Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
DC Motor
Transféré par
Kamal PDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DC Motor
Transféré par
Kamal PDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
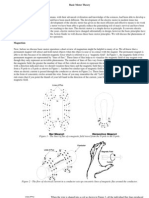
DC MOTOR
A direct current (DC) motor is a fairly simple electric motor that uses electricity
and a magnetic field to produce torque, which turns the motor. At its most simple, a DC
motor requires two magnets of opposite polarity and an electric coil, which acts as an
electromagnet. The repellent and attractive electromagnetic forces of the magnets provide
the torque that causes the DC motor to turn.
If you've ever played with magnets, you know that they are polarized, with a
positive and a negative side. The attraction between opposite poles and the repulsion of
similar poles can easily be felt, even with relatively weak magnets. A DC motor uses
these properties to convert electricity into motion. As the magnets within the DC motor
attract and repel one another, the motor turns.
A DC motor requires at least one electromagnet. This electromagnet switches the
current flow as the motor turns, changing its polarity to keep the motor running. The
other magnet or magnets can either be permanent magnets or other electromagnets.
Often, the electromagnet is located in the center of the motor and turns within the
permanent magnets, but this arrangement is not necessary.
To imagine a simple DC motor, think of a wheel divided into two halves between
two magnets. The wheel of the DC motor in this example is the electromagnet. The two
outer magnets are permanent, one positive and one negative. For this example, let us
assume that the left magnet is negatively charged and the right magnet is positively
charged.
Electrical current is supplied to the coils of wire on the wheel within the DC
motor. This electrical current causes a magnetic force. To make the DC motor turn, the
wheel must have be negatively charged on the side with the negative permanent magnet
and positively charged on the side with the permanent positive magnet. Because like
charges repel and opposite charges attract, the wheel will turn so that its negative side
rolls around to the right, where the positive permanent magnet is, and the wheel's positive
side will roll to the left, where the negative permanent magnet is. The magnetic force
causes the wheel to turn, and this motion can be used to do work.
When the sides of the wheel reach the place of strongest attraction, the electric
current is switched, making the wheel change polarity. The side that was positive
becomes negative, and the side that was negative becomes positive. The magnetic forces
are out of alignment again, and the wheel keeps rotating. As the DC motor spins, it
continually changes the flow of electricity to the inner wheel, so the magnetic forces
continue to cause the wheel to rotate.
.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ProjectDocument25 pagesProjectAsif MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeDocument6 pagesWorking Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeHumair AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- EMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysDocument25 pagesEMI Unit 4 Part 2 - DC, AC, Stepper Motot and RelaysAyushman SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Drain CleanerDocument45 pagesAutomatic Drain CleanerArun Kumar Yadav70% (10)
- What Is A DC MotorDocument9 pagesWhat Is A DC MotorKylaeunice GuerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric MotorsDocument25 pagesElectric MotorsGular JabrayilovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument19 pagesElectric Motors and GeneratorsImran AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro 3 Finals Task PerformanceDocument23 pagesElectro 3 Finals Task PerformanceJuan Miguel TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors-Abdulla AlhashmiDocument3 pagesElectric Motors-Abdulla AlhashmiAbdulla Al HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Generators and MotorsDocument9 pagesGenerators and Motorseng.muhammad.waterPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motor Intrinsic NotesDocument3 pagesDC Motor Intrinsic Notesimran kadriPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity LightDocument97 pagesGravity LightArun Kumar Yadav100% (1)
- What Is A DC Motor?Document14 pagesWhat Is A DC Motor?karthick LPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument21 pagesElectric Motors and Generatorsaskartik3Pas encore d'évaluation
- G10 MagnetismDocument78 pagesG10 MagnetismTricia RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Ac DCDocument10 pagesAssignment Ac DCKamil KhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument48 pagesBasic Motor Theoryantoniogh2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3-5 Physics Elec MagDocument34 pages3-5 Physics Elec MagPrecious BalgunaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC MotorDocument12 pagesDC MotoraadhargilhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motor: Rotor (Document3 pagesElectric Motor: Rotor (qwert qwertPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument39 pagesBasic Motor Theoryarfat_ahmad_khanPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Motor: Figure 1: Jedlik's "Electromagnetic Self-Rotor"Document7 pagesDC Motor: Figure 1: Jedlik's "Electromagnetic Self-Rotor"StanzaPelangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solenoid:: The Electric MotorDocument2 pagesSolenoid:: The Electric MotorBooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Fe31 Morosanu Ioana LoredanaDocument4 pagesFe31 Morosanu Ioana Loredanaloredana ardeleanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Brushed DC Electric Motor - WikipediaDocument63 pagesBrushed DC Electric Motor - WikipediaKISHORE PERUMALLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Permanent Magnet D.CDocument5 pagesPermanent Magnet D.CNidhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesApplication of DC Shunt MotorPrajwal Deep RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Motor TheoryDocument26 pagesBasic Motor TheoryRoberth Salsr LpzPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of DC Shunt Motor: Lovely Professional University Amit Raj ROLL NO-RB4802A28 Reg. No-10803543 B.Tech - MEDocument5 pagesApplication of DC Shunt Motor: Lovely Professional University Amit Raj ROLL NO-RB4802A28 Reg. No-10803543 B.Tech - MEshailesh singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current Brake PDFDocument32 pagesEddy Current Brake PDFpraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current BrakeDocument32 pagesEddy Current BrakepraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To DC Electric MotorsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To DC Electric MotorsJames Adrian Abalde SaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy Current Brake - WikipediaDocument29 pagesEddy Current Brake - WikipediaSurya KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- THE ELECTRIC MOTOR. Describing FunctionsDocument3 pagesTHE ELECTRIC MOTOR. Describing FunctionsMihai CiocirlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument2 pagesElectric Motors and GeneratorsNURSHAHADAH ISMAELPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Definitons and Other ChurvaDocument7 pagesAC Definitons and Other ChurvaErvin GohPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic - DC Moto-Wps OfficeDocument3 pagesTopic - DC Moto-Wps OfficeSanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Part A: Theory/ Scientific PrincipleDocument11 pagesPart A: Theory/ Scientific PrincipleJay CherizPas encore d'évaluation
- DC MotorDocument4 pagesDC MotorTarakPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Electric Motor BasicsDocument13 pages1 Electric Motor BasicsPandaGendutPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor WorksDocument8 pagesMotor WorksBhavesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Type of NC SystemDocument20 pagesType of NC Systemamit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- How Does An AC Motor Work?: Stator Squirrel CageDocument4 pagesHow Does An AC Motor Work?: Stator Squirrel CageQuen EscletoPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 2018Document5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current 2018Rohit NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Induction (AC) Motor OperationDocument5 pagesBasic Induction (AC) Motor OperationMathews IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical MachinesDocument15 pagesElectrical Machinesraj sekharPas encore d'évaluation
- Research 1Document23 pagesResearch 1John Paul BaquiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternator ToyotaDocument5 pagesAlternator ToyotaAYON_MSNPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics - Electro-Magnetic InductionDocument3 pagesPhysics - Electro-Magnetic InductionNikhil YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Tapassss Bbhhaaiiiiiiii FinalDocument16 pagesTapassss Bbhhaaiiiiiiii FinalSunilPas encore d'évaluation
- DC & AC Machines and Speed ControlDocument53 pagesDC & AC Machines and Speed ControlInsane Clown Prince60% (5)
- Mechanism and Principle: Ice 3 EditDocument6 pagesMechanism and Principle: Ice 3 Editvishnu kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Prime MoversDocument90 pagesChapter 2 Prime Moversaimi wahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentJulia NithdalePas encore d'évaluation
- Generating Electrical CurrentDocument6 pagesGenerating Electrical Currentjavierruizleon100% (5)
- Chapter 1 EIC For StudentDocument10 pagesChapter 1 EIC For StudentSeysa Estoque NidoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction - Electric MotorsDocument28 pagesIntroduction - Electric Motorsgurunathan14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of DC MotorDocument49 pagesConstruction of DC MotorAvanish Verma100% (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysD'EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Authentic Lab ExperimentDocument4 pagesAuthentic Lab ExperimentKangPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrator Information V2.8.2-131-Gf324cd6e2, 2022-05-28Document17 pagesIntegrator Information V2.8.2-131-Gf324cd6e2, 2022-05-28Juan Carlos LesmasPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Worldwide AC Voltages and FrequenciesDocument3 pagesList of Worldwide AC Voltages and FrequencieskrishnandrkPas encore d'évaluation
- User's Manual: Study of Dielectric ConstantDocument10 pagesUser's Manual: Study of Dielectric ConstantJagjiwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Trickle Bed Reactor ScaleupDocument15 pagesTrickle Bed Reactor ScaleupAks KasPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg & Tech DiplomaDocument28 pagesEngg & Tech DiplomaAbir ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Persentasi Momen GayaDocument28 pagesPersentasi Momen Gayayoan04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blue SeaDocument144 pagesBlue Seabrendanc55323Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Practicals 1 and 2Document184 pagesPhysics Practicals 1 and 2Zahid ArainPas encore d'évaluation
- TransfrormerDocument91 pagesTransfrormerArial96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum MechanicalDocument110 pagesCurriculum MechanicalpraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Vibrations - M Ghosh BHELDocument9 pagesBasics of Vibrations - M Ghosh BHELSuhas JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipho 1977Document9 pagesIpho 1977Lâm Văn Sa HuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- A Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan On Nature of ForcesDocument5 pagesA Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan On Nature of ForcesButz GeonzonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Low-Speed CommissioningDocument20 pages2 - Low-Speed CommissioningQuang Pham DuyPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Marking Scheme 2019-20Document24 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Marking Scheme 2019-20fociwePas encore d'évaluation
- 30Document15 pages30UpandawayPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Interview Questions Part 14Document13 pagesElectrical Interview Questions Part 14Veera RagavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Document13 pagesWind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Jayant LakhlaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-II-Resultant-of-a-Force-2.6-2.7-2.8 (1) B273 LrcturesDocument6 pagesChapter-II-Resultant-of-a-Force-2.6-2.7-2.8 (1) B273 LrcturesMickyleee ChannelPas encore d'évaluation
- Merlin Gerin Medium VoltageDocument10 pagesMerlin Gerin Medium VoltagekjfenPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Biomecanico de La Tecnica GYAKU TSUKI de Karate de Un Equipo Donde Un Karateca Presenta Lesion de RodillaDocument14 pagesAnalisis Biomecanico de La Tecnica GYAKU TSUKI de Karate de Un Equipo Donde Un Karateca Presenta Lesion de Rodillajesusisasis21Pas encore d'évaluation
- January 2012 QP - M1 OCRDocument4 pagesJanuary 2012 QP - M1 OCRMohammad Abdul OhabPas encore d'évaluation
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument7 pagesBrushless DC MotorsRonald LugwirePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Point Method / Measurement of Low Resistances: (Item No.: P2410101)Document20 pages4 Point Method / Measurement of Low Resistances: (Item No.: P2410101)fatjonmusli2016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clamp Meters Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsDocument4 pagesClamp Meters Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsTEUKUPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between MPCB and MCCB - Electrical ClassroomDocument4 pagesDifference Between MPCB and MCCB - Electrical ClassroomNakka Srikanth RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Question Paper - Acadecraft !Document8 pagesPhysics Question Paper - Acadecraft !Amit Shrivastava100% (1)
- 2 Chapter 2 - A Student AnsDocument87 pages2 Chapter 2 - A Student Ansfullmetal Aesir100% (1)
- ELEQ GSA Broschyr enDocument4 pagesELEQ GSA Broschyr enJaime Salazar ArayaPas encore d'évaluation