job.
No individual shall lift any material over 60lbs.
Use mechanical equipment to lift and move items, when necessary. Lift
with your legs, not your back.
Do not lift awkwardly sized items and those items over 60 pounds.
Get assistance when necessary.
If a worker loses control of item, STAND CLEAR and DO NOT try to
prevent its fall.
Assure path is clear while transporting items manually (housekeeping).
Keep hands and feet clear of moving/suspended materials and equipment.
Wear steel toe/shank safety shoes/boots.
Use a drum dolly or forklift to move drums.
Label all drums as to their contents.
Do not move bulging or leaking drums.
Assure path is clear while transporting items manually (housekeeping).
Do not stand on drums, boxes, or bags of stored materials.
Get assistance when necessary.
Use mechanical equipment to lift and move items when necessary.
Use cotton or leather work gloves for materials handling.
Wear eye protection as needed (i.e., safety glasses/goggles, and face
shield)
Wear appropriate protective clothing and chemical resistant gloves as
specified.
Training Requirements:
Hazardous Chemicals Handling
Safe lifting practices
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Motor Vehicle Operations/Traffic
Equipment to be Used:
Passenger vehicles
Traffic cones
Orange vests
Barricades
Flag person(s)
Inspection Requirements:
Continuous
Monthly Vehicle
Inspection
Extended Work Shifts/Multiple
Crews
Vehicle accidents
Personal injury
Fatigue
Reduced productivity.
Increased incident
potential.
Increased hazard
exposure potential.
Inattention.
Control Measures
Place physical (i.e., barricades, fencing) around work areas regularly
occupied by pedestrians.
If working adjacent to roadways, have workers wear fluorescent orange
vests.
Use warning signs or lights to alert oncoming traffic.
Assign flag person(s) if necessary to direct local traffic.
Set up temporary parking locations outside the immediate work area.
Motor vehicle operators shall obey all posted traffic signs, signals, and
speed limits.
Wear seat belts when vehicles are in motion.
Contractor employees are not authorized to operate motor vehicles without
authorization form the Site Project Manager.
Passenger vehicles and light trucks yield to heavy equipment.
Training Requirements:
Defensive Driver Training
Driver's license
No employee or contractor is authorized to work when they are overly
fatigued.
If driving a motor vehicle (non-CMV) is part of their assignment, then
workers will not work more than 14 hours in a 24 hour period.
Heavy equipment will not be operated by one individual for more than 12
hours in any 24 hour period without a minimum of 8 hours off duty.
Employees experiencing negative effects of extended work shifts shall be
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Equipment to be Used:
Multiple Crews
Portable lights
Inspection Requirements:
Employee fatigue
Availability of work space
Adverse Weather
Lightening Strikes
Control Measures
instructed to rest off duty for a sufficient time period to eliminate the
negative effects.
Operators which may extend shifts beyond 12 hours per day, six days a
week or which will have multiple shifts operating shall be reviewed by the
Site HS Coordinator.
Training Requirements:
General safety awareness
Whenever possible, halt activities and take cover.
If outdoors, stay low to the ground, but limit the body surface area that is in
contact with the ground (i.e., kneeling on one knee is better than laying on
the ground).
Seek shelter in a building if possible.
Stay away from windows
If available, crouch under a group of trees instead of one single tree.
Keep 6 feet away from tree trunk if seeking shelter beneath tree(s).
If in a group, keep 6 feet of distance between people.
Suspend drill rig/crane operations if thunderstorm/lightning is in immediate
vicinity.
When lighting is in the area all operations shall be halted for 30 minutes
after lighting is seen.
Listen to the radio or TV announcements for pending weather information.
Cease field activities during thunderstorm or tornado warnings, as directed
Thunderstorms
Tornadoes
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Earthquakes
Equipment to be Used:
Radios
Shelter
Inspection Requirements:
Throughout work
activities
Pressurized Water Cleaning
Noise
Struck by high pressure
stream
Equipment to be Used:
Steam Cleaner
Pressure Washer
Hydro-blaster
Inspection Requirements:
Daily inspection by operator
Check hoses, fittings,
connections, and safety devices
Control Measures
by the Project Manager.
Seek shelter. Do not try to outrun a tornado.
Do not stand near windows or door glass.
Seek immediate shelter (i.e., door jambs, desks, etc).
Do not stand near windows or door glass.
Training Requirements:
General awareness
FA/CPR (American Red Cross)
See page for Noise Hazards
Secure work area.
Use safety devices as required by manufacturer
Do not hold material to be cleaned.
Do not aim stream at self or other personnel.
Operator of gun/wand/lance shall have full control of the dump valve.
Use only dead man type dump valve controls.
Follow work practices per manufacturer .
For shot-gunning:
Wear metatarsal guards and leg guards
Other Safety Equipment: Hardhat, face shield, safety goggles (impact
rated), heavy water resistant suit, ear plugs, chemical resistant boots
and gloves.
Training Requirements:
High Pressure Water Hazards
Hands-on operational training with specific equipment to be operated, per
manufacturer guidelines
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Welding, Cutting and Other Hot
Work
Welding flash
Welding burns
Fire
Equipment to be Used:
Welder
Cutter
Gas cylinders (acetylene
and
oxygen)
Inspection Requirements:
Prior to each use check
equipment
Control Measures
Cutting, welding, or other operations that produce excessive heat, open
sparks, or flames shall not be permitted within 50 feet of a potential liquid
fuel source.
One 10A:20BC multipurpose dry chemical fire extinguisher shall be readily
available in the hot works area.
Complete a Hot Work Permit prior to initiation of hot works.
The area shall be monitored with a combustible gas meter to ensure <10%
LEL.
Work will not be permitted in atmospheres >10% LEL.
The worker shall be protected from sparks or flame by wearing leather
guards (Tyvek is not protective against heat sources).
Welders shall wear welding goggles or hood.
Complete a Hot Work Permit for each shift and when conditions change.
Compressed gas cylinders shall be secure in an upright position.
Gas regulators shall be in proper working order.
Cylinders shall be marked or stenciled to identify the type of gas in the
cylinder.
Oil and oily rags shall be kept away from oxygen equipment.
Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished and when cylinders
are empty or moved.
Objects to be welded, cut, or heated shall be moved to a safe location
when possible.
Remove all potential fire hazards in the vicinity.
Review possibility of chemical coating on item(s) to be welded, cut, or
heated; provide appropriate respirators protection, if needed, to operator.
Acetylene regulators shall not be adjusted to permit a discharge >15 psig.
Fuel/oxygen combination used for cutting, welding, or heating shall
have reverse-flow check valves between torch and regulator.
Training Requirements:
Qualified welder
Hot Works Permit
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Mobilization/Demobilization
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Physical Injury
Vehicular accidents/collisions.
All personnel shall attend site orientation prior to start of work activities.
All personnel shall wear all required PPE for jobsite conditions.
All personnel shall familiarize themselves to hazards, emergency
procedures, operational aspects & heavy equipment use, and change(s) in
site/work conditions. Daily housekeepin
Place physical (i.e., barricades, fencing) around work areas regularly
occupied by pedestrians.
If working adjacent to roadways, have workers wear fluorescent orange
vests.
Use warning signs or lights to alert oncoming traffic.
Assign flag person(s) if necessary to direct local traffic.
Set up temporary parking locations outside the immediate work area.
Motor vehicle operators shall obey all posted traffic signs, signals, and
speed limits.
Wear seat belts when vehicles are in motion.
Contractor employees are not authorized to operate motor vehicles without
authorization from the Site Project Manager.
Passenger vehicles and light trucks yield to heavy equipment.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across walking
pathwa
Hand or Power tools.
Slips, Trips, Falls.
Heat Stress
Heat rash
Heat Stress
Keep the skin clean and dry.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Insect
Heat cramps
Heat exhaustion
Heat stroke
Hazards
Ticks
Bees
Wasp
Ants
Poisonous Snakes and Animals
Rabies
Bites
Allergic Reaction
Equipment to be Used:
Cooling vests
Core control suits
Inspection Requirements:
Daily
Watch for signs &
Control Measures
Change perspiration-soaked clothing, as necessary.
Bathe at end of work shift or day.
Apply powder to affected areas.
Wear clean/dry undergarments
Heat Cramps
Drink plenty of cool fluids even when not thirsty.
Provide cool fluids for work crews.
Move victim to shaded, cool area.
Inform Supervisor of cramps even if occurring off the job.
Heat exhaustion
Physiological worker monitoring as needed (i.e., heart rate, oral
temperature).
Set up work/rest periods.
Use the buddy system.
Allow workers time to acclimate.
Have ice packs available for use on breaks.
Heat Stroke
Evaluate possibility of night work.
Wear body cooling devices.
Wear light colored clothing (can see ticks better).
Mow vegetated and small brush areas.
Wear insect repellant.
Wear long sleeves and long pants.
Visually check self promptly and frequently after exiting the work area.
Identify infested areas to the Site Supervisor.
Workers who are allergic or capable of allergic reactions to bee, wasp, or
ant stings or bites shall notify their Supervisor(s).
Evaluate need for sensitive workers to have prescribed antibiotic or
medicine to combat onset of symptoms.
Keep work areas clear of vegetation and small brush.
Avoid placing hands or feet into obscure areas (i.e., beneath rocks, well
pads, brush piles).
Wear rubber or PVC boots into vegetated areas where poisonous snakes or
animals inhabit.
Use the buddy system.
Postpone work in areas where poisonous snakes or animals are nested.
Inspect protected areas before entering.
Inform HS and Project Manager if allergic to bites, and carry emergency kit
as required.
Training Requirements:
Valid Drivers License
Heat Stress.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Oral thermometers
Watch
Topical ointment
Clothing for barrier
Pile Driving
Potential Hazards
symptoms at each break
Personal Injury
Control Measures
Prevention, Symptoms, Treatment
Identification of poisonous plants
Proper Planning
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
Locate all electric, gas, water, steam, sewer, and other services lines to be
shut off, capped, or controlled, before pile driving is started.
All workers should be informed of the location of any existing or relocated
utility service.
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
All workers working near or on water shall wear a type III PFD.
Life ring shall be provided while workers are working on or near water
Slips, Trips, Falls
The use of sheet pile stirrups as a fall protection method is prohibited
If an employee is required to go aloft on sheet piling, the employee shall
use an aerial device or ladder.
Workers exposed to fall hazards shall be protected from falling to a lower
level by the use of standard guardrail, work platforms, safety nets,
engineered fall protection systems, or personal fall arrest systems.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Barricade or cover and flag inconspicuous holes to protect against falls
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
The use of sheet pile stirrups as a fall protection method is prohibited;
Hand & Power Tools
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Hazardous Energy
Electrocution
Electrical burns
Fire
Control Measures
Pinch Points/Caught between
Heavy Equipment Operations
10
Contact Louisiana One Call or State appropriate company prior to any work.
When working within 20 feet of Natural gas line and hydrogen line confirm
through Clovelly oil and Airproducts that lines have been depressurized.
Maintain a safe working distance from all underground utlities
Maintain a minimum distance of 20 feet between overhead electrical lines.
Portable electrical tools and equipment will be double-insulted.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Identify the location of underground/overhead electrical lines in the work
area, as appropriate.
Power tools shall be tagged and removed from service when not
functioning properly.
Lockout/tagout procedures shall be implemented when employees need to
perform repair or maintenance on electrical equipment where the
unexpected energization, or start-up of stored energy could cause injury.
Extension cords shall not be fastened with staples, hung from nails, or
suspended by bare wire.
A qualified Master Electrician will inspect all high voltage electrical
connections prior to energizing.
Remain alert at all times
Do not place hand in between objects being lifted.
Always have a means of escape
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
If crane does not have Anti-Two Block the operator must have a visual aid
(flag, tape, or ball) attached to the hoist line 8 to 10 feet above the rigging.
If the crane is operating at a boom angle that hinders the visual aid the
visual aid may be placed near the drum so the operator can see it.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator.
No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
11
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the rig.
The load capacity shall be posted and clearly visible on the rig.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Cranes, derricks, drill rigs, booms or similar equipment shall have a
minimum 20 feet clearance from overhead electrical power lines.
Guy, outriggers, thrust outs, or counter-balances shall be provided to
maintain stability of pile-driver rigs.
Swinging (hanging) leads shall have fixed ladders.
All employees shall be kept clear when piling is being hoisted.
Steel pilings shall be lifted by use of a closed shackle or other positive
attachment that will prevent accidental disengagement.
If an employee is required to go aloft on sheet piling, the employee shall
use an aerial device or ladder.
Taglines shall be used for controlling unguided piles and free hanging
(flying) hammers.
Employees shall be prohibited from remaining on leads or ladders while
pile is being driven.
Fixed pile-driver leads shall be provided with decked landings having guard
rails, intermediate rails, and toe boards.
Fixed ladders or stairs shall be provided for access to landings and head
blocks.
Fixed leads shall be provided with rings or attachment points so that
workers exposed to falls of 6 ft (1.8 m) or greater may attach their safety
harnesses to the leads.
Landings or leads shall not be used for storage of any kind.
Pile-driver leads shall have stop blocks to prevent the hammer from being
raised against the head block.
A blocking device, capable of supporting the weight of the hammer, shall
be provided for placement in the leads under the hammer at all times while
employees are working under the hammer.
All hose connections to pile-driver hammers shall be securely attached with
an adequate length of alloy steel chain at least inch, or equal strength
wire, to prevent whipping.
If piling cannot be pulled without exceeding the load rating of equipment, a
pile extractor shall be used.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Noise
Control Measures
Rigging
Personal Injury
Faulty Rigging
Failure to control load
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Provide annual audiograms for employees.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Personal Injury
Rigging must be done by a Qualified Rigger.
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging equipment shall not be loaded in excess of its recommended
safe working load.
Verify load weight of product to be lifted.
A positive latching device shall be used to secure the load and rigging
Select and inspect the proper rigging equipment for the job at hand.
Rigger must remain alert at all times.
Rigger must keep all unnecessary personnel out of the lifting area.
Rigger should alert the operator to any unsafe conditions or practices
during lifting.
Rigger must know and demonstrate competency in using all signals
used in material handling.
Faulty Rigging
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging shall be stored properly immediately after use.
Defective rigging must be tagged, cut, or removed from service.
Keep rigging clear of any welding or burning.
Hooks, shackles, rings, pad eyes, and other fittings that show excessive
wear or that have been bent, twisted, or otherwise damaged shall be
removed from service.
Only marked shackles (marked by manufacturer with name or trademark of
manufacturer, rated load and size) shall be used.
Failure to Control Load
Crane or hoisting equipment shall not be used when wind speeds onsite
12
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Unstable/inclined Surfaces
Equipment Damage
Fire
Heat Stress
Heat rash
Heat cramps
Heat exhaustion
Heat stroke
exceed owners safety manual.
At wind greater than 20 mph the operator, rigger, and lift supervisor shall
cease all crane operations, evaluate conditions and determine if the lift
shall proceed.
Tag lines shall be used at all time.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent
person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All mechanized equipment shall have proper fire extinguishing equipment.
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling..
All equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by a
competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
Heat Stress
Keep the skin clean and dry.
Change perspiration-soaked clothing, as necessary.
Bathe at end of work shift or day.
Apply powder to affected areas.
Wear clean/dry undergarments
Heat Cramps
Drink plenty of cool fluids even when not thirsty.
Provide cool fluids for work crews.
Move victim to shaded, cool area.
Inform Supervisor of cramps even if occurring off the job.
Heat exhaustion
Physiological worker monitoring as needed (i.e., heart rate, oral
13
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
temperature).
Set up work/rest periods.
Use the buddy system.
Allow workers time to acclimate.
Have ice packs available for use on breaks.
Heat Stroke
Evaluate possibility of night work.
Wear body cooling devices.
Complete a Hot Work Permit for each shift and when conditions change.
Cutting, welding, or other operations that produce excessive heat, open
sparks, or flames shall not be permitted within 50 feet of a potential liquid
fuel source.
The area shall be monitored with a combustible gas meter to ensure <10%
LEL. Work will not be permitted in atmospheres >10% LEL.
The worker shall be protected from sparks or flame by wearing leather
guards (Tyvek is not protective against heat sources).
Welders shall wear welding goggles or hood.
Compressed gas cylinders shall be secure in an upright position.
Cylinders shall be marked or stenciled to identify the type of gas in the
cylinder.
Oil and oily rags shall be kept away from oxygen equipment.
Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished and when cylinders
are empty or moved.
Acetylene regulators shall not be adjusted to permit a discharge >15 psig.
Fuel/oxygen combination used for cutting, welding, or heating shall have
reverse-flow check valves between torch and regulator.
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
Hot Work Permit
Qualified Rigger
Hot Work
Equipment to be used
Pile Driver Rig
Slings Shackles
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
14
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Structural Demolition
Potential Hazards
Personal Injury
Control Measures
Slips, Trips, Falls
Hand & Power Tools
15
Proper Planning
Complete an engineer survey of the structure.
All projects will be evaluated for the potential to contact asbestoscontaining material (ACM) and lead-based paint (LBP).
Locate all electric, gas, water, steam, sewer, and other services lines to be
shut off, capped, or controlled, before demolition work is started.
All workers should be informed of the location of any existing or relocated
utility service.
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
GFCI.s shall be used on all power tools, extension cords, and all equipment
connected to temporary power supplies. Extension cords, power tools, and
lighting equipment shall be inspected before each use, protected from
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Heat Stress
Heat rash
Heat cramps
Heat exhaustion
Heat stroke
Hazardous Energy
Electrocution
Electrical burns
Fire
Pinch Points/Caught between
Control Measures
damage, and kept out of wet areas.
Heat Stress
Keep the skin clean and dry.
Change perspiration-soaked clothing, as necessary.
Bathe at end of work shift or day.
Apply powder to affected areas.
Wear clean/dry undergarments
Heat Cramps
Drink plenty of cool fluids even when not thirsty.
Provide cool fluids for work crews.
Move victim to shaded, cool area.
Inform Supervisor of cramps even if occurring off the job.
Heat exhaustion
Physiological worker monitoring as needed (i.e., heart rate, oral
temperature).
Set up work/rest periods.
Use the buddy system.
Allow workers time to acclimate.
Have ice packs available for use on breaks.
Heat Stroke
Evaluate possibility of night work.
Wear body cooling devices.
Maintain a minimum distance of 20 feet between overhead electrical lines
and any part of equipment.
Portable electrical tools and equipment will be double-insulted.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Identify the location of underground/overhead electrical lines in the work
area, as appropriate.
Power tools shall be tagged and removed from service when not
functioning properly.
Lockout/tagout procedures shall be implemented when employees need to
perform repair or maintenance on electrical equipment where the
unexpected energization, or start-up of stored energy could cause injury.
Extension cords shall not be fastened with staples, hung from nails, or
suspended by bare wire.
A qualified Master Electrician will inspect all high voltage electrical
connections prior to energizing.
Remain alert at all times
Do not place hand/feet in between objects being lifted
16
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Heavy Equipment Operations
Control Measures
Unstable/Inclined Surface
Noise
17
Always have a means of escape
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator. No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
No person shall be permitted in any area that can be affected by demolition
when using heavy machinery.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
If piling cannot be pulled without exceeding the load rating of equipment, a
pile extractor shall be used.
Piling shall not be pulled by tipping the crane, releasing the load brake
momentarily, and catching the load before the crane has settled.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
When going uphill track with the arm in front of you.
If extra counterweight is required fill the bucket
Avoid overfilling bucket when near embankment.
Never slew with a full bucket at maximum reach.
Do not undercutting the ground from beneath the excavator.
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Provide annual audiograms for employees.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Personal Injury
Rigging must be done by a Qualified Rigger.
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging equipment shall not be loaded in excess of its recommended
safe working load.
Verify load weight of product to be lifted.
A positive latching device shall be used to secure the load and rigging
Select and inspect the proper rigging equipment for the job at hand.
Rigger must remain alert at all times.
Rigger must keep all unnecessary personnel out of the lifting area.
Rigger should alert the operator to any unsafe conditions or practices
during lifting.
Rigger must know and demonstrate competency in using all signals
used in material handling.
Faulty Rigging
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging shall be stored properly immediately after use.
Defective rigging must be tagged, cut, or removed from service.
Keep rigging clear of any welding or burning.
Hooks, shackles, rings, pad eyes, and other fittings that show excessive
wear or that have been bent, twisted, or otherwise damaged shall be
removed from service.
Only marked shackles (marked by manufacturer with name or trademark of
manufacturer, rated load and size) shall be used.
Failure to Control Load
Crane or hoisting equipment shall not be used when wind speeds onsite
exceed owners safety manual.
At wind greater than 20 mph the operator, rigger, and lift supervisor shall
cease all crane operations, evaluate conditions and determine if the lift
shall proceed.
Tag lines shall be used at all time.
Rigging
Personal Injury
Faulty Rigging
Failure to control load
Unstable Structure
18
Shore or brace walls and floors of structures that have been damaged by
fire, water explosion or other cause.
Place signs warning of the hazard of falling materials at the opening of
each side of the door opening to be demolished.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Equipment Damage
Control Measures
Fire
Hot Work
19
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent
person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling.
Heating devices shall be place where they are not likely overturn.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Complete a Hot Work Permit for each shift and when conditions change.
Cutting, welding, or other operations that produce excessive heat, open
sparks, or flames shall not be permitted within 50 feet of a potential liquid
fuel source.
The area shall be monitored with a combustible gas meter to ensure <10%
LEL. Work will not be permitted in atmospheres >10% LEL.
The worker shall be protected from sparks or flame by wearing leather
guards (Tyvek is not protective against heat sources).
Welders shall wear welding goggles or hood.
Compressed gas cylinders shall be secure in an upright position.
Cylinders shall be marked or stenciled to identify the type of gas in the
cylinder.
Oil and oily rags shall be kept away from oxygen equipment.
Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished and when cylinders
are empty or moved.
Acetylene regulators shall not be adjusted to permit a discharge >15 psig.
Fuel/oxygen combination used for cutting, welding, or heating shall have
reverse-flow check valves between torch and regulator.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Equipment to be used
Excavator or back hoe
Oxygen & acetylene
Hand & Power tools
Slings & Shackles
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
Hot Work Permit
Qualified Rigger
Lock Out/Tag Out
Installation silt fence/Geotextile
Slips, Trips, Falls
Lifting Strains & Sprains
Equipment Operations
20
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
No individual employee is permitted to lift any object that weighs over 60
pounds.
Proper lifting techniques shall be used.
Multiple employees or the use of mechanical lifting are for lifting objects
over the 60-pound limit.
Materials shall be inspected for sharp edges prior to being handled, and
avoid pinch point
hazards.
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Hazardous Energy
Hand and Power Tools
21
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator. No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Locate all underground utilities thru Louisiana One Call
Maintain a safe working distance from underground utilities.
Maintain a minimum distance of 20 feet between overhead electrical lines
and any part of equipment.
Portable electrical tools and equipment will be double-insulted.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Identify the location of underground/overhead electrical lines in the work
area, as appropriate.
Power tools shall be tagged and removed from service when not
functioning properly.
Lockout/tagout procedures shall be implemented when employees need to
perform repair or maintenance on electrical equipment where the
unexpected energization, or start-up of stored energy could cause injury.
Extension cords shall not be fastened with staples, hung from nails, or
suspended by bare wire.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
GFCI.s shall be used on all power tools, extension cords, and all equipment
connected to temporary power supplies. Extension cords, power tools, and
lighting equipment shall be inspected before each use, protected from
damage, and kept out of wet areas.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Equipment to be Used:
Hand and Power Tools
GFCI
Inspection Requirements:
Daily
Training Requirements:
Qualified Operator
Aggregate Placement/Excavation
Personal Injury
Slips, Trips, Falls
22
Proper Planning
All workers have the right to shut down a job b/c of an unsafe act.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
Locate all electric, gas, water, steam, sewer, and other services lines to be
shut off, capped, or controlled, before excavation to start.
Call Louisiana One Call or appropriate authority to locate underground
utilities.
All workers should be informed of the location of any existing or relocated
utility service.
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
All workers should be aware of their surroundings and aware of
simultaneous operations.
All equipment shall have initial and daily inspections.
Workers shall not stand behind or gather directly behind dump trucks.
Workers exposed to fall hazards shall be protected from falling to a lower
level by the use of standard guardrail, work platforms, safety nets,
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Hand & Power Tools
Pinch Points/Caught between
Trucking Operations
23
engineered fall protection systems, or personal fall arrest systems.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Barricade or cover and flag inconspicuous holes to protect against falls
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
The use of sheet pile stirrups as a fall protection method is prohibited
Workers shall maintain 3-point contact while measuring dump trucks.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Remain alert at all times
Do not place hand in between objects being lifted.
Remain clear of dump trucks while backing up.
Always have a means of escape
Use qualified and trained operators
All dump trucks brought on USACE jobsite shall be inspected upon arrival.
Drivers shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
If a signal person or spotter is not used, operators will walk behind their
vehicle to view the area for possible hazards before backing their vehicle
Text messaging is strictly prohibited while operating motor vehicles .
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Trucks should not be operated in a manner that will endanger persons or
property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads be exceeded.
Getting off or on any truck while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the truck.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Equipment operators
Control Measures
Noise
Unstable/inclined Surfaces
24
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator.
No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the rig.
The load capacity shall be posted and clearly visible on the rig.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Cranes, derricks, drill rigs, booms or similar equipment shall have a
minimum 10 feet clearance from overhead electrical power lines.
Guy, outriggers, thrust outs, or counter-balances shall be provided to
maintain stability
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Equipment Damage
Fire
Equipment to be used
Excavator
Tri-axle Dump Truck
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
Cofferdam/whaler system
Physical Injury
Control Measures
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All mechanized equipment shall have proper fire extinguishing equipment.
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling..
All equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by a
competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
Class A CDL
Slip, trip, fall
25
All personnel shall be properly trained
A confined space plan shall be in place and followed before entry.
The confined space shall be monitored for a hazardous atmosphere before
entry.
An attendant shall monitor all employees entering the confined space at all
times.
All employees shall sign in and out before entering the confined space.
All employees have the right to know the hazards before entering a
confined space.
A rescue plan shall be in place before anyone enters the confined space.
Employees shall maintain proper hand and foot placement.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathway.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when entering or exiting confined
space.
Confined space shall be air monitored before entry.
If atmosphere exceeds exposure limits all employees shall evacuate the
area immediately.
Forced air flow may be used if determined necessary.
Lockout tag out shall be utilized if energy source or engulfment is possible.
Air purifying or air supplying respirators may be used depending on the
atmosphere conditions.
Only air supplying respirators shall be used in oxygen deficient
atmospheres.
Heat Stress
Keep the skin clean and dry.
Change perspiration-soaked clothing, as necessary.
Bathe at end of work shift or day.
Apply powder to affected areas.
Wear clean/dry undergarments
Heat Cramps
Drink plenty of cool fluids even when not thirsty.
Provide cool fluids for work crews.
Move victim to shaded, cool area.
Inform Supervisor of cramps even if occurring off the job.
Heat exhaustion
Physiological worker monitoring as needed (i.e., heart rate, oral
temperature).
Set up work/rest periods.
Use the buddy system.
Allow workers time to acclimate.
Have ice packs available for use on breaks.
Heat Stroke
Evaluate possibility of night work.
Wear body cooling devices.
Wear light colored clothing (can see ticks better).
Mow vegetated and small brush areas.
Wear insect repellant.
Wear long sleeves and long pants.
Visually check self promptly and frequently after exiting the work area.
Hazardous Atmosphere/energy
Heat Stress
Heat rash
Heat cramps
Heat exhaustion
Heat stroke
Insect
Hazards
Ticks
Bees
Wasp
Ants
26
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Poisonous Snakes and Animals
Rabies
Bites
Allergic Reaction
Welding flash
Welding burns
Fire
27
Identify infested areas to the Site Supervisor.
Workers who are allergic or capable of allergic reactions to bee, wasp, or
ant stings or bites shall notify their Supervisor(s).
Evaluate need for sensitive workers to have prescribed antibiotic or
medicine to combat onset of symptoms.
Keep work areas clear of vegetation and small brush.
Be aware of surrounding while working near water.
Avoid placing hands or feet into obscure areas (i.e., beneath rocks, well
pads, brush piles).
Wear rubber or PVC boots into vegetated areas where poisonous snakes or
animals inhabit.
Use the buddy system.
Postpone work in areas where poisonous snakes or animals are nested.
Inspect protected areas before entering.
Inform HS and Project Manager if allergic to bites, and carry emergency kit
as required.
Cutting, welding, or other operations that produce excessive heat, open
sparks, or flames shall not be permitted within 50 feet of a potential liquid
fuel source.
One 20lb ABC multipurpose dry chemical fire extinguisher shall be readily
available in the hot works area.
Complete a Hot Work Permit prior to initiation of hot works.
The area shall be monitored with a combustible gas meter to ensure <10%
LEL.
Work will not be permitted in atmospheres >10% LEL.
The worker shall be protected from sparks or flame by wearing leather
guards (Tyvek is not protective against heat sources).
Welders shall wear welding goggles or hood.
Complete a Hot Work Permit for each shift and when conditions change.
Compressed gas cylinders shall be secure in an upright position.
Gas regulators shall be in proper working order.
Cylinders shall be marked or stenciled to identify the type of gas in the
cylinder.
Oil and oily rags shall be kept away from oxygen equipment.
Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished and when cylinders
are empty or moved.
Objects to be welded, cut, or heated shall be moved to a safe location
when possible.
Remove all potential fire hazards in the vicinity.
Review possibility of chemical coating on item(s) to be welded, cut, or
heated; provide appropriate respirators protection, if needed, to operator.
Acetylene regulators shall not be adjusted to permit a discharge >15 psig.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Equipment to be Used:
Cooling vests
Core control suits
Oral thermometers
Watch
Topical ointment
Clothing for barrier
Manual lifting
Minor cuts and bruises
Chemical contact
Inspection Requirements:
Daily
Watch for signs &
symptoms at each break
Fuel/oxygen combination used for cutting, welding, or heating shall
have reverse-flow check valves between torch and regulator.
Size up the job, think it through.
Lift with your legs, not your back. Use mechanical equipment
whenever possible.
Get assistance when manually lifting awkwardly-sized items or those
items over 60 pounds.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
Tools not functioning properly shall be removed from service
immediately and tagged.
Workers shall wear cotton or leather work gloves when handling
equipment.
Have at least two persons on site trained in First Aid/CPR.
All crew personnel on site shall use the buddy system (working in pairs
or teams).
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) shall be obtained for chemicals
brought on site.
MSDSs shall be reviewed with project personnel before using the
chemical material.
Training Requirements:
Heat Stress.
Prevention, Symptoms, Treatment
Identification of poisonous plants
28
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Rebar Placement
Potential Hazards
Physical Injury
Slip, trip, fall
Control Measures
Poor housekeeping
Manual lifting
Pinch Points
Minor cuts and bruises
29
All personnel shall wear proper PPE for the Job.
All personnel shall attend site orientation prior to start of work activities.
All personnel shall wear all required PPE for jobsite conditions.
All personnel shall familiarize themselves to hazards, emergency
procedures, operational aspects & heavy equipment use, and change(s) in
site/work conditions. Daily housekeeping
All protruding rebar shall be capped with OSHA approved rebar caps
Site employees will be required to wear hard hat, safety glasses with side
shields, work gloves, and steel-toe boots beyond the Main Office Complex
and other field offices.
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
Flag or cover inconspicuous holes to protect against falls.
Work areas will be kept clean and orderly.
Garbage, trash, and scrap will be disposed of daily in approved refuse
containers.
Tools and accessories will be properly maintained and stored.
Work areas and floors will be kept free of dirt, grease, and slippery
materials.
Materials shall be stored to allow clear access to aisles, pathways, and
travel routes.
Field vehicles will be kept clean and orderly.
Size up the job, think it through.
Lift with your legs, not your back. Use mechanical equipment
whenever possible.
Size up the job.
No individual shall lift any material over 60lbs.
Do not lift awkwardly sized items and those items over 60 pounds.
Get assistance when necessary.
If a worker loses control of item, STAND CLEAR and DO NOT try to
prevent its fall.
Assure path is clear while transporting items manually.
Use cotton or leather work gloves for materials handling.
Keep hands and feet clear of moving/suspended materials and equipment.
Wear steel toe/shank safety shoes/boots.
Always have a means of escape.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
Tools not functioning properly shall be removed from service
immediately and tagged.
Workers shall wear cotton or leather work gloves when handling
equipment.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Concrete Placement
Potential Hazards
Personal Injury
Control Measures
Slips, Trips, Falls
Hand & Power Tools
Pinch Points/Caught between
30
Proper Planning
Workers shall wear proper PPE.
Safety glasses shall be worn during all concrete operations.
All workers have the right to shut down a job b/c of an unsafe act.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts,
open-toe shoes, jewelry).
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
All workers should be aware of their surroundings and aware of
simultaneous operations.
All equipment shall have initial and daily inspections.
Workers shall not stand behind or gather directly behind dump trucks.
Workers exposed to fall hazards shall be protected from falling to a lower
level by the use of standard guardrail, work platforms, safety nets,
engineered fall protection systems, or personal fall arrest systems.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Barricade or cover and flag inconspicuous holes to protect against falls
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
The use of sheet pile stirrups as a fall protection method is prohibited
Workers shall maintain 3-point contact while measuring dump trucks.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Remain alert at all times
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Trucking Operations
Control Measures
Equipment operators
31
Do not place hand in between objects being lifted.
Remain clear of dump trucks while backing up.
Always have a means of escape
Use qualified and trained operators
All dump trucks brought on USACE jobsite shall be inspected upon arrival.
Drivers shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
If a signal person or spotter is not used, operators will walk behind their
vehicle to view the area for possible hazards before backing their vehicle
Text messaging is strictly prohibited while operating motor vehicles .
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Trucks should not be operated in a manner that will endanger persons or
property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads be exceeded.
Getting off or on any truck while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the truck.
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator.
No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Scaffolding
Noise
Unstable/inclined Surfaces
Equipment Damage
Fire
32
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the rig.
The load capacity shall be posted and clearly visible on the rig.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Cranes, derricks, drill rigs, booms or similar equipment shall have a
minimum 10 feet clearance from overhead electrical power lines.
Guy, outriggers, thrust outs, or counter-balances shall be provided to
maintain stability
Scaffold shall only be erected, moved, dismantled, or altered under the
supervision of competent persons.
If scaffold is not tagged green fall protection must be worn.
3-point contact shall be used when climbing on and off of scaffolding.
All loose scaffold material shall be picked up and stored properly to prevent
falls.
An access ladder or equivalent safe access shall be provided.
Scaffolds shall be plumb and level.
Scaffolds shall bear on base plates upon mud sills or other adequate
foundation.
When the scaffold height exceeds four times the minimum scaffolds base
dimension, the scaffold shall be secured to the wall or structure.
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All mechanized equipment shall have proper fire extinguishing equipment.
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Equipment to be used
Excavator
Tri-axle Dump Truck
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
Discharge pipe removal
Personal Injury
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling..
All equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by a
competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
Class A CDL
Slips, Trips, Falls
Hand & Power Tools
33
Proper Planning
Personnel shall be aware of potential pinch points.
Locate all electric, gas, water, steam, sewer, and other services lines to be
shut off, capped, or controlled, before demolition work is started.
All workers should be informed of the location of any existing or relocated
utility service.
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across
walking pathways.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
GFCI.s shall be used on all power tools, extension cords, and all equipment
connected to temporary power supplies. Extension cords, power tools, and
lighting equipment shall be inspected before each use, protected from
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Crane operations
Control Measures
Hazardous Energy
Electrocution
Electrical burns
Fire
34
damage, and kept out of wet areas.
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
If crane does not have Anti-Two Block the operator must have a visual aid
(flag, tape, or ball) attached to the hoist line 8 to 10 feet above the rigging.
If the crane is operating at a boom angle that hinders the visual aid the
visual aid may be placed near the drum so the operator can see it.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator.
No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the rig.
The load capacity shall be posted and clearly visible on the rig.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Cranes, derricks, drill rigs, booms or similar equipment shall have a
minimum 20 feet clearance from overhead electrical power lines.
Guy, outriggers, thrust outs, or counter-balances shall be provided to
maintain stability of pile-driver rigs.
Maintain a minimum distance of 20 feet between overhead electrical lines
and any part of equipment.
Portable electrical tools and equipment will be double-insulted.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Identify the location of underground/overhead electrical lines in the work
area, as appropriate.
Power tools shall be tagged and removed from service when not
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Pinch Points/Caught between
Heavy Equipment Operations
Unstable/Inclined Surface
35
functioning properly.
Lockout/tagout procedures shall be implemented when employees need to
perform repair or maintenance on electrical equipment where the
unexpected energization, or start-up of stored energy could cause injury.
Extension cords shall not be fastened with staples, hung from nails, or
suspended by bare wire.
A qualified Master Electrician will inspect all high voltage electrical
connections prior to energizing.
Remain alert at all times
Do not place hand/feet in between objects being lifted
Always have a means of escape
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator. No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
No person shall be permitted in any area that can be affected by demolition
when using heavy machinery.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
If piling cannot be pulled without exceeding the load rating of equipment, a
pile extractor shall be used.
Piling shall not be pulled by tipping the crane, releasing the load brake
momentarily, and catching the load before the crane has settled.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
When going uphill track with the arm in front of you.
If extra counterweight is required fill the bucket
Avoid overfilling bucket when near embankment.
Never slew with a full bucket at maximum reach.
Do not undercutting the ground from beneath the excavator.
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Noise
Rigging
Personal Injury
Faulty Rigging
Failure to control load
Control Measures
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Personal Injury
Rigging must be done by a Qualified Rigger.
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging equipment shall not be loaded in excess of its recommended
safe working load.
Verify load weight of product to be lifted.
A positive latching device shall be used to secure the load and rigging
Select and inspect the proper rigging equipment for the job at hand.
Rigger must remain alert at all times.
Rigger must keep all unnecessary personnel out of the lifting area.
Rigger should alert the operator to any unsafe conditions or practices
during lifting.
Rigger must know and demonstrate competency in using all signals
used in material handling.
Faulty Rigging
Rigging shall be visually inspected at the beginning of each shift by a
competent person.
Rigging shall be stored properly immediately after use.
Defective rigging must be tagged, cut, or removed from service.
Keep rigging clear of any welding or burning.
Hooks, shackles, rings, pad eyes, and other fittings that show excessive
wear or that have been bent, twisted, or otherwise damaged shall be
removed from service.
Only marked shackles (marked by manufacturer with name or trademark of
manufacturer, rated load and size) shall be used.
Failure to Control Load
Crane or hoisting equipment shall not be used when wind speeds onsite
exceed owners safety manual.
At wind greater than 20 mph the operator, rigger, and lift supervisor shall
cease all crane operations, evaluate conditions and determine if the lift
shall proceed.
36
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Tag lines shall be used at all time.
Unstable Structure
Scaffolding
Shoring or bracing underneath the discharge pipe shall be provided if
deemed necessary.
Scaffold shall only be erected, moved, dismantled, or altered under the
supervision of competent persons.
If scaffold is not tagged green fall protection must be worn.
3-point contact shall be used when climbing on and off of scaffolding.
All loose scaffold material shall be picked up and stored properly to prevent
falls.
An access ladder or equivalent safe access shall be provided.
Scaffolds shall be plumb and level.
Scaffolds shall bear on base plates upon mud sills or other adequate
foundation.
When the scaffold height exceeds four times the minimum scaffolds base
dimension, the scaffold shall be secured to the wall or structure.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling.
Heating devices shall be place where they are not likely overturn.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Workers shall wear safety glasses at all times while handling coal tar.
Workers shall wear long sleeve shirts and gloves while handling coal tar.
Respirators shall be worn if ventilation is not adequate.
MSDS will be located in the office trailer onsite.
Complete a Hot Work Permit for each shift and when conditions change.
Cutting, welding, or other operations that produce excessive heat, open
Equipment Damage
Fire
Coal Tar Application
Eye injury
Inhalation
absorption
Hot Work
37
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Equipment to be used
Crane
Excavator or back hoe
Oxygen & acetylene
Hand & Power tools
Slings & Shackles
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
Roofing
Slips, Trips, Falls
Control Measures
sparks, or flames shall not be permitted within 50 feet of a potential liquid
fuel source.
The area shall be monitored with a combustible gas meter to ensure <10%
LEL. Work will not be permitted in atmospheres >10% LEL.
The worker shall be protected from sparks or flame by wearing leather
guards (Tyvek is not protective against heat sources).
Welders shall wear welding goggles or hood.
Compressed gas cylinders shall be secure in an upright position.
Cylinders shall be marked or stenciled to identify the type of gas in the
cylinder.
Oil and oily rags shall be kept away from oxygen equipment.
Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished and when cylinders
are empty or moved.
Acetylene regulators shall not be adjusted to permit a discharge >15 psig.
Fuel/oxygen combination used for cutting, welding, or heating shall have
reverse-flow check valves between torch and regulator.
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
Hot Work Permit
Qualified Rigger
Lock Out/Tag Out
Falls greater than 6
38
The employer shall determine if the walking/working surfaces on which its
employees are to work have the strength and structural integrity to support
employees safely
When the roof is slippery from rain, snow, frost or dew, the best precaution
is to wait until the roof surface is dry .
Workers must have proper soled shoes to prevent slips.
Tools, electric cords and other loose items not in use should be removed
from the roof.
Fasten wood cleats or adjustable roof jacks to the roof deck to provide
temporary toe-holds. Remove the cleats or roof jacks as the roofing is
installed.
Ladders shall not be climbed by more than one person at a time.
Portable ladders shall have slip-resistant feet .
Each employee on a walking/working surface with an unprotected side or
edge which is 6 feet or more above a lower level shall be protected from
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Lifting Strains & Sprains
Equipment Operations
Hazardous Energy
39
falling by the use of guardrail systems, safety net systems, or personal fall
arrest systems.
Each employee on walking/working surfaces shall be protected from falling
through holes (including skylights) more than 6 feet, by personal fall arrest
systems, covers, or guardrail systems erected around such holes.
Ladders should extend above the eaves by 3 and sit on a firm level base.
Leveling can be attained by digging or by use of adjustable leg levelers.
The distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall supporting it should be
one quarter (1/4) of the height of the wall.
The length of portable stepladders shall not exceed 20 ft
Ladders shall be secured by top, bottom, and intermediate fastenings, as
necessary to hold them rigidly in place and to support the loads that will be
imposed upon them.
No individual employee is permitted to lift any object that weighs over 60
pounds.
Proper lifting techniques shall be used.
Multiple employees or the use of mechanical lifting are for lifting objects
over the 60-pound limit.
Materials shall be inspected for sharp edges prior to being handled, and
avoid pinch point
hazards.
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator. No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Maintain a minimum distance of 20 feet between overhead electrical lines
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Hand and Power Tools
Equipment to be Used:
Hand and Power Tools
GFCI
Inspection Requirements:
Daily
Clearing and Grubbing
Personal Injury
and any part of equipment.
Portable electrical tools and equipment will be double-insulted.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces.
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
Identify the location of underground/overhead electrical lines in the work
area, as appropriate.
Power tools shall be tagged and removed from service when not
functioning properly.
Lockout/tagout procedures shall be implemented when employees need to
perform repair or maintenance on electrical equipment where the
unexpected energization, or start-up of stored energy could cause injury.
Extension cords shall not be fastened with staples, hung from nails, or
suspended by bare wire.
Prior to use all tools must be inspected. Any damaged or defective tools
will be tagged and removed from service for repair and/or discarded.
Workers will not handle electrical equipment or wires if their hands are wet
or they are standing on wet surfaces
Electrical cords shall be pulled from the outlet by the plug, not the
electrical cord.
GFCI.s shall be used on all power tools, extension cords, and all equipment
connected to temporary power supplies. Extension cords, power tools, and
lighting equipment shall be inspected before each use, protected from
damage, and kept out of wet areas.
Training Requirements:
Qualified Personal
40
Proper Planning
All workers have the right to shut down a job b/c of an unsafe act.
Workers shall wear appropriate field attire (i.e., no tank tops, shorts, opentoe shoes, jewelry).
Locate all electric, gas, water, steam, sewer, and other services lines to be
shut off, capped, or controlled, before excavation to start.
Call Louisiana One Call or appropriate authority to locate underground
utilities.
All workers should be informed of the location of any existing or relocated
utility service.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Slips, Trips, Falls
Pinch Points/Caught between
Trucking Operations
Equipment operators
41
No overhead work shall be performed when, as a result of that work, the
possibility of a falling object striking any person exists.
All workers should be aware of their surroundings and aware of
simultaneous operations.
All equipment shall have initial and daily inspections.
Workers shall not stand behind or gather directly behind dump trucks.
Housekeeping in the immediate work area should be addressed on a daily
basis.
Trip hazards shall be identified and marked or removed
Barricade or cover and flag inconspicuous holes to protect against falls
Personnel will use proper footwear for wet and/or muddy conditions.
Personnel shall maintain 3-point contact when mounting or dismounting
mobile equipment
Whenever possible, avoid routing cords, ropes, and hoses across walking
pathways.
Remain alert at all times
Do not place hand in between objects being lifted.
Remain clear of dump trucks while backing up.
Always have a means of escape
Use qualified and trained operators
All dump trucks brought on USACE jobsite shall be inspected upon arrival.
Drivers shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
If a signal person or spotter is not used, operators will walk behind their
vehicle to view the area for possible hazards before backing their vehicle
Text messaging is strictly prohibited while operating motor vehicles.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Trucks should not be operated in a manner that will endanger persons or
property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads be exceeded.
Getting off or on any truck while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the truck.
Use qualified and trained operators
Operators shall accept signals only from the designated signalmen.
Moving heavy equipment must have properly functioning back-up alarms.
Spotters on the ground will assist operators in manipulating vehicles and
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Noise
Unstable/inclined Surfaces
Equipment Damage
Fire
42
equipment into tight or confined spaces.
Operators shall maintain a constant awareness of personnel and equipment
in the work areas.
Machinery or equipment shall not run unattended unless secured by the
operator.
No equipment shall be left running beyond a shift's end.
Machinery or equipment shall not be operated in a manner that will
endanger persons or property nor shall the safe operating speeds or loads
be exceeded.
Getting off or on any equipment while it is in motion is prohibited.
Safety belts shall be used by the operator while equipment is in use.
All mobile equipment and the areas in which they are operated shall be
adequately illuminated.
Ground personnel shall not be allowed to work under suspended loads.
Be aware of pinch points and crushing hazards.
The operator shall not exceed the load capacity rating for the rig.
The load capacity shall be posted and clearly visible on the rig.
Be aware of possible thunderstorm activity, shut down and disperse from
mast area if thunderstorm in near vicinity.
Cranes, derricks, drill rigs, booms or similar equipment shall have a
minimum 10 feet clearance from overhead electrical power lines.
Guy, outriggers, thrust outs, or counter-balances shall be provided to
maintain stability
Review elements of Hearing Conservation Program.
Employees shall be informed of high noise areas where hearing protection
is required and these areas marked.
Conduct noise surveys on activities in question.
Provide hearing protection on site.
Require use of hearing protection when noise levels are at exceed 85 dBA.
Exposure to impulse or impact noise should not exceed 140 dBA peak
sound level.
Use engineering controls (i.e., guards, mufflers, distance) to reduce worker
exposure.
Only go straight up and straight down an incline, with the track drive to the
rear
Never try to cross an incline at an angle
If ground is unsuitable mats may be required.
All wiring or equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by
a competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
All mechanized equipment shall have proper fire extinguishing equipment.
ACTIVITY HAZARD ANALYSIS
Principle Steps
Potential Hazards
Control Measures
Equipment to be used
Hard Hat
Steel Toe Boots
Class II Vest
Excavator
Tri-axle Dump Truck
Inspection Requirements
Daily inspections
Per manufactures specs.
Prior to start-up
All potential sources of ignition should be evaluated.
Roadways between and around combustible storage piles should be at
least 15 feet wide and maintained free from accumulation of rubbish,
equipment, or other materials.
A temporary or permanent water supply of volume should be made
available.
Shutdown all equipment before refueling..
All equipment providing light, heat, or power shall be installed by a
competent person.
Shutdown all equipment before fueling.
Training Requirements
Qualified Operator
CDL
43
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Activity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityDocument14 pagesActivity Hazard Analysis (AHA) : Risk Assessment Code (RAC) Matrix Severity ProbabilityThomas100% (4)
- Generic Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesGeneric Risk Assessmentmorgojoyo100% (3)
- USAMRICD AHA Underground UtilitiesDocument14 pagesUSAMRICD AHA Underground UtilitiesKenneth Bia Martin100% (2)
- Hazards of Structural Steel WorkDocument3 pagesHazards of Structural Steel WorkRobbie Grose100% (3)
- Topaz Tangaroa Tiamat Vessel SpecsDocument5 pagesTopaz Tangaroa Tiamat Vessel SpecsDhil SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Toolbox TalksDocument1 pageToolbox TalksMohammad Abubakar SiddiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Confined Space Rescue Plan TemplateDocument10 pagesConfined Space Rescue Plan Templateaby131Pas encore d'évaluation
- JSA-009a Drilling and Mon Well Construction-SonicDocument4 pagesJSA-009a Drilling and Mon Well Construction-SonicDedi Apriadi83% (6)
- Grinding Equipment Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesGrinding Equipment Risk Assessmentdroffilcz270% (1)
- Daily Vehicle Inspection Checklist 11 09 WfeelefyoppyDocument1 pageDaily Vehicle Inspection Checklist 11 09 Wfeelefyoppyrajesh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa R B 6 ForkliftDocument3 pagesJsa R B 6 ForkliftsinghajitbPas encore d'évaluation
- Trades Guidelines - Excavation and TrenchingDocument6 pagesTrades Guidelines - Excavation and TrenchingMohammed Atef100% (1)
- AhaDocument6 pagesAhaCarlits MacallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toolbox TalksDocument23 pagesToolbox TalksWali ul Islam100% (1)
- Man Machine InterfaceDocument22 pagesMan Machine Interfaceamdarrif3723100% (1)
- IG2, Hendry Lukas Timothy, 00663146, Redhat Safety TrainingDocument39 pagesIG2, Hendry Lukas Timothy, 00663146, Redhat Safety Trainingjashuva lenka88% (8)
- VOL II - Technical-Co Boiler Dismantling PDFDocument538 pagesVOL II - Technical-Co Boiler Dismantling PDFSteven100% (1)
- Jsa For Weld and GrindingDocument6 pagesJsa For Weld and GrindingTanzeel LiaqatPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil JSA Form Application of Protective Coating On Sump PitsDocument1 pageCivil JSA Form Application of Protective Coating On Sump PitsdrmuhsinPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA of Loading & Un Loading ActivitiesDocument3 pagesJSA of Loading & Un Loading ActivitiesMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- CIVIL WORKS SAFETY ANALYSISDocument7 pagesCIVIL WORKS SAFETY ANALYSISMoaatazz Nouisri67% (3)
- Manual Handling Assessment - RPS Floor SortingDocument5 pagesManual Handling Assessment - RPS Floor SortingBayu Aji S100% (1)
- JSA For Dismantalling of PVC Pipe (5cm) by Acetylene Gas CuttingDocument4 pagesJSA For Dismantalling of PVC Pipe (5cm) by Acetylene Gas CuttingMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- Activity Hazard AnalysisDocument4 pagesActivity Hazard AnalysisGerrard Singh100% (1)
- Very Very Good Risk Assessment EnvironmentDocument8 pagesVery Very Good Risk Assessment EnvironmentSalley Bukhari100% (1)
- 28 Job Safety AnalysisDocument7 pages28 Job Safety Analysisashish_kamat100% (3)
- Lockout Tagout TRNG GuideDocument7 pagesLockout Tagout TRNG GuideSyed Mujtaba Ali Bukhari100% (1)
- JsaDocument39 pagesJsajithin shankar100% (3)
- Jsa-Jha For Using of Hand ToolsDocument2 pagesJsa-Jha For Using of Hand ToolsKamran Khan50% (2)
- JSA For Fab Erec of STRL Steel StackDocument5 pagesJSA For Fab Erec of STRL Steel StackkrishnakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel RefuelingDocument3 pagesDiesel RefuelingAMINPas encore d'évaluation
- First Aid Cases RecordDocument1 pageFirst Aid Cases RecordFrancis Enriquez TanPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA TemplateDocument2 pagesJSA TemplateRassie ErasmusPas encore d'évaluation
- JHA FORM CompleteDocument5 pagesJHA FORM Completeangelo177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Confined Spaces Management PlanDocument32 pagesConfined Spaces Management PlanIdris AdeniranPas encore d'évaluation
- Crane Lifting Materials SafelyDocument4 pagesCrane Lifting Materials SafelyAbu Maaz100% (1)
- Akk Jha Installation of Diesel TankDocument3 pagesAkk Jha Installation of Diesel TankDouglas Delly0% (1)
- Jsa Grinding Welding Gas CuttingDocument4 pagesJsa Grinding Welding Gas CuttingMark Roger Huberit IIPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA M36 Hydro Testing Spool Pieces & PipeworkDocument4 pagesJSA M36 Hydro Testing Spool Pieces & PipeworkMianPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample AHADocument55 pagesSample AHAdavidbteammira100% (3)
- JSA's ModelsDocument56 pagesJSA's ModelsSaberDjet80% (5)
- Jsa FormDocument3 pagesJsa Formmiaicarba100% (1)
- Excavation and Trenching Safety PlanDocument21 pagesExcavation and Trenching Safety Planleonardo Garais100% (1)
- Competent Person Designation ProcedureDocument8 pagesCompetent Person Designation ProcedurearunmirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Job Safety/Hazard Analysis Job #: Location/Description: OwnerDocument33 pagesConstruction Job Safety/Hazard Analysis Job #: Location/Description: OwnerHortencio SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- SS JSP - 007 Excavation Work Using EquipmentDocument6 pagesSS JSP - 007 Excavation Work Using EquipmentFarhat SetharPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA For New EmployeesDocument20 pagesJSA For New EmployeesNilayPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Safety Analysis: Trench Preparation & Thrust Boring Activity Required References Jsa ReviewDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Trench Preparation & Thrust Boring Activity Required References Jsa ReviewMoaatazz Nouisri100% (1)
- Scaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating ProceduresDocument1 pageScaffolding-Fixed and Mobile: Safety Operating Proceduresmohammed muzammilPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa Fueling Equipment On DeckDocument2 pagesJsa Fueling Equipment On DeckIlya BordonosovPas encore d'évaluation
- Confined Space Entry Program 11 2021Document16 pagesConfined Space Entry Program 11 2021zaka ullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand and Power ToolsDocument25 pagesHand and Power ToolsVishwash Goyal100% (1)
- Site Specipic PlanDocument26 pagesSite Specipic Planrashid zamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Hand Drill Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesElectric Hand Drill Risk AssessmentTariq AkhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- STOP WORK POLICY EXPLAINEDDocument3 pagesSTOP WORK POLICY EXPLAINEDfirdous tantaryPas encore d'évaluation
- JHA No. 06, Manual Excavation and Instalasi Formwork For Barier Pole Dan Concrete Slab HydrantDocument4 pagesJHA No. 06, Manual Excavation and Instalasi Formwork For Barier Pole Dan Concrete Slab HydrantDarmawan OnradPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument3 pagesJob Hazard AnalysisChristine YasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa SKDocument10 pagesJsa SKEngr Tahir UL Haq100% (2)
- Jsa & Hip PlanDocument7 pagesJsa & Hip Plansaquib_jamadar100% (1)
- GSPC PLQPDocument5 pagesGSPC PLQPAnonymous rYZyQQot55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basket: Esvagt Safe PersonnelDocument14 pagesBasket: Esvagt Safe PersonnelObodoruku StanleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual-P1250 9510 PDFDocument82 pagesManual-P1250 9510 PDFThiện Nguyễn Bá50% (2)
- FPS 013 - Use of Boatswain chairREV1Document4 pagesFPS 013 - Use of Boatswain chairREV1grantPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Standing 7.5Document35 pagesFree Standing 7.5Arif WidyatmokoPas encore d'évaluation
- EuroCargo MY13 Euro VI BodybuilderDocument228 pagesEuroCargo MY13 Euro VI Bodybuilderkowal100% (2)
- Tadano Tr-500ex Rough Terrain Crane Network PDFDocument6 pagesTadano Tr-500ex Rough Terrain Crane Network PDFmangjitPas encore d'évaluation
- Method Ststement For Chiller ErectionDocument7 pagesMethod Ststement For Chiller Erectionk md adnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Odisha Power Generation Technical Specs for 10T EOT CraneDocument32 pagesOdisha Power Generation Technical Specs for 10T EOT CraneNikki ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- AC-665-2060 En-Operation Manual of ChassisDocument48 pagesAC-665-2060 En-Operation Manual of ChassisArslan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- QP Latest Vendor List QFM-DT-017-05 Rev 0 2010-02-23 PVL List ApprovedDocument78 pagesQP Latest Vendor List QFM-DT-017-05 Rev 0 2010-02-23 PVL List Approvedavivekprasath40% (5)
- v550 EnglishDocument3 pagesv550 EnglishEdmil PabellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix II - Marine Specification (Installation)Document184 pagesAppendix II - Marine Specification (Installation)haydarburedahPas encore d'évaluation
- NTCC FinalDocument43 pagesNTCC FinalNihar NanyamPas encore d'évaluation
- BV NR526Document158 pagesBV NR526Pedro SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- 1HC0079419 E - Rev. AADocument18 pages1HC0079419 E - Rev. AAKhắc Đồng TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Liebherr Tower Cranes enDocument42 pagesLiebherr Tower Cranes enRaman Iyer100% (1)
- 206 - LTM 1100-5.2 - PN - 206.01.e02.2014 - 10535-2Document18 pages206 - LTM 1100-5.2 - PN - 206.01.e02.2014 - 10535-2Pedro SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Overhead Cranes Design StandardsDocument30 pagesOverhead Cranes Design StandardsVicky GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat. Handling EquipmentDocument33 pagesMat. Handling EquipmentNabendu MajiPas encore d'évaluation
- इंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगDocument16 pagesइंटरनेट मानक का उपयोगUdit Kumar SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Test ProcedureDocument5 pagesLoad Test ProcedureAlzaki Abdullah80% (5)
- Adjustable transportable davit crane with 3000 lb capacityDocument4 pagesAdjustable transportable davit crane with 3000 lb capacityAutodesktest2018Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Hoisting Rigging Plan 10-6-14 Final Posted To WebsiteDocument23 pages2014 Hoisting Rigging Plan 10-6-14 Final Posted To WebsiteSudiatmoko Supangkat100% (1)
- 2015 Advance Industrial Tyres Data Book GuideDocument11 pages2015 Advance Industrial Tyres Data Book GuideAtul KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- Wire Rope Sling Capacity ChartsDocument9 pagesWire Rope Sling Capacity ChartsRiko Bin ZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Armado PC5500 PDFDocument104 pagesManual Armado PC5500 PDFclaudioPas encore d'évaluation